Create and Configure the Auto Scaling Group in EC2.
Introduction.
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling is a service that automatically adjusts the number of EC2 instances running in your environment to meet the demands of your application. This ensures that your application can scale up to handle increased load and scale down during periods of low demand, optimizing both performance and cost-efficiency.
An Auto Scaling Group (ASG) is a key component in this process. It defines the minimum, maximum, and desired number of EC2 instances, as well as scaling policies that determine when to add or remove instances based on metrics like CPU utilization or request count.
By configuring an ASG, you can ensure high availability and resilience for your applications, as the system can automatically recover from instance failures. This approach helps you maintain consistent application performance while reducing manual intervention.

Setting up an Auto Scaling Group in EC2 requires careful planning of instance types, desired capacity, scaling policies, and other configurations to meet the specific needs of your application.
STEP 1: Navigate EC2 and select security group.
- Click on create security group.
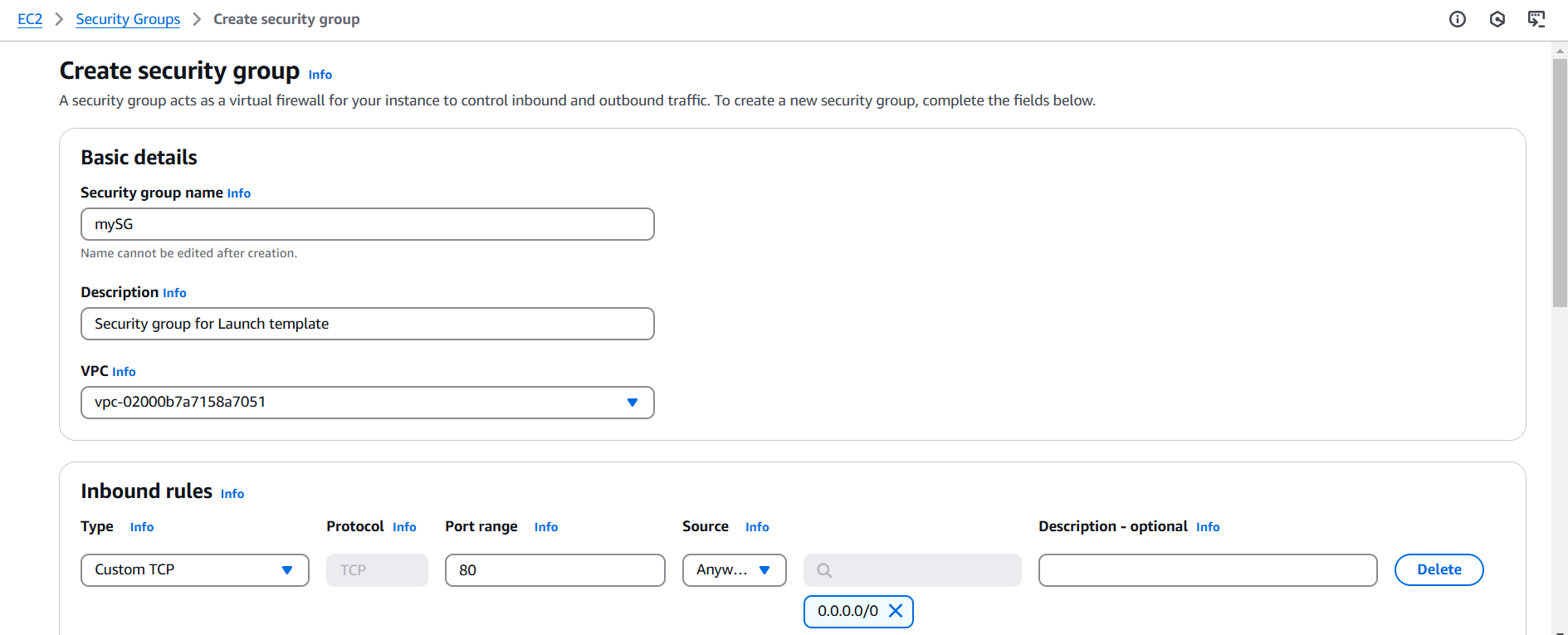
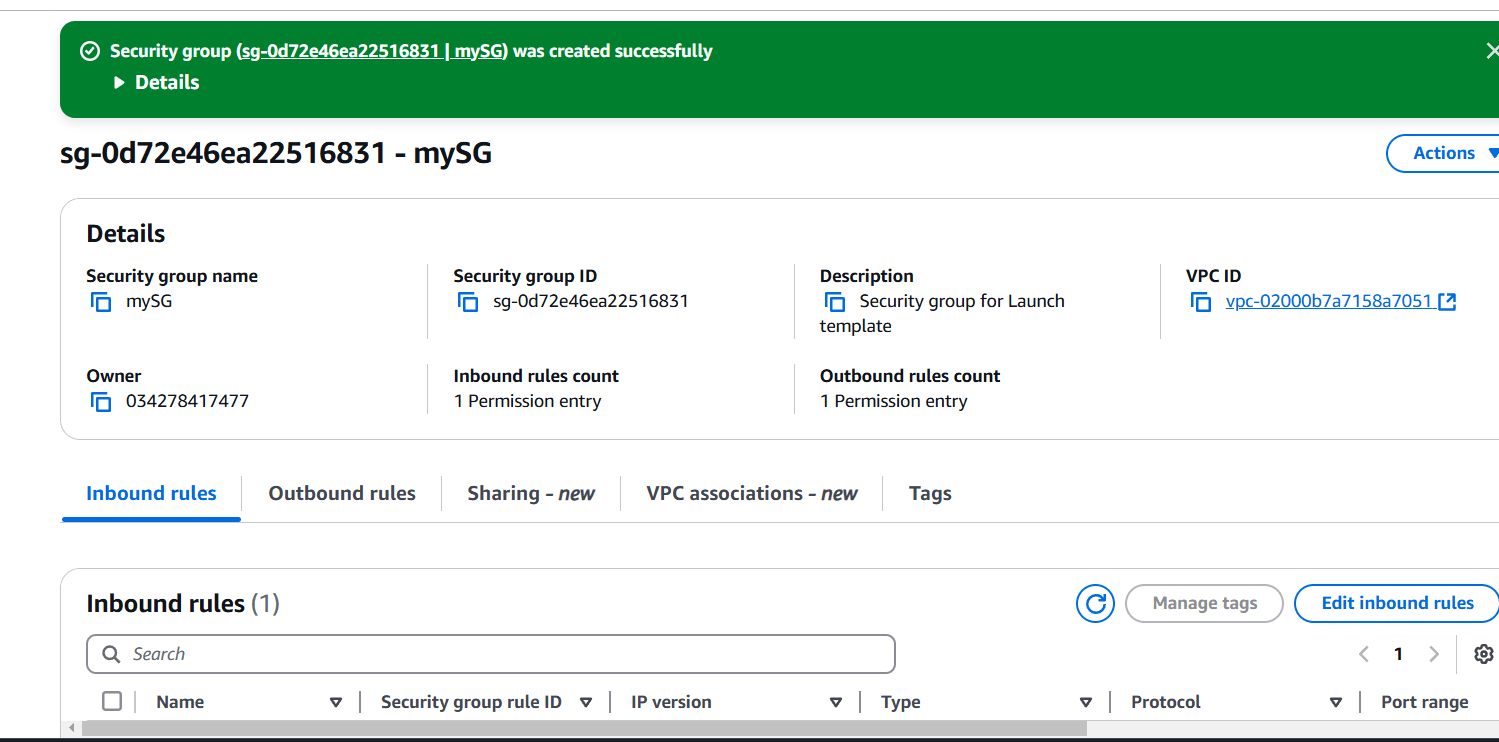
STEP 2: Enter security group name and discription.
- Select default VPC.
- Add port number 80.
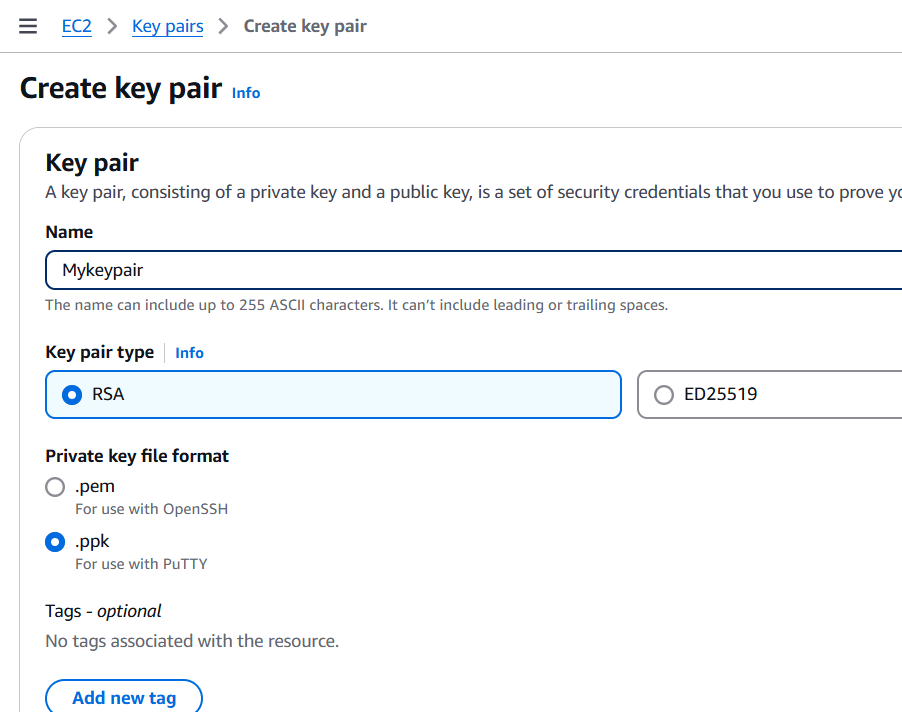
STEP 3: Next click on keypair and create a keypair.
