How to Access an AWS RDS Instance from an EC2 Instance.
EC2 Instance.
An EC2 instance functions much like a virtual machine (VM) and can run various operating systems such as Linux, Windows, or custom AMIs (Amazon Machine Images). You can choose from a wide range of instance types optimized for different workloads, such as compute-intensive, memory-intensive, or storage-heavy applications. EC2 instances can scale up or down based on your workload requirements. You can start with a single instance and scale out to hundreds or thousands as needed. This is possible through features like Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing (ELB).

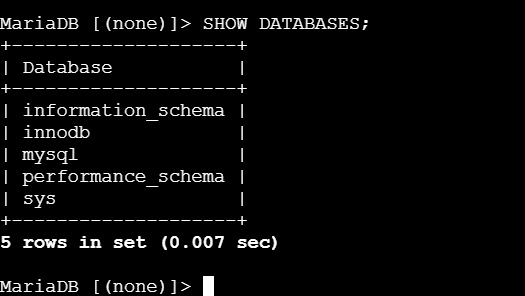
Amazon RDS.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is a fully managed database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. RDS automates common database management tasks such as backups, patch management, scaling, and failover, allowing you to focus more on application development rather than managing the database infrastructure.
RDS supports a variety of popular relational database engines:
- Amazon Aurora (AWS’s own high-performance database)
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle Database
- SQL Server
STEP 1: Navigate the EC2 Instance and Create the instance.
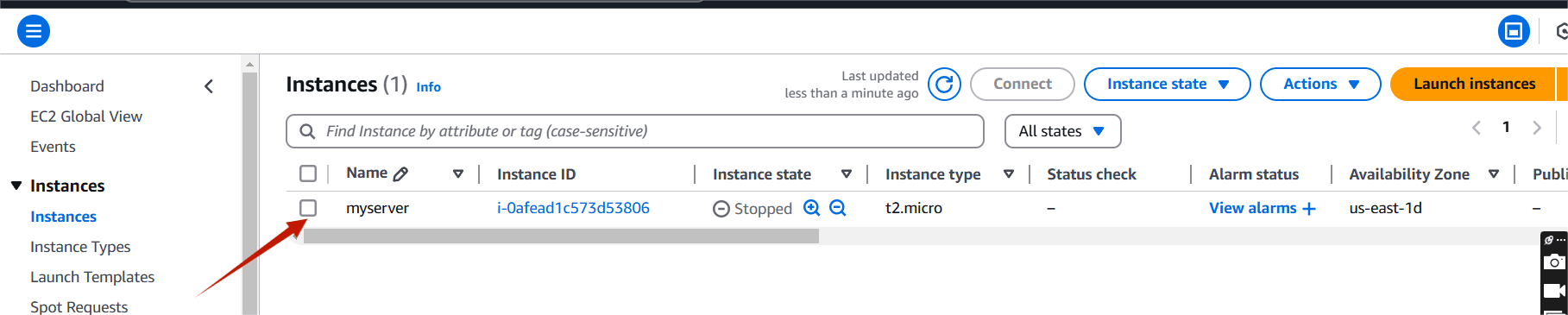
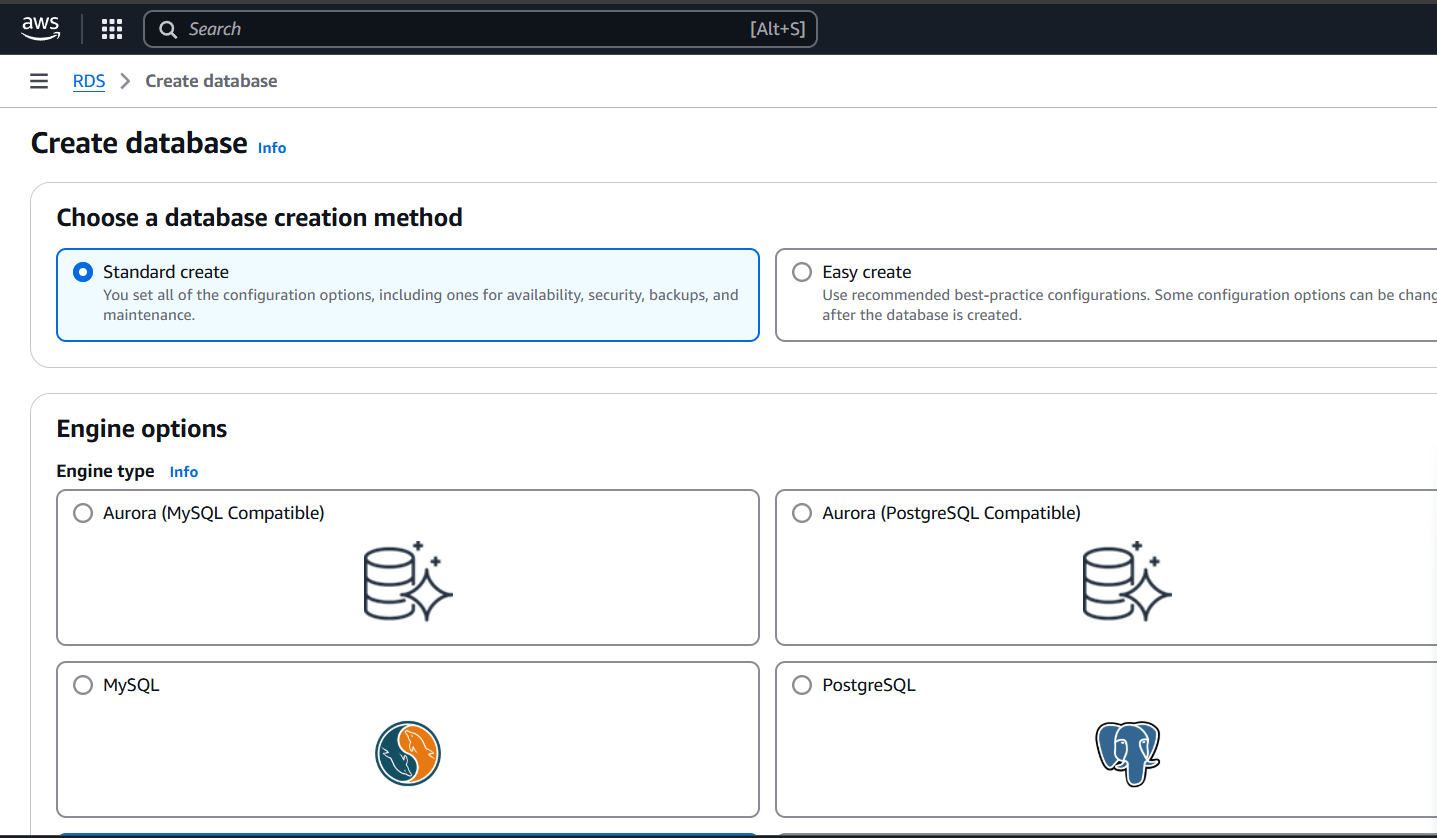
STEP 2: Navigate the Amazon RDS .
- Click create database.
- Select the standard create and select mariadb.
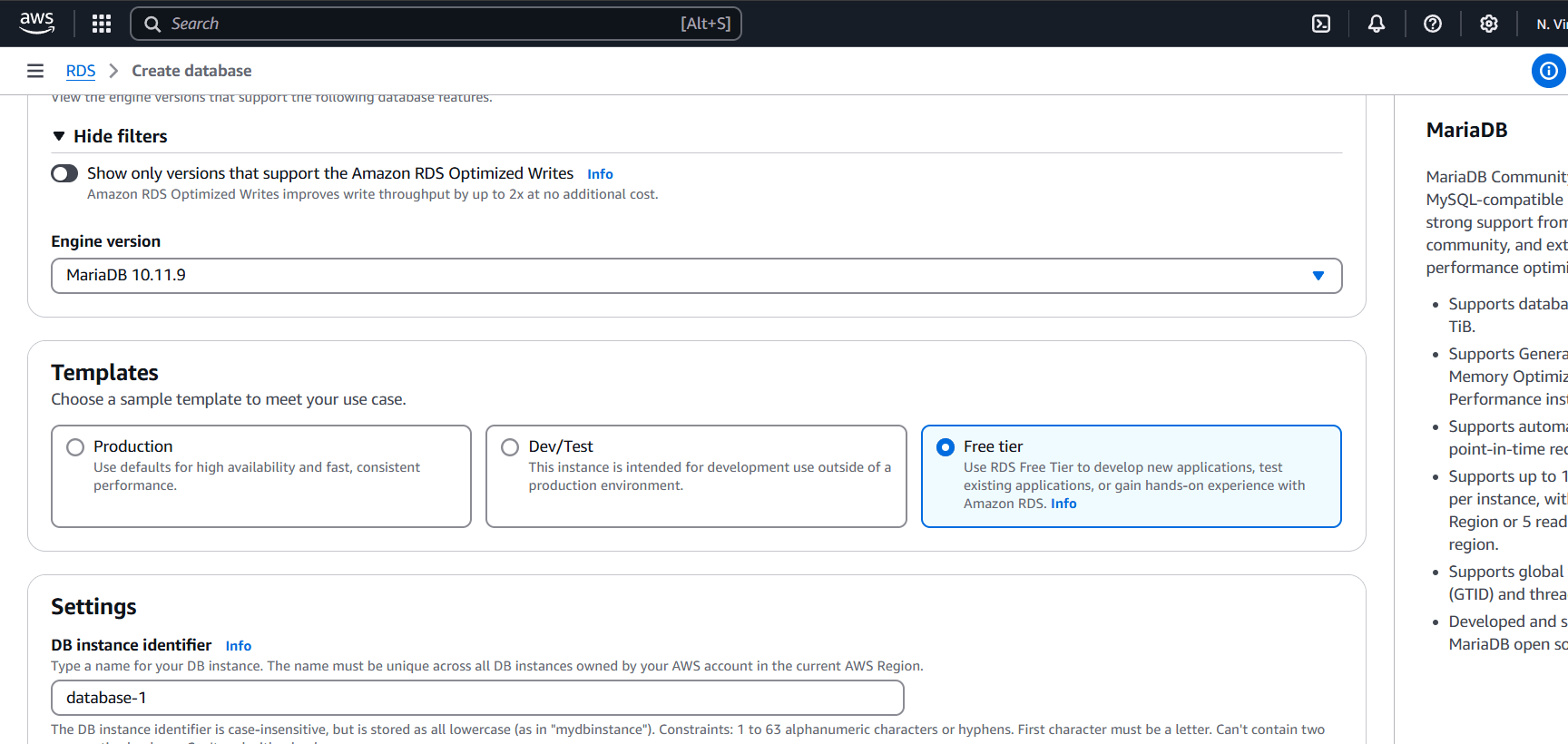
STEP 3: Click on free tier.
- Enter the password.
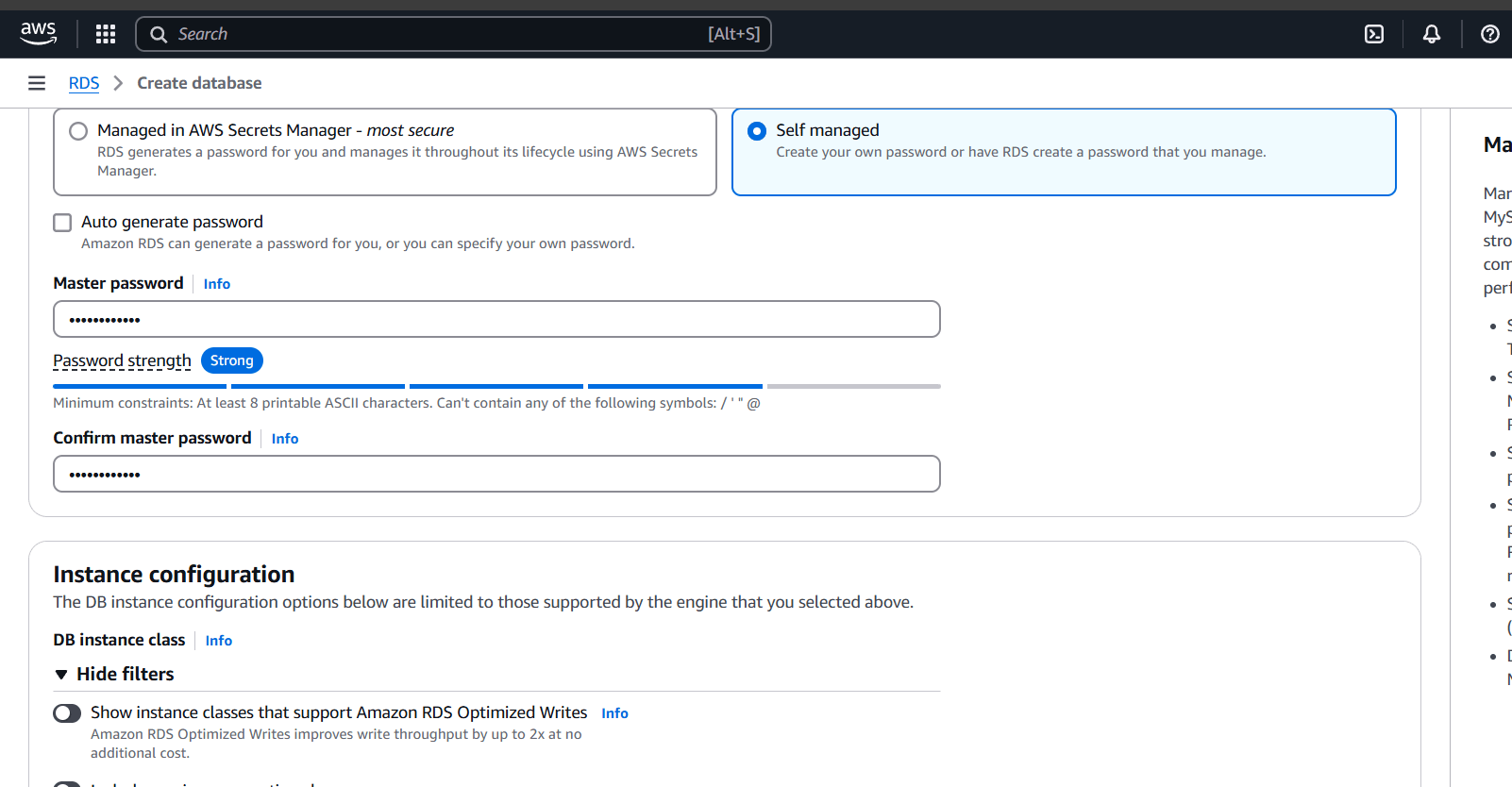
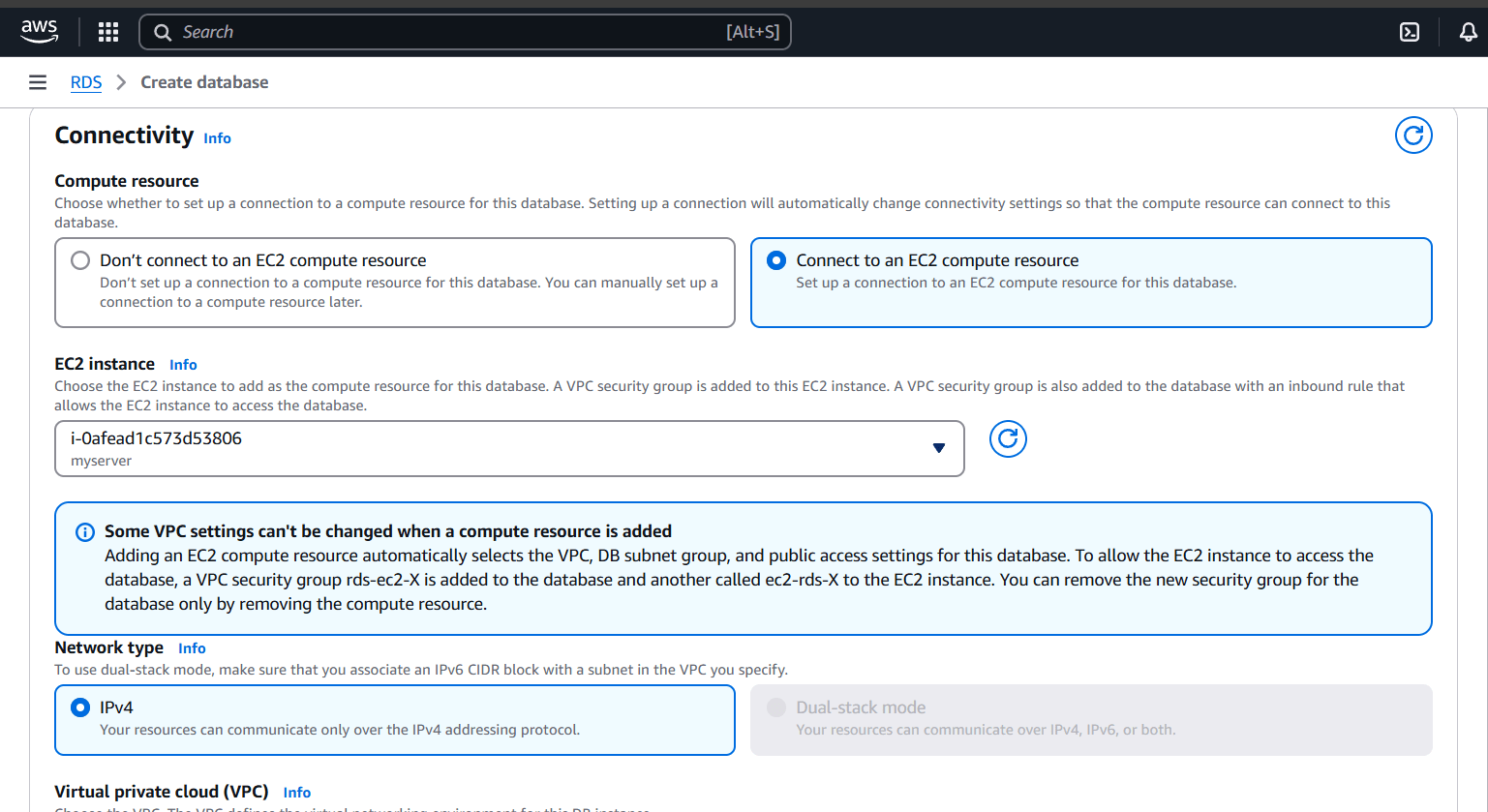
STEP 4: Click on connect to an EC2 compute resource and select your instance.
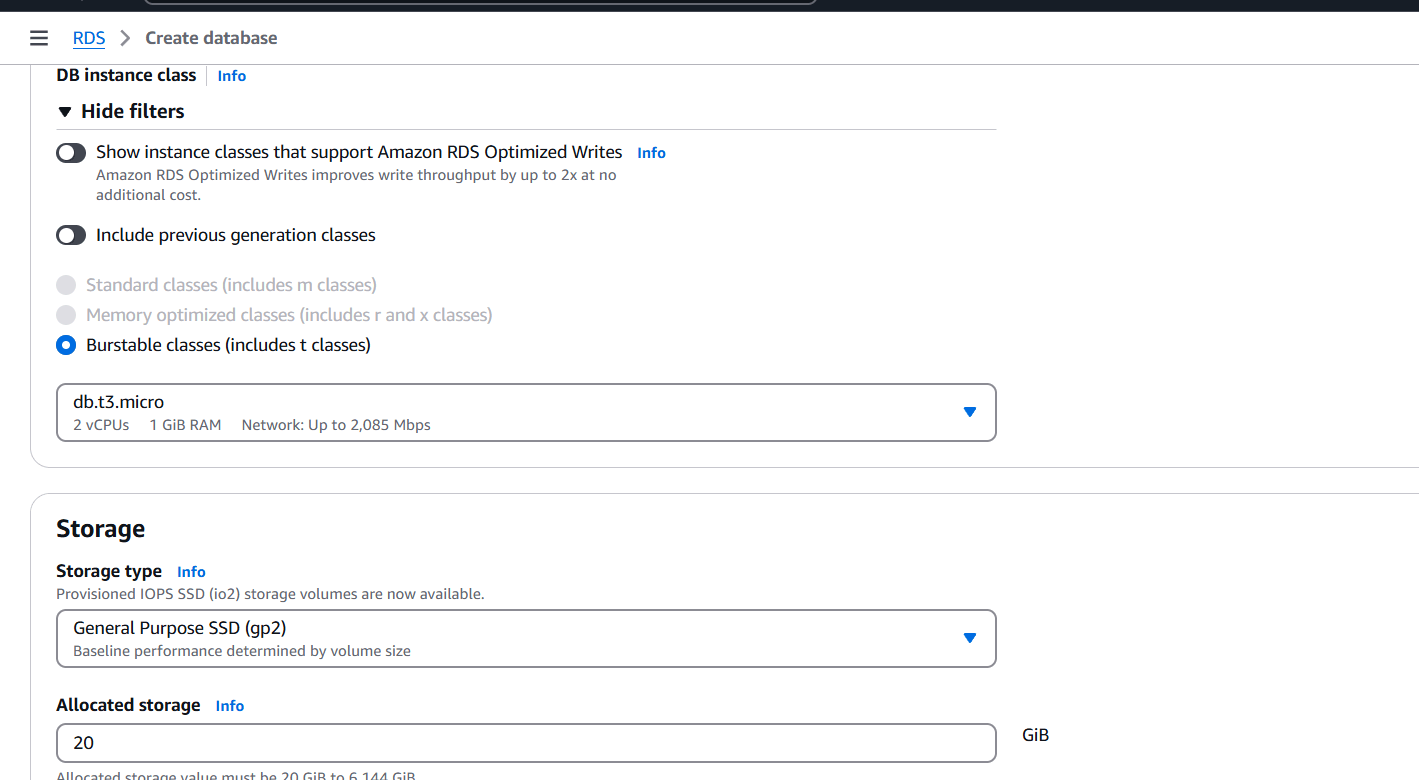
STEP 5: Select db.t3.micro.
- Click on create.
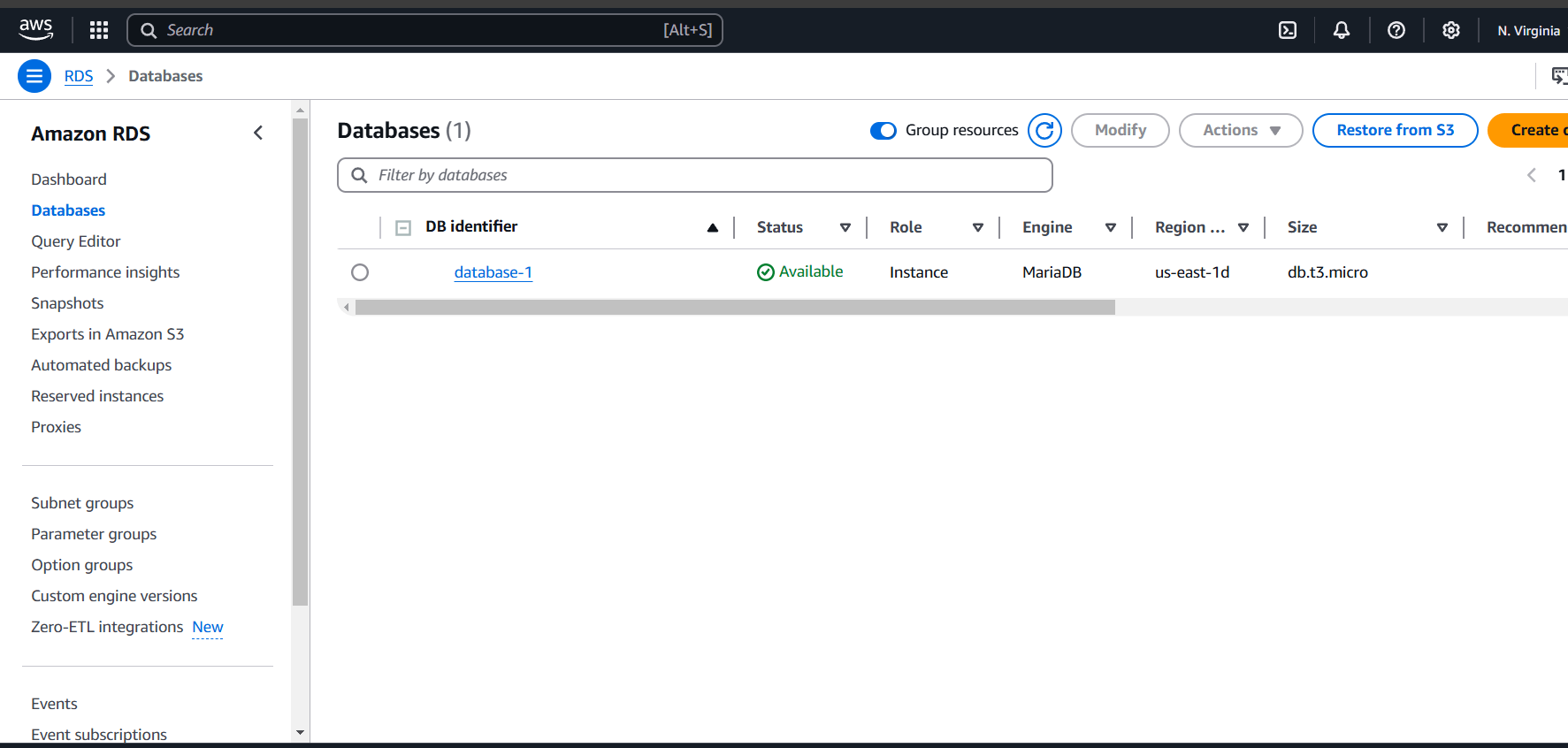
STEP 6: Accessing EC2 with SSH.
sudo su -
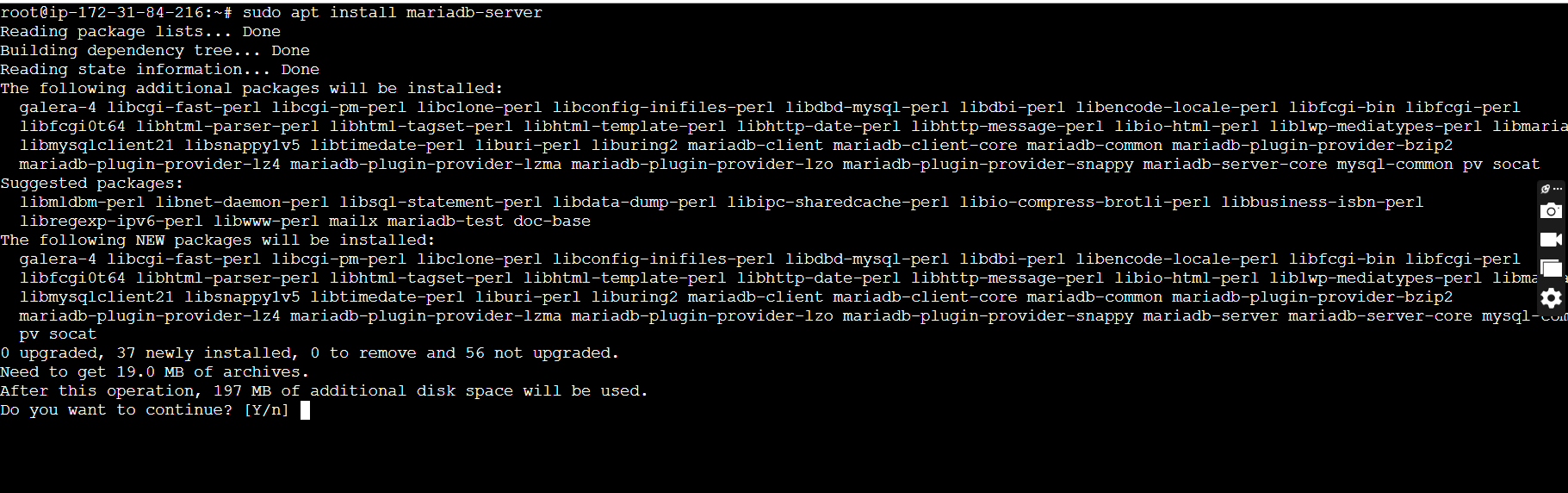
sudo apt install mariadb-server
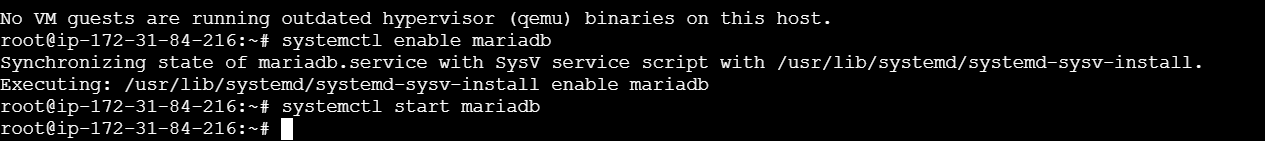
systemctl enable mariadb
systemctl start mariadb
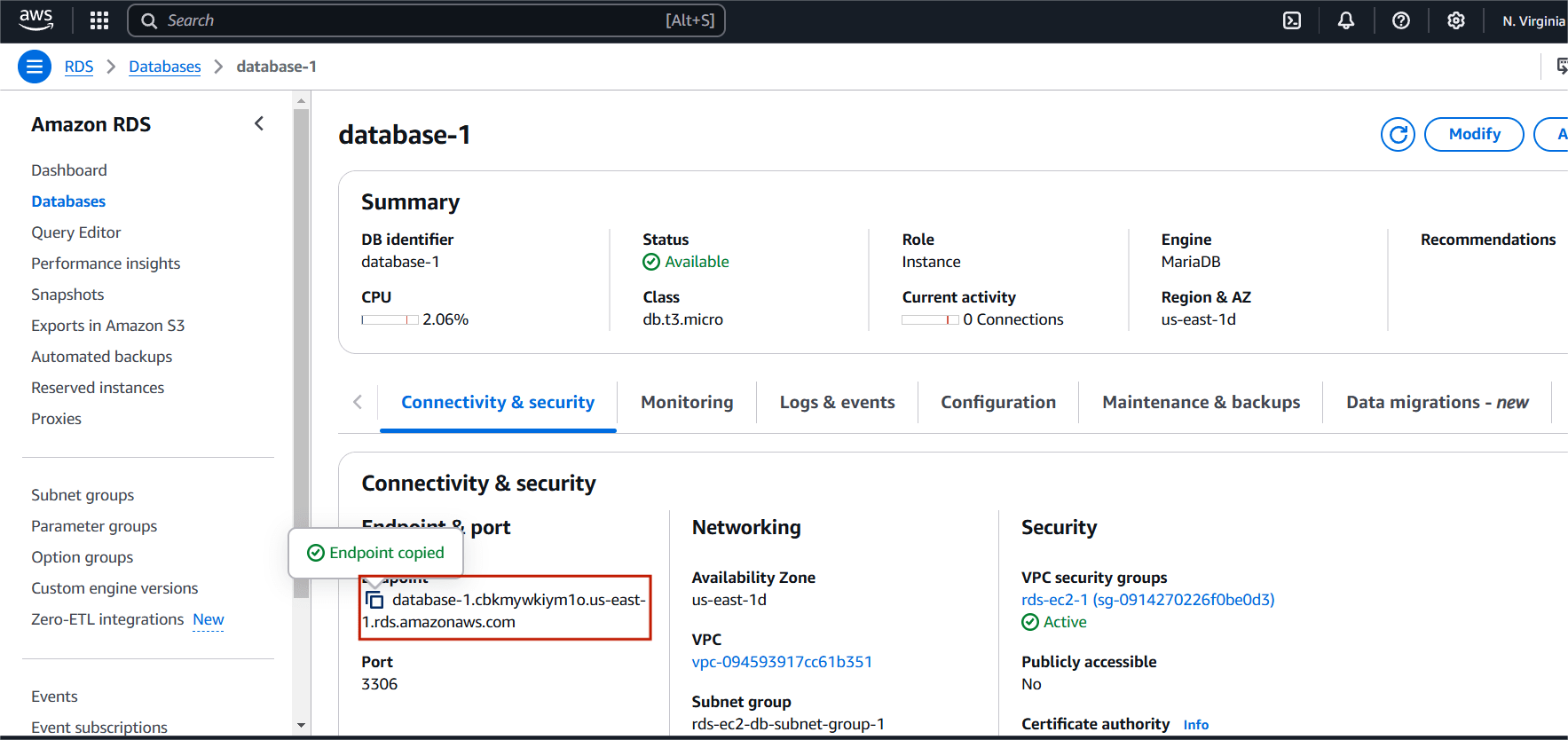
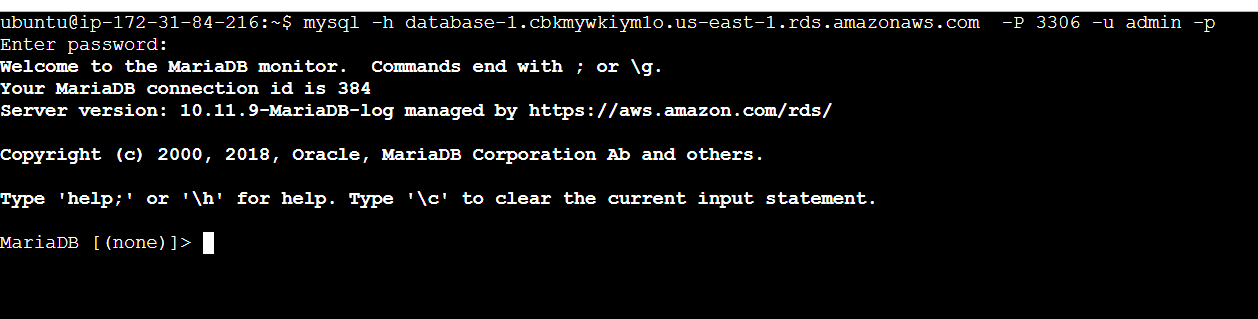
STEP 7: Connect the instance use the following command.
mysql -h <RDS endpoint> -p 3306 -u <username> -p

Conclusion.
Amazon RDS is a powerful service for managing relational databases in the cloud. It eliminates the overhead of database management tasks such as hardware provisioning, patching, backups, and scaling. With support for multiple database engines, high availability features, and robust security, RDS is an ideal choice for businesses of all sizes to manage their data in a cost-effective and efficient manner. Whether you’re running a small application or a large enterprise system, Amazon RDS makes it easier to deploy and manage relational databases at scale.
Deploying an EC2 Instance in Terraform Using VSC.
EC2 Instance:
An EC2 instance in AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a virtual server that runs applications and services in the cloud. It is part of the Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) service, which allows users to launch and manage virtual machines (VMs) in the cloud. EC2 instances provide a flexible, cost-effective way to run applications and services in the cloud without the need for physical hardware.