- Enter the name and select ppk or .pem.
- Click on create.
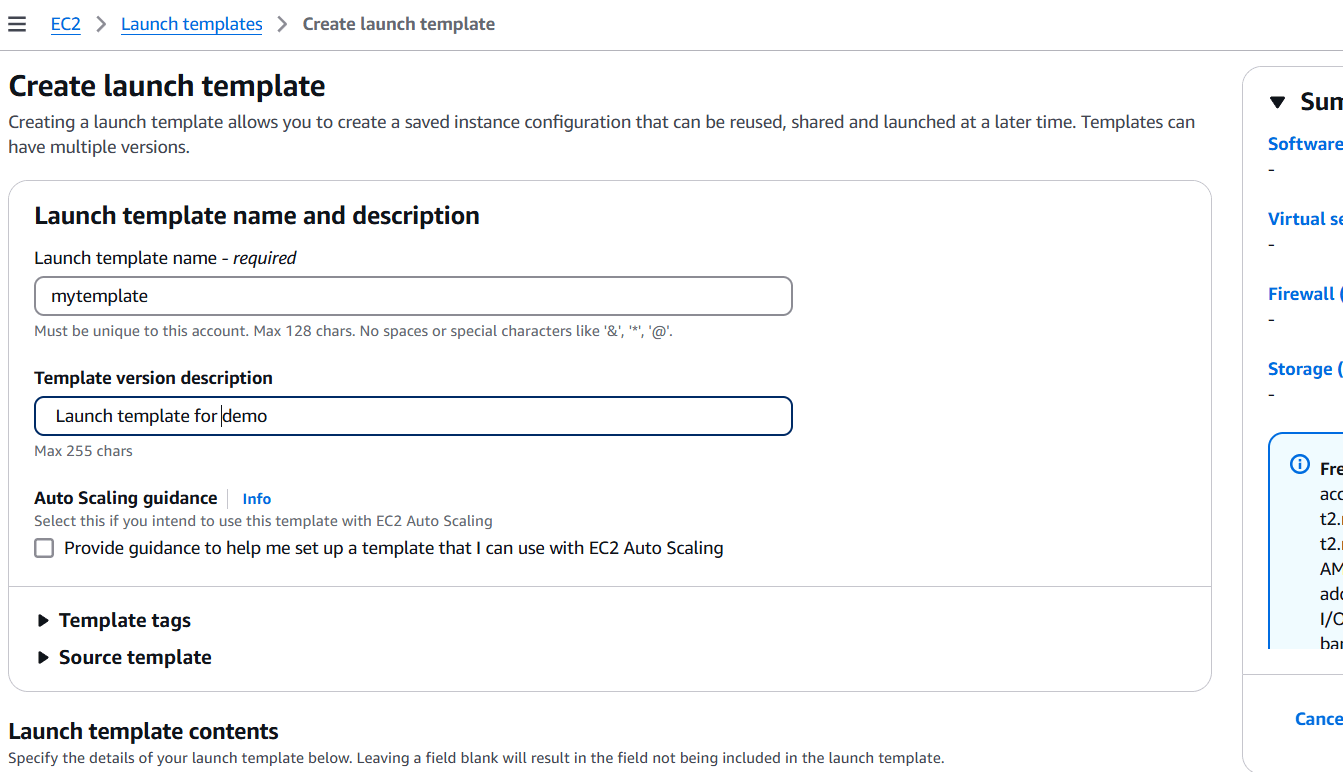
STEP 4: Select launch templates.
- Click on create launch templates.
- Enter the name and discription.
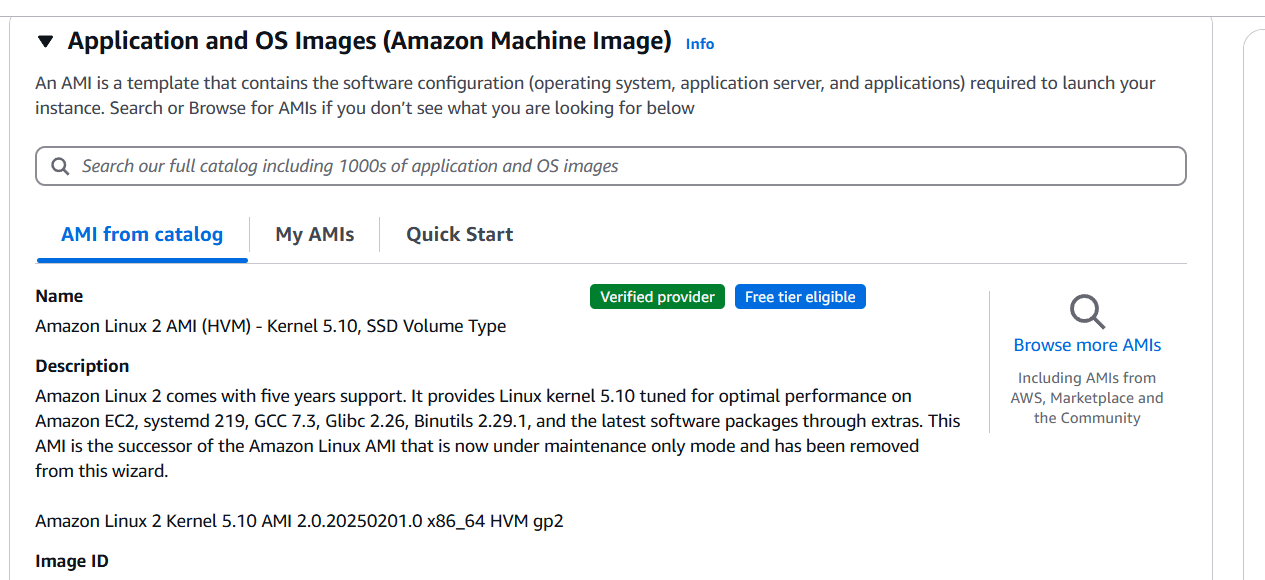
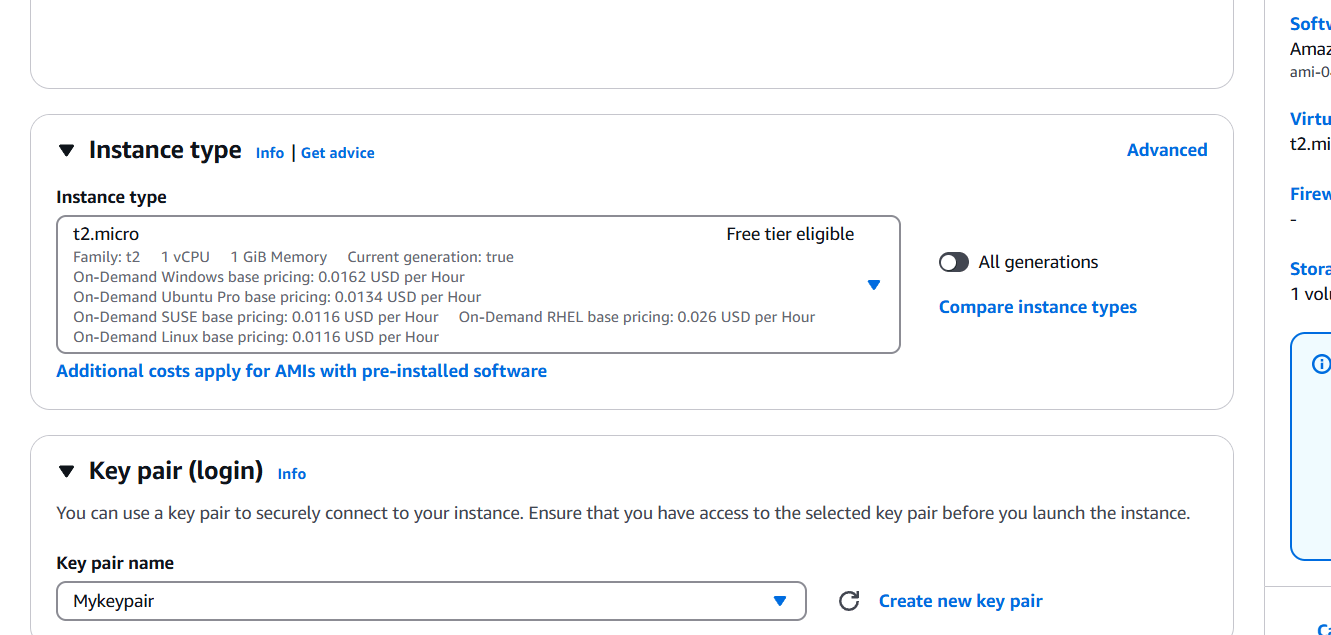
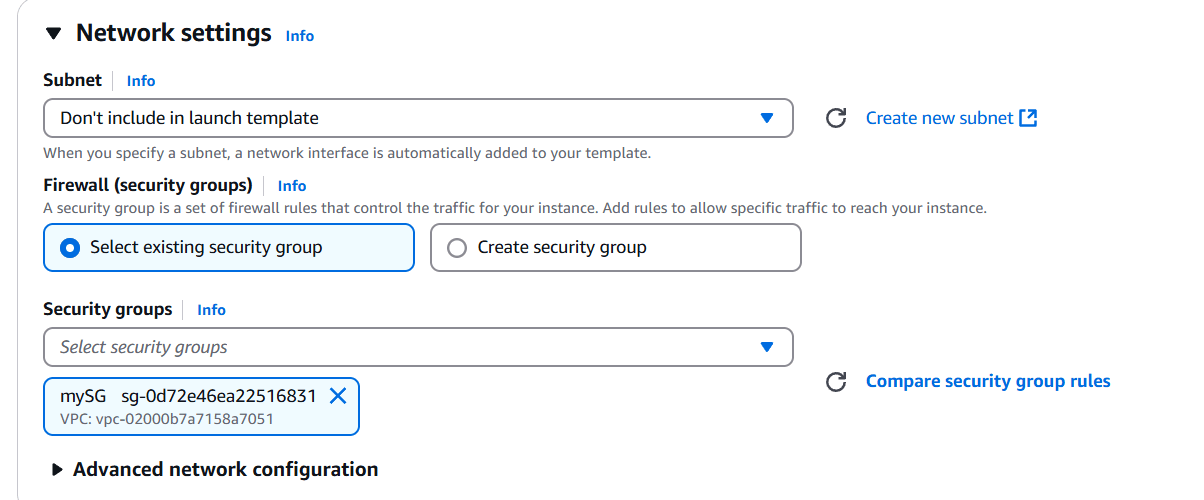
- Select instance type and AMI, keypair, security group.