Terraform:
Terraform is an open-source Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool developed by HashiCorp, that lets you build, change, and version cloud and on-prem resources safely and efficiently in human-readable configuration files that you can version, reuse, and share.
In this article, I will demonstrate how to launch an Amazon EC2 instance using a Terraform script, with Visual Studio Code (VSCode) as the code editor.
Requirements:
- AWS Cloud Account.
- IAM User with Access and Secret Access keys.
- AWS CLI installed on your local machine.
- Terraform Installed on your local machine.
- Visual Studio Code.
STEP 1: Go to Visual studio code and select your folder.
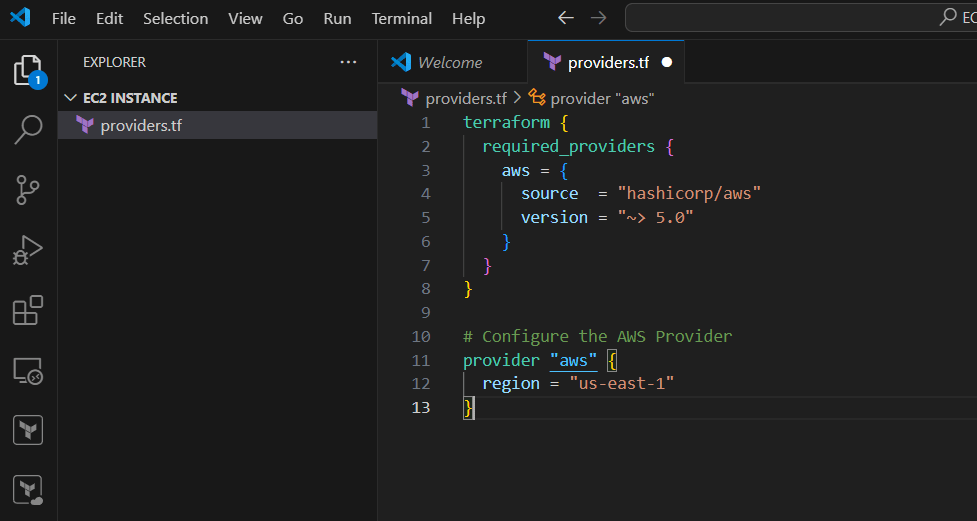
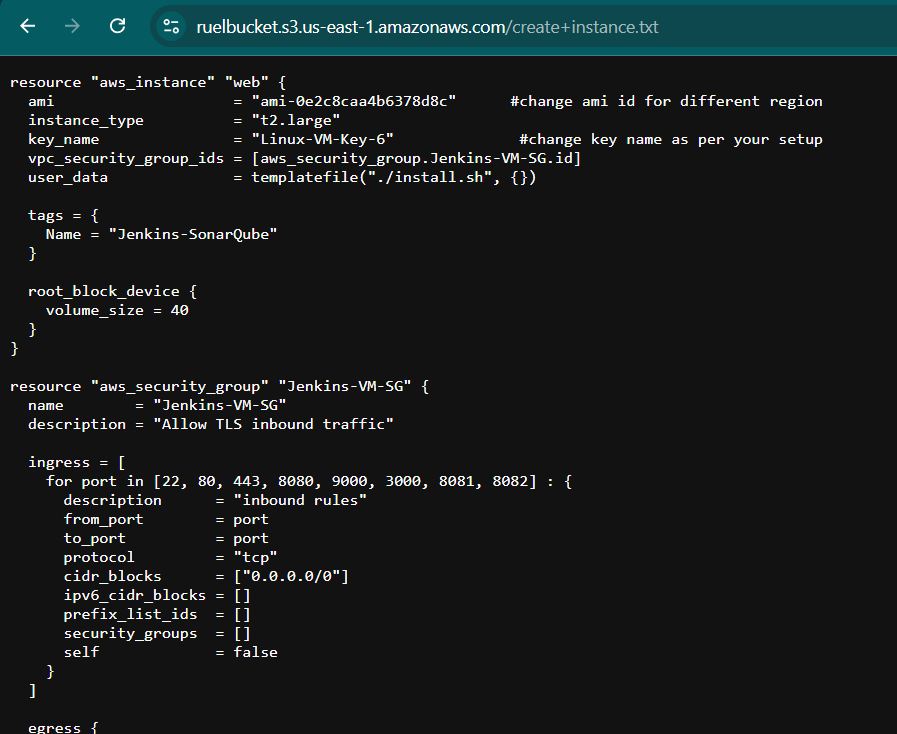
- Create providers.tf file Enter the following command and save it.
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 5.0" } } } # Configure the AWS Provider provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" }
STEP 2: Now, Create a another file main.tf.
- Enter the command and save it.
- AMI : Find the AMI ID on the ‘Launch Instance’ page of the Amazon EC2 console, as shown below.
- NAME : your instance name.
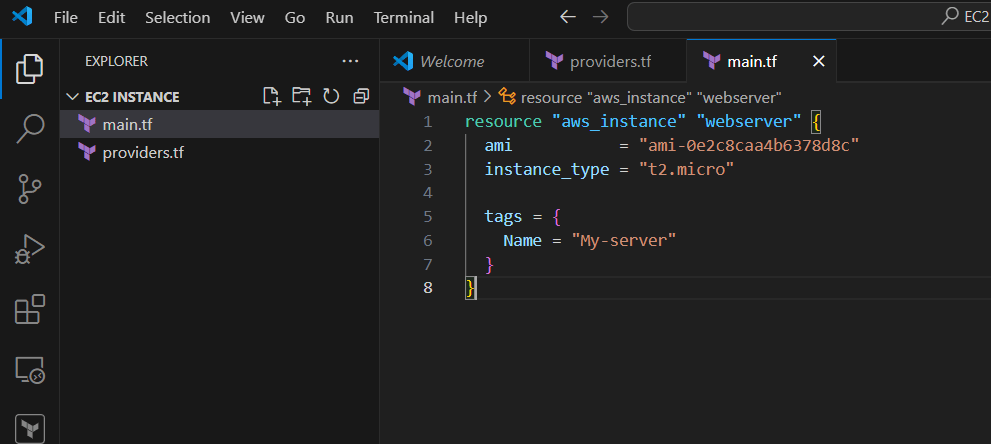
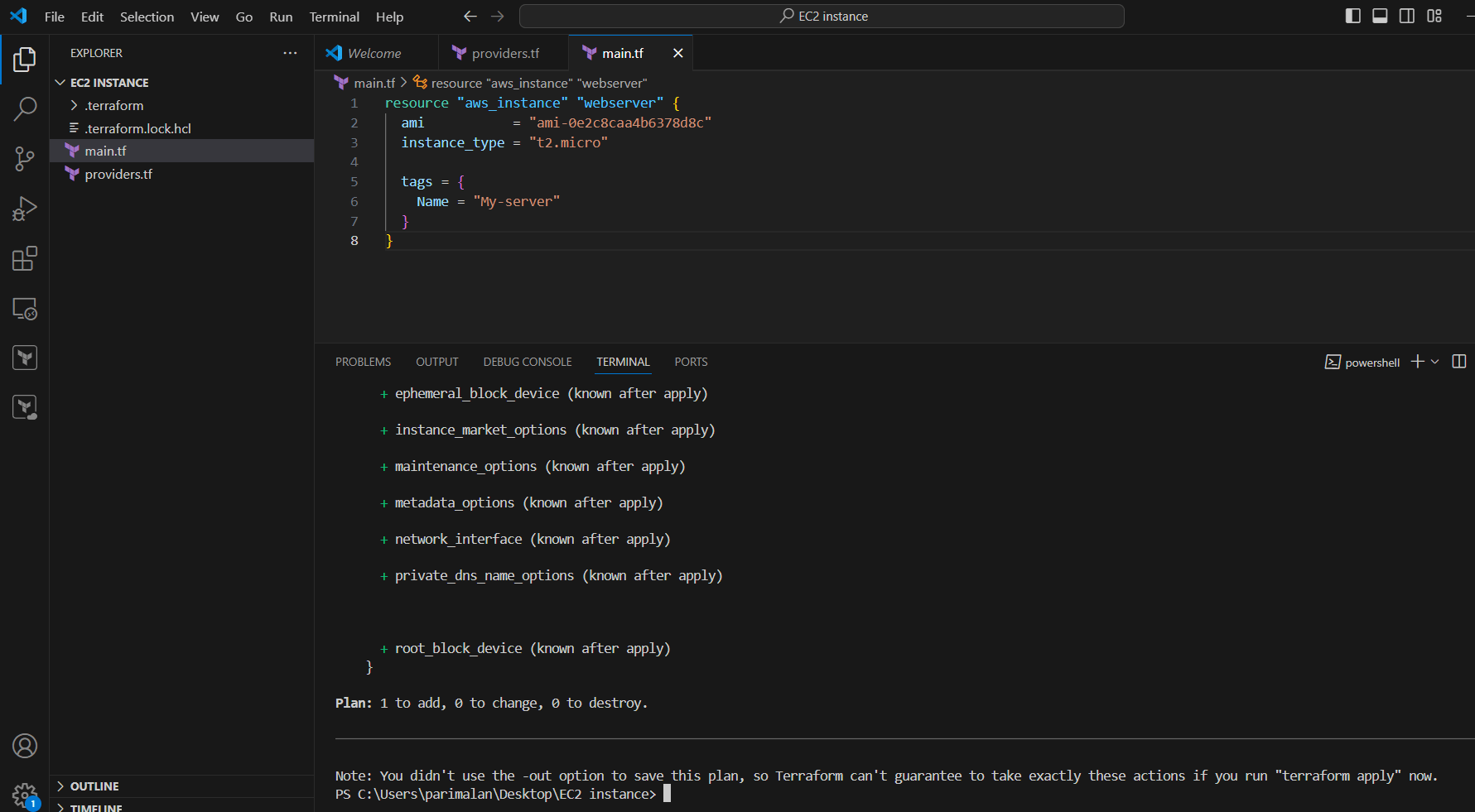
resource "aws_instance" "webserver" {
ami = "ami-0e2c8caa4b6378d8c"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags = {
Name = "My-server"
}
}
STEP 3: Go to view and Click on Terminal.
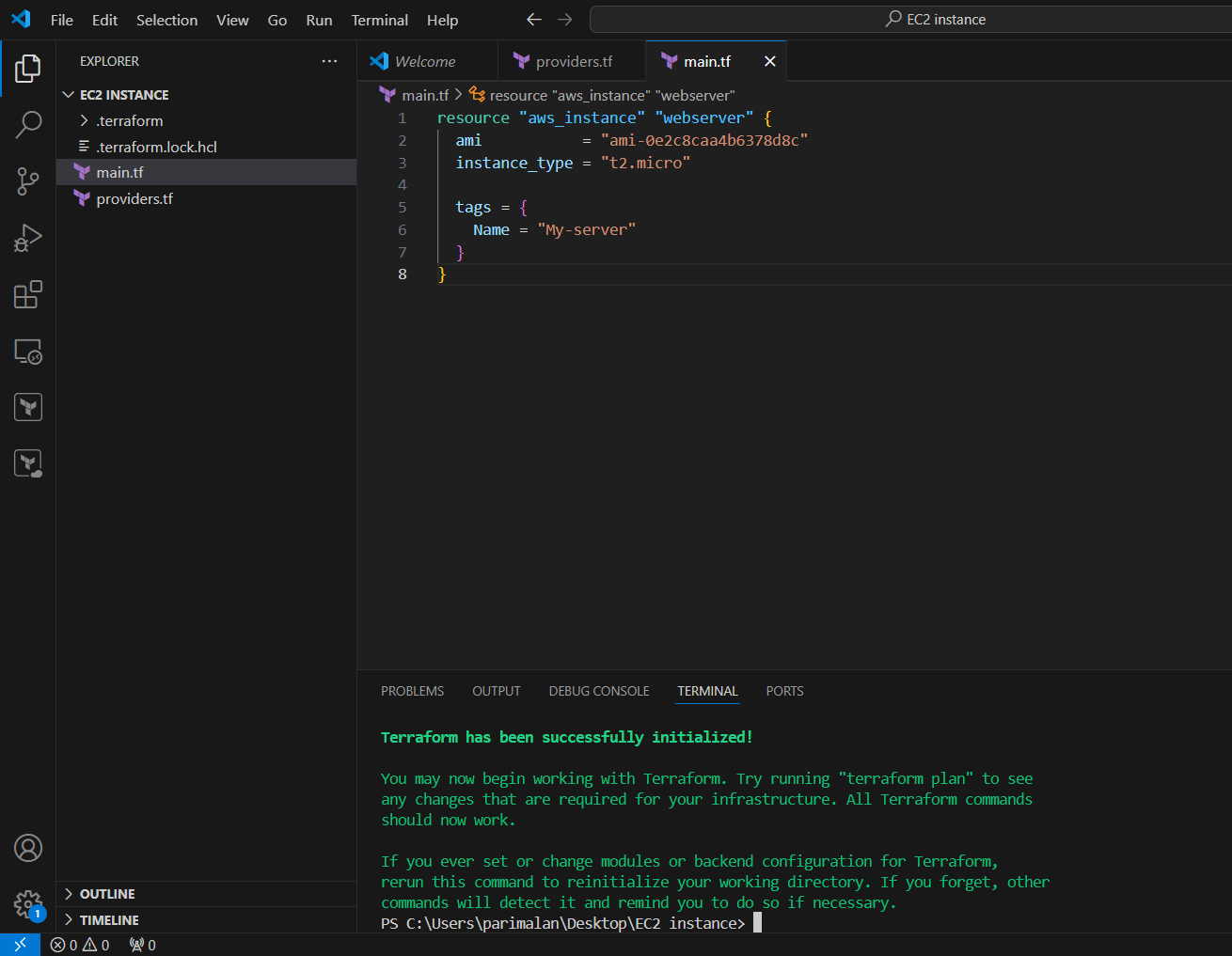
STEP 4: Initialize the configuration directory. Enter the following command.
terraform init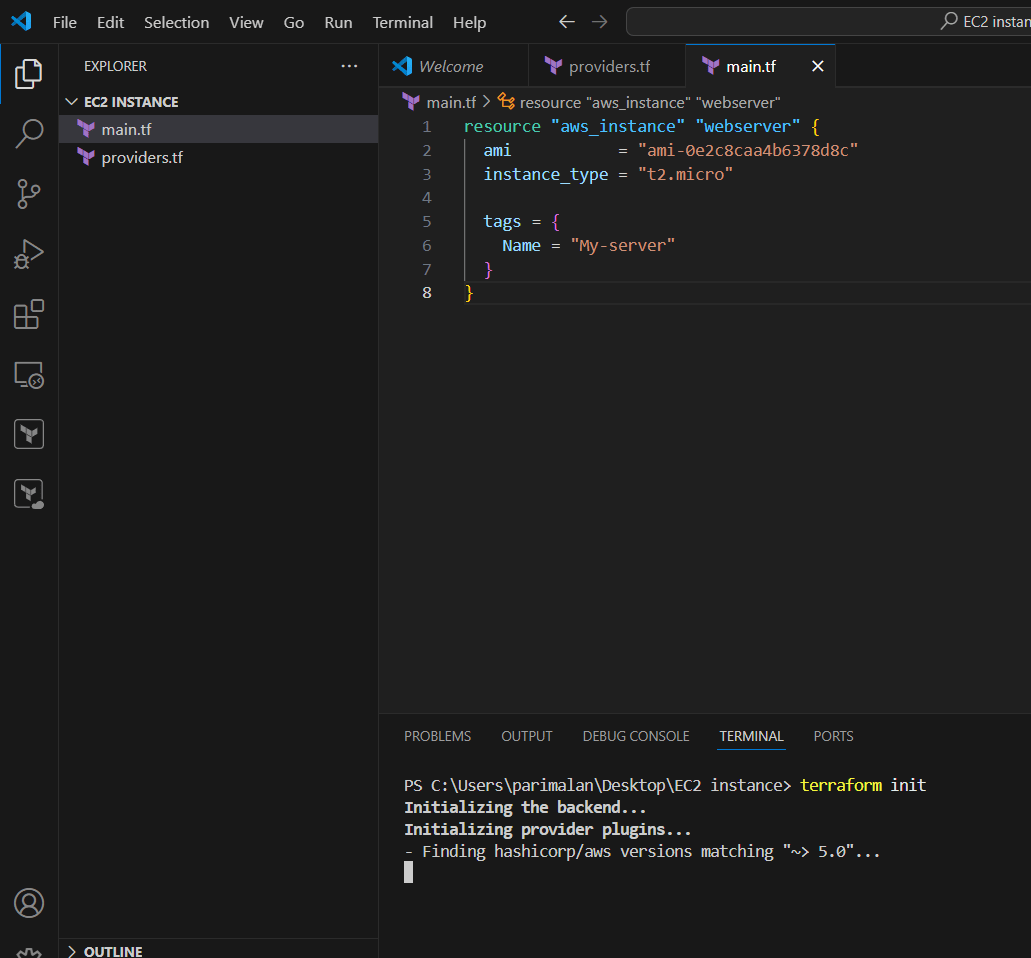
STEP 5: Generate an execution plan using the command.
terraform plan
STEP 6: Finally, apply the configuration to create our infrastructure using the command below.
terraform apply --auto-approve
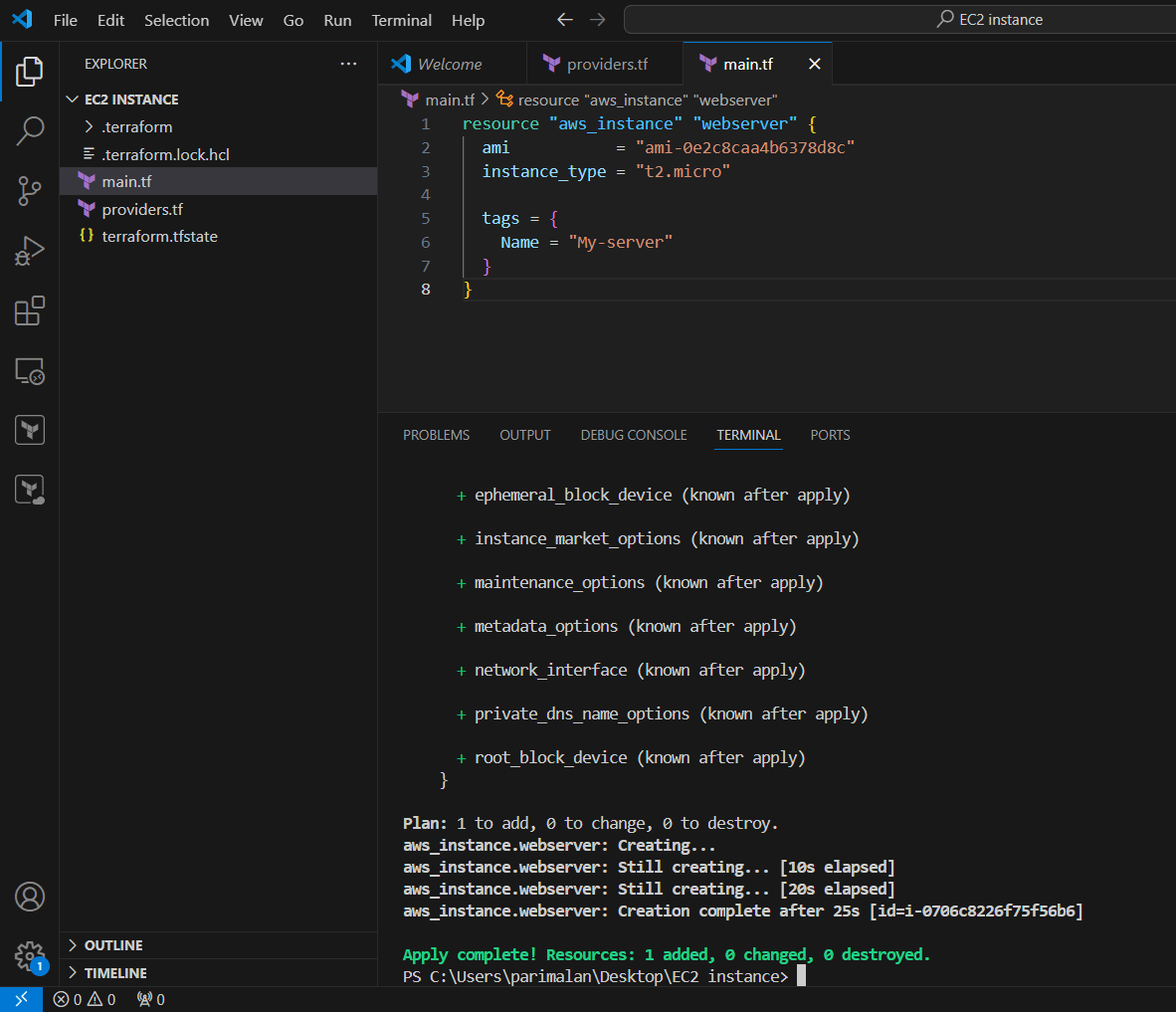
STEP 7: Go to AWS EC2 dashboard you will see your instance.
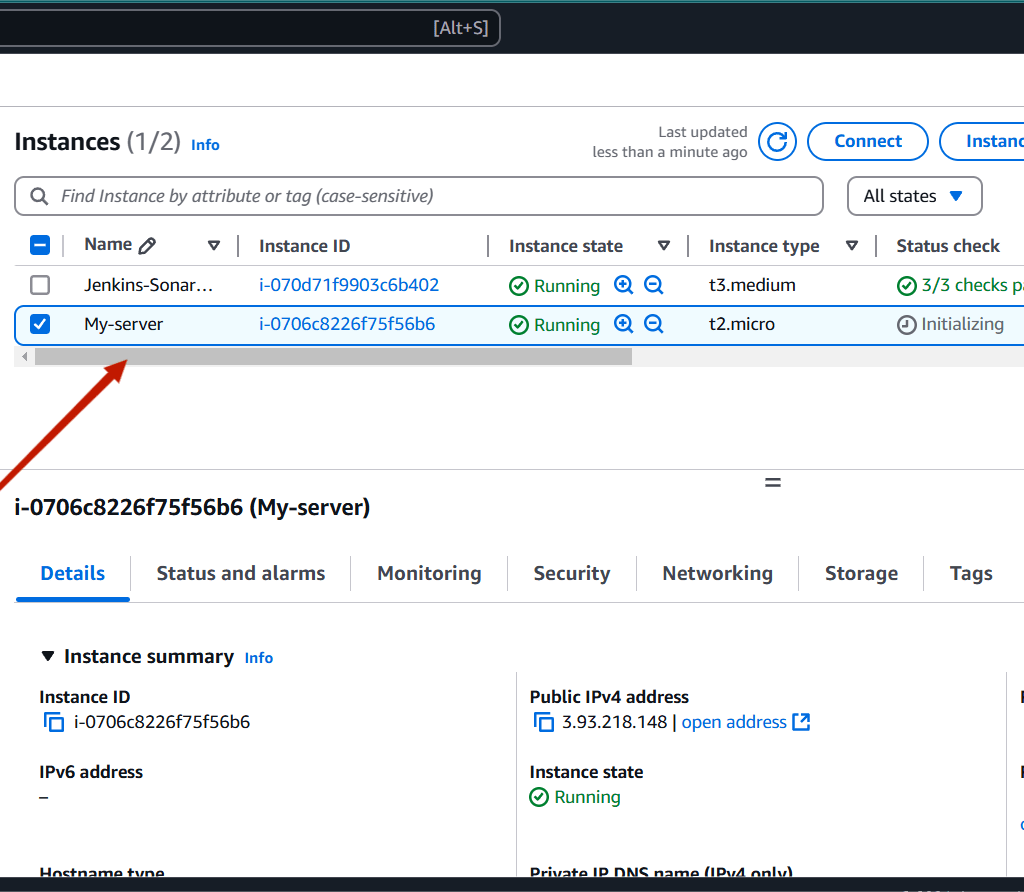

Conclusion.
Now that you’ve learned how to launch an EC2 instance with Terraform, you can start exploring more advanced Terraform features like modules, state management, and integrations with other AWS services. The possibilities are endless!
Step-by-Step Guide to Hosting a Static Website on AWS S3.
Introduction.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a scalable, high-performance cloud storage service that allows businesses and developers to store and retrieve data from anywhere on the web. It is probably the most commonly used, go-to storage service for AWS users given the features like extremely high availability, security, and simple connection to other AWS Services. Includes features like versioning, lifecycle management, and replication (cross-region or same-region replication). S3 is designed for 99.999999999% (11 9s) of durability, meaning your data is safe and highly available.

Let’s begin creating a static website hosting setup on AWS S3.
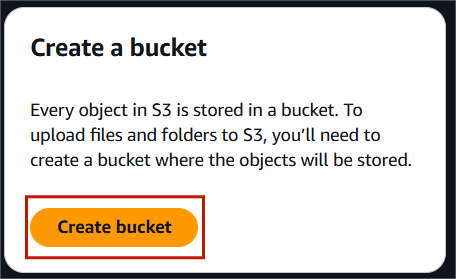
STEP 1: Navigate the S3 bucket and click on create bucket.
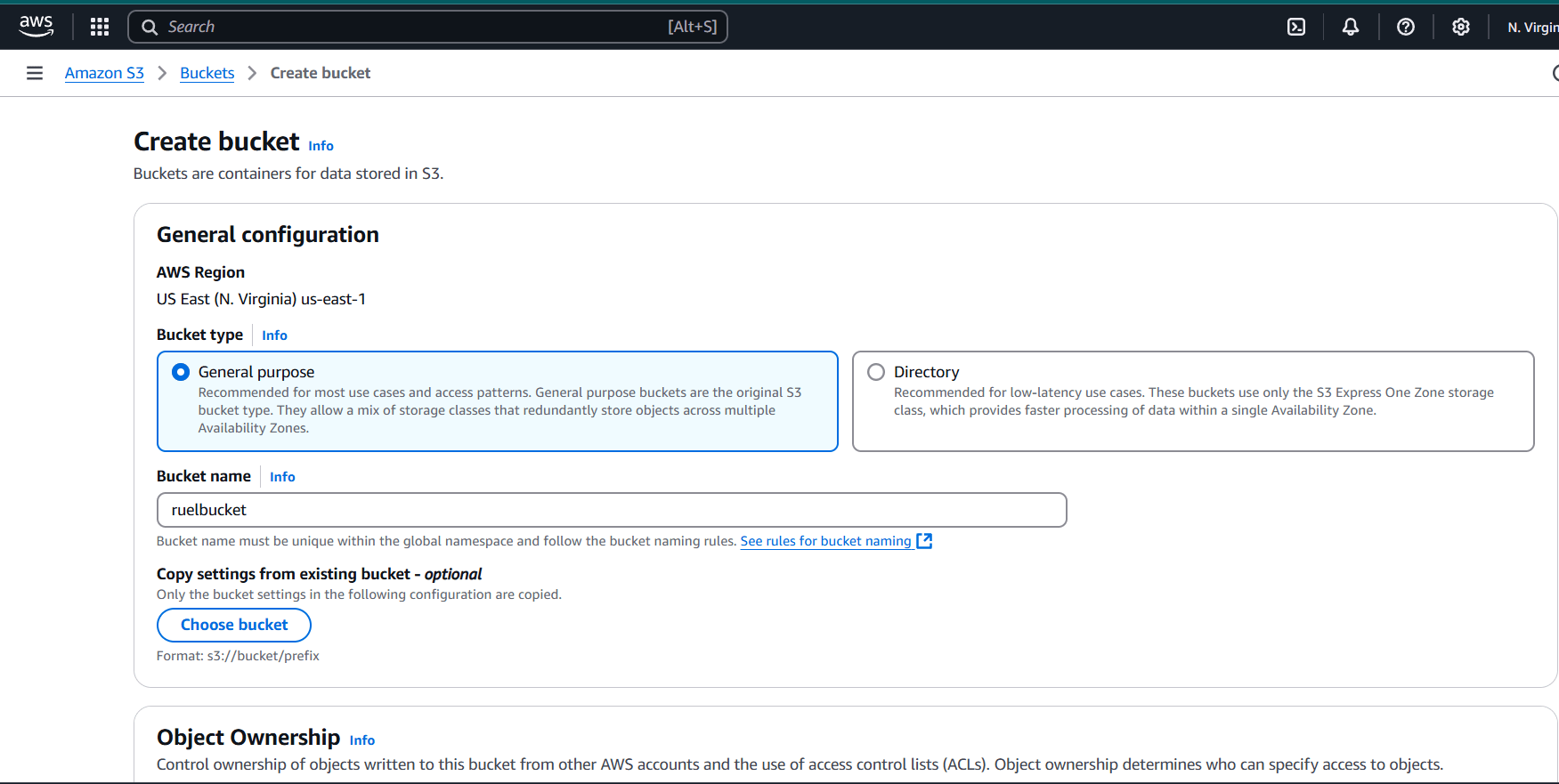
STEP 2: Bucket type : General purpose.
- Enter the bucket name.
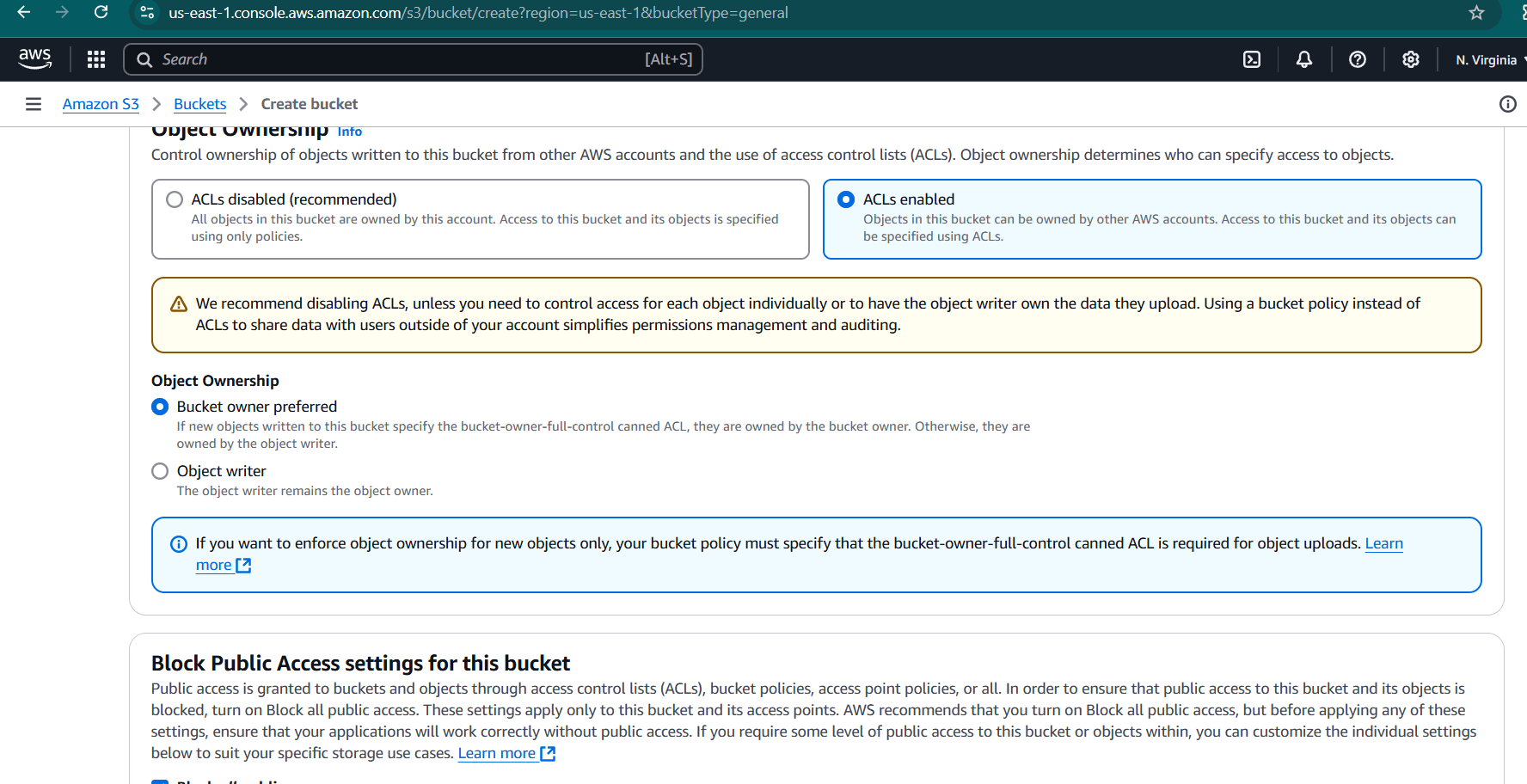
STEP 3: Object onwnership : ACLs enabled.
- Select the bucket owner preferred.
STEP 4: Place a tick on the marked.
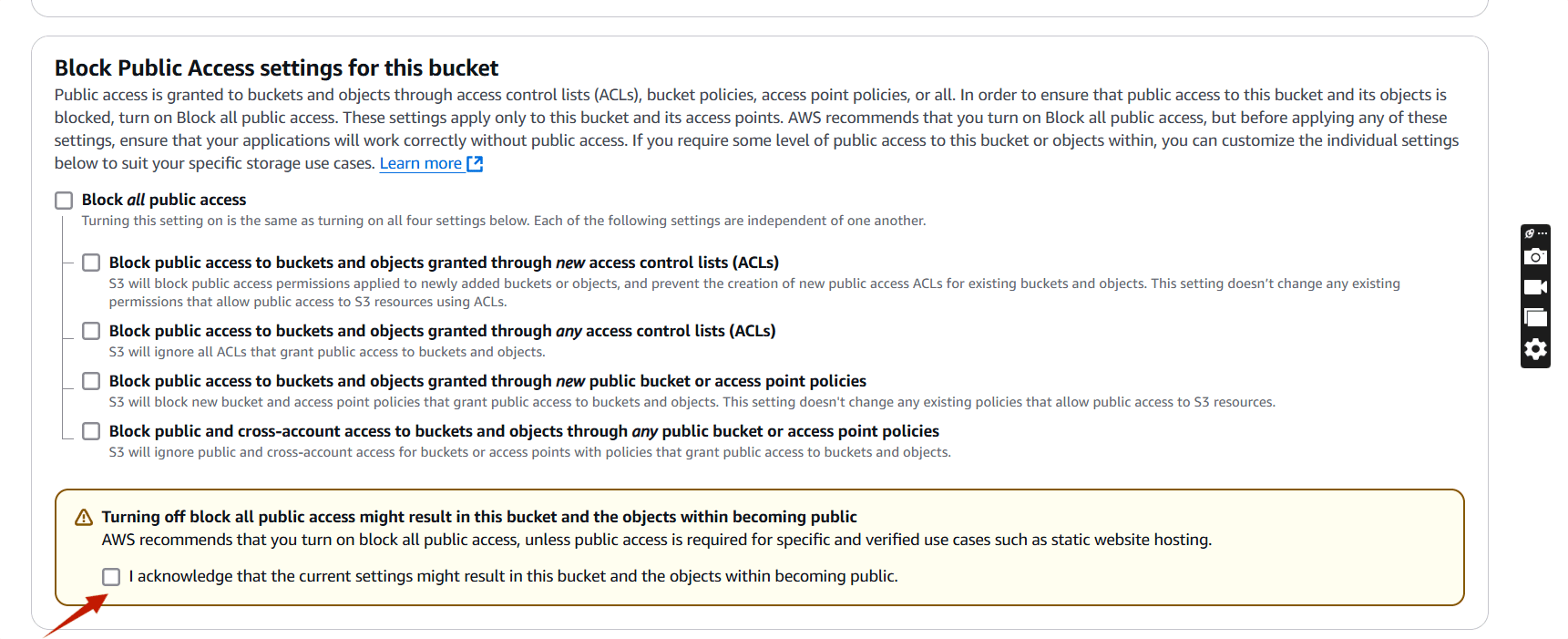
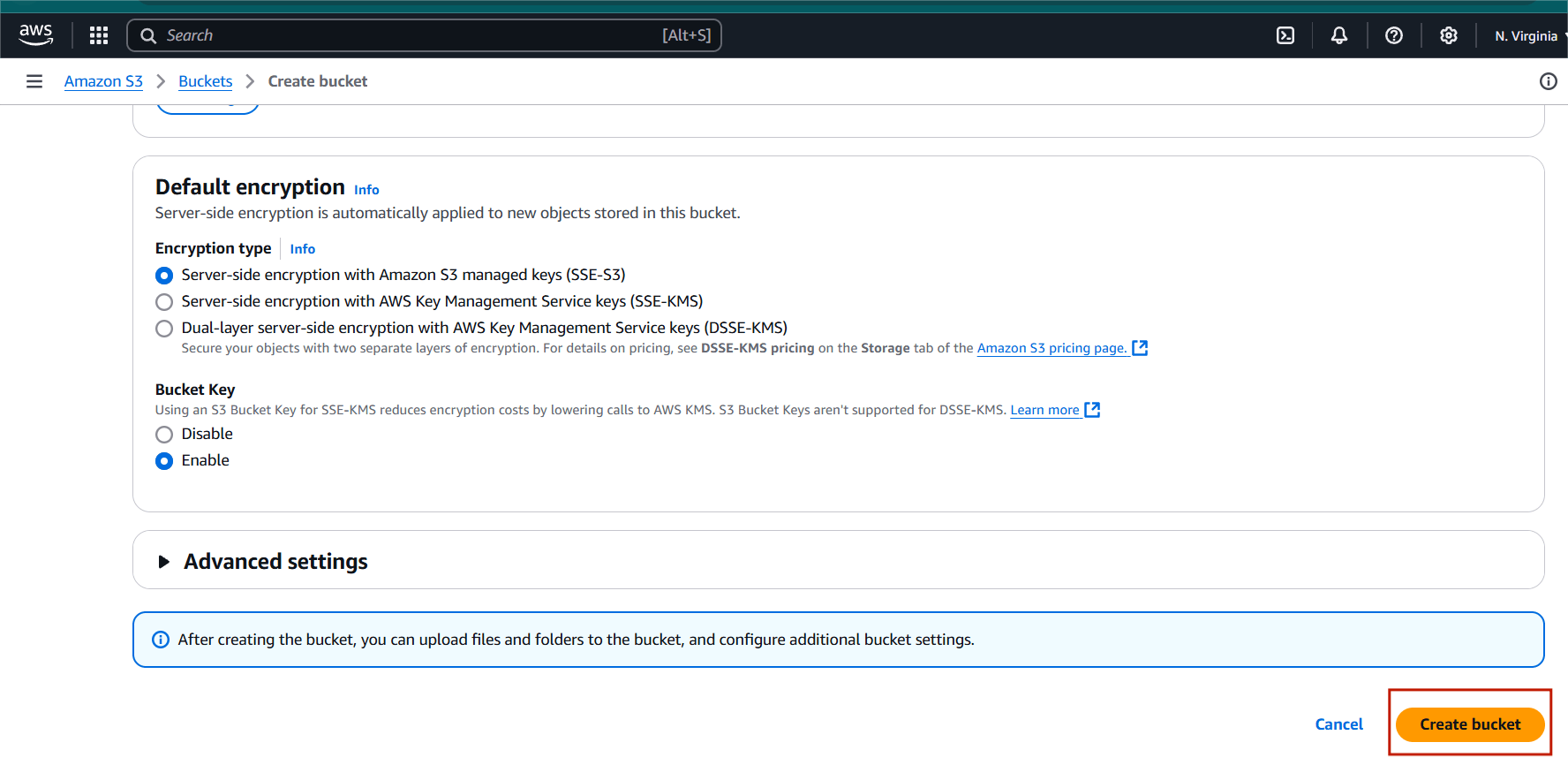
STEP 5: Click on create bucket.
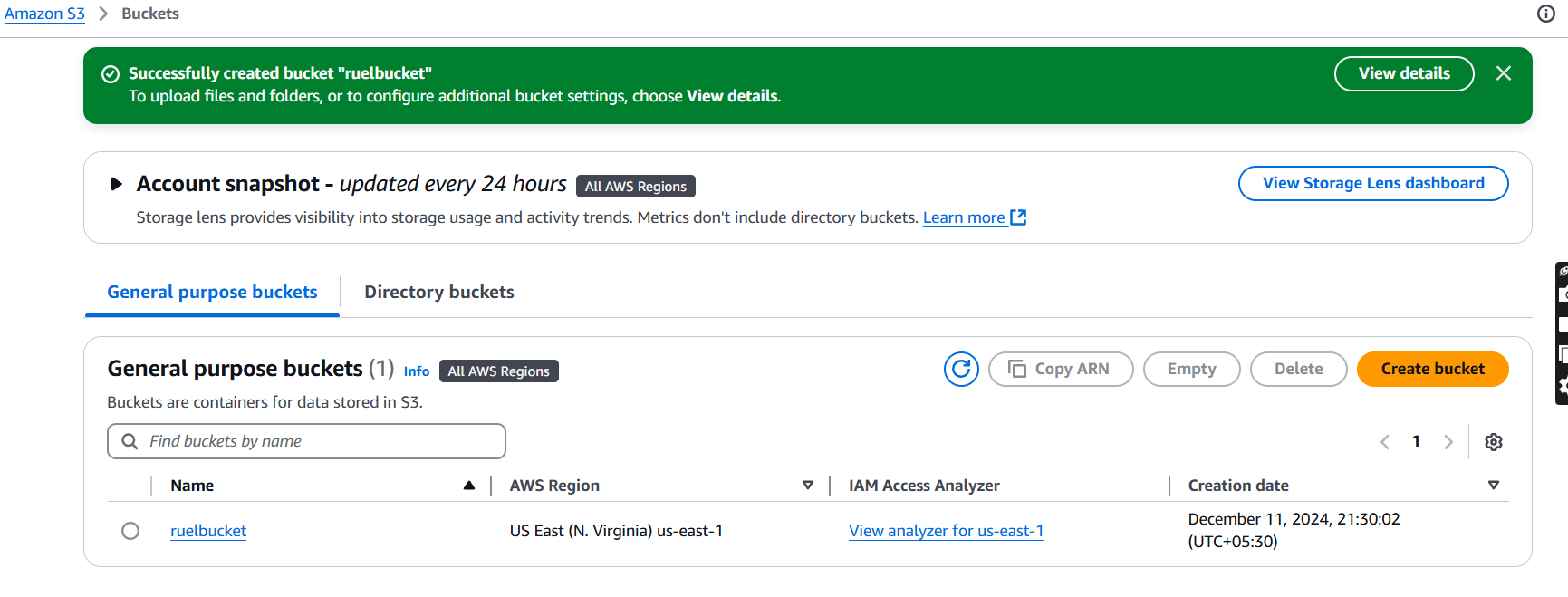
STEP 6: Select your bucket and upload the file.
- Click upload button.
- Select the add file.
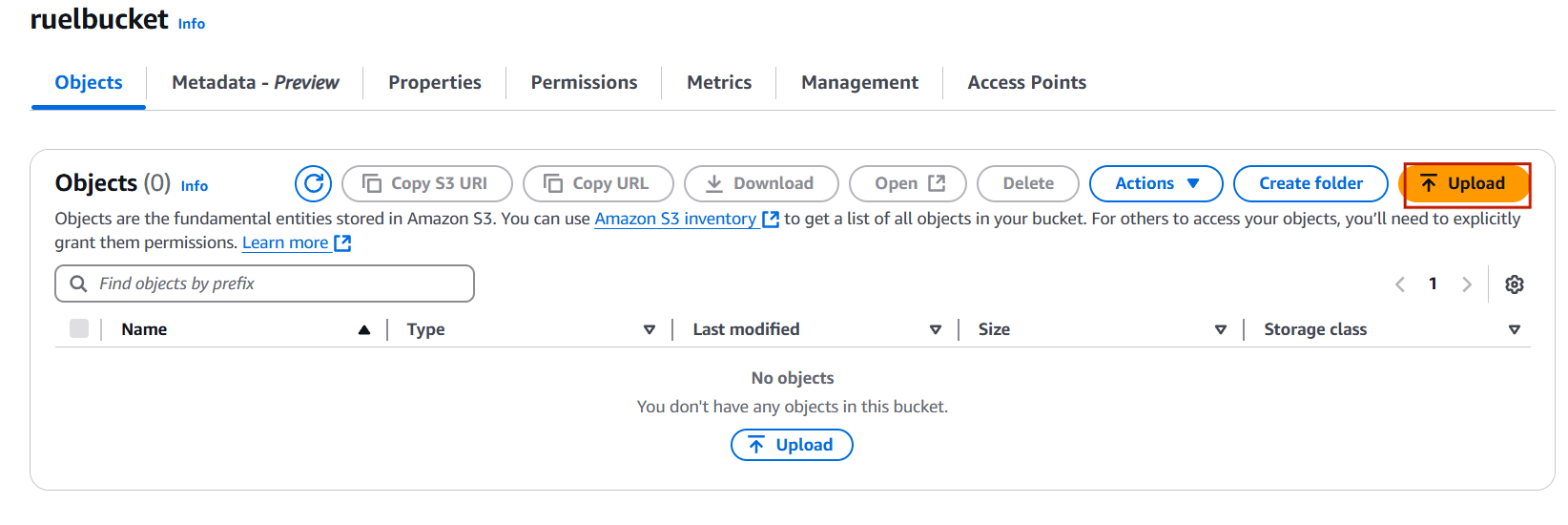
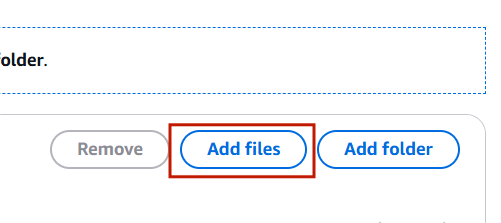
STEP 6: Add your file.
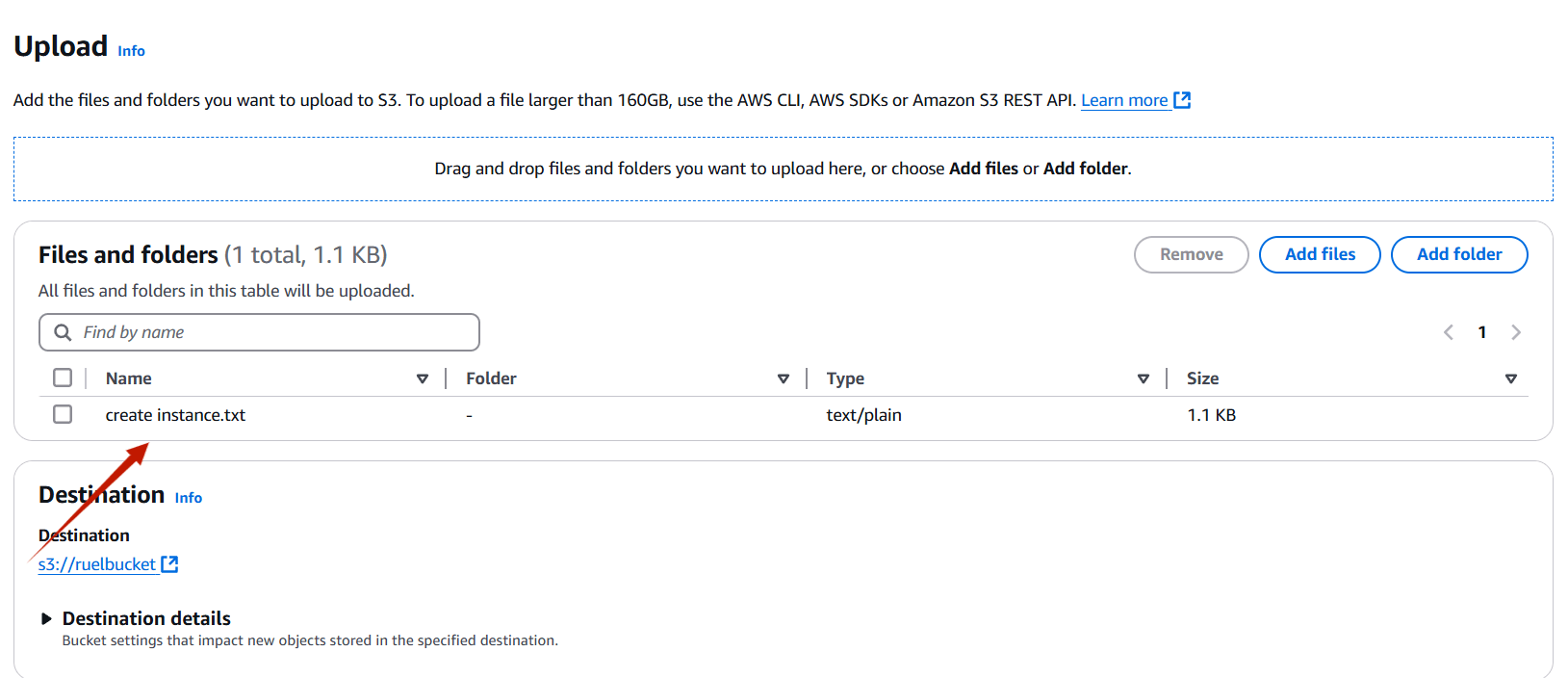
STEP 7: Click on permissions and Select the edit under bucket policy.
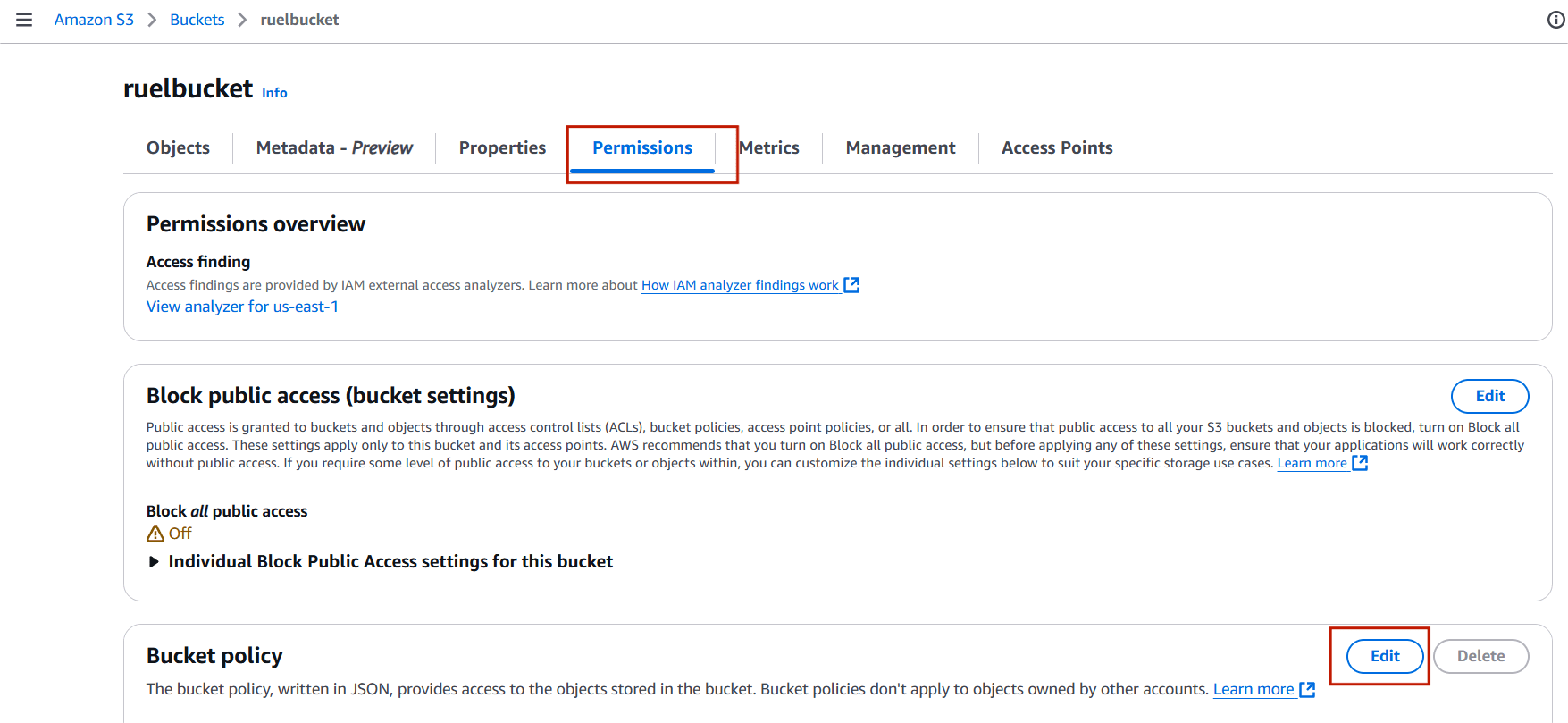
STEP 8: Uncheck Block all public access.
- Click on save changes.
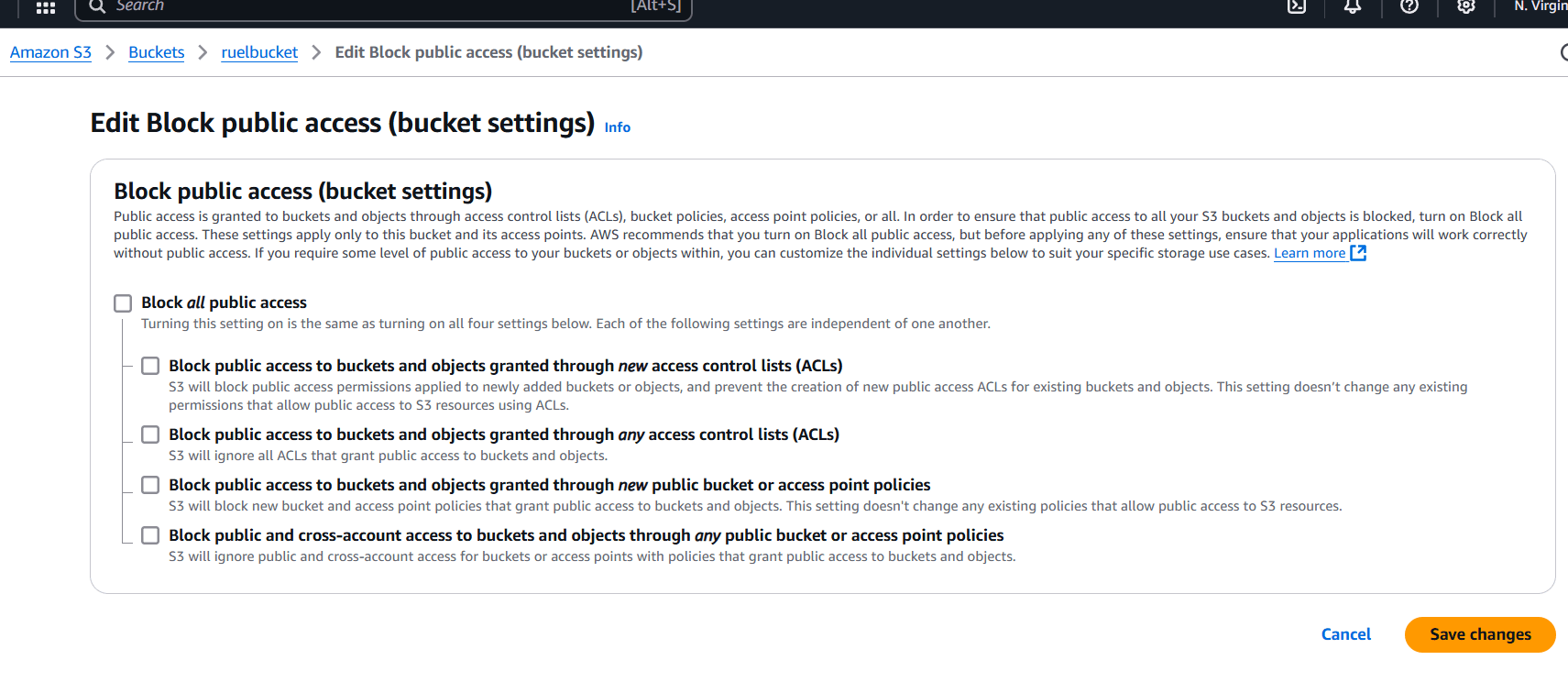
STEP 9: Next, Click on edit under object ownership.
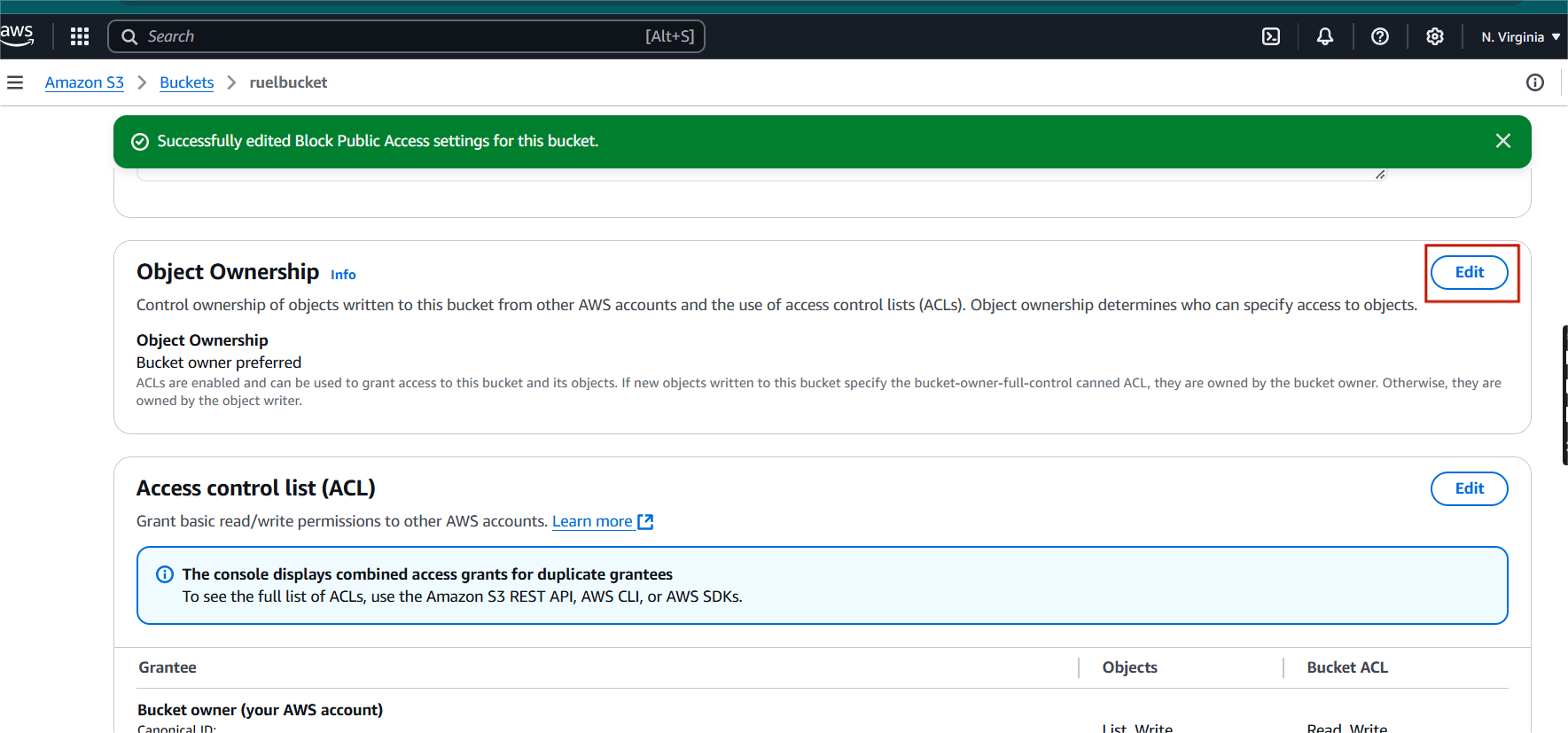
Step 10: Select ACLs enabled.
- Click on save changes.