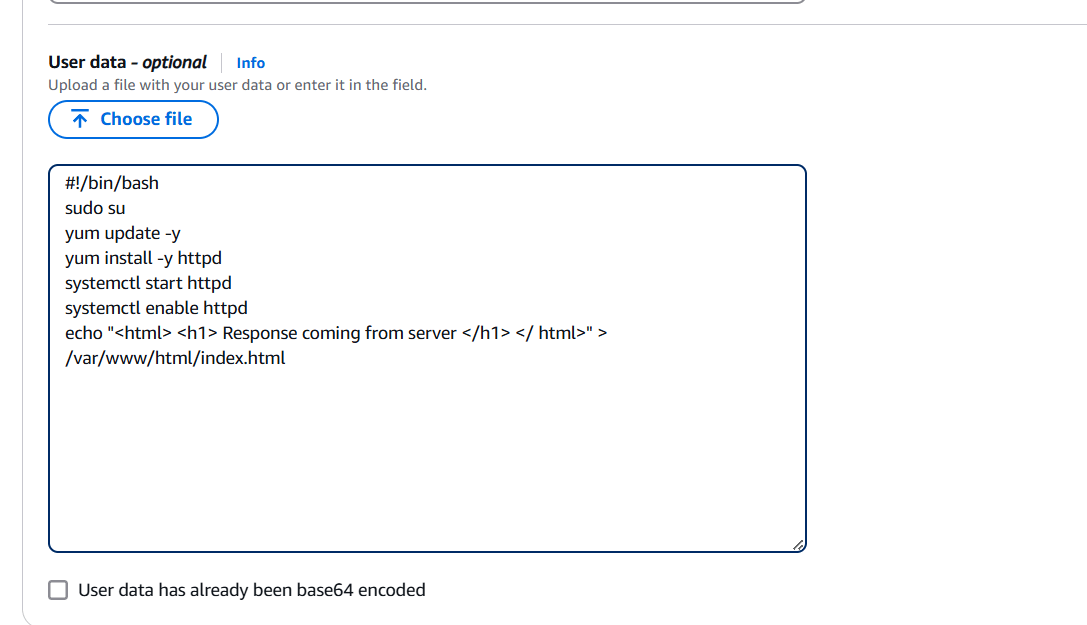
- Enter the following command in user data.
#!/bin/bash
sudo su
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
echo "<html> <h1> Response coming from server </h1> </ html>" > /var/www/html/index.html
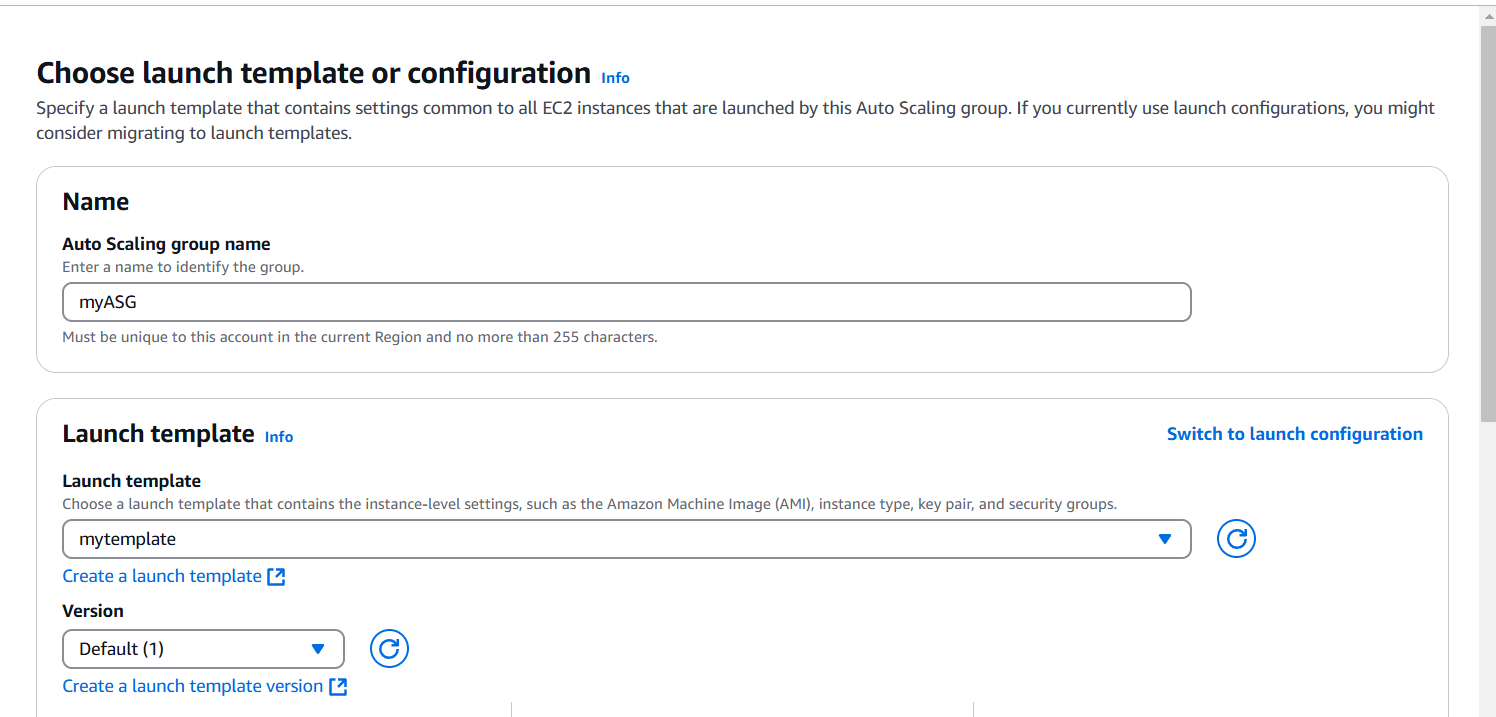
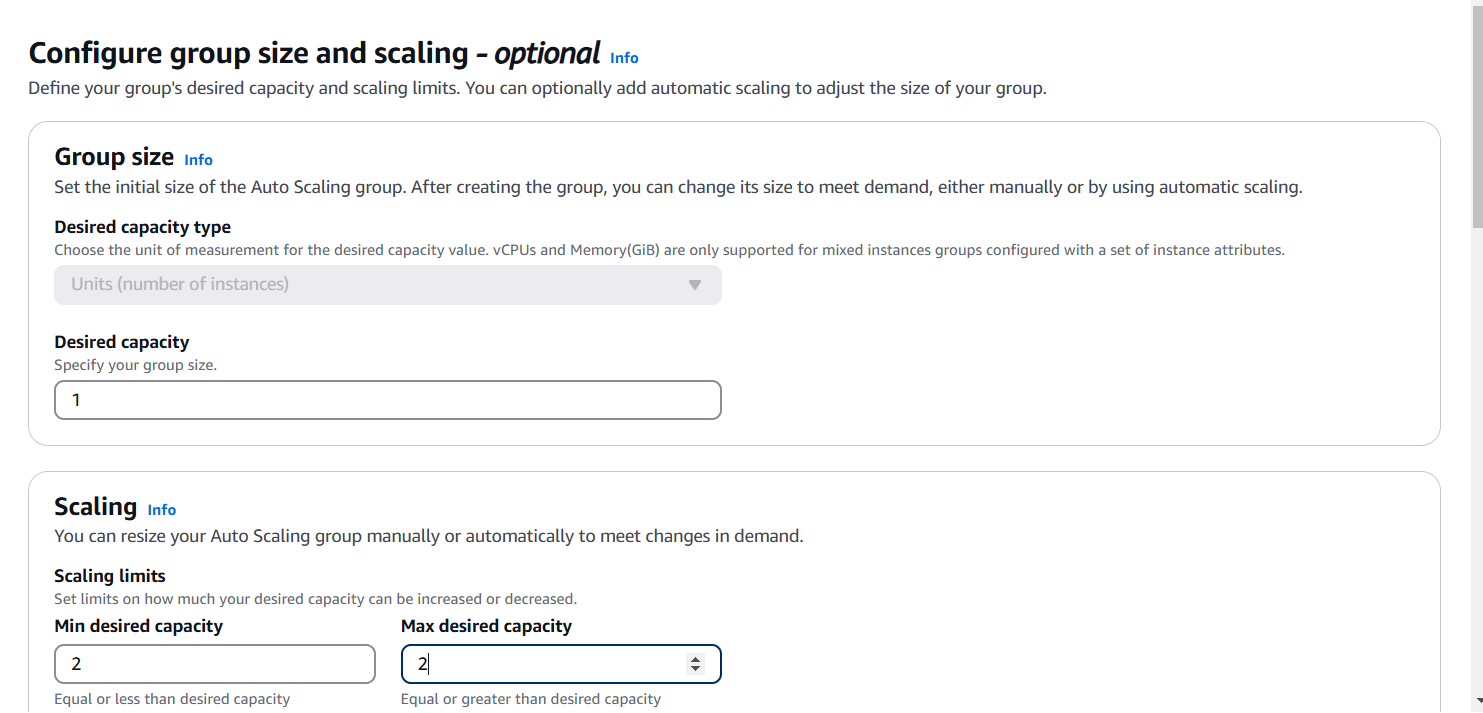
STEP 5: Now, Create a auto scaling group.