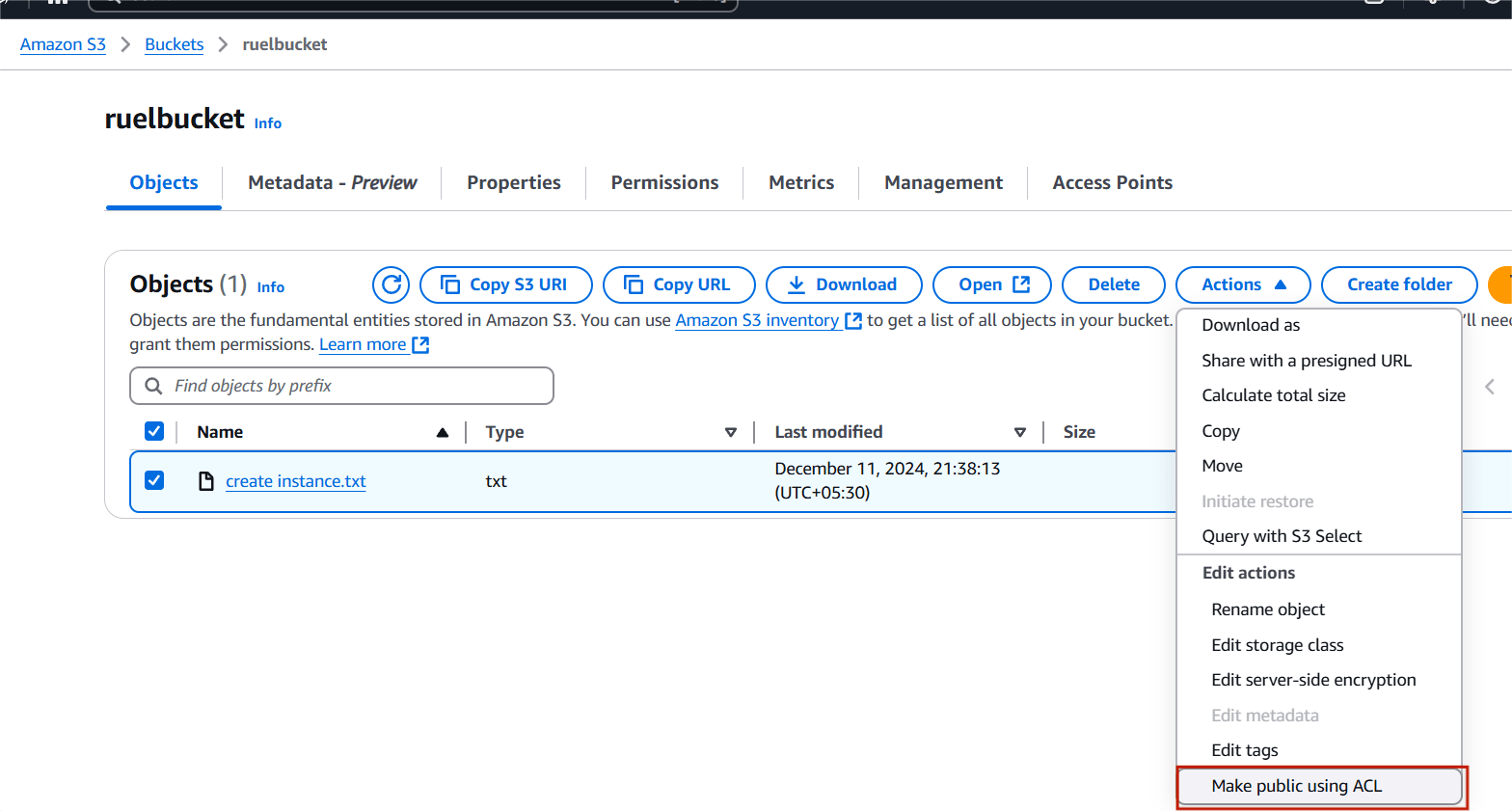
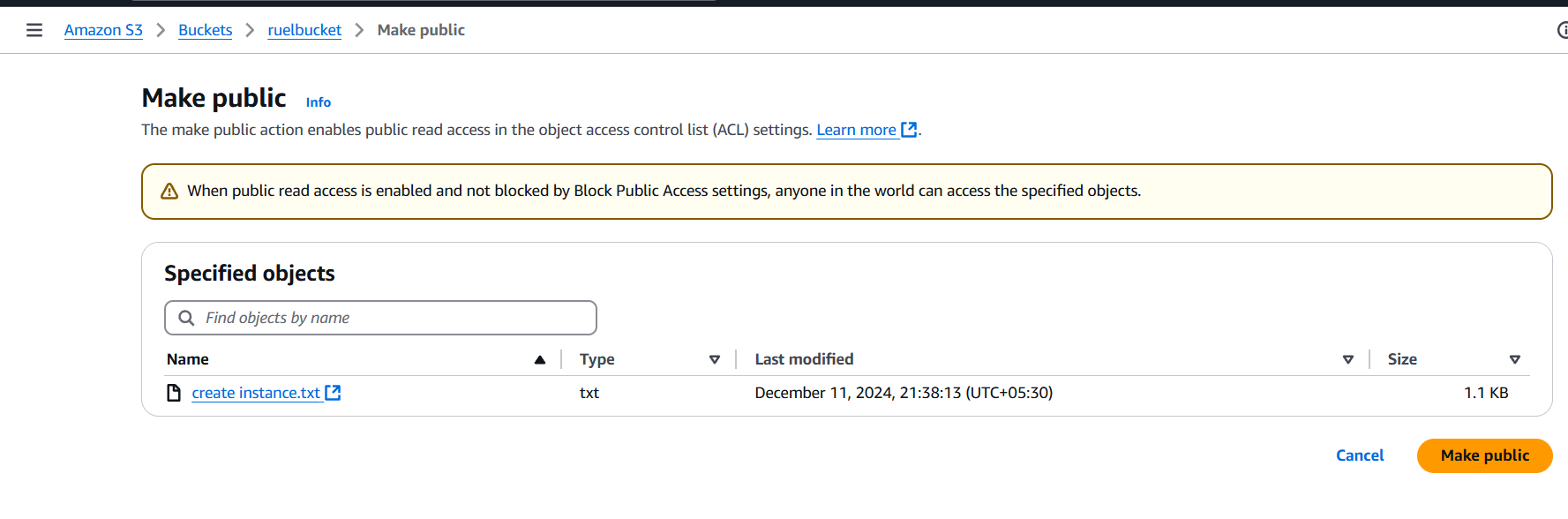
STEP 11: Select your code file and click on action button.
- Select make public using ACL.
- And click make changes.
STEP 12: Copy your object URL and paste your browser.
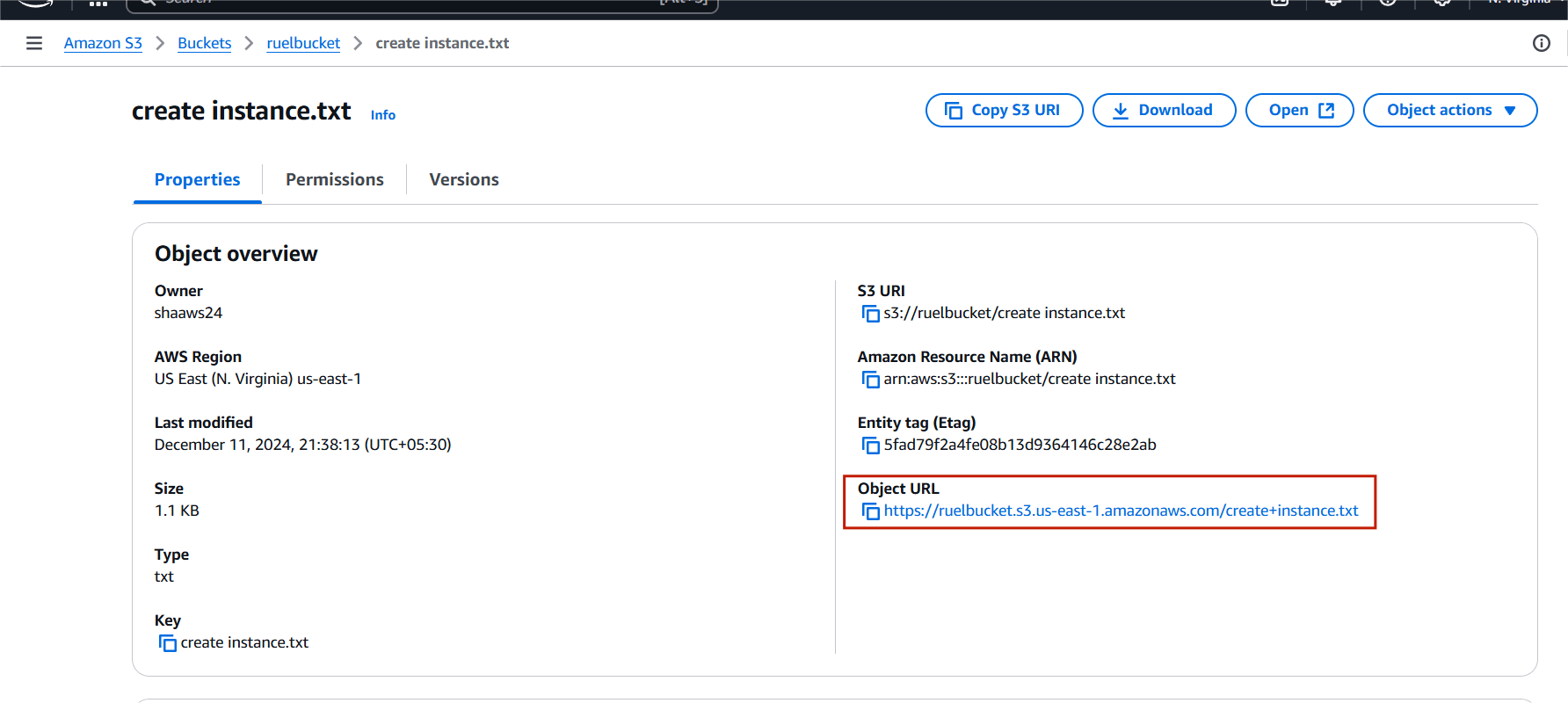

STEP 13: You will see your code file on your browser.

Conclusion.
Well done! Your website is now available to the public. This guide has shown how easy it is to host a static website on AWS S3—an essential skill for any modern developer. S3 bucket Store backups and archive data with S3 Glacier for long-term storage. It’s Automatically moves data to the most cost-effective storage tier based on access patterns. Low-cost storage for data archiving and backup, with retrieval times ranging from minutes to hours.
How to Install Docker and Use Basic Commands.
Introduction.
Docker is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of applications by packaging them into lightweight, portable containers. Containers package up everything an application needs to run: the code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings.
Core Components:
- Images : Docker images are read-only templates, meaning they cannot be altered after creation. Changes result in a new image being created.
- Containers : Containers are created from Docker images and provide an isolated environment for running applications.
- Registries : A Docker registry is a centralized repository where Docker images are stored, managed, and distributed. It allows developers and teams to share and access Docker images, enabling efficient deployment of applications across different environments.
- Docker Engine : Docker Engine provides the foundation for Docker’s functionality, including building images, managing containers, and networking.

Docker installation.
STEP 1: Terminate any running Docker containers and remove their associated files from the system.
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io
sudo apt-get update
STEP 2: Install the docker use the following command,
sudo apt install docker.io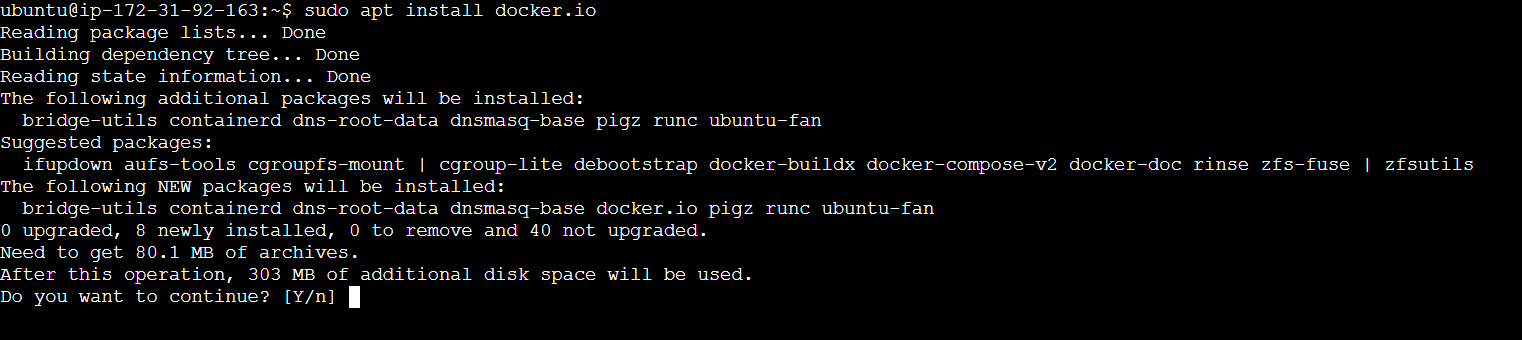
STEP 3: Enable and start the server.
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl status docker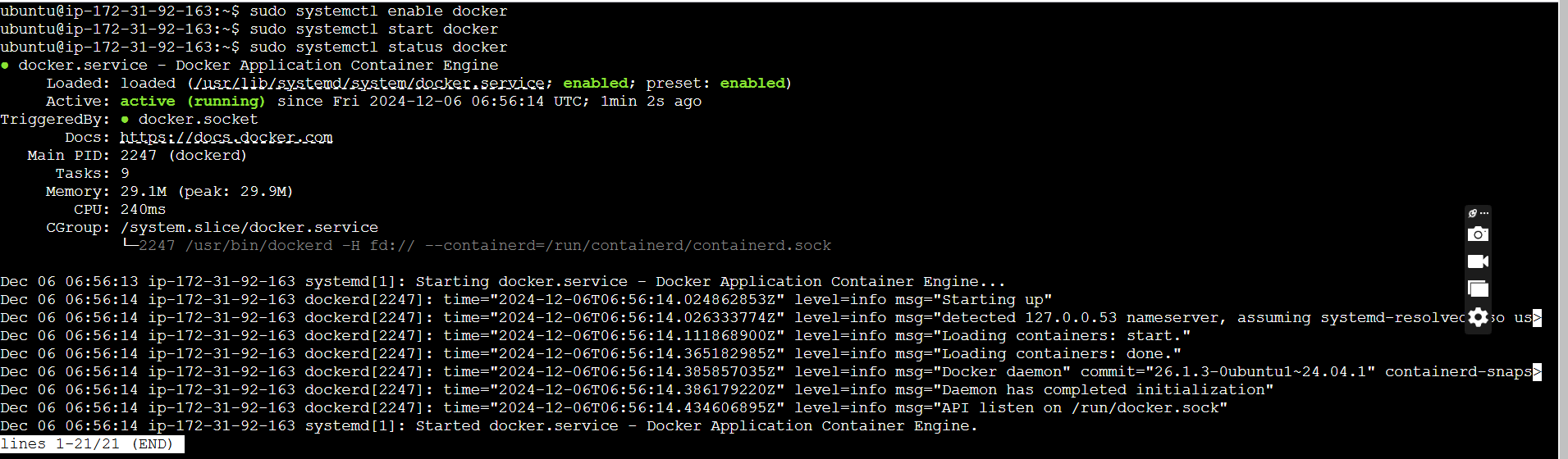
STEP 4: Check the version installed using the following command.
docker --version
STEP 5: Check the docker images.
sudo docker images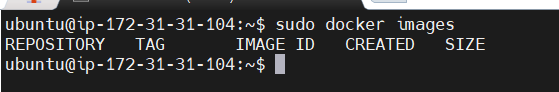
There are no Docker images on my system.
STEP 6: Pull an image from the Docker hub.
sudo docker run hello-world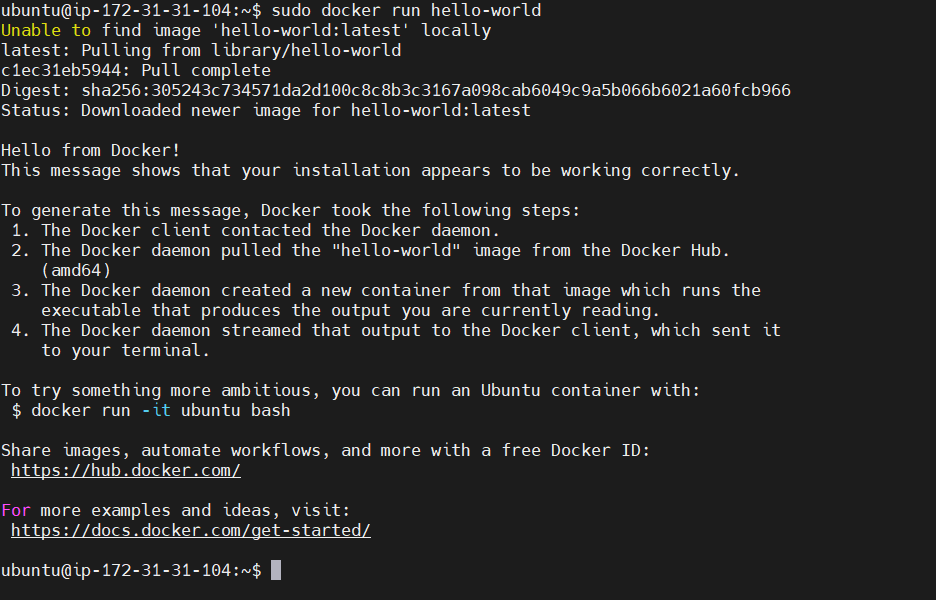
STEP 7: Now I check my images.
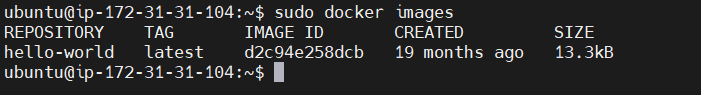
STEP 8: Display all the containers pulled.
sudo docker ps -a
STEP 9: Create the docker group.
sudo groupadd docker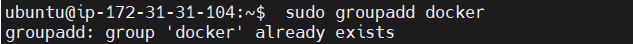
STEP 10: As the next step, add the user to the Docker group by executing the following command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER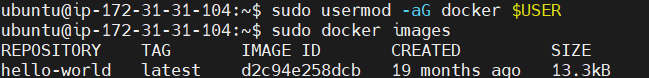
STEP 11: Docker to list all images stored on the system.
sudo docker images -a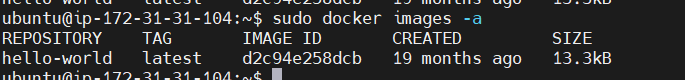
STEP 12: Search for Docker images in the Docker Hub repository.
sudo docker search <image-name>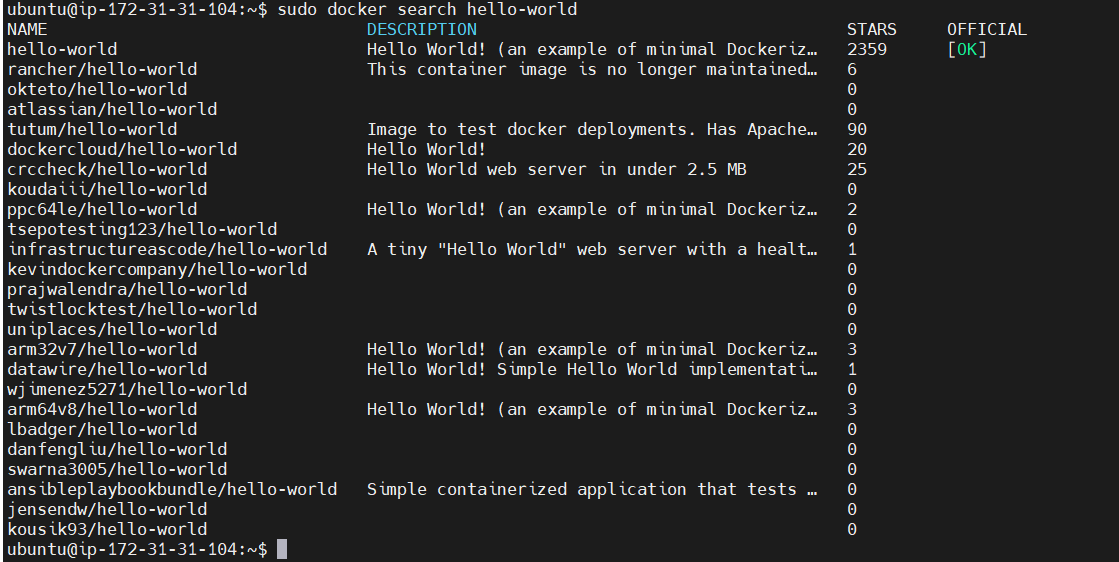
STEP 13: Pull the ubuntu docker image.
sudo docker pull ubuntu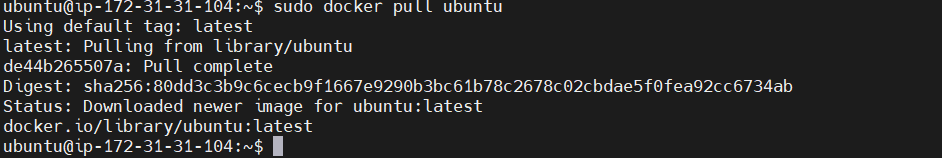
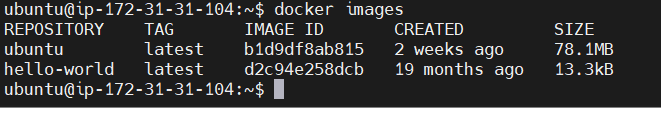
STEP 14: Activate the Container.
“b1d9df8ab815” Replace your Image ID.
sudo docker run -it b1d9df8ab815 bin/bash

Conclusion.
Docker has become an integral tool in modern application development and operations. Its seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines and orchestration tools like Kubernetes ensures that modern teams can adopt faster, more agile, and error-free development practices.
How to Create a Billing Alarm in Minutes.
Introduction.
Cloudwatch:
AWS CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service that provides actionable insights into your AWS resources, applications, and services. We can use cloud watch to collect metrics of the applications and services we are running in real-time. Amazon Cloudwatch services collect metrics from each aws resource If required you can enable detailed monitoring as well.

CloudWatch Alarms.
Cloudwatch alarm is used to monitor a single cloud watch metric or the result of Match expression using cloud watch metrics. They are tightly integrated with CloudWatch metrics and are used for operational alerts and automated responses. it sends out a notification based on the threshold we set for each service in the cloud watch alarm.
Diagram.
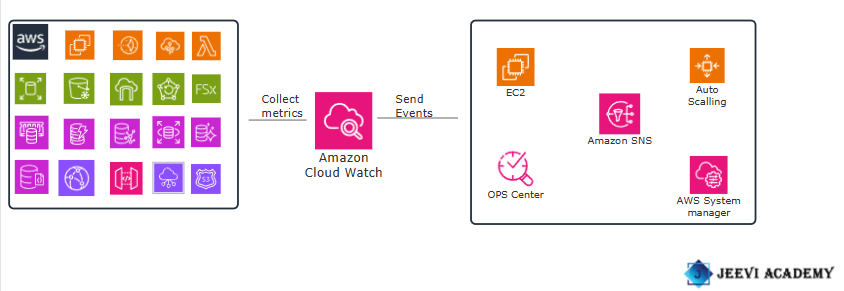
Let’s get started with creating a billing alarm.
Enable Billing Metrics in CloudWatch.
STEP 1: Log in to your AWS Management Console.
- Go to the Billing Dashboard.
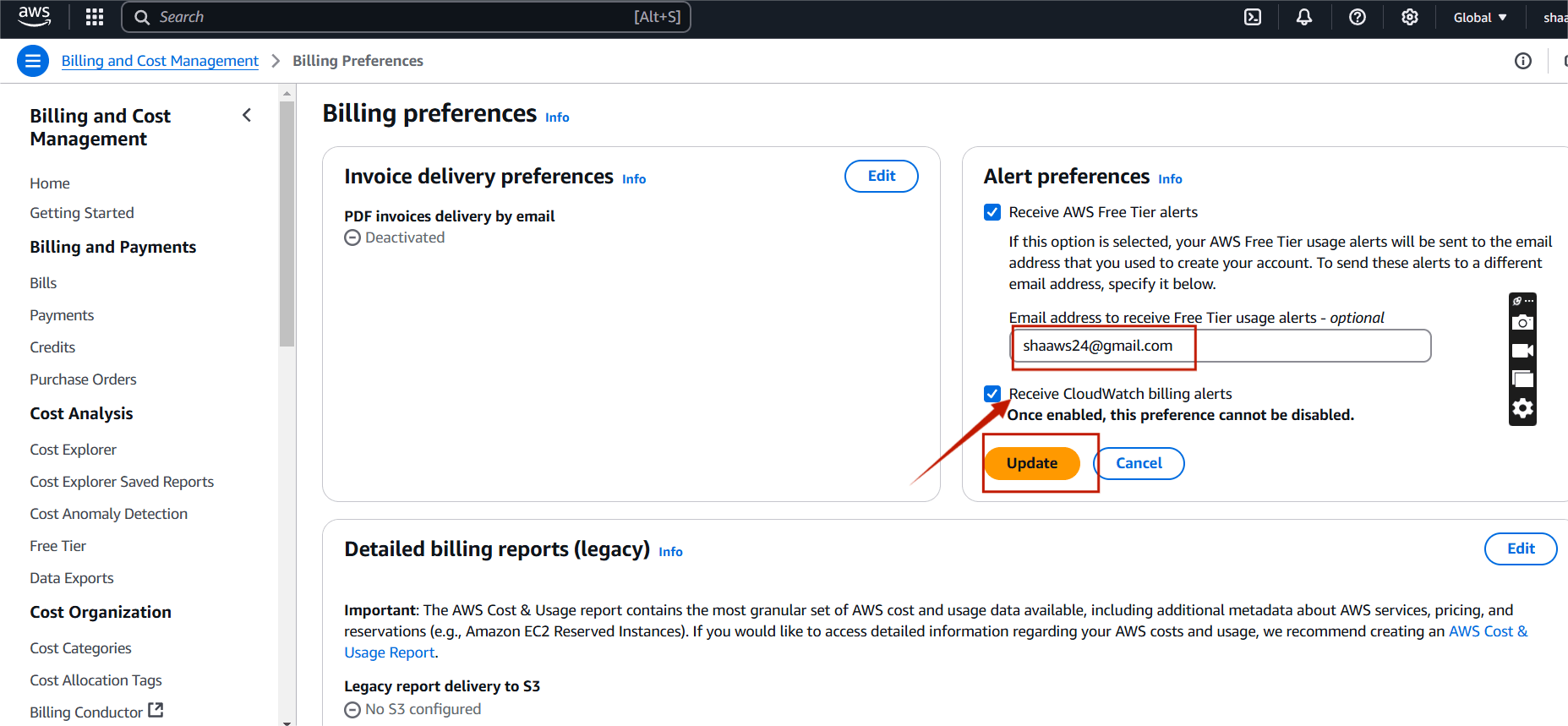
STEP 2: Scroll down and select billing preferences.
STEP 3: Enter your mail ID and tick recive cloudwatch billing alerts.
- Click update.
CloudWatch.
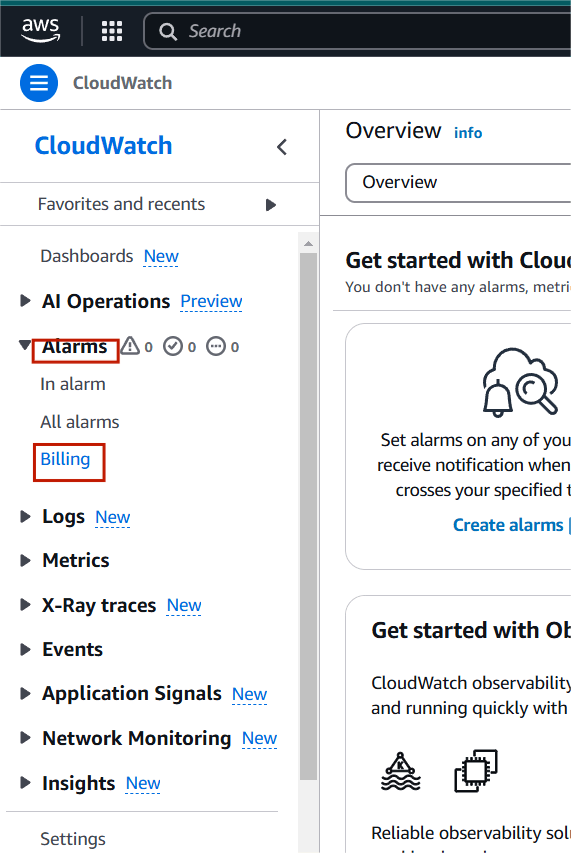
STEP 1: Navigate the cloudwatch.
- Select alarm and click billing.
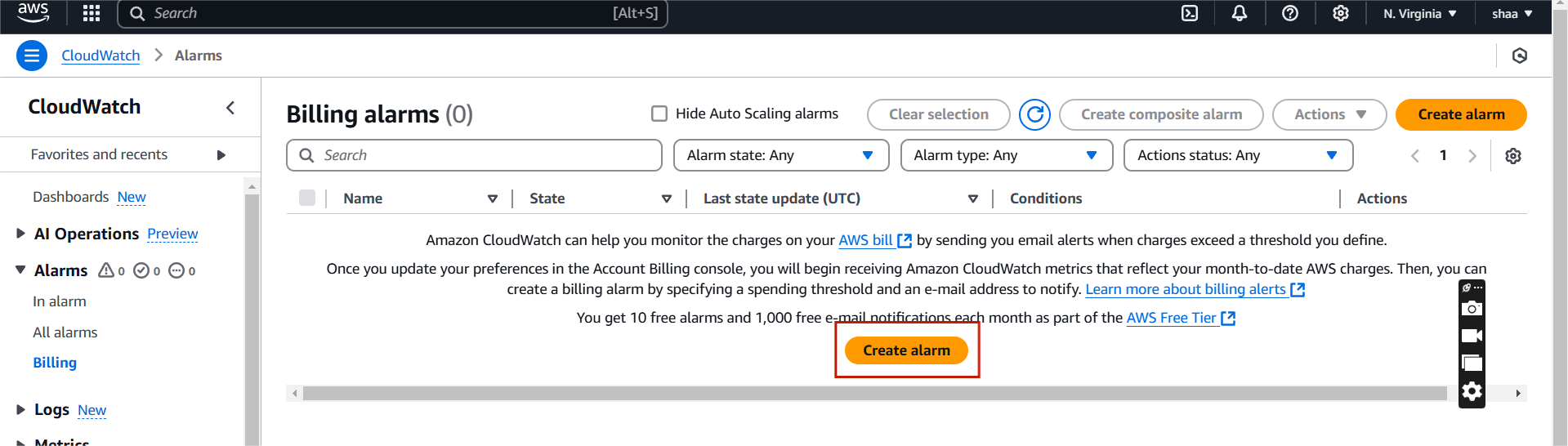
STEP 2: Click Create a new alarm.
- Select your USD.
- Click next.
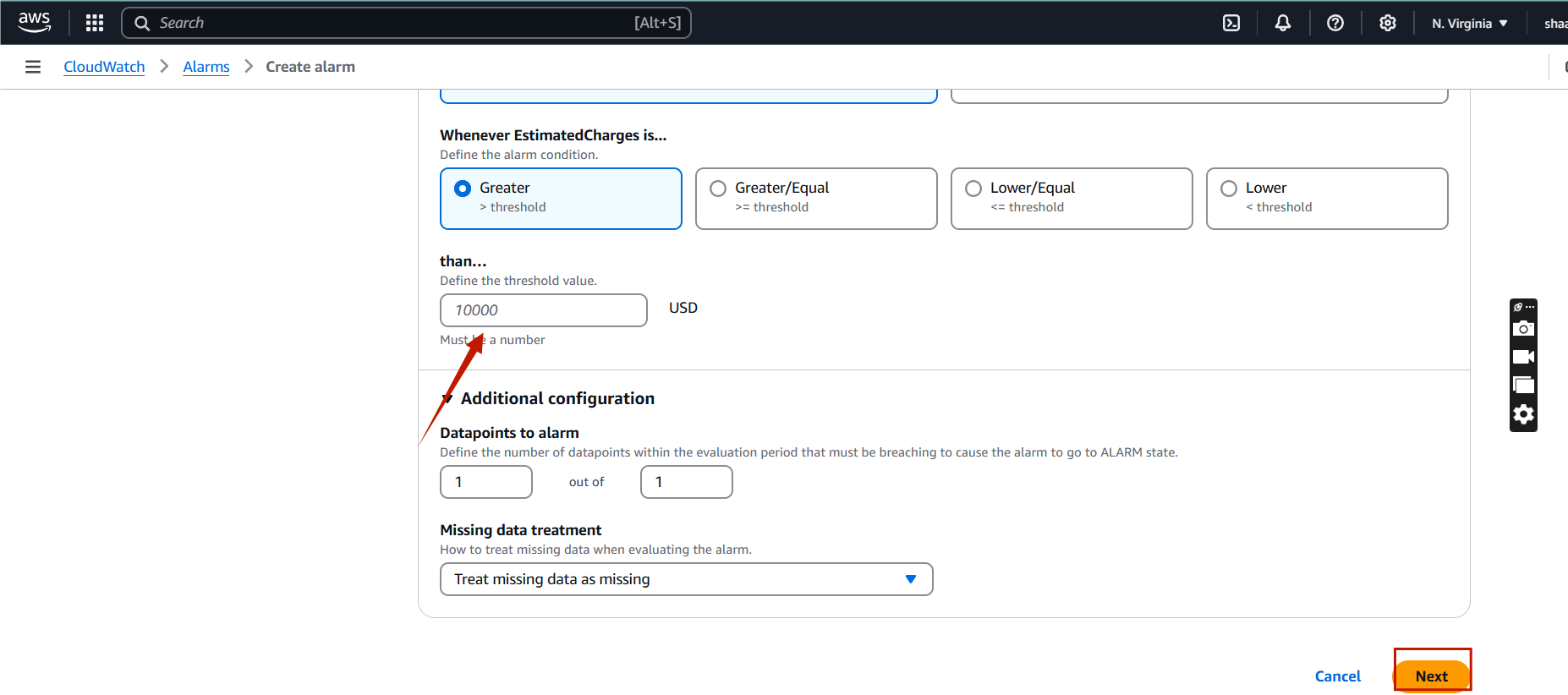
STEP 3: Then, you will click on next button.
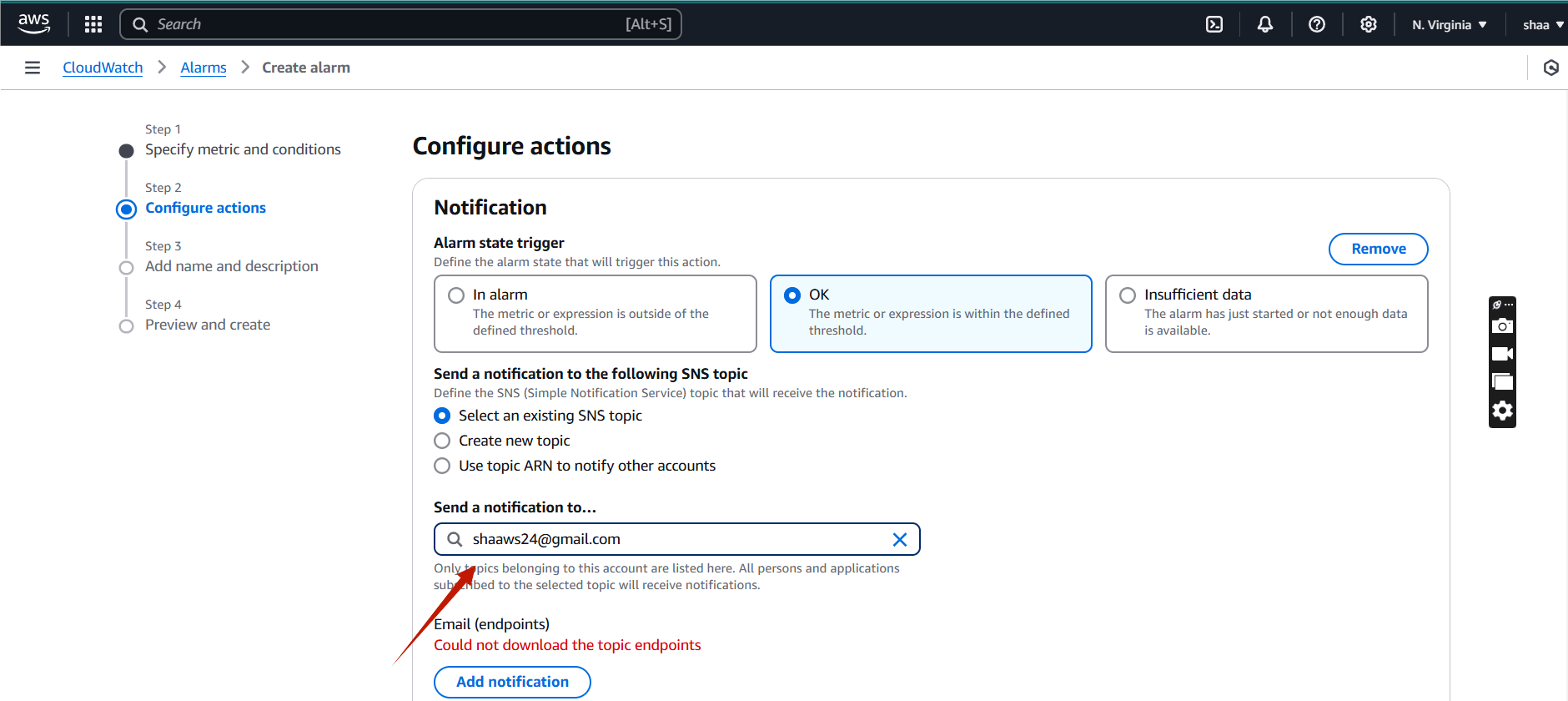
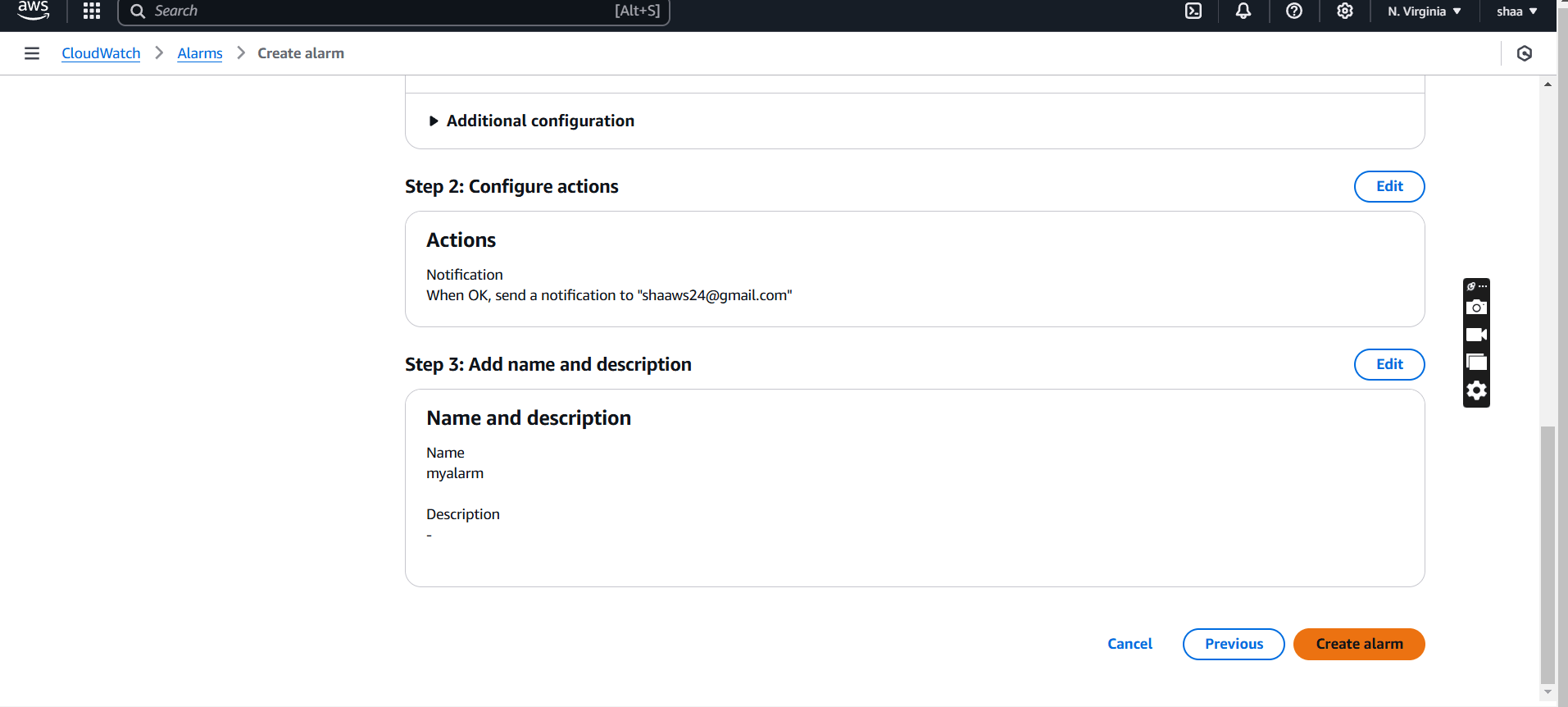
- Notification : OK
- Send your notification to….. : Your mail.
- Click on next.
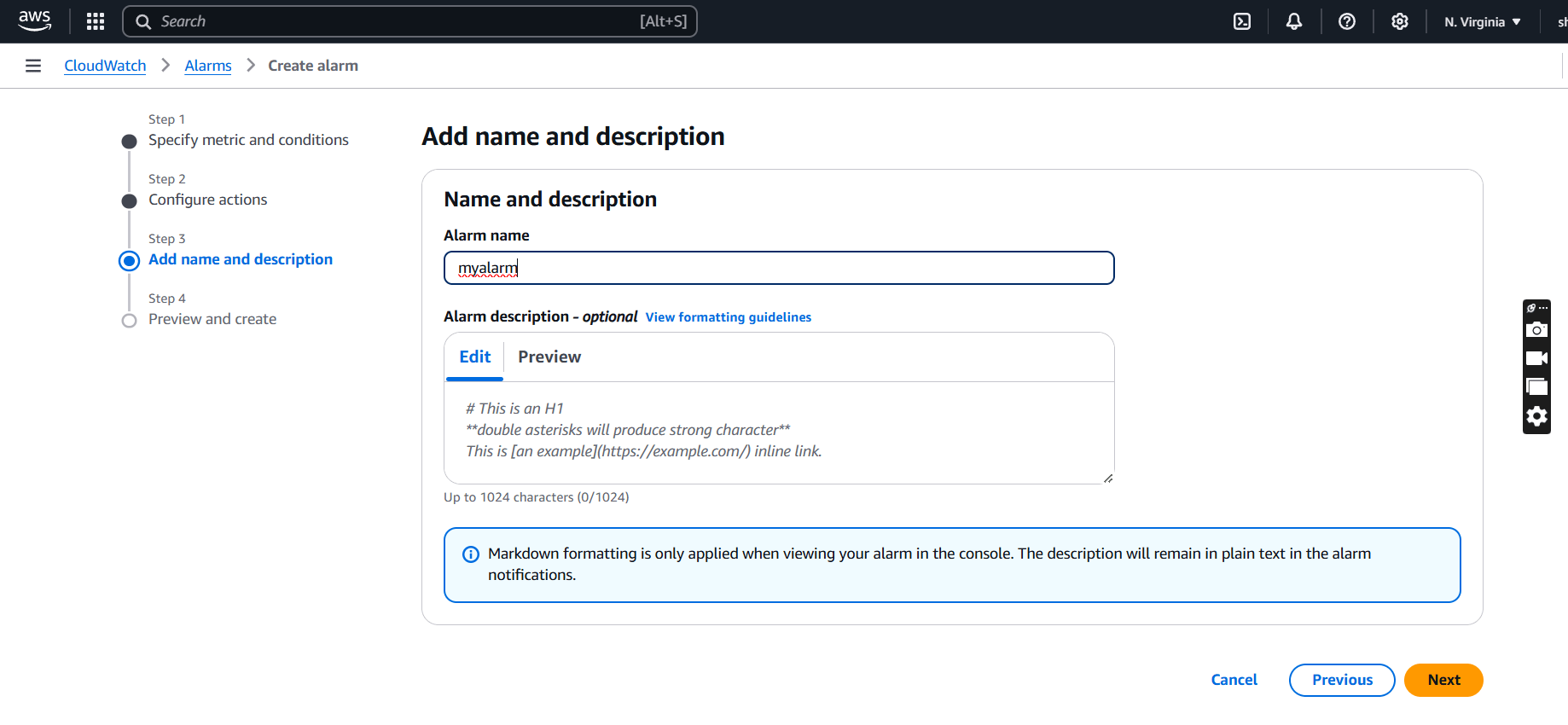
STEP 4: Enter the alarm name and click on next button.
STEP 5: Preview your alarm and click on create alarm.
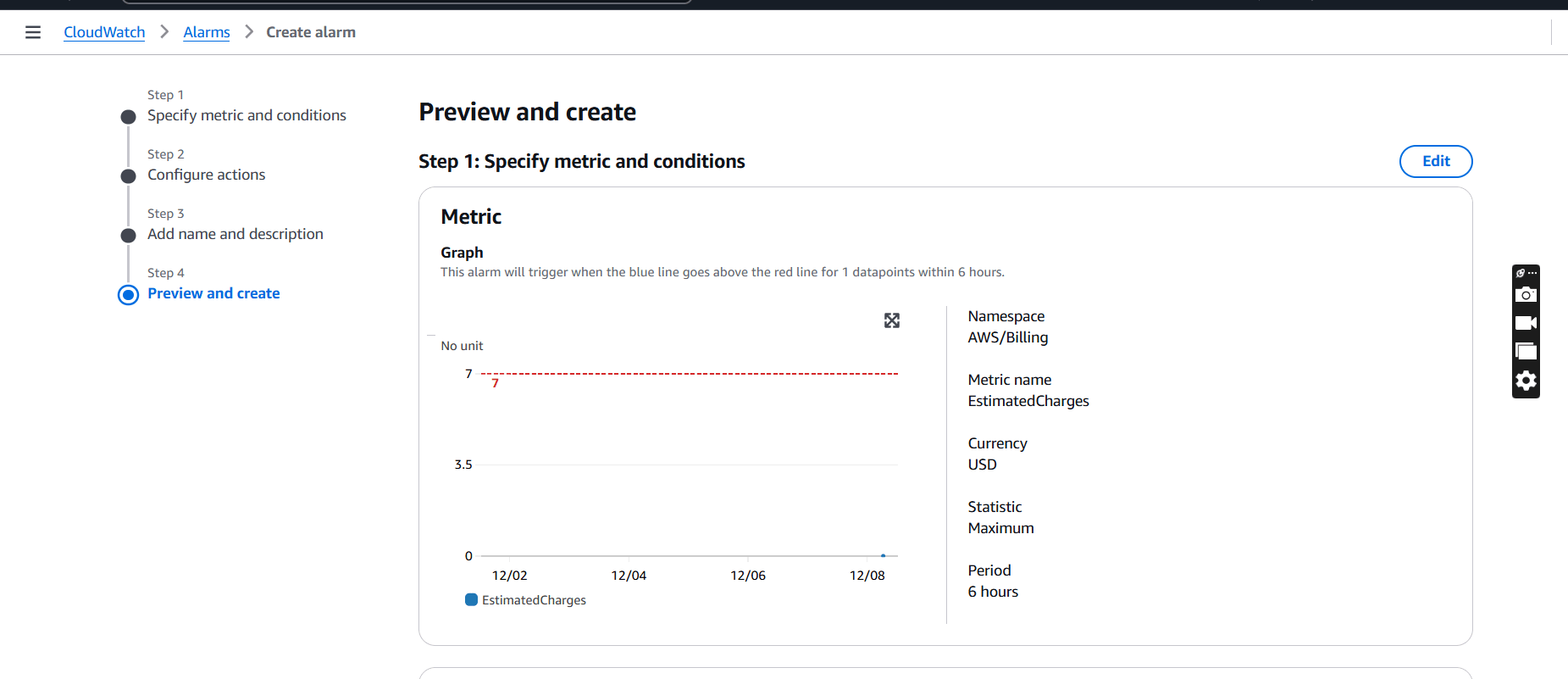
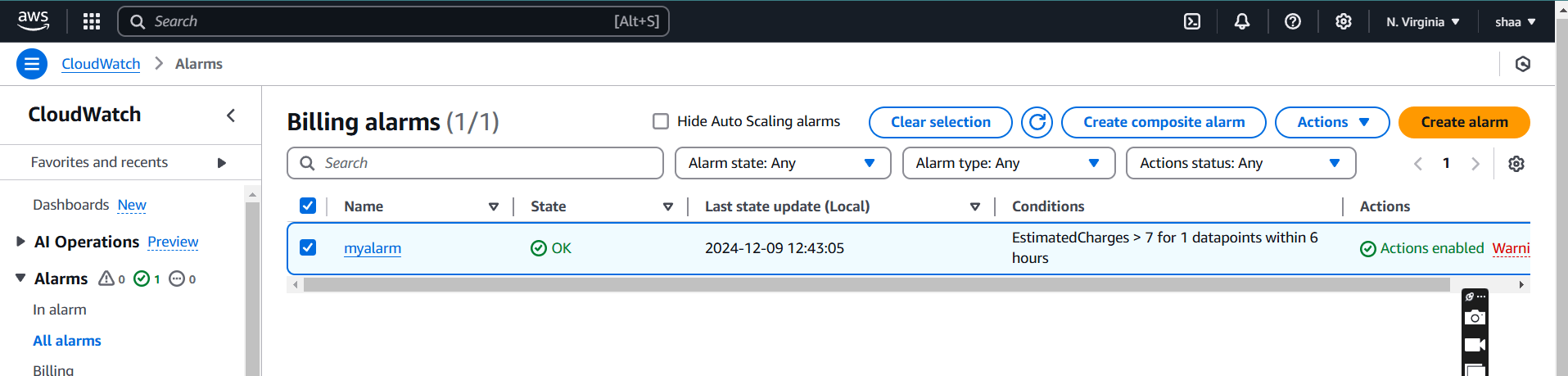
STEP 6: The alarm will be ready in 2-3 minutes.
Monitor.
STEP 1: Once the alarm is created, CloudWatch will monitor your billing metric.
- Click your alarm name and you will see the graph.
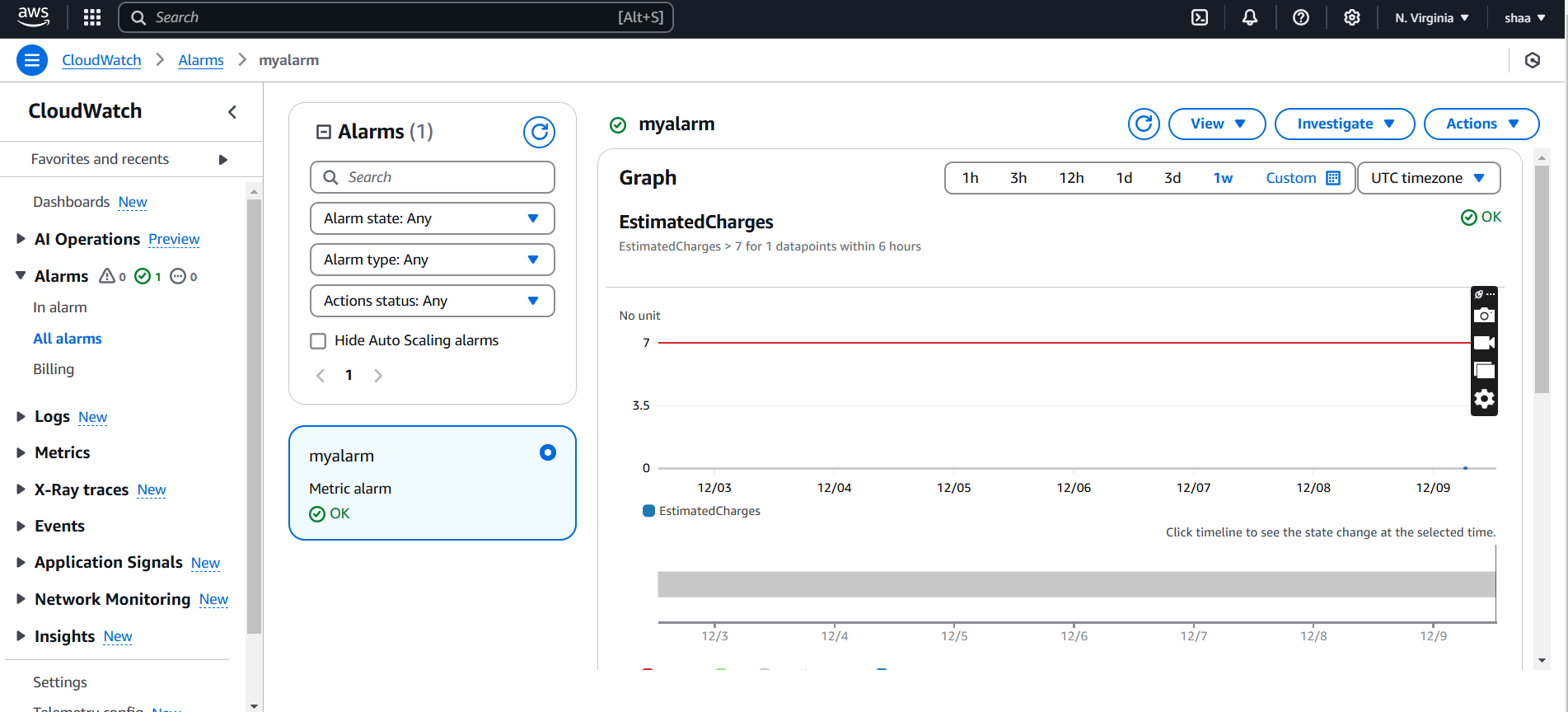
If your charges exceed the threshold, an email or other notification (as configured) will be sent to your subscribed contacts.

Conclusion.
CloudWatch Alarms provide a powerful way to proactively monitor the health, performance, and costs of your AWS resources. By setting thresholds and automating actions based on metric conditions, you can minimize downtime, enhance application reliability, and ensure cost-effective operations. Leveraging these alarms enables teams to respond promptly to issues, optimize resources, and maintain better control over their AWS environments.
Essential Git Commands for Beginners.
Overview.
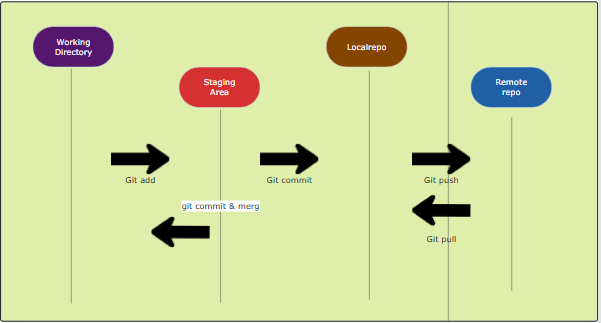
Version Control System (VCS) is a software that helps software developers to work together and maintain a complete history of their work. Git is a version control system that helps programmers and developers manage and track changes to their code at any time. It allows multiple developers to work on a project simultaneously, maintain a history of changes, and revert to previous versions if needed.
In this article, we’ll explore a list of essential Git commands, such as git push, git commit, git pull, and others, that can enhance your workflow and boost productivity.

Git Installation:
Use the following command to install git.
sudo apt install git
git --version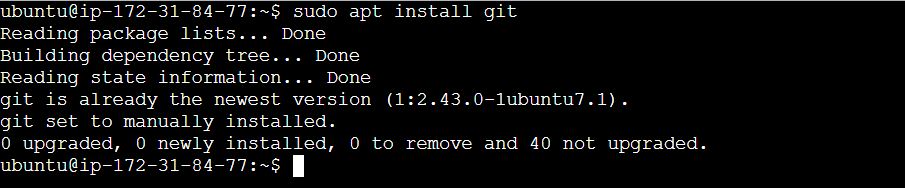
Git Config:
To set the basic configurations on Git like your name and email.
The git config --list command is used to display all the configuration settings Git is currently using.
git config --global user.name "your name"
git config --global user.email "your email"
git config --list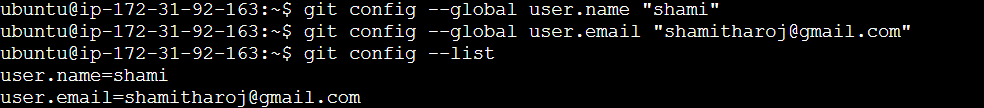
Git init:
create a local git repository for us in our store folder. This will help to manage the git commands for that particular repository. This is a initialized empty git repository.
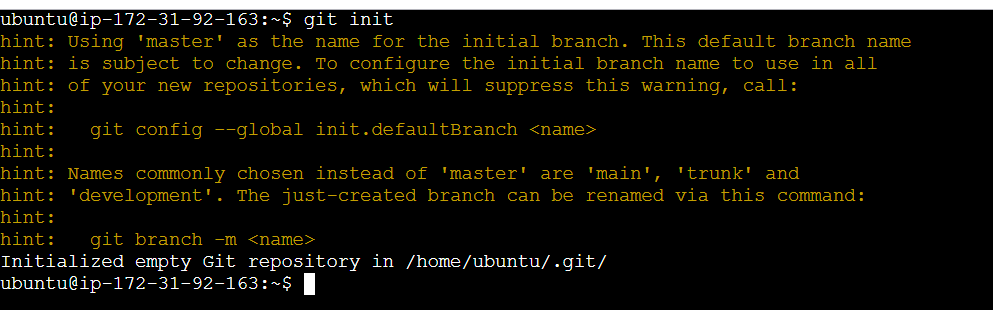
Git status:
The git status command is used to display the current state of your Git repository. It shows information about changes in your working directory and staging area, helping you keep track of what needs to be committed, staged, or ignored.
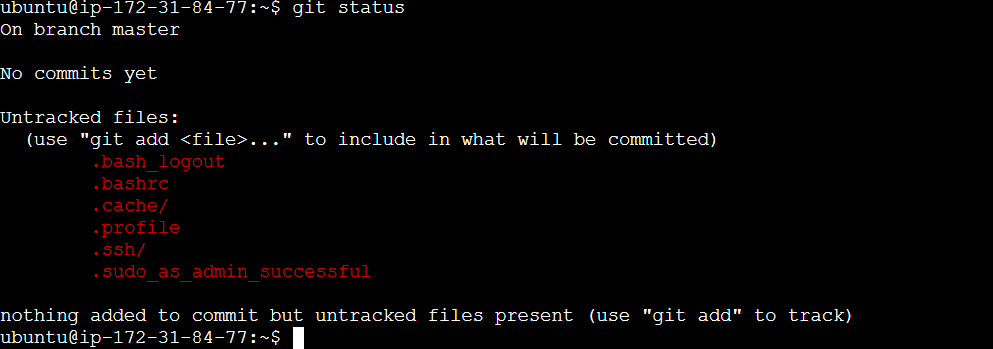
This files are untracked files.
Git clone:
The git clone command is used to create a local copy of a remote Git repository. This command downloads the entire repository, including its history, branches, and files, to your local system.
Copy your repository url in your github.
git clone <your repository url>
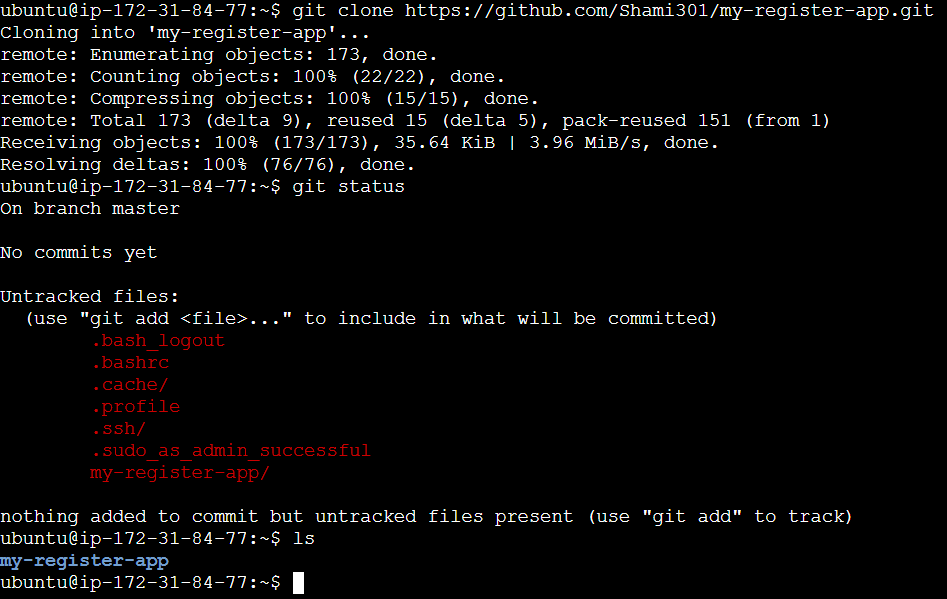
My-register-app is my repo. Go to repo use cd <repo name>/ command and listout my files use ls command.
cd my-register-app/
ls
Git add:
Add a specific list of files to the staging area.
git add .Add all files of the current directory to the staging area.
git add --all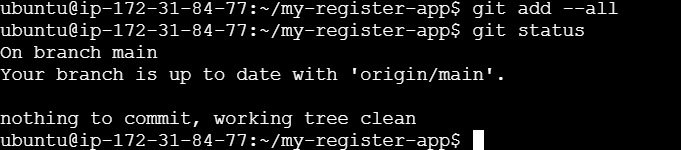
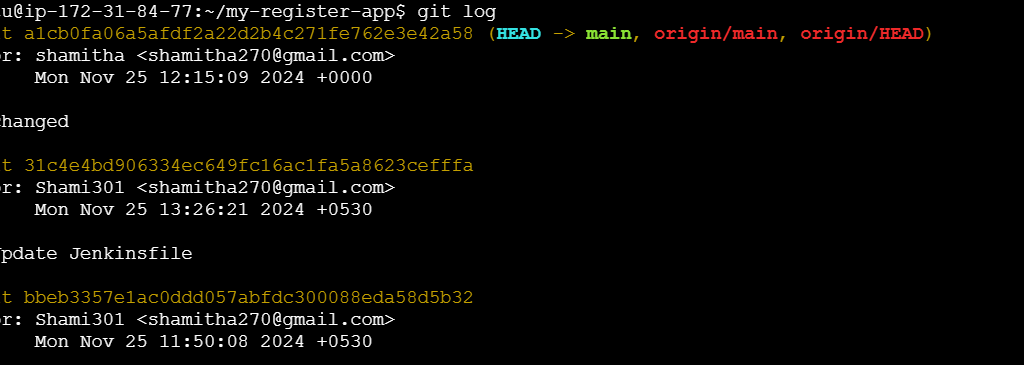
Git log:
The git log command is used to display the commit history of a Git repository. It shows details about each commit, such as the commit hash, author, date, and message. This is essential for understanding the changes made over time in a project.
Create a new branch:
The git branch command is used to manage branches in a Git repository. Branches are essential for creating separate lines of development, enabling multiple developers to work on different features or fixes simultaneously.
git branch <branch name>See all the branches present and current branches that we are working on.
git branch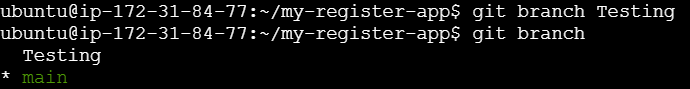
Git checkout:
Switch to branch Testing from the master branch.
git checkout <branch name>
See hidden directories and files within the current directory.
ls -a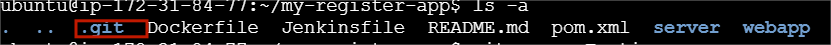
Create New Repo:
The mkdir command is used to create new directories (folders) in a file system.
mkdir <newreponame>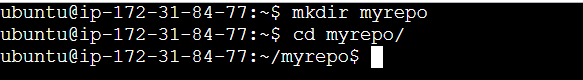
Create a File:
The touch command is primarily used to create empty files.
toch <file name>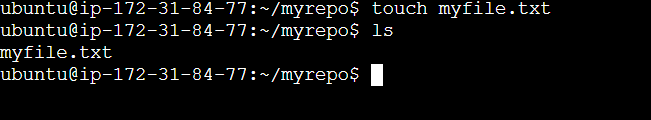

Conclusion.
Git is a powerful tool for version control and collaboration. By mastering its basic commands, such as git clone, git commit, and git push, you can efficiently manage your projects and contribute to team workflows. Start practicing today to build your expertise!
Explore and Learn: Introduction to the Bedrock Chat Playground.
Introduction.
Amazon Bedrock is a service offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows developers to build and scale generative AI applications without the need to manage underlying infrastructure or fine-tune models manually. Central to its functionality is the provision of a diverse selection of foundation models (FMs) developed by top AI companies like AI21 Labs, Anthropic, Cohere, Meta, Mistral AI, Stability AI, and Amazon itself. These FMs serve as the cornerstone for various AI applications, each optimized for specific use cases and industry requirements.