- Enter a name and Select your template.
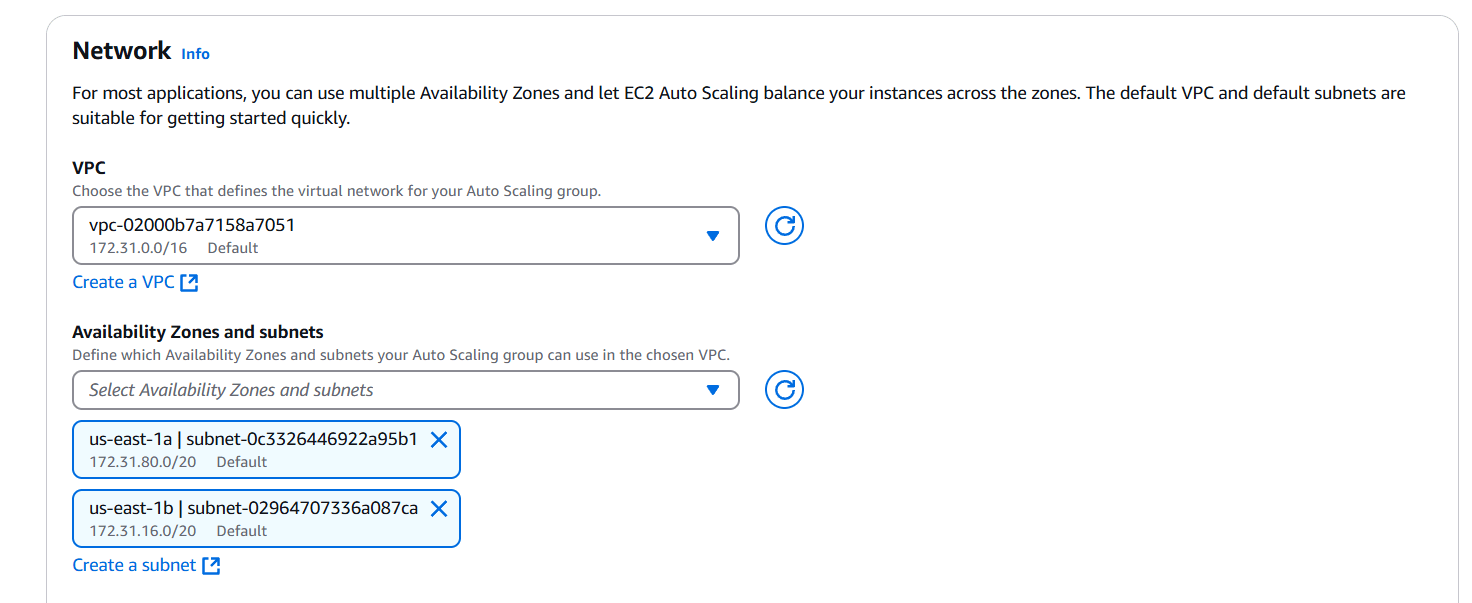
- Select VPC and Subnet.
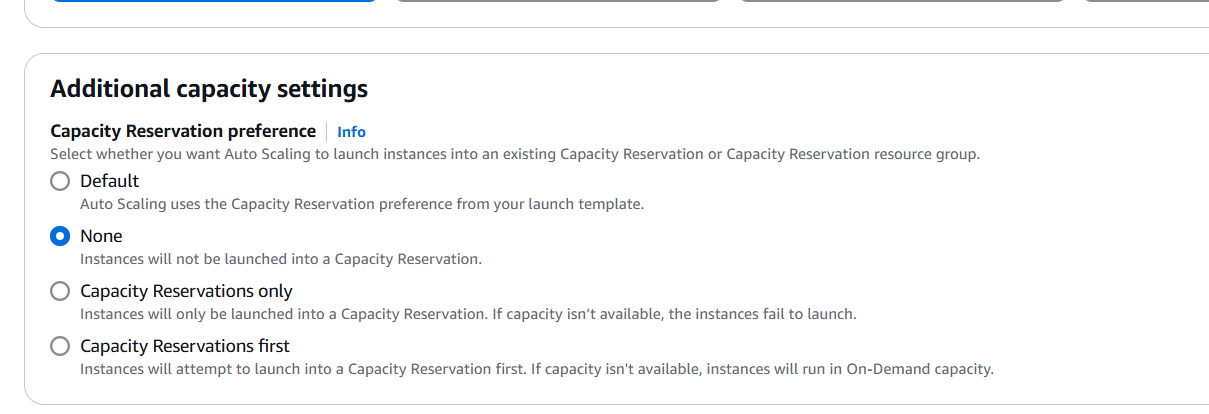
- Select addition capacity setting.
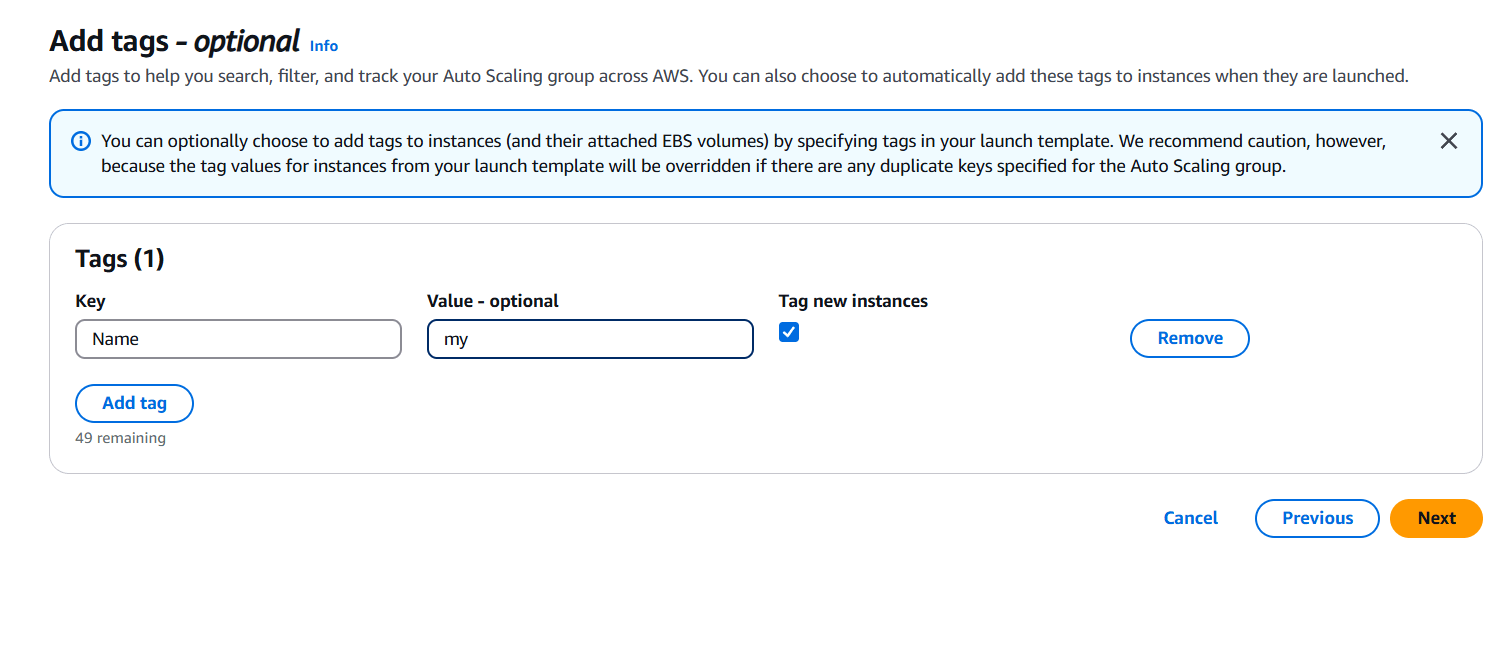
- Add tags.
- And click on next.