Diagram
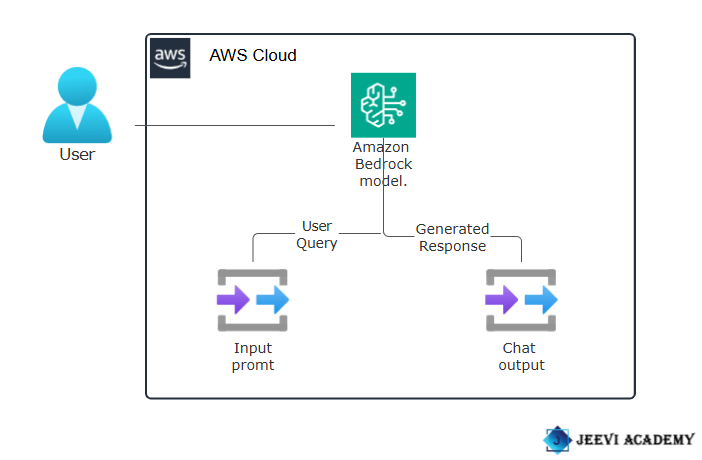
STEP 1: Navigate the Amazon bedrock .
STEP 2: Scroll down click on model access, in your left side panel.
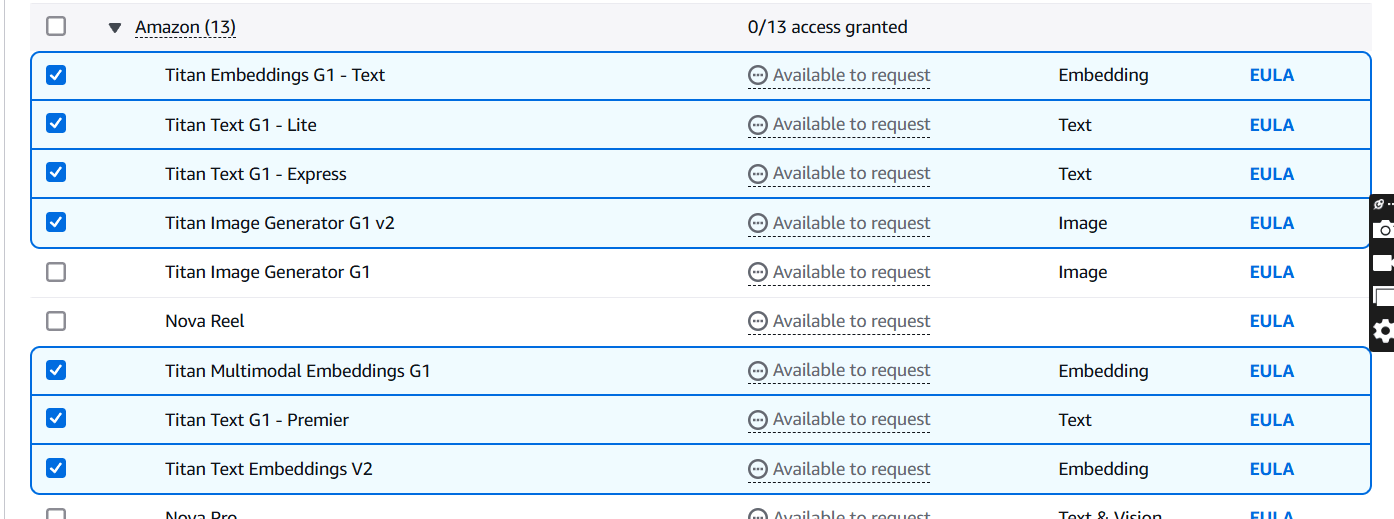
STEP 3: Scroll to the Amazon models section and check if access is granted.
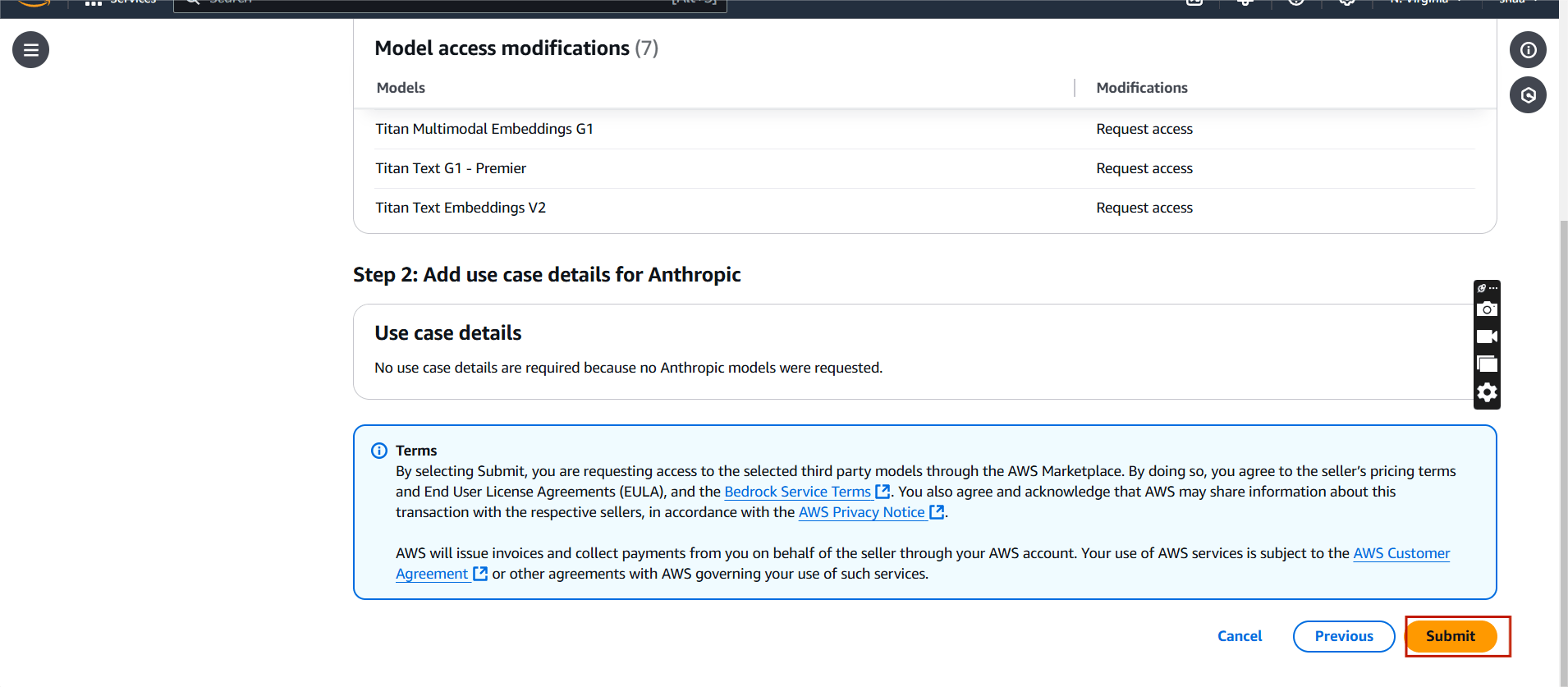
- Click on next and submit.
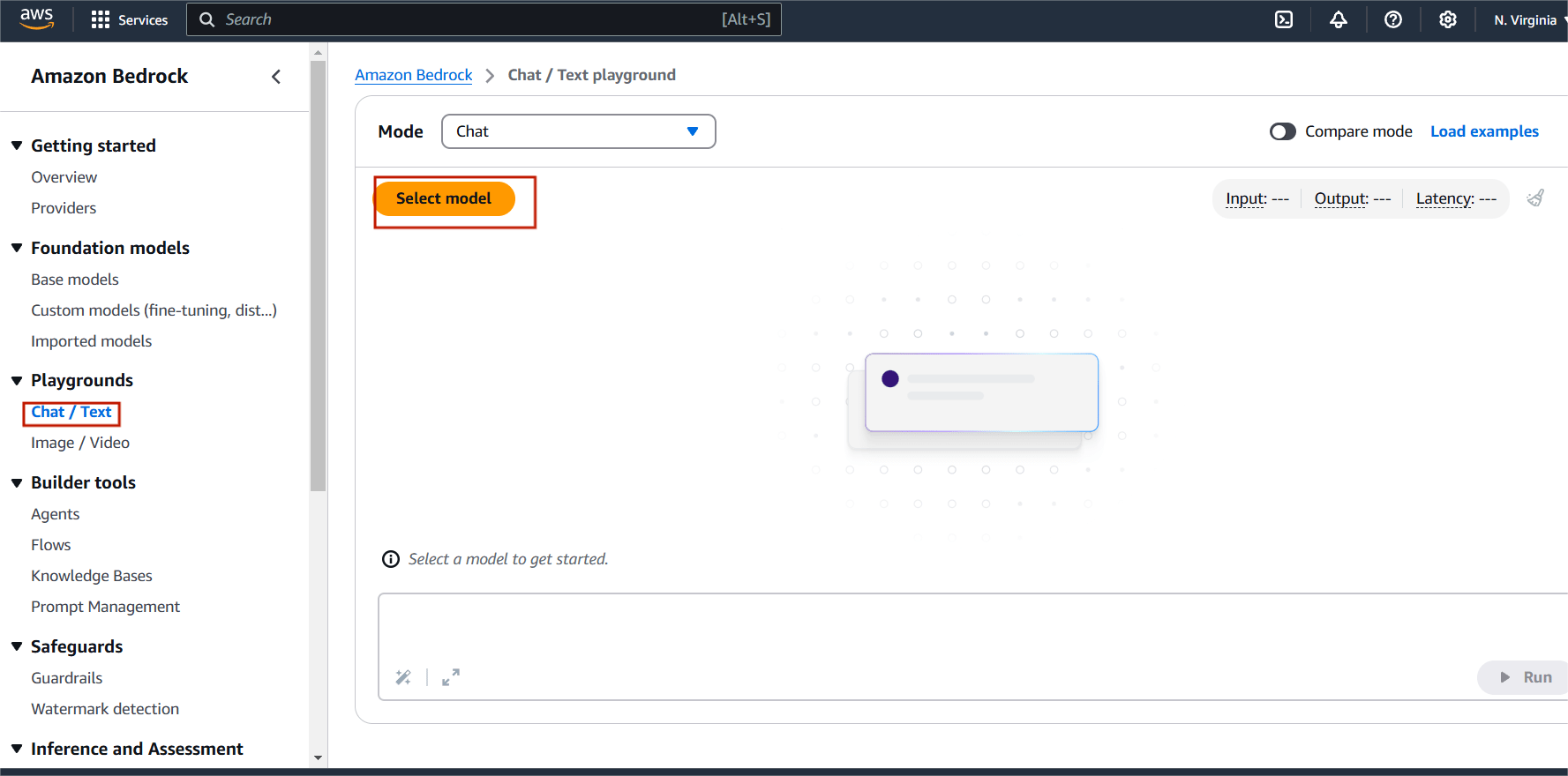
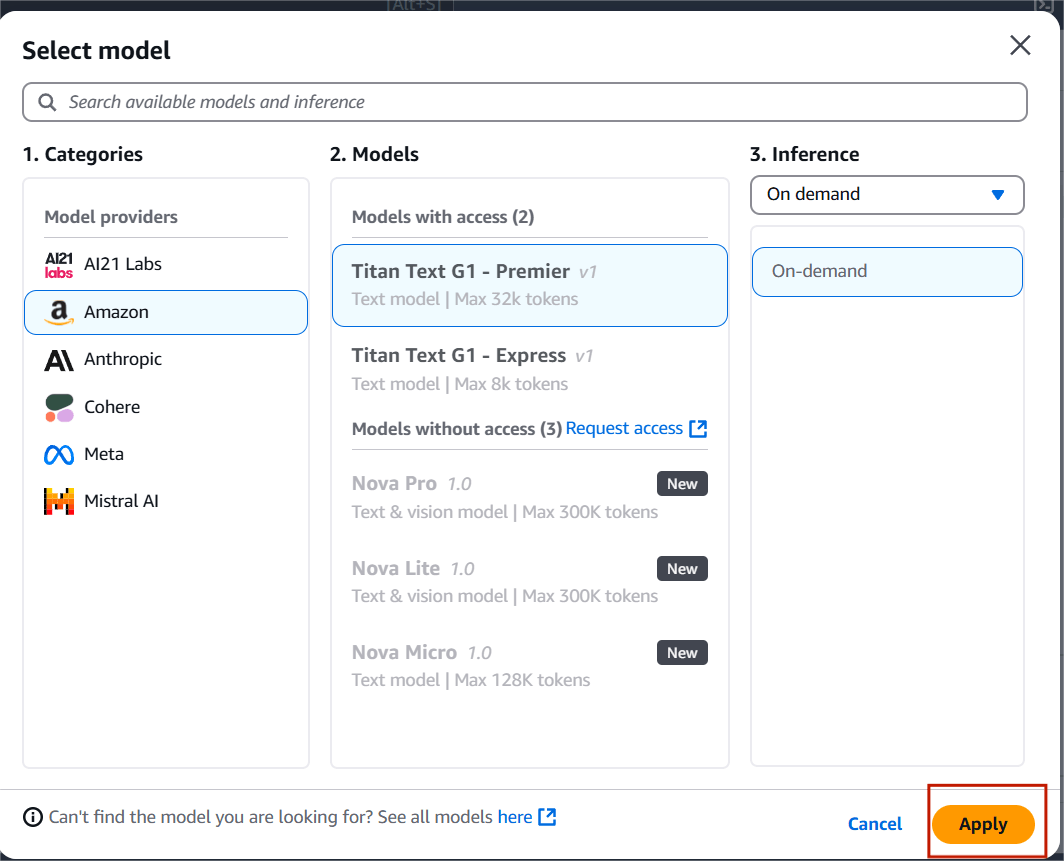
STEP 4: Select chat and click on select model.
STEP 5: Click amazon and select titan text G1-Premier.
- Click apply.
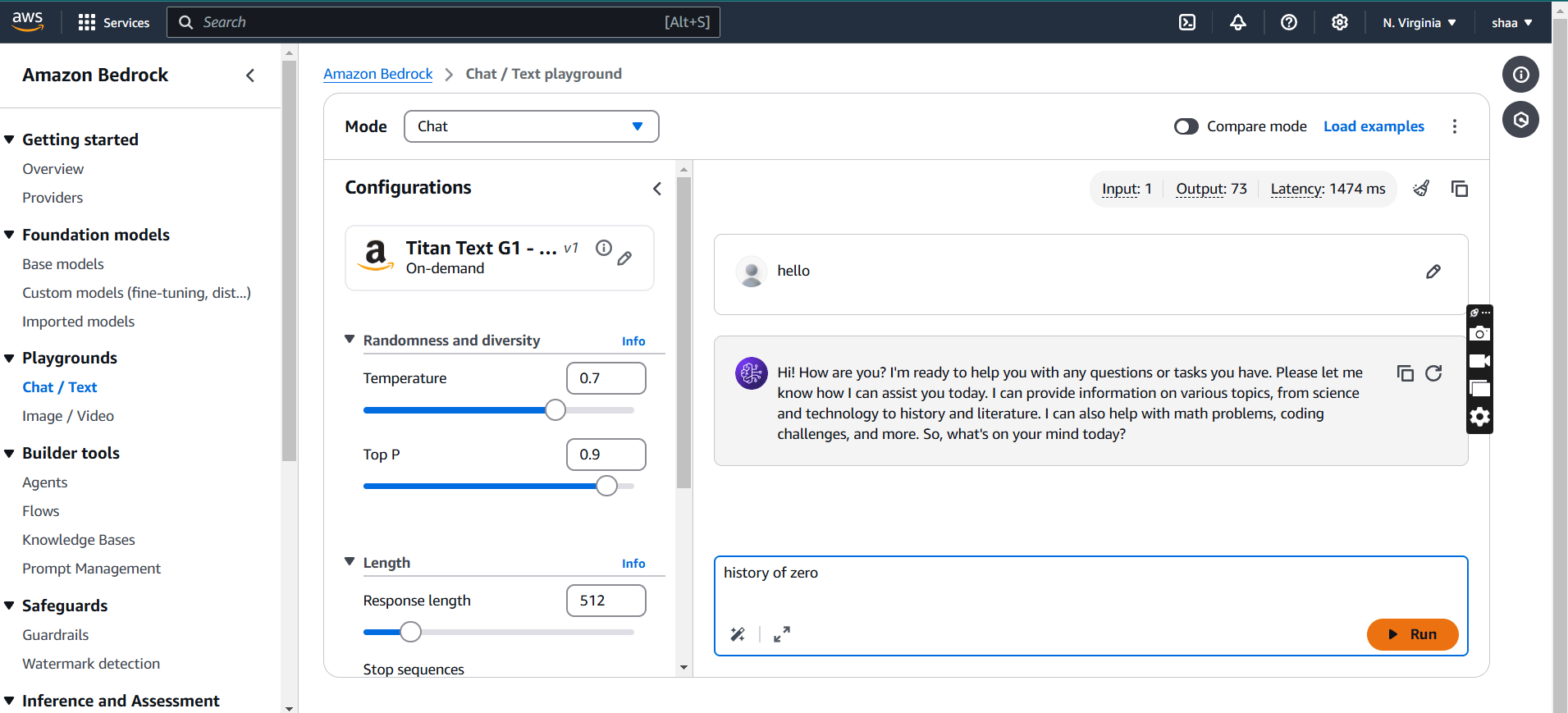
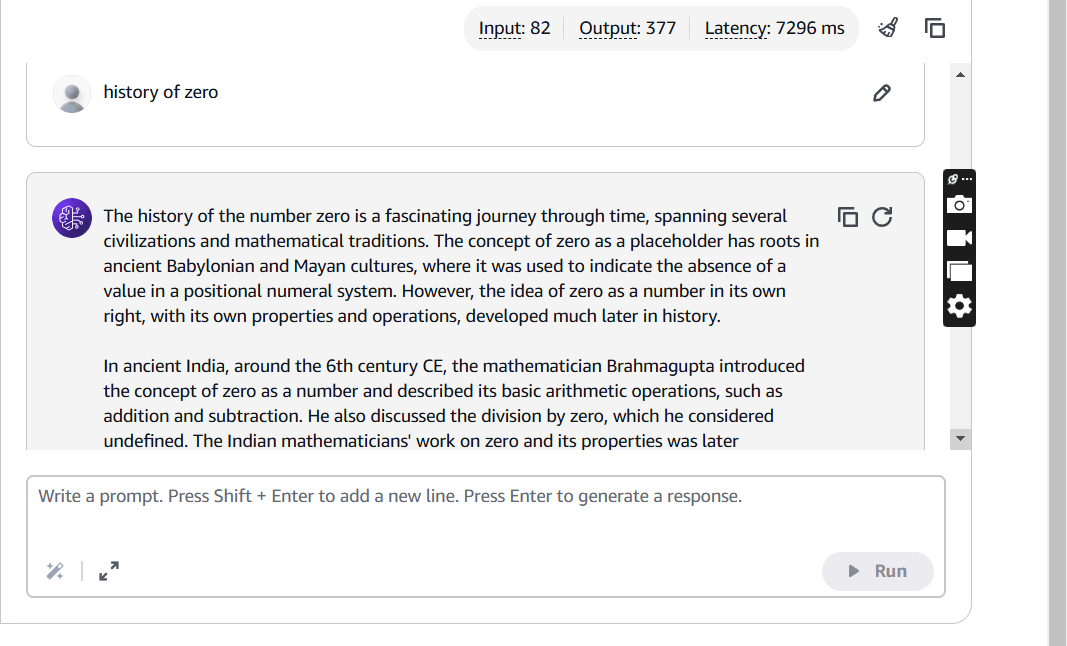
STEP 6: In the input field, type your Quries and press Enter.
- Observe and analyze the model’s response to the input.

Conclusion.
By bridging the gap between complex AI models and practical implementation, AWS Bedrock makes generative AI more accessible to developers and enterprises alike. Bedrock offers a robust platform for organizations to experiment, grow, and succeed in leveraging generative AI technologies.
How to Launch a WordPress Website on Amazon EC2 Server: A Beginner’s Guide.
What is Amazon web service (AWS)?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive and widely used cloud computing platform provided by Amazon. It is a secure cloud services platform. AWS offers over 200 fully featured services like compute power, database storage, content delivery, and other functionality to help businesses scale and grow.
What is Amazon EC2?
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a web service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that offers resizable compute capacity in the cloud. EC2 offers a variety of instance types tailored for different workloads, such as compute-optimized, memory-optimized, or GPU-powered instances.

What is WordPress?
WordPress is a popular open-source content management system (CMS) that allows users to create and manage websites with ease. WordPress has become one of the most widely used platforms for building websites, blogs, and e-commerce stores due to its flexibility, ease of use, and large community support. WordPress provides an intuitive interface, making it easy for users with little to no coding experience to build and manage a website.
STEP 1 : Navigate the EC2 instance and click on launch instance.
STEP 2 : Enter instance name.
- AMI : WordPress.
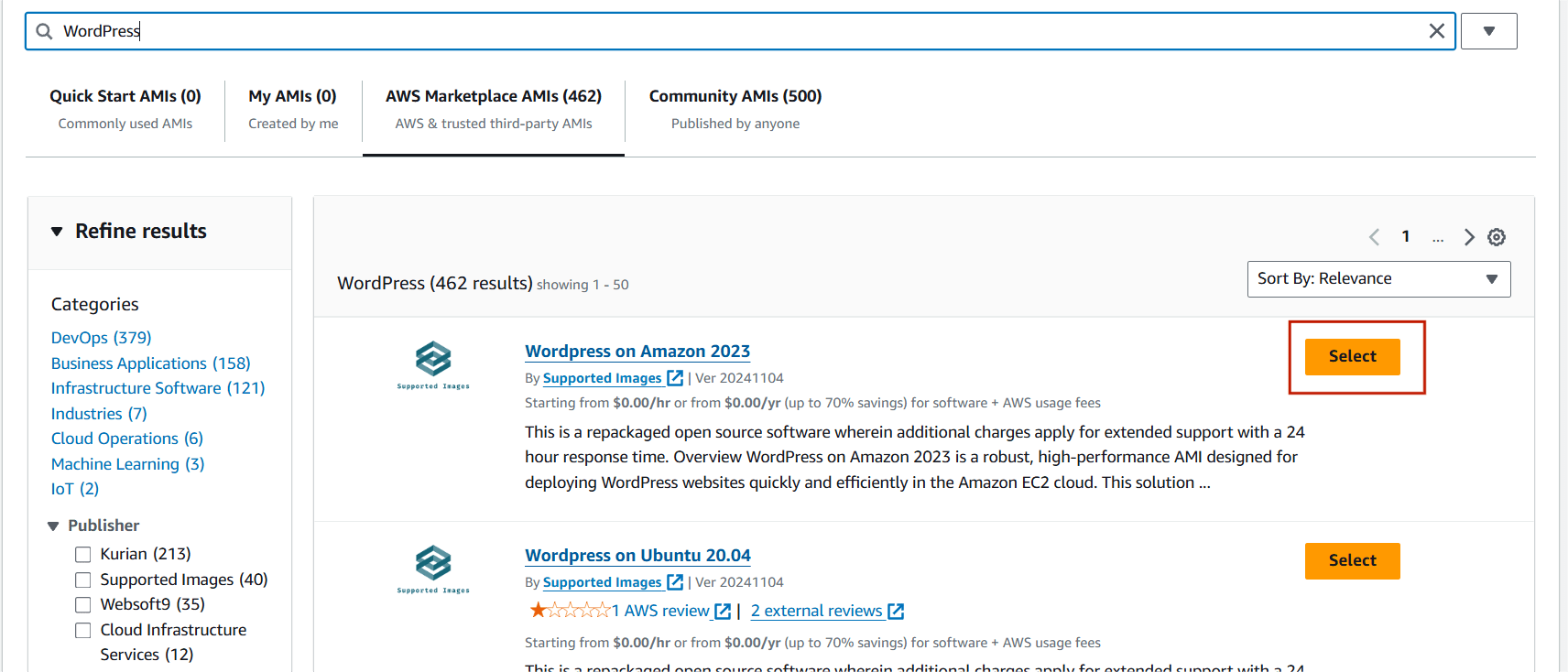
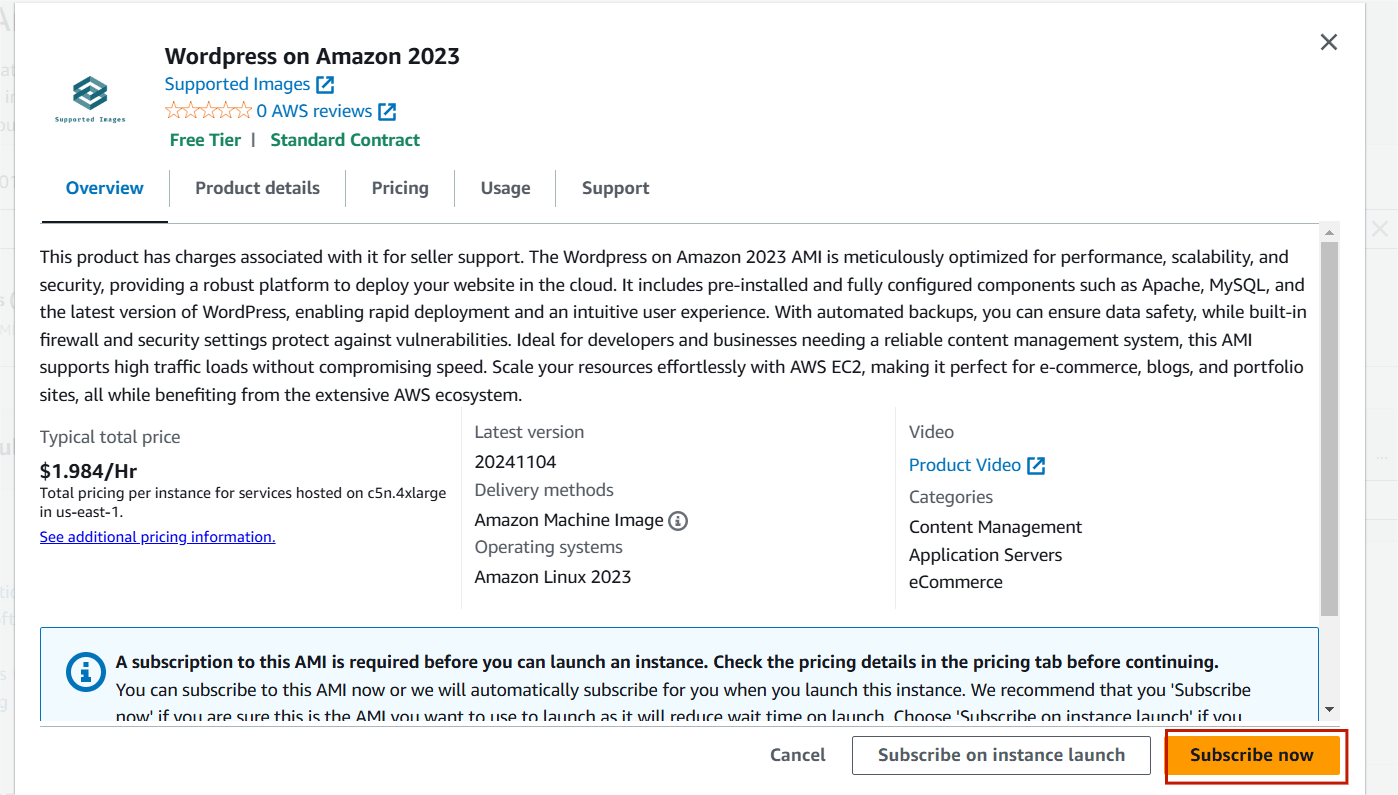
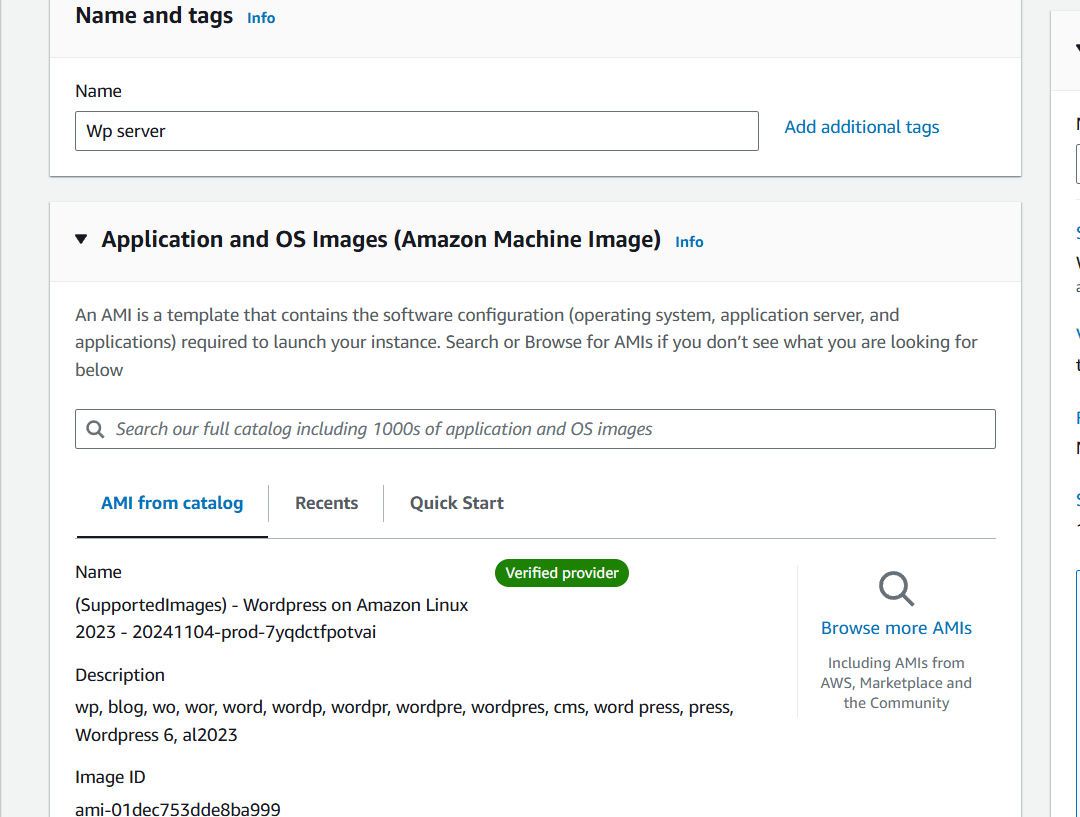
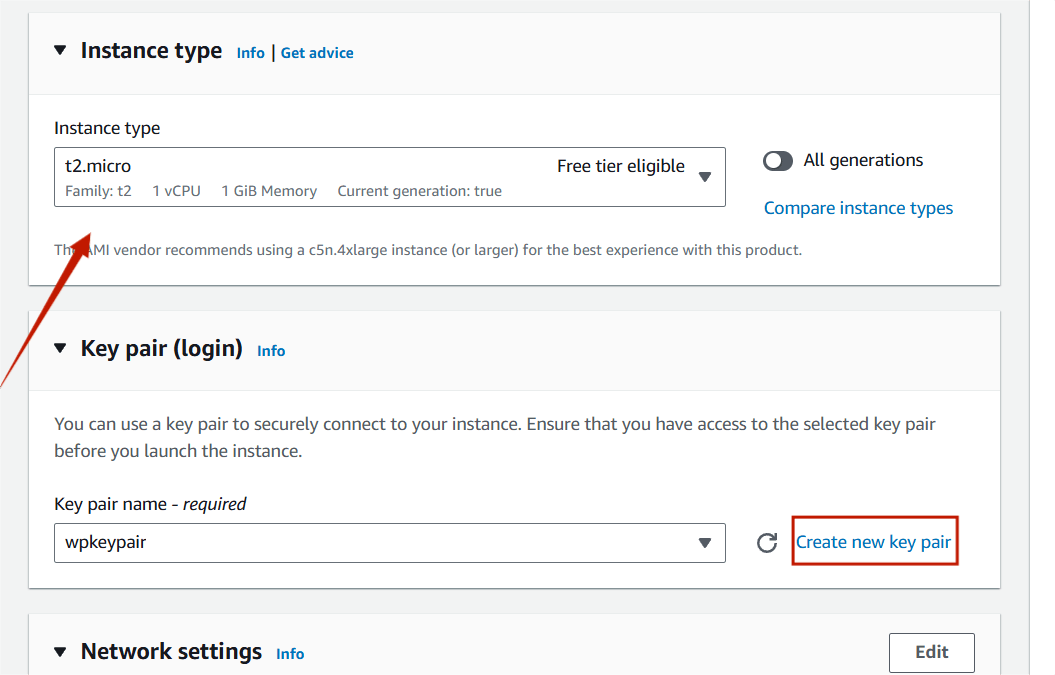
STEP 3 : Instance type : t2.micro.
- Create New keypair.
STEP 4 : Select launch instance.
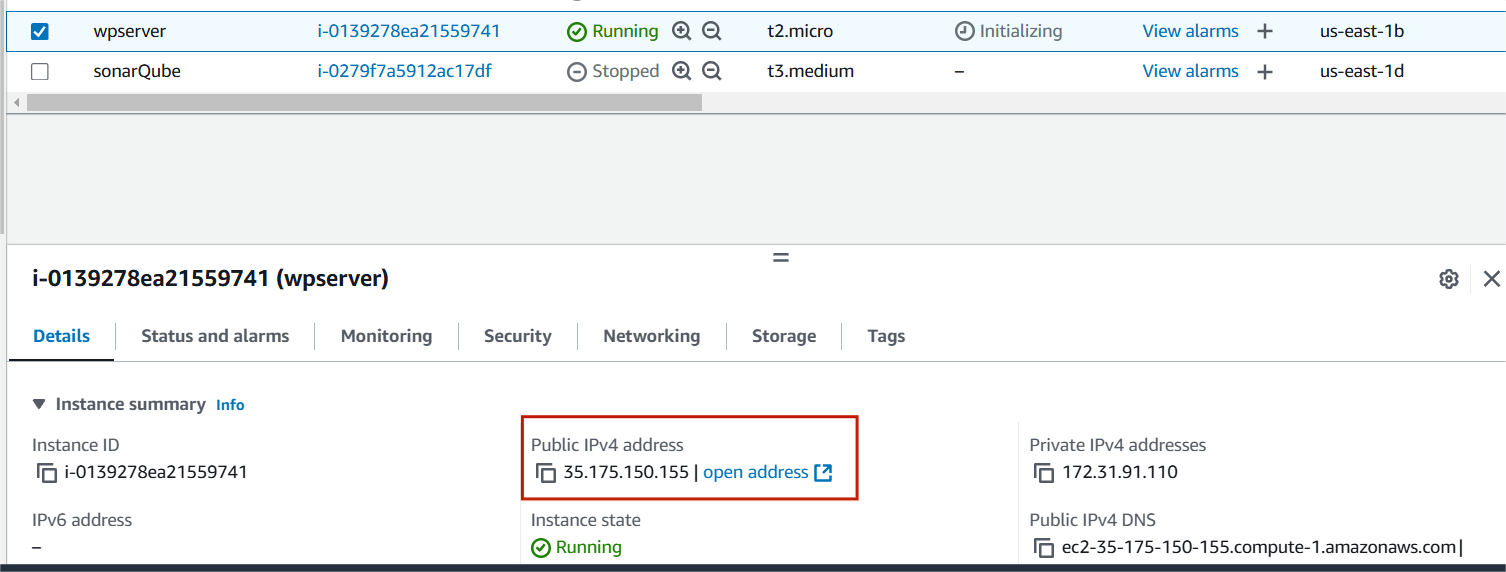
STEP 5 : Copy the public IP address in your instance.
Step 6 : Paste the IP address in your browser.
STEP 7 : Select English and click continue.
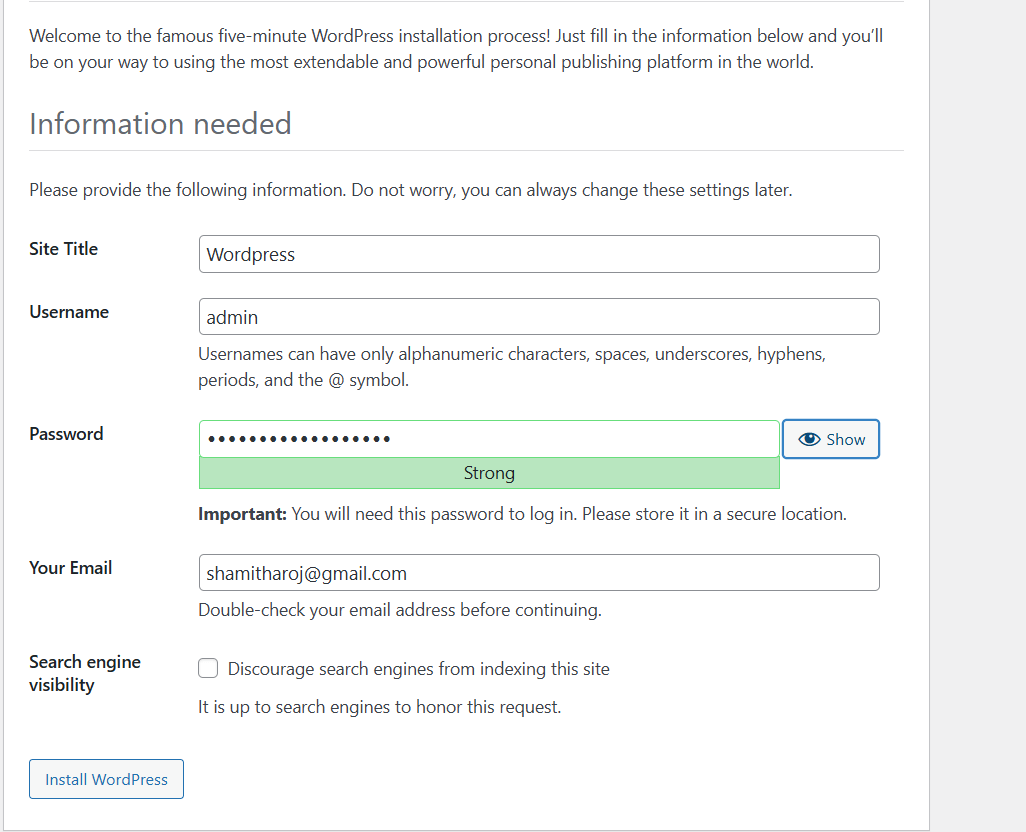
STEP 8 : Enter the Title , Username , Email.
- Click on WordPress.
Step 9 : Click on Log In button.
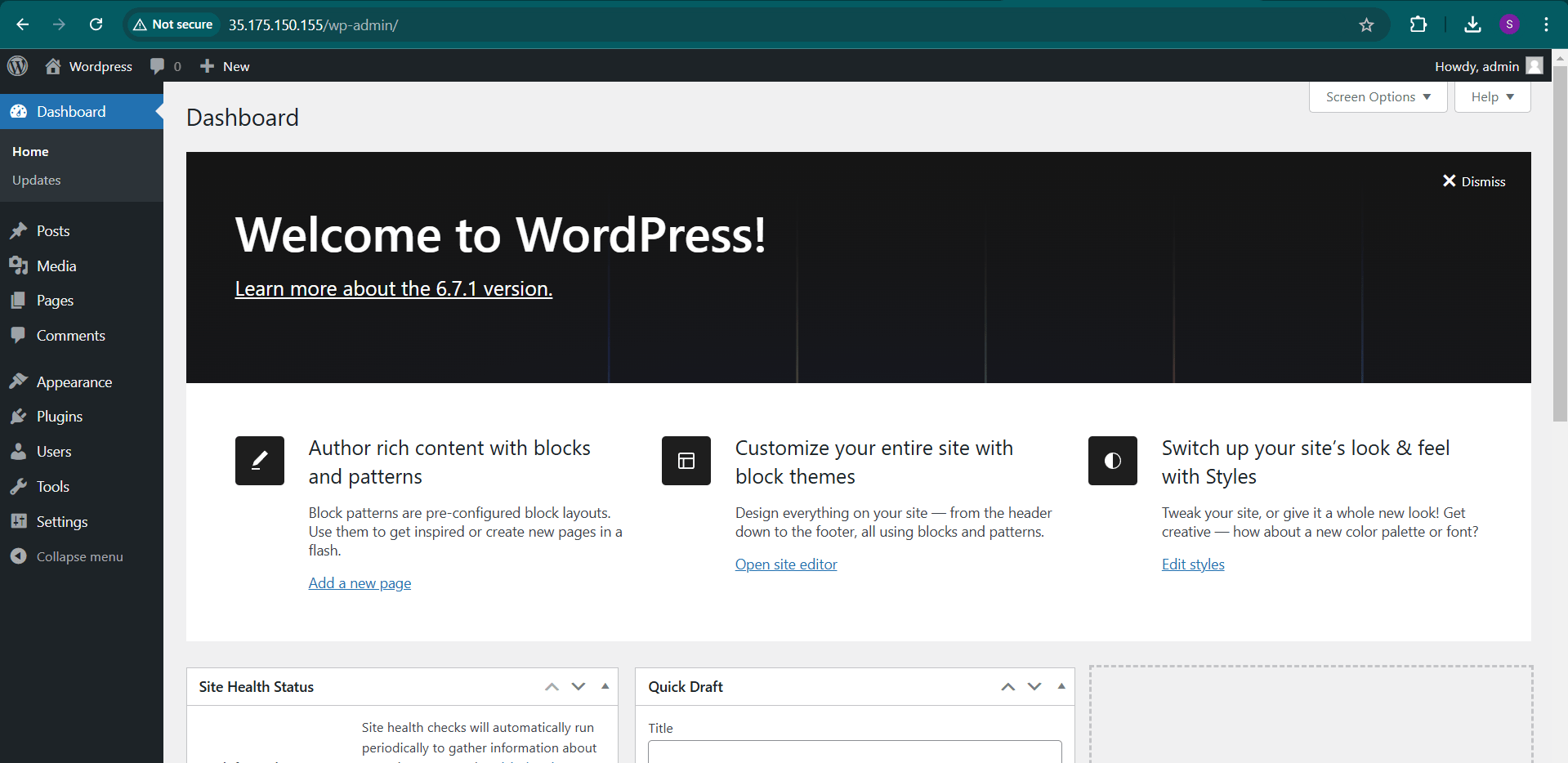
STEP 10 : Now you will see wordpress dashboard.

Conclusion.
Congratulations! You’ve completed the process of launching your WordPress website on Amazon EC2, opening up new possibilities for a scalable and secure online presence.
Step-by-Step Guide: Creating Audio Transcripts with Amazon Transcribe.
Introduction.
Amazon Transcribe is a cloud-based speech-to-text service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It converts audio into text, making it useful for transcribing phone calls, video content, and various audio recordings. Supports multiple languages and accents, making it suitable for global use. Automatically adds punctuation, capitalization, and formatting to transcriptions. It can distinguish between multiple speakers in a conversation (speaker diarization).
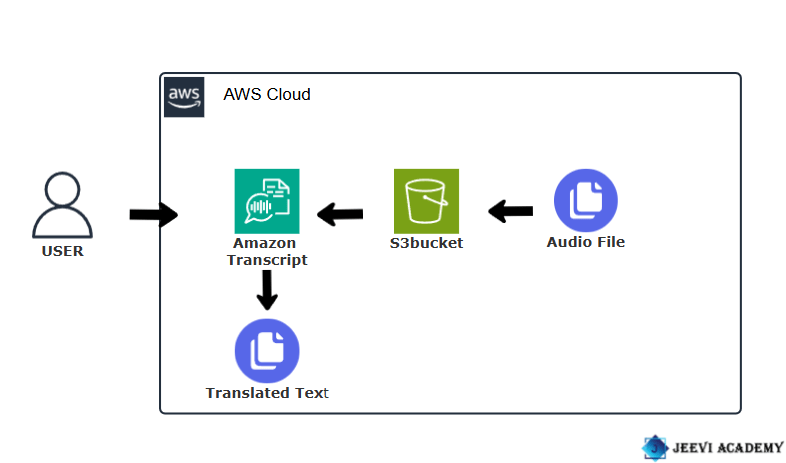

Start Now, Create an Audio Transcript with Amazon Transcribe.
STEP 1 : Navigate the S3bucket, Click on create bucket.
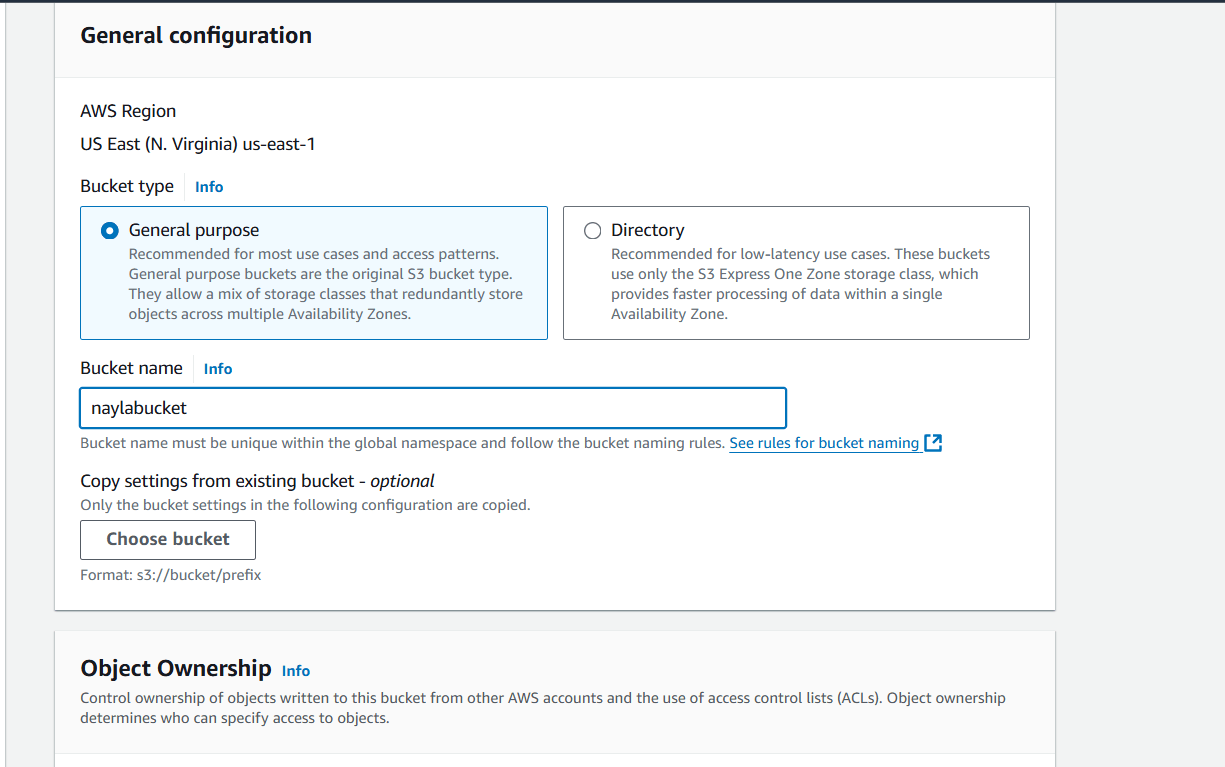
STEP 2 : Enter the bucket name.
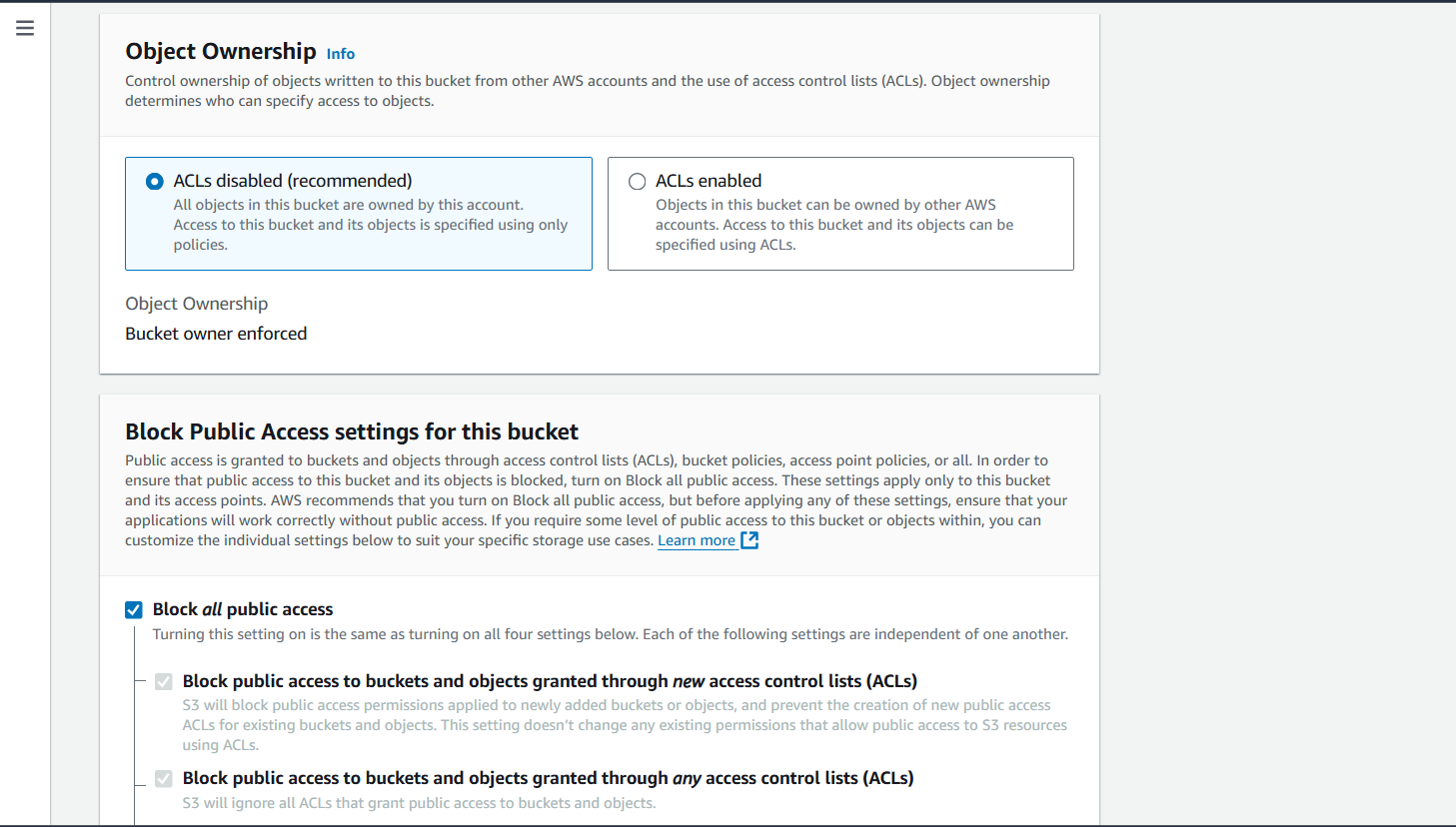
STEP 3 : Click create bucket.
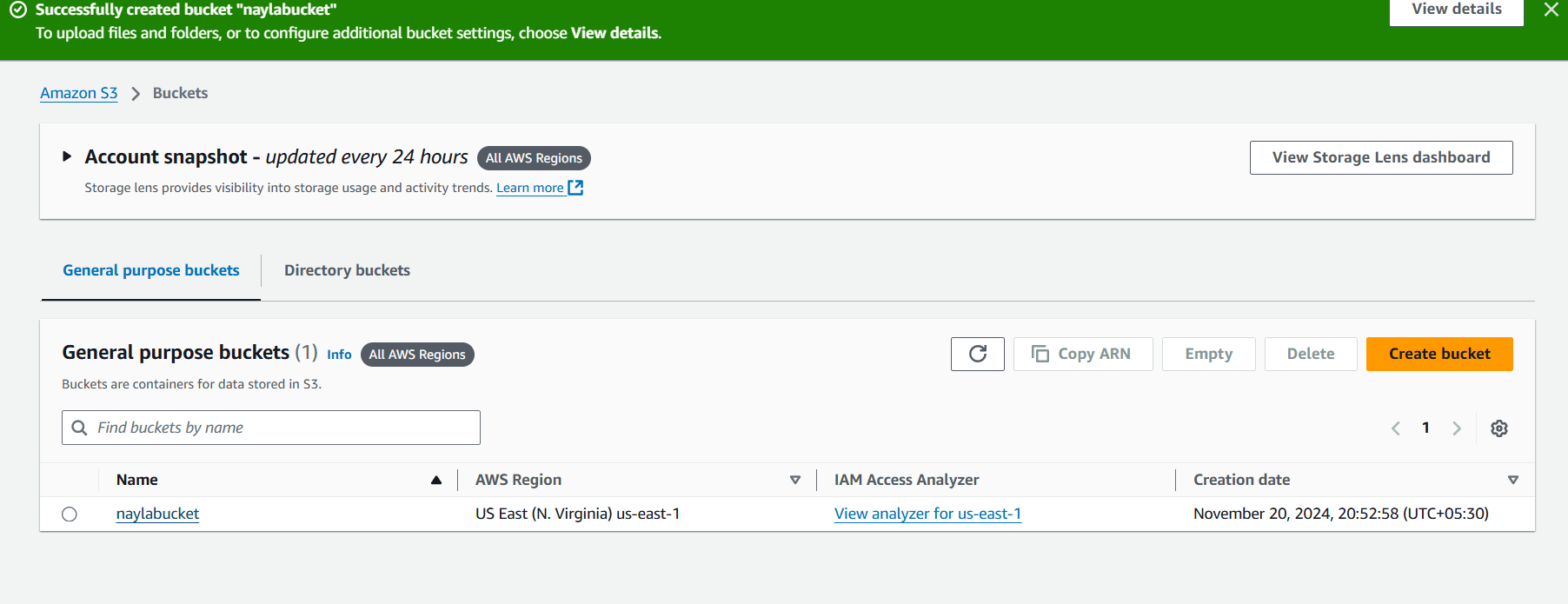
STEP 4 : Click your bucket name.
STEP 5 : You will see this page, Click on upload.
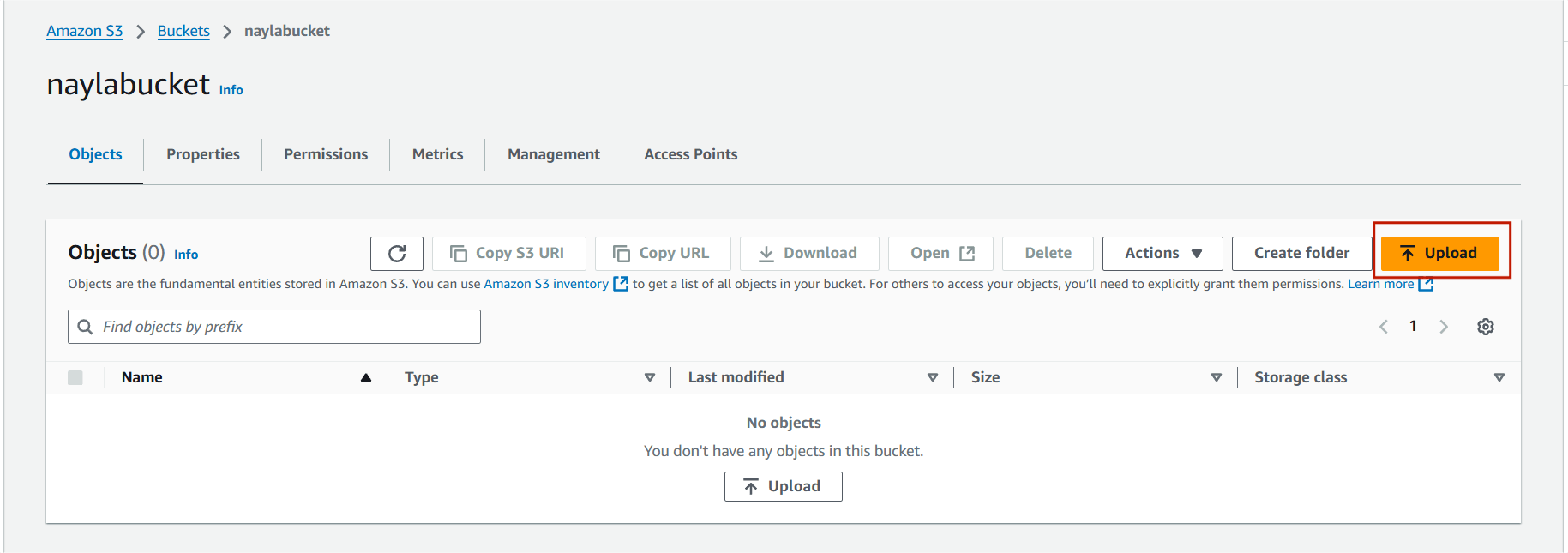
STEP 6 : Select add file, Upload your transcript audio.
STEP 7 : Click on upload.
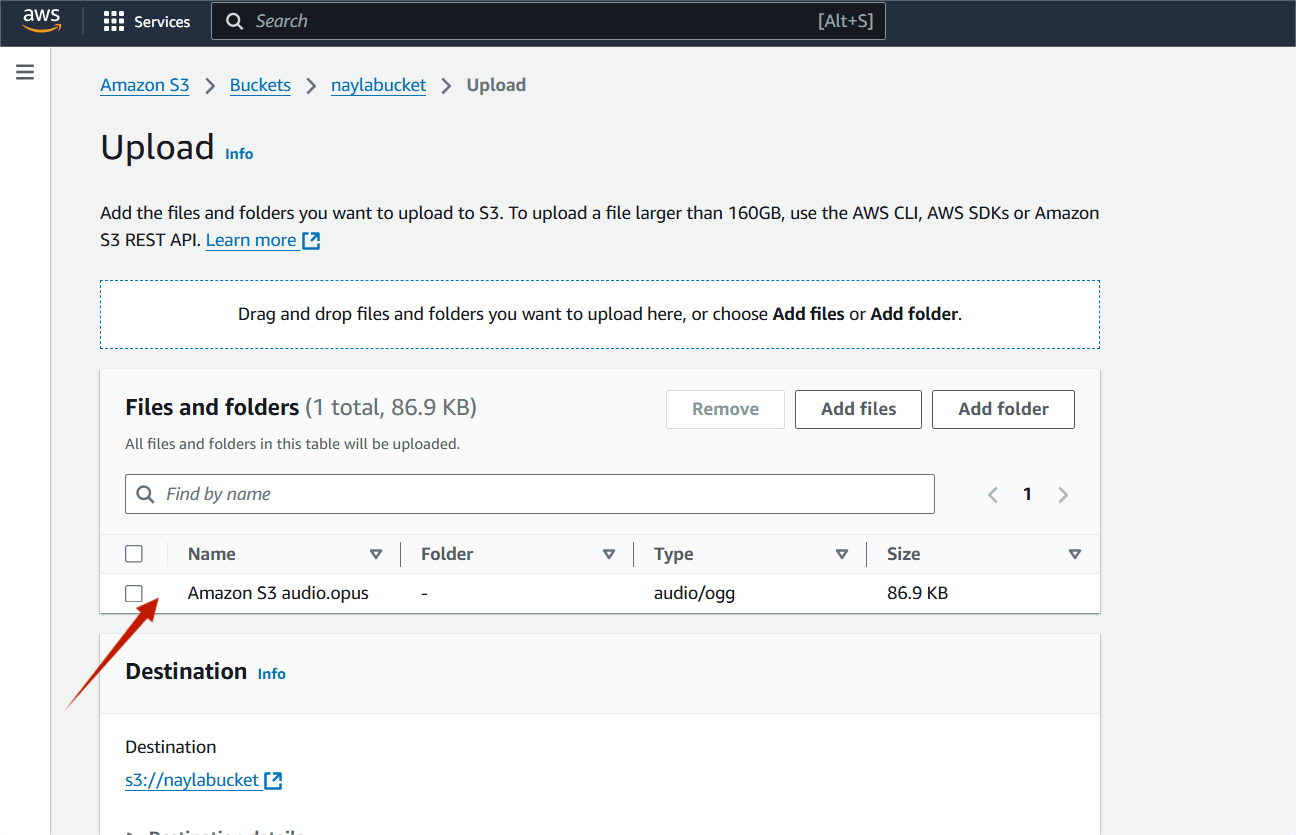
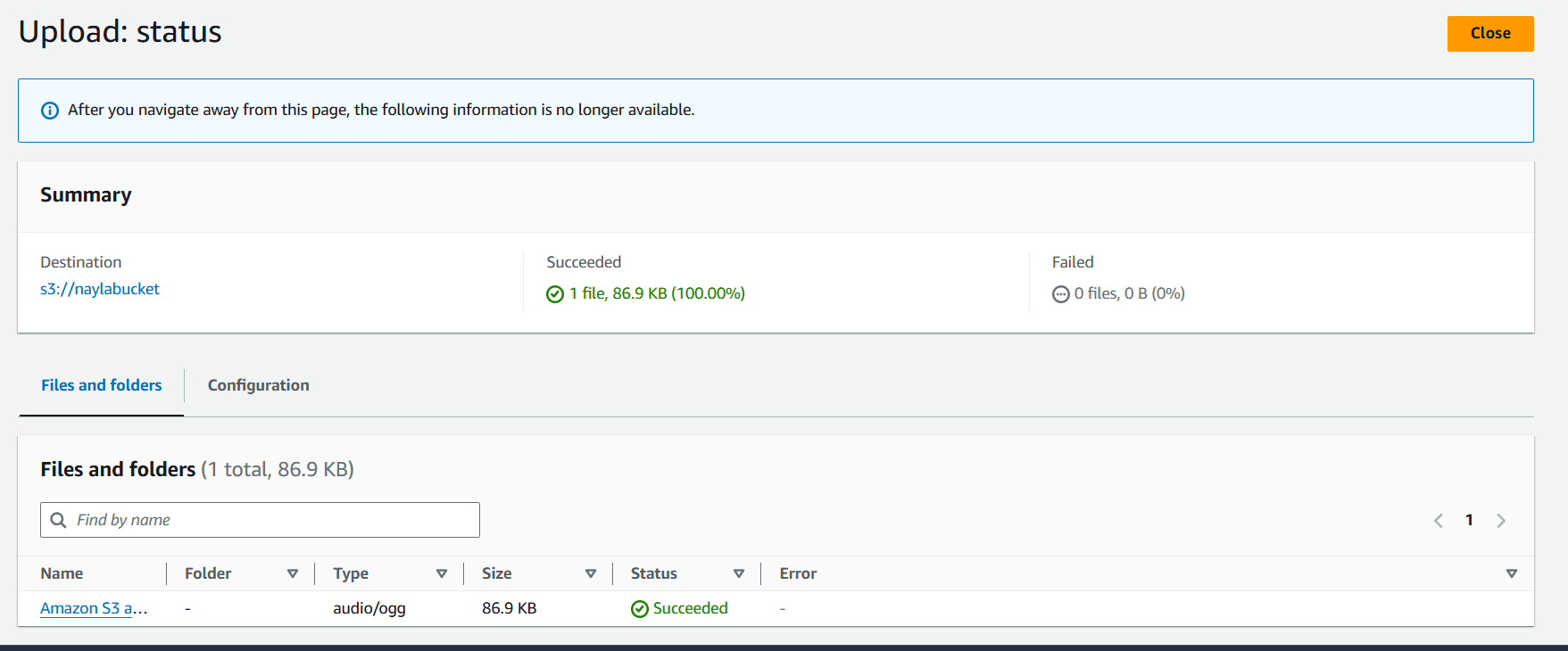
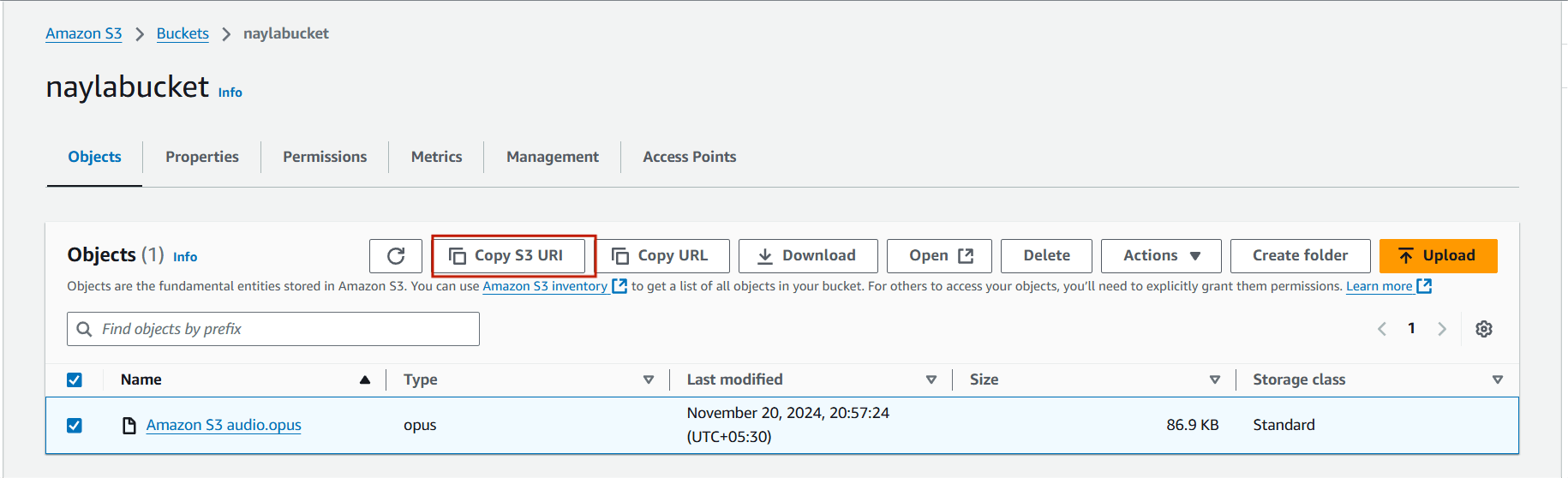
STEP 8 : Copy your audio S3 URI.
STEP 9 : Navigate Amazon Transcript.
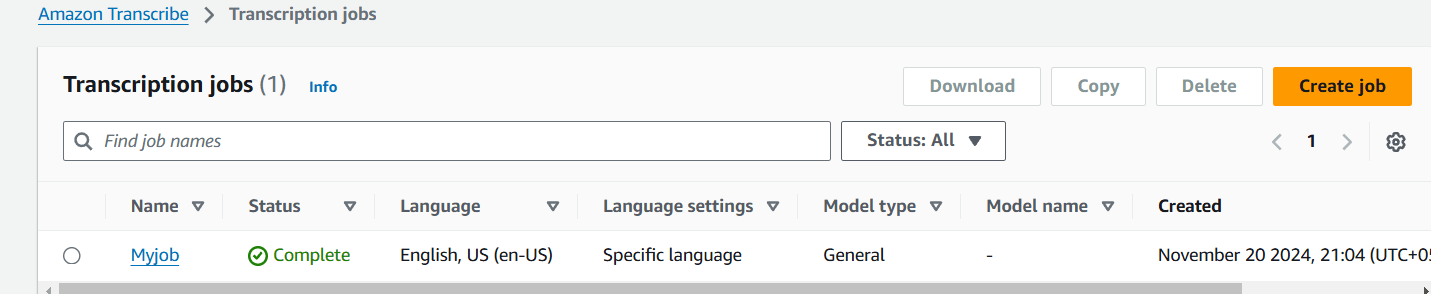
STEP 10 : Select transcription jobs and click create job.
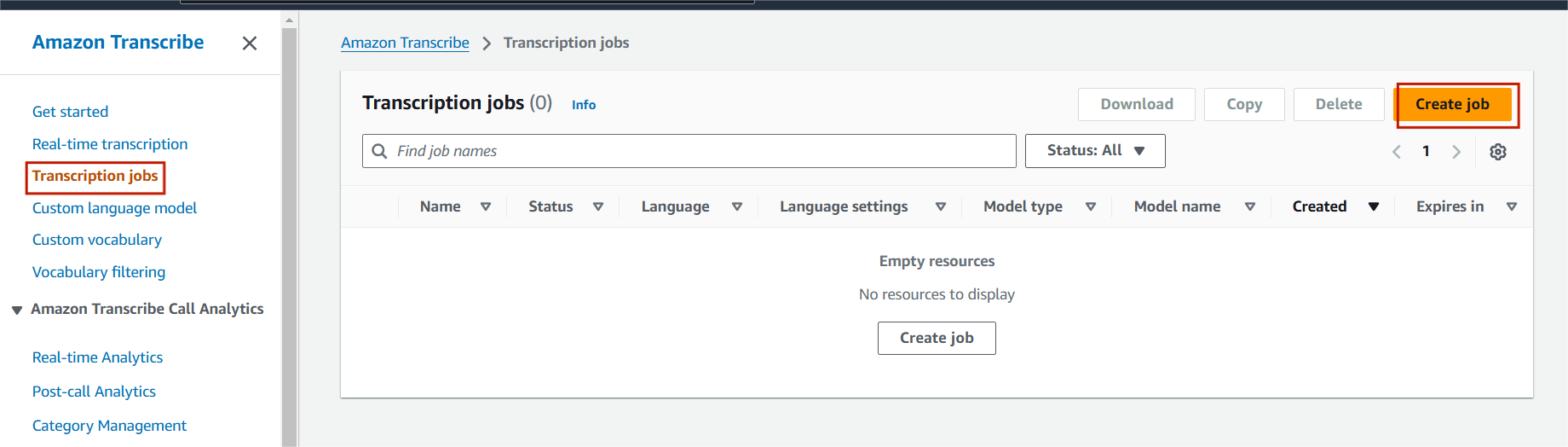
STEP 11 : Enter the job name.
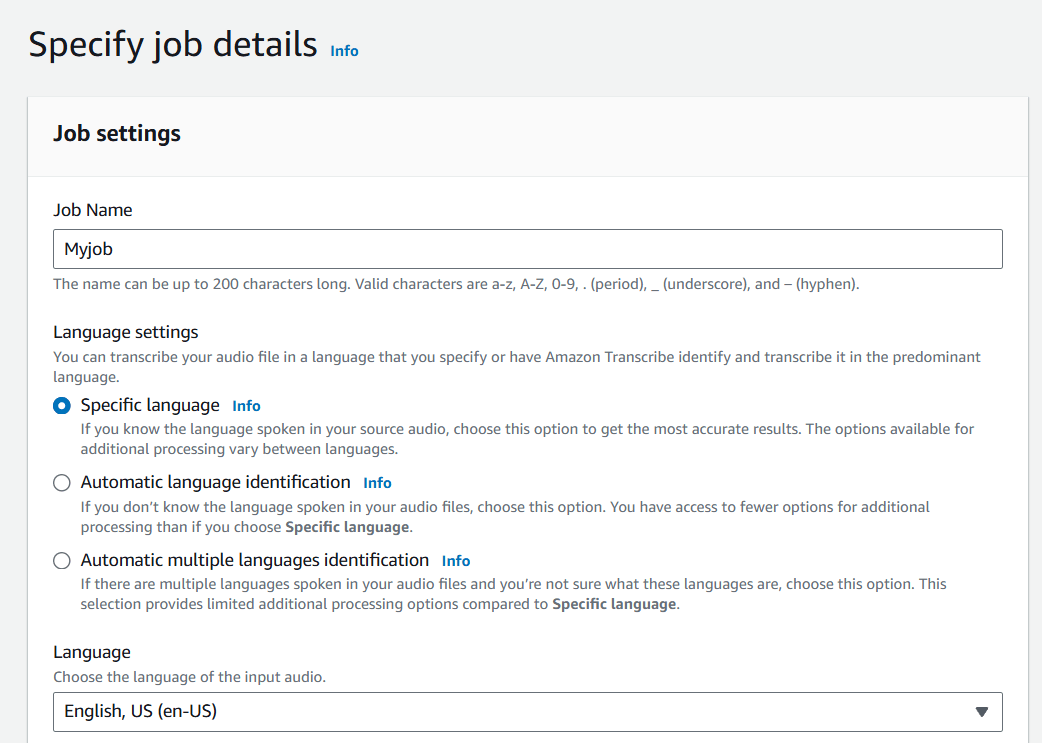
STEP 12 : Paste your S3 URI.
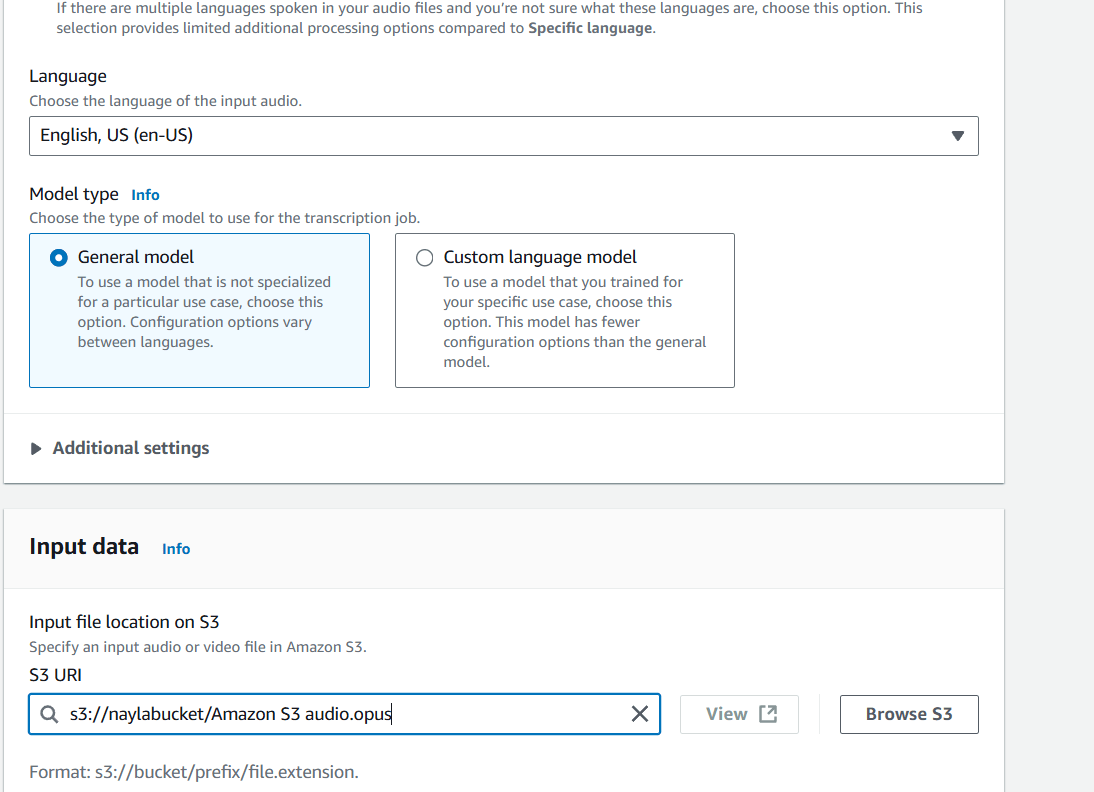
STEP 13 : Click on next.
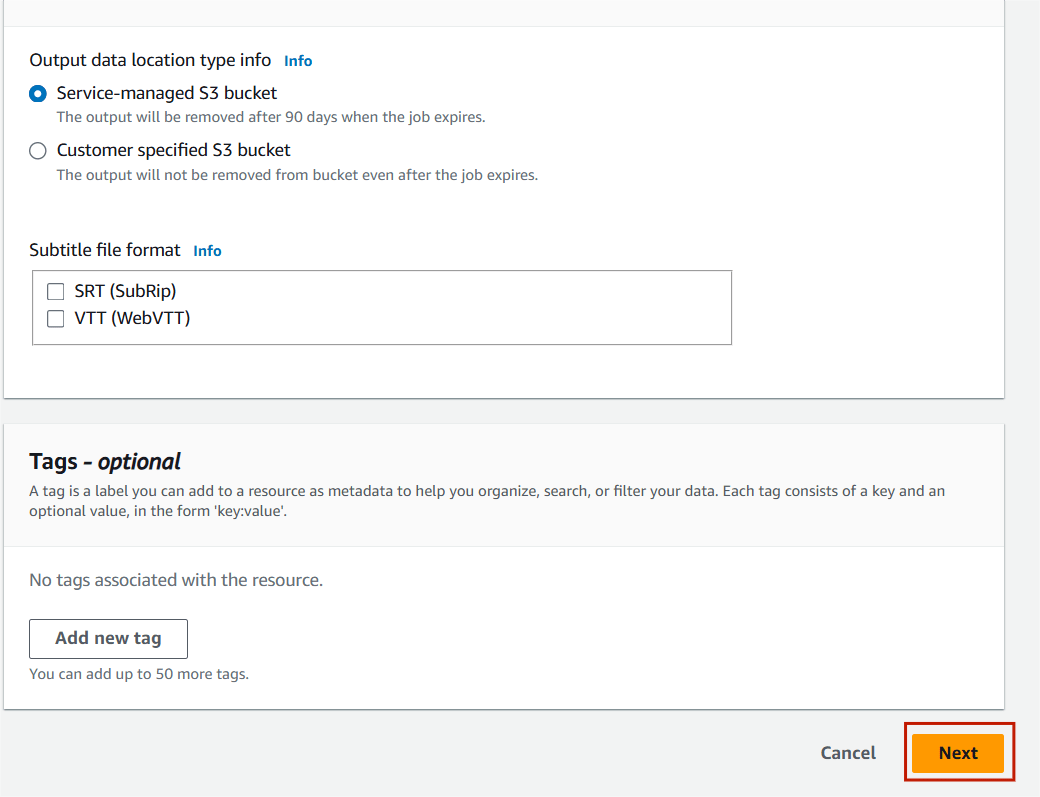
STEP 14 : Select create job.
STEP 15 : Once the status is completed Click on your job.
- Scroll down to the Transcription panel to view the transcription job output. In the JSON pane you can view the transcription results as it would be returned from the Transcribe API.
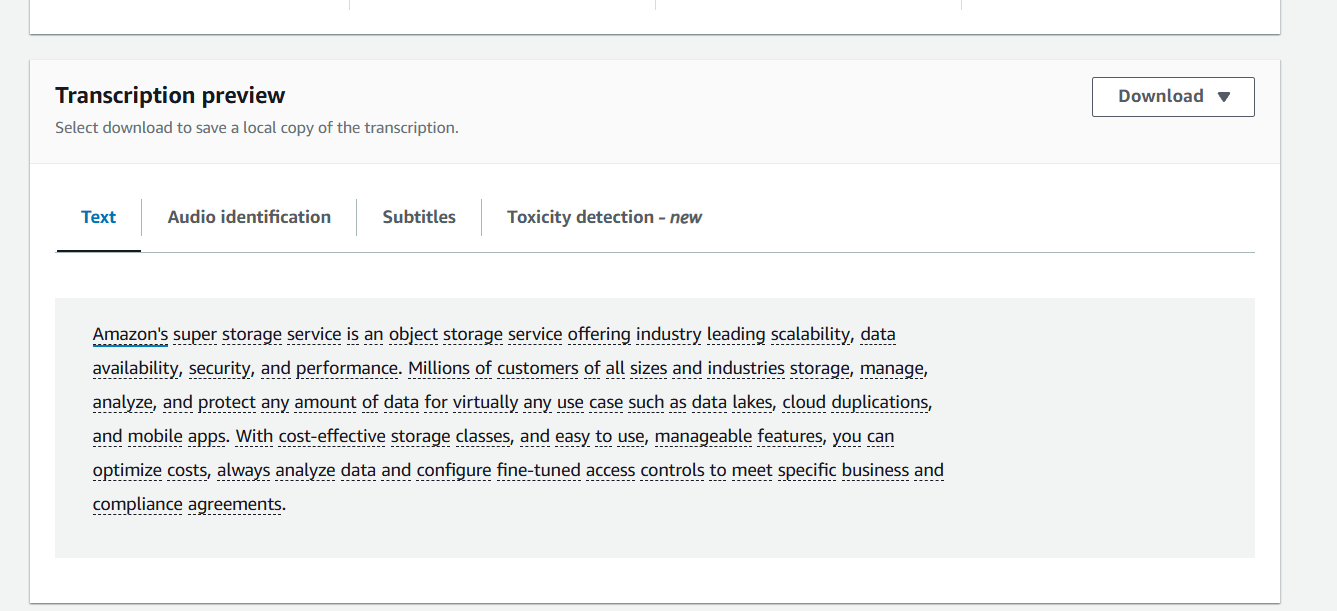