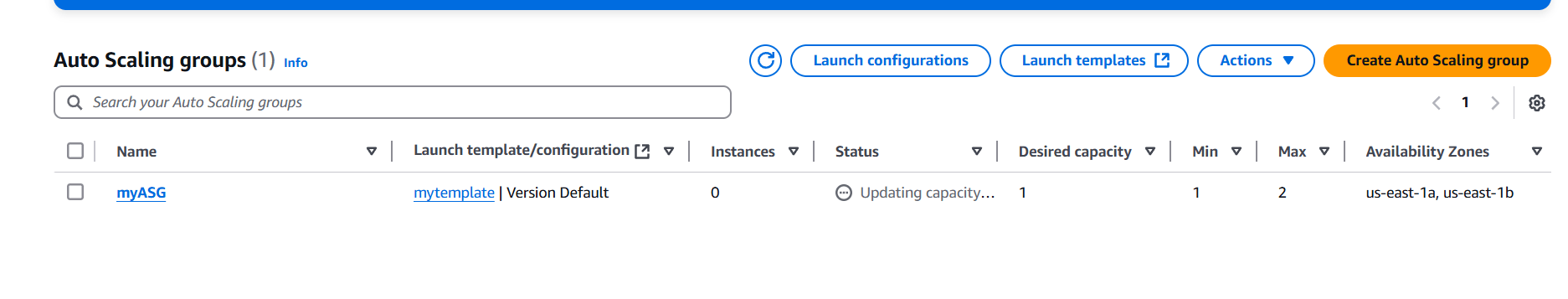
STEP 6: Go to instance and verify the Create the instance.

STEP 7: Next, Checking the ASG.
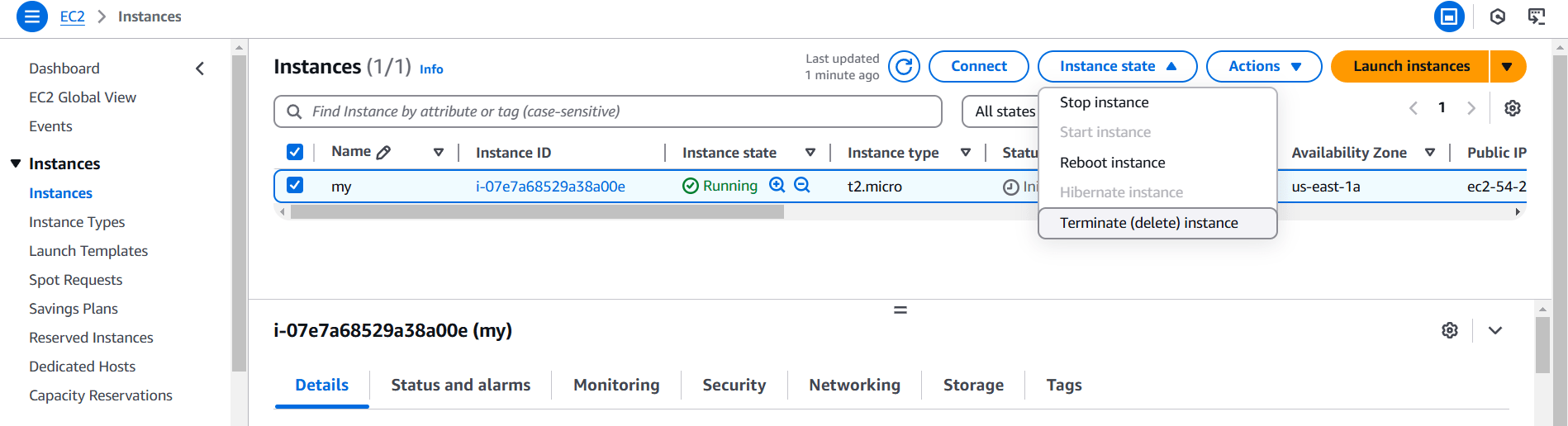
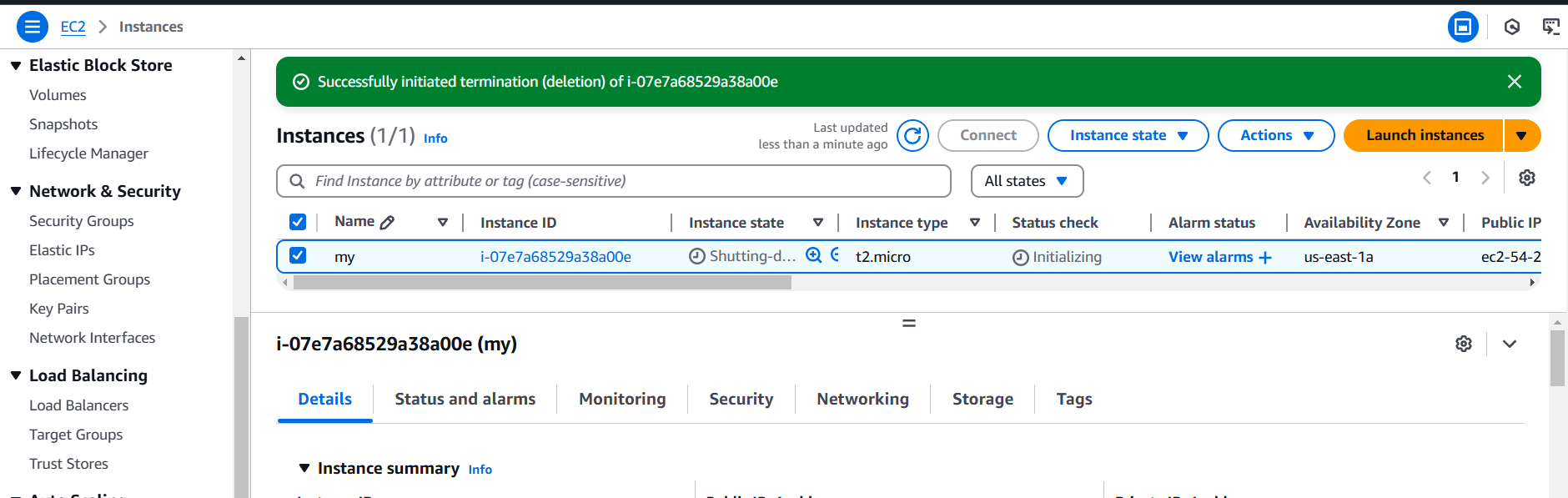
STEP 8: Click on instance and terminate the instance.
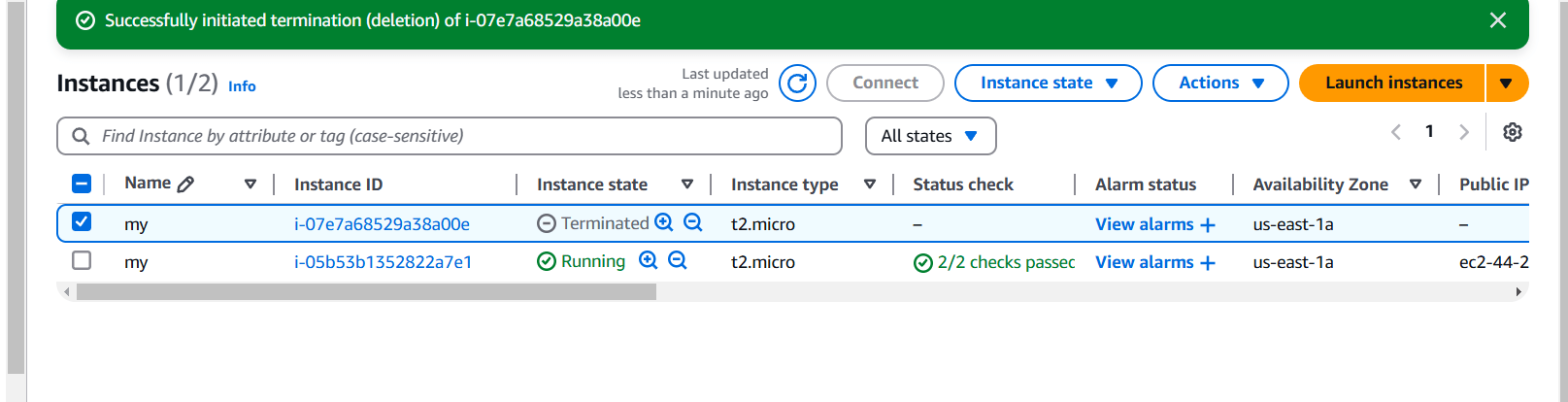
STEP 9: Set up automation to create instances in under 5 minutes.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, EC2 Auto Scaling provides a powerful solution for managing the scalability and availability of your applications in the cloud. By creating and configuring an Auto Scaling Group, you can automate the scaling of your infrastructure, ensuring that it meets varying demand efficiently.
This service reduces the need for manual intervention, allowing for quicker responses to traffic changes and minimizing costs by only running the necessary instances. It enhances reliability by ensuring that the required number of instances is always running, even in the event of failures.
Proper configuration of Auto Scaling policies, instance types, and capacity settings is essential to ensure the system operates smoothly. Ultimately, EC2 Auto Scaling ensures that your application remains performant, cost-effective, and resilient, contributing to a better user experience and more efficient cloud resource management.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install Imagick for PHP on Amazon Linux EC2.
Introduction.
If you’re running a web application on an AWS EC2 instance using Amazon Linux, you might need to process images dynamically. Imagick, a powerful image manipulation library for PHP, can help with this by allowing you to create, edit, and convert images in various formats. However, installing Imagick on Amazon Linux can sometimes be a bit tricky for those unfamiliar with the process.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to install the Imagick extension for PHP on an Amazon Linux EC2 instance, ensuring that you can leverage all the benefits of this robust image processing tool. Whether you’re building a custom application or managing a CMS like WordPress, Imagick will give you the flexibility and power you need to handle images effectively.

STEP 1: Start by updating the system to ensure you have the latest packages.
sudo yum update -y
STEP 2: Install the required dependencies to build the Imagick extension.
sudo yum install -y gcc libtool make autoconf php-pear php-devel ImageMagick ImageMagick-devel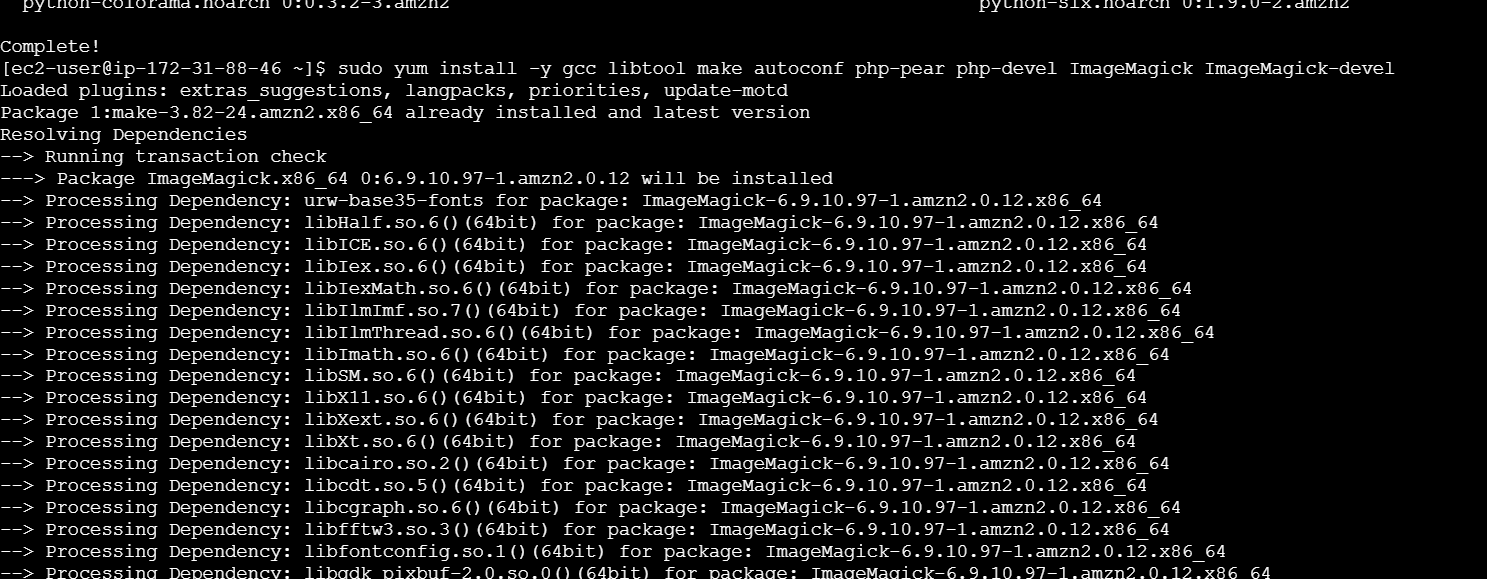
STEP 3: Use PECL (PHP Extension Community Library) to install the Imagick PHP extension.
sudo pecl install imagick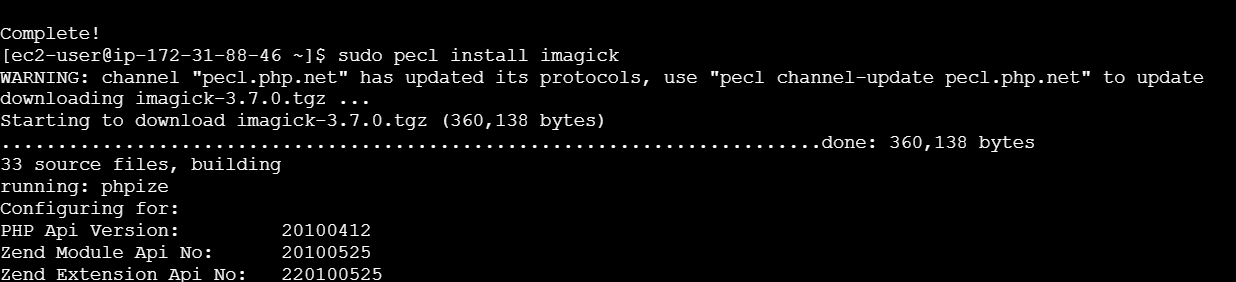
STEP 4: Once the installation is complete, add the extension to the PHP configuration file. You need to create a new imagick.ini file in the PHP configuration directory.
echo "extension=imagick.so" | sudo tee /etc/php.d/20-imagick.ini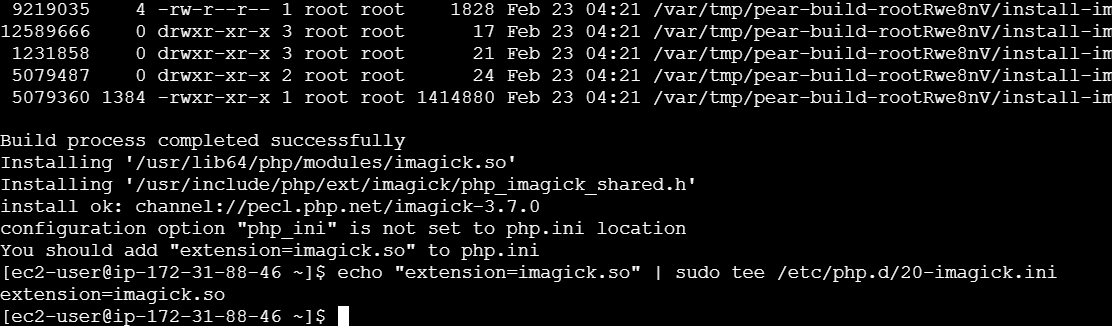
STEP 5: Restart the Web Server.
sudo systemctl restart httpd
sudo systemctl restart php-fpmSTEP 6: Verify the Installation.
php -m | grep imagick
Check ImageMagick Version:
convert --version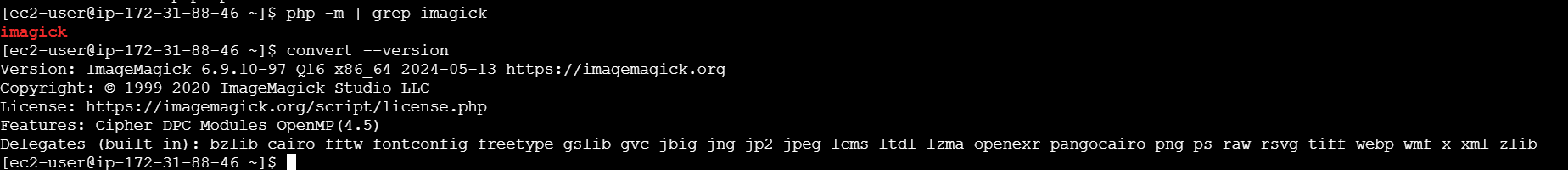

Conclusion.
Installing the Imagick extension for PHP on an Amazon Linux EC2 instance is a straightforward process once you know the right steps. By following this guide, you’ve successfully set up a powerful image manipulation tool that can enhance the capabilities of your PHP applications. Whether you’re working with dynamic image processing, optimizing image sizes, or converting formats, Imagick provides the performance and flexibility you need.
With Imagick now installed and configured, you’re ready to integrate it into your projects and take advantage of its full potential. If you run into any issues, remember to double-check the dependencies, restart your web server, and verify your PHP setup. Happy coding!
Deploying a Three-Tier Architecture Using Docker Containers.
Introduction.
In modern application development, scalability, flexibility, and maintainability are key goals. One effective way to achieve this is by implementing a three-tier architecture, which separates an application into three distinct layers: the presentation layer, the logic layer, and the data layer. Docker containers, with their ability to isolate and package applications, provide an ideal environment for deploying each of these layers independently, while ensuring consistency across various platforms.
In this blog, we will walk you through the process of deploying a three-tier architecture using Docker containers. We will break down the components, explore how Docker can enhance the deployment process, and provide a step-by-step guide to getting your three-tier application up and running. Whether you’re new to Docker or a seasoned developer, this guide will help you leverage containers to create a robust, scalable, and easy-to-manage application architecture.

STEP 1: Create a EC2instance.
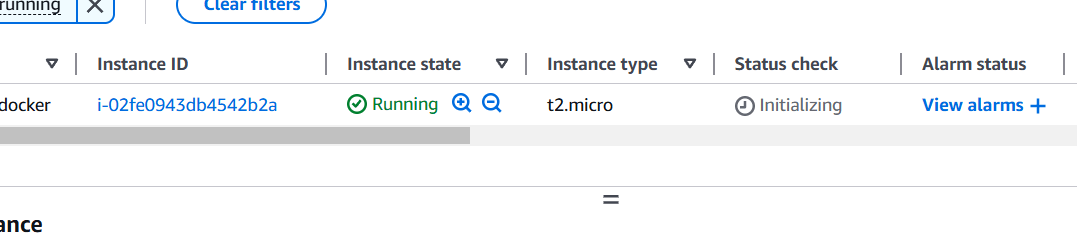
STEP 2: SSH into EC2 Instance.