Conclusion.
You’ve now successfully created an audio transcript with Amazon Transcribe! If you plan to use this service frequently, consider automating the process with AWS SDKs or APIs. This feature, called Automatic Language Identification, can handle audio containing multiple languages and accurately transcribe it, making it an invaluable tool for global businesses and multilingual environments.
Cloud-Based Solution for Translating Text and Documents.
Translation Text :
Translating Text in AWS refers to the use of Amazon Translate, a fully managed machine translation service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). Translate text instantly for applications like chat or customer support. Amazon Translate supports a wide range of languages, enabling global communication. It allows you to translate text between multiple languages efficiently and accurately.
Use Cases:
- Translate product descriptions and reviews to cater to international markets.
- Facilitate seamless communication across global teams.
- Provide multilingual customer support by translating customer queries and responses in real-time.

Translation Documents :
Translation of Documents in AWS refers to the use of Amazon Translate along with other AWS services to perform document translation. Translate the content of documents in various formats (e.g., Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF) by extracting text, translating it, and reconstructing the translated document.
Use Cases:
- Translate legal documents or compliance reports for international regulatory needs.
- Translate contracts, reports, or internal documents for global teams.
- Localize marketing materials, product documentation, or training manuals for different regions.
Simplify Text Translation with Amazon Translate.
STEP 1 : Navigate the Amazon Translate.
STEP 2 : Select Text ,
- Source Language : English.
- Target Language : Italian.
- In the Source Code box, copy then paste the following text.
Amazon Translate lets you localize content for diverse global users and translate and analyze large volumes of text to activate cross-lingual communication between users.STEP 3 : Once the translation is complete, the results will appear in the Target Language section automatically.
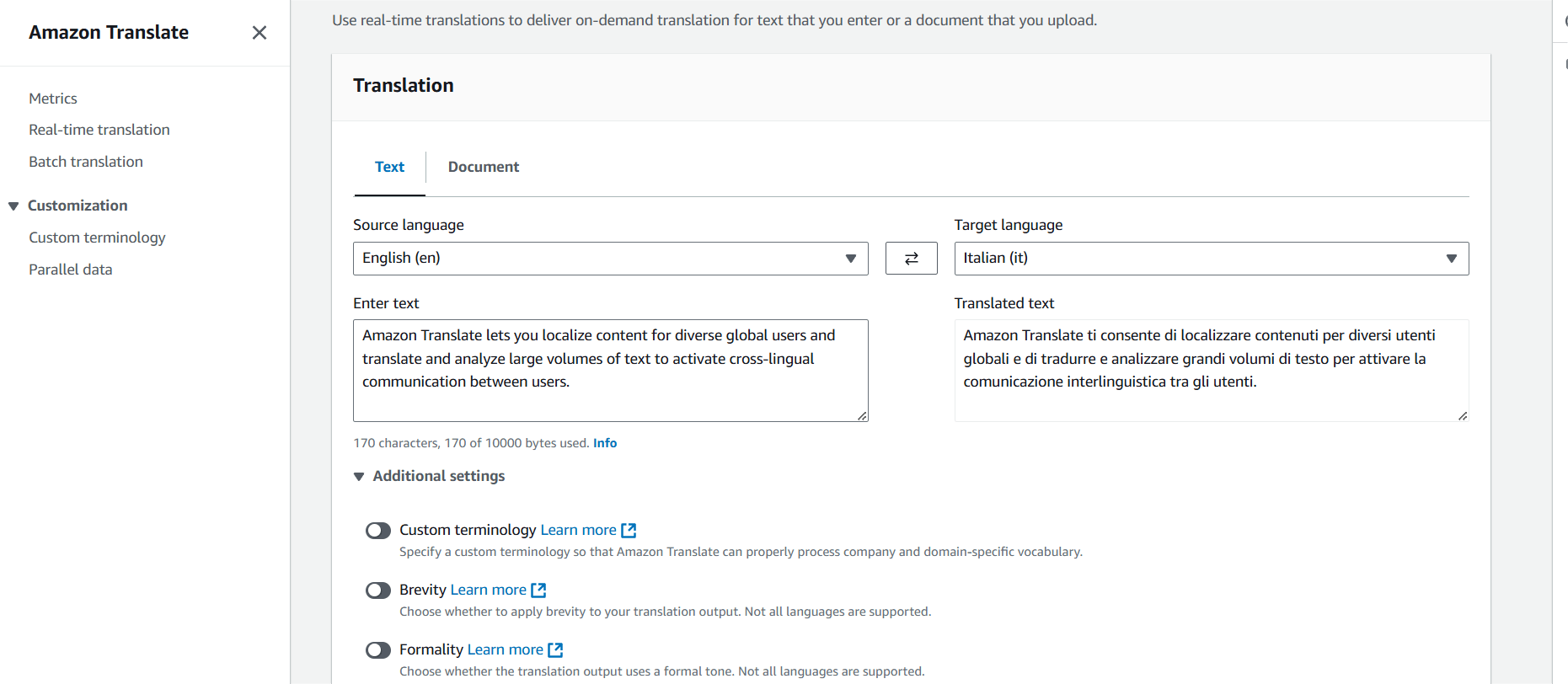
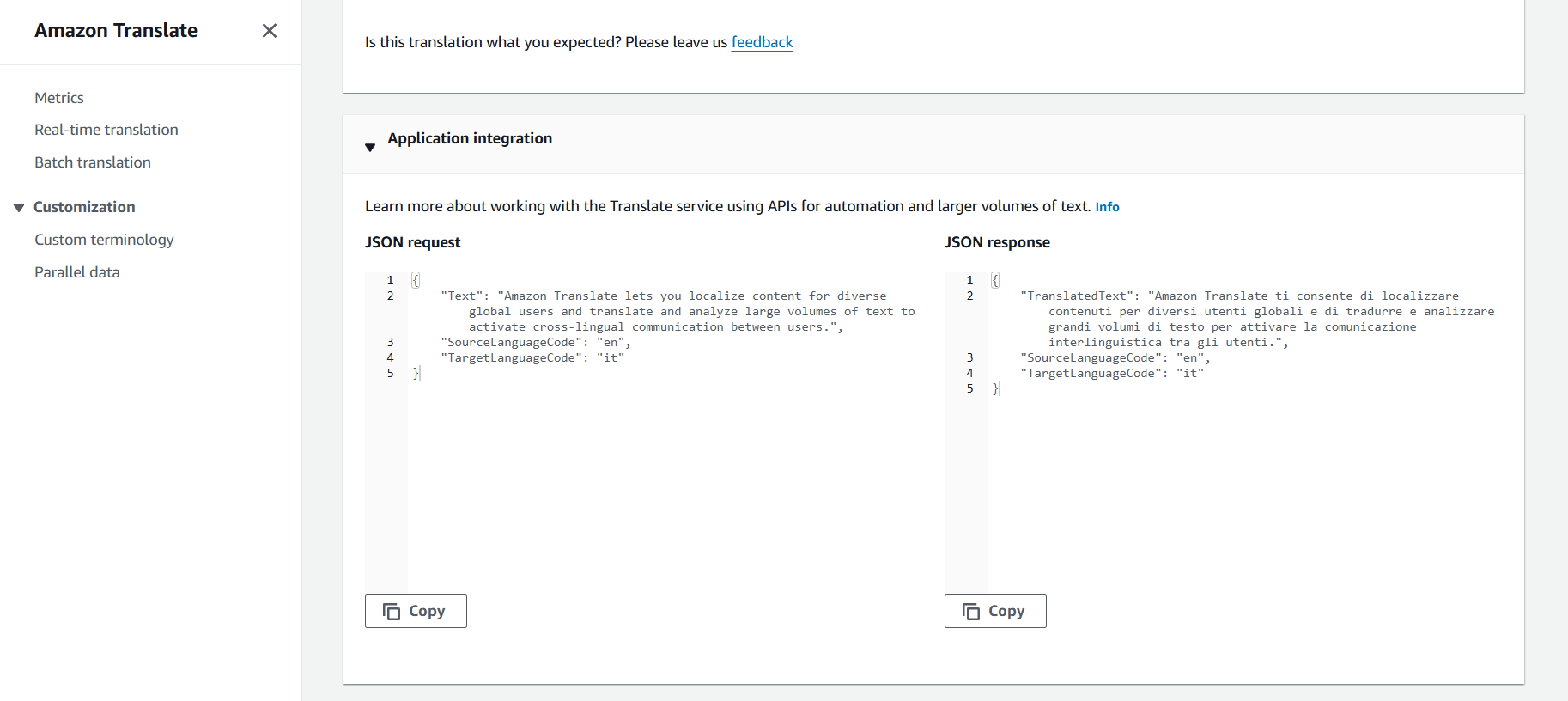
STEP 4 : To see the JSON request and response samples, expand the Application Integration section.
Simplify Document Translation with Amazon Translate.
STEP 1 : Click on ‘Real-time Translation’ in the left navigation pane, and then select the ‘Document’ tab.
- Source Language : English.
- Target Language : Tamil.
- Upload your translate document . https://pdf.ac/AySpN
- Document Type : Plain text (txt)
- Click on Translate and download.
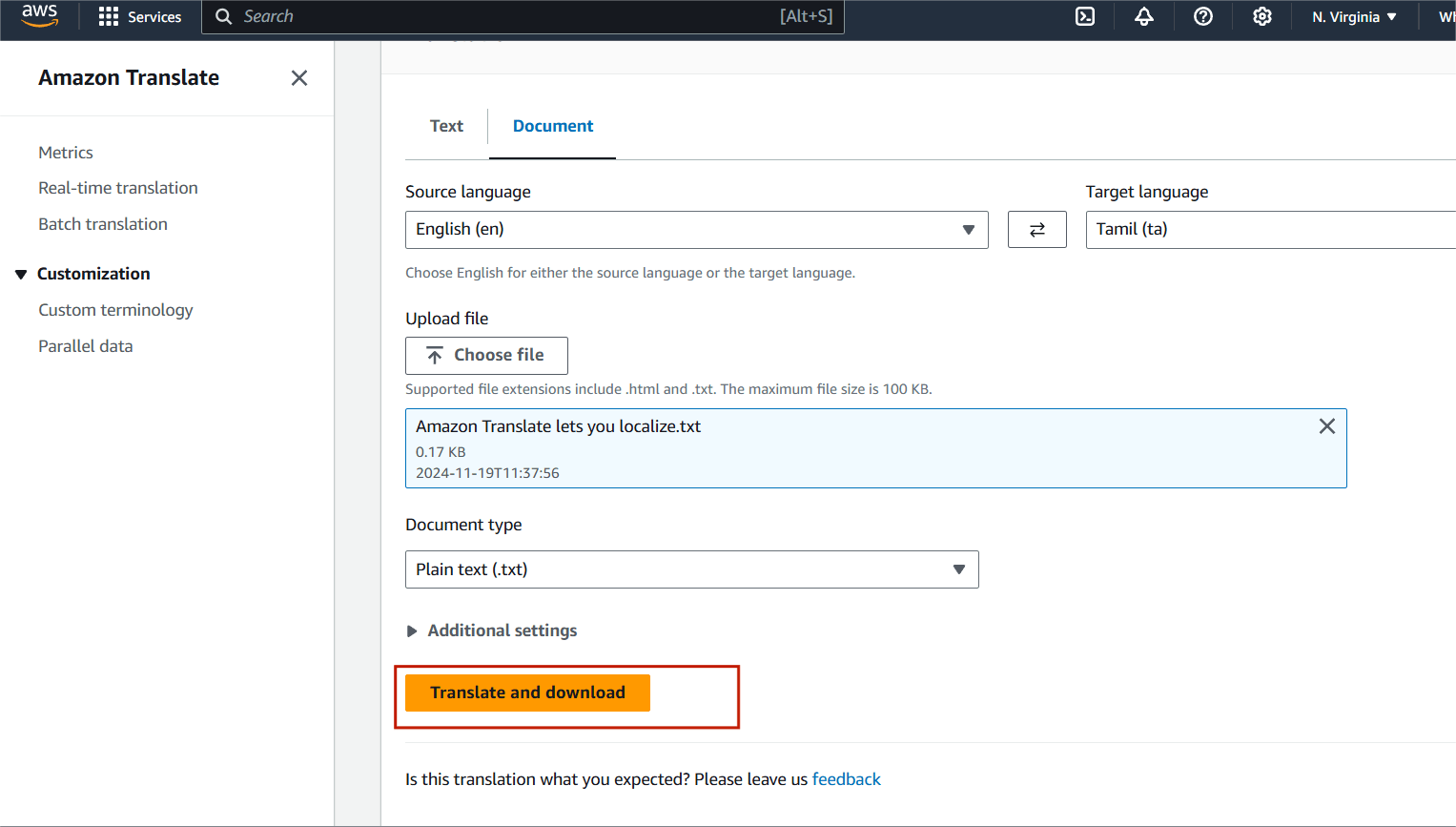
STEP 2 : This will download the translated document in you local.
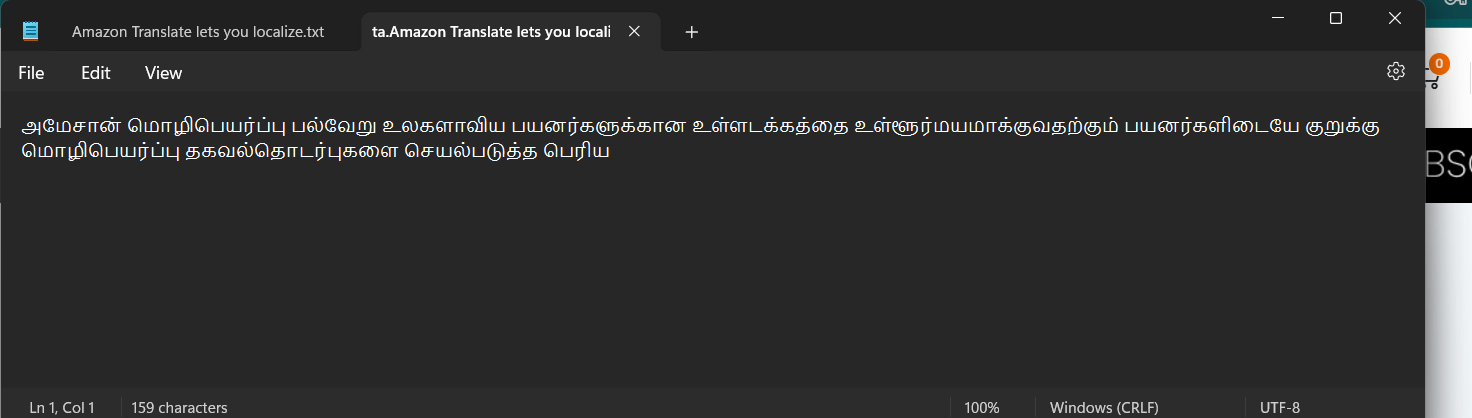

Conclusion.
In conclusion, Amazon Translate offers a powerful and seamless solution for translating text and documents. By integrating this service into your workflow, you can easily handle multilingual content, ensuring accessibility and broadening your global reach. It also continuously improves its translation quality through machine learning, ensuring accurate and natural translations across over 75 languages.