- Create a project directory.
- Change the present directory to project directory.
- Create a file named docker-compose.yml
nano docker-compose.yaml
STEP 3: Enter the following script.
version: '3'
services:
web:
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- "8080:80"
depends_on:
- app
app:
image: node:alpine
working_dir: /app
volumes:
- ./api:/app
command: sh -c "cd /app && npm install && node app.js"
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: mysql:5.7
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root_password
MYSQL_DATABASE: sample_db
MYSQL_USER: app_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: app_password
ports:
- "3306:3306"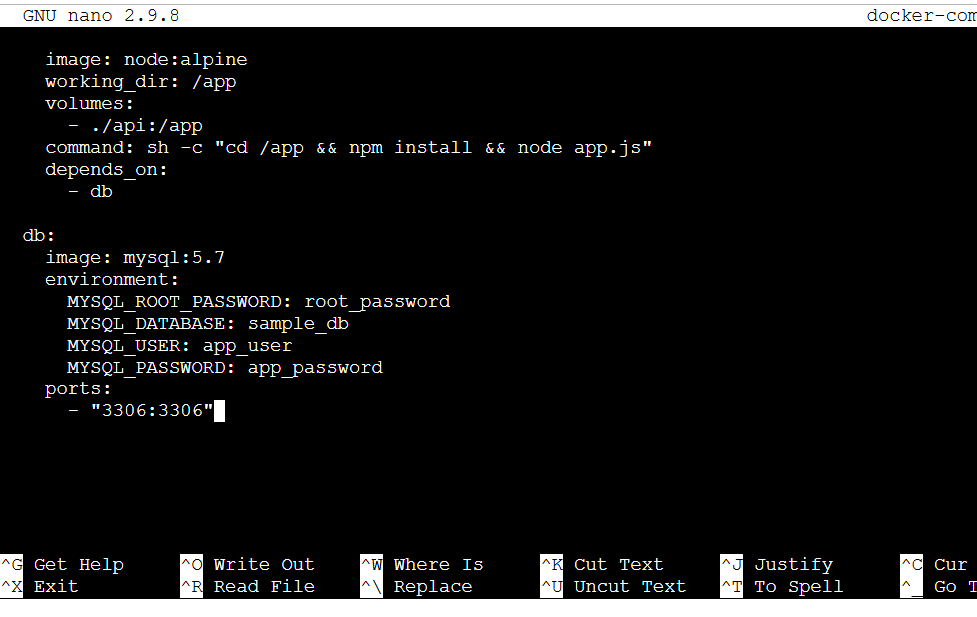
STEP 4: Create Application Files.
mkdir api
cd api
nano index.html
Enter the following command.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title> Docker Compose Lab</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello from Docker Compose!</h1>
</body>
</html>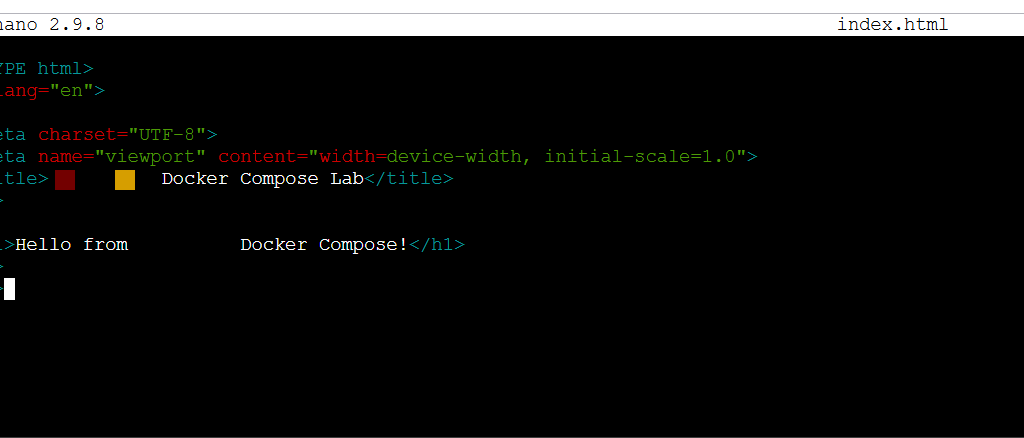
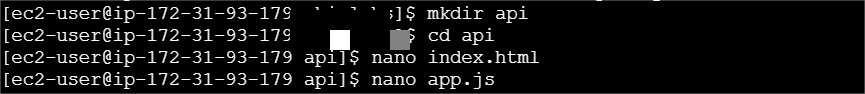
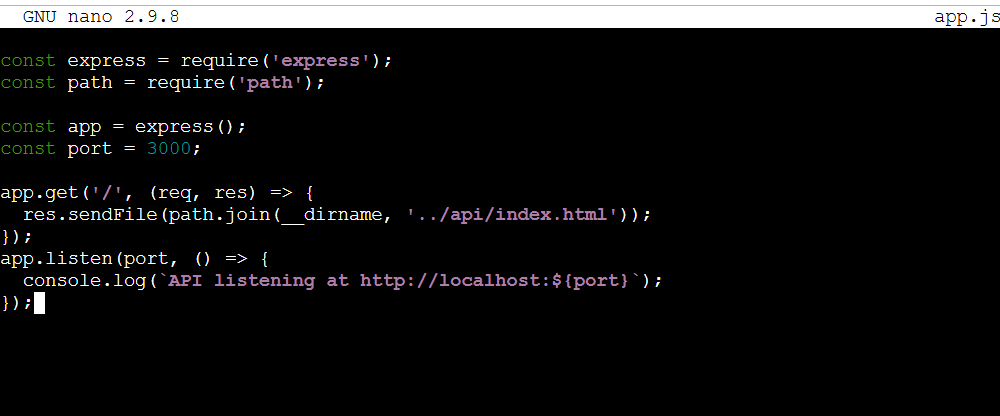
STEP 5: create a file named app.js.
nano app.js
Enter the following command.
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, '../api/index.html'));
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`API listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
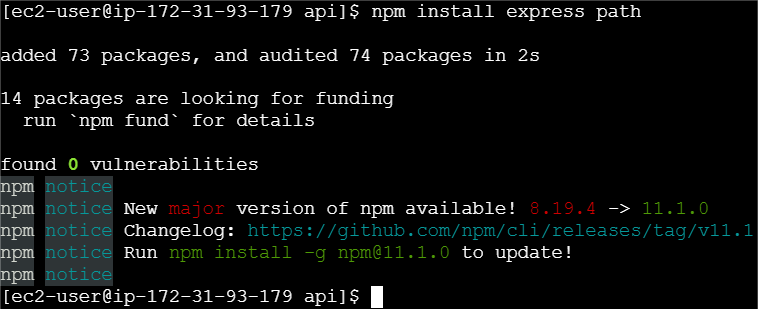
STEP 6: Intialize a node application using the following command.
npm init -y
npm install express path
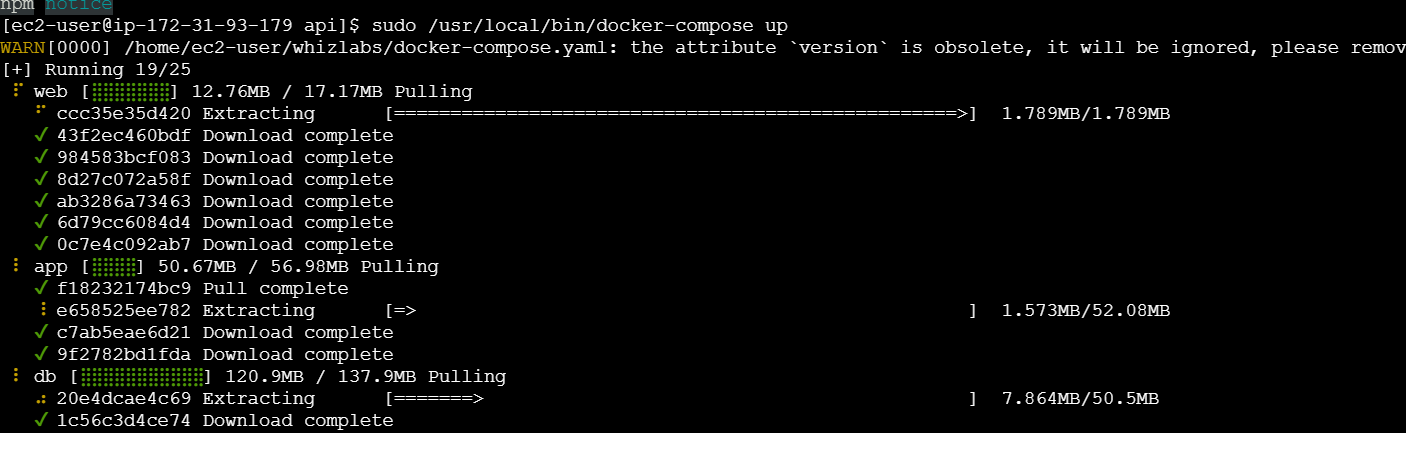
sudo /usr/local/bin/docker-compose up
STEP 7: Copy the IPv4 DNS of the EC2 instance and paste it in the address tab. Then, add [: 8080] behind the DNS name and press Enter.
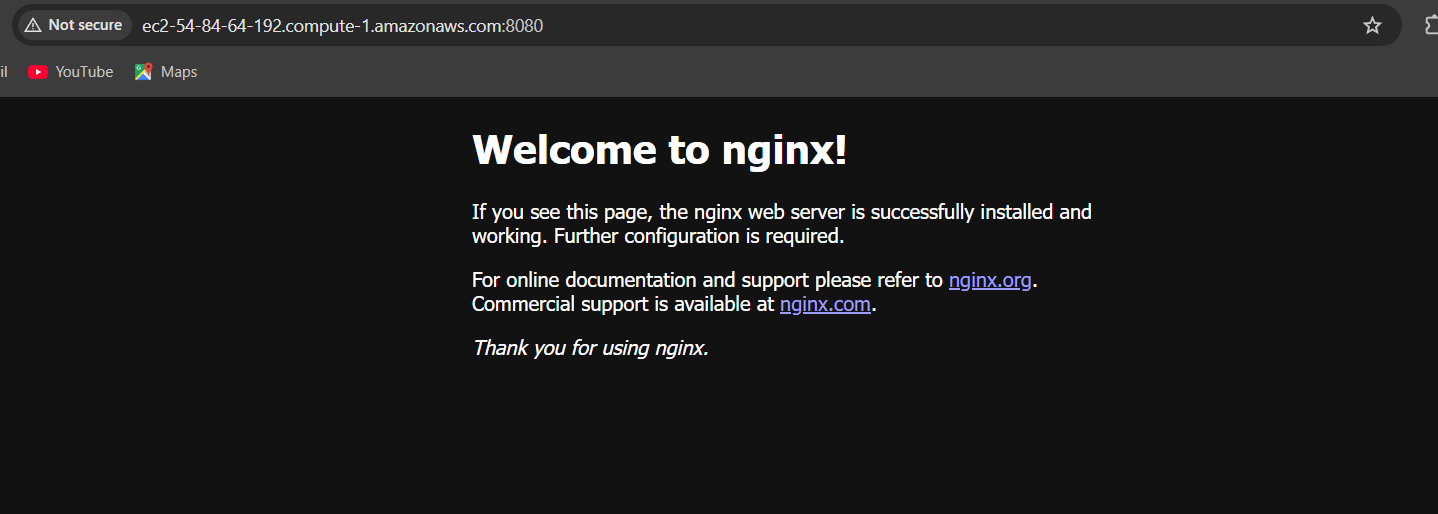

Conclusion.
Deploying a three-tier architecture using Docker containers not only simplifies the management of your application’s layers but also enhances scalability, security, and portability. By isolating each tier in its own container, you can achieve a highly modular system that is easier to update, maintain, and scale as your application grows.
In this guide, we’ve explored how Docker’s containerization can streamline the process of deploying a robust, production-ready three-tier architecture. By leveraging Docker’s power, you can create an efficient and flexible environment that is ready for both development and deployment, while ensuring consistency across different environments.
With this foundation, you are now equipped to implement your own three-tier architecture with Docker. As you continue to refine your application, Docker will be a key tool in helping you optimize and scale with ease.
Building Scalable Real-Time Data Pipelines with Docker.
Introduction.
Building scalable real-time data pipelines is crucial for businesses that need to process and analyze large volumes of data as it streams in. Docker, a platform that allows developers to package applications and their dependencies into containers, has become an essential tool for managing complex systems. By utilizing Docker, you can create isolated, consistent environments for each component of a real-time data pipeline, enabling scalability and flexibility.
In this blog, we will explore how Docker can streamline the development and deployment of real-time data pipelines. We’ll cover the key steps for setting up a scalable pipeline, from containerizing data processing tools to integrating them into a microservices architecture. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how Docker enables faster, more efficient data processing, without compromising on performance or reliability.

Whether you are working with real-time analytics, streaming data, or complex event processing, Docker can help you manage workloads more efficiently. This article will also discuss best practices, common pitfalls, and how to optimize Docker containers for real-time data workflows. Let’s dive into the world of scalable real-time data pipelines with Docker!
STEP 1: Create a instance.
STEP 2: Accessing SSH Connection.
- Install Docker Compose.
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
docker-compose --version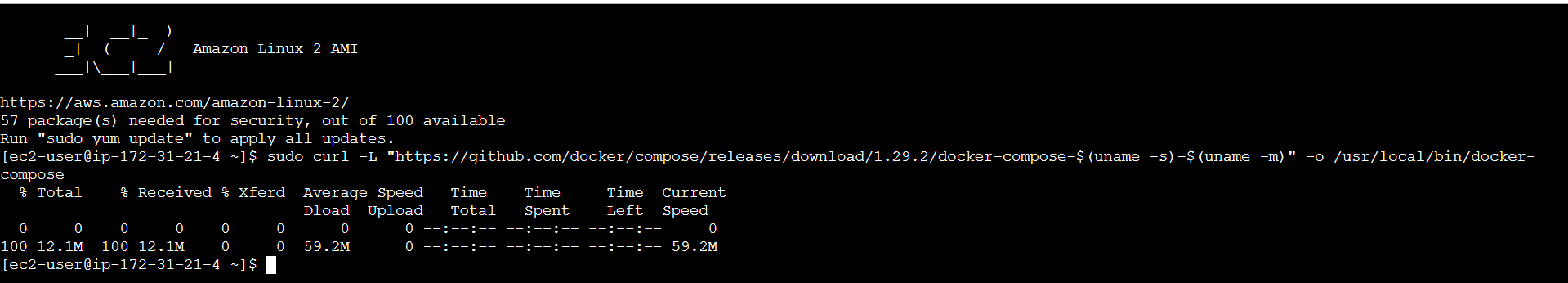
STEP 3: Complete Docker Compose Setup.
mkdir real-time-data-pipeline
cd real-time-data-pipeline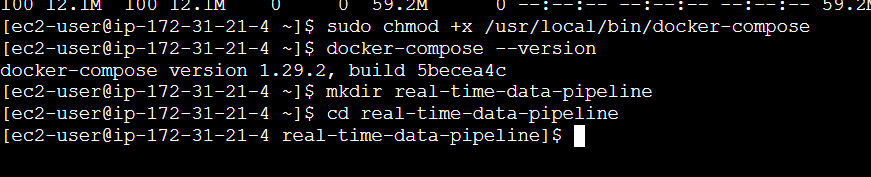
STEP 4: Create a file.
nano docker-compose.ymlversion: '3.8'
services:
zookeeper:
image: wurstmeister/zookeeper:3.4.6
ports:
- "2181:2181"
kafka:
image: wurstmeister/kafka:2.13-2.7.0
ports:
- "9092:9092"
environment:
KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS: INSIDE://kafka:9092,OUTSIDE://localhost:9092
KAFKA_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP: INSIDE:PLAINTEXT,OUTSIDE:PLAINTEXT
KAFKA_LISTENERS: INSIDE://0.0.0.0:9092,OUTSIDE://0.0.0.0:9092
KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper:2181
depends_on:
- zookeeper
producer:
build: ./producer
depends_on:
- kafka
consumer:
build: ./consumer
depends_on:
- kafka
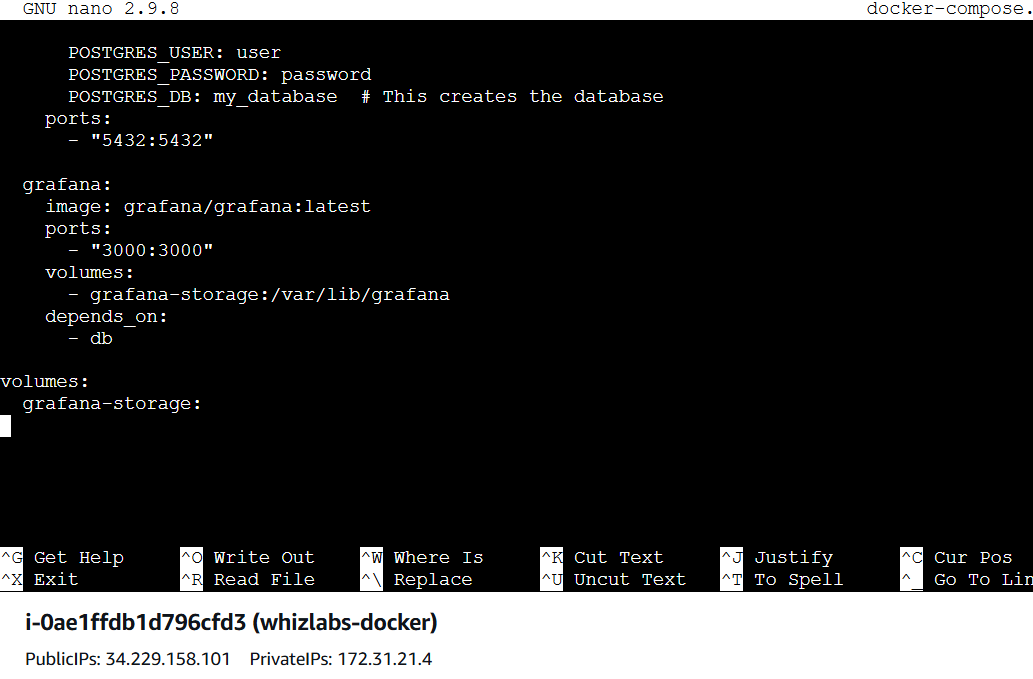
db:
image: postgres:13
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: user
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: password
POSTGRES_DB: my_database # This creates the database
ports:
- "5432:5432"
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:latest
ports:
- "3000:3000"
volumes:
- grafana-storage:/var/lib/grafana
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
grafana-storage:
STEP 5: Create Producer and Consumer Services,
mkdir producer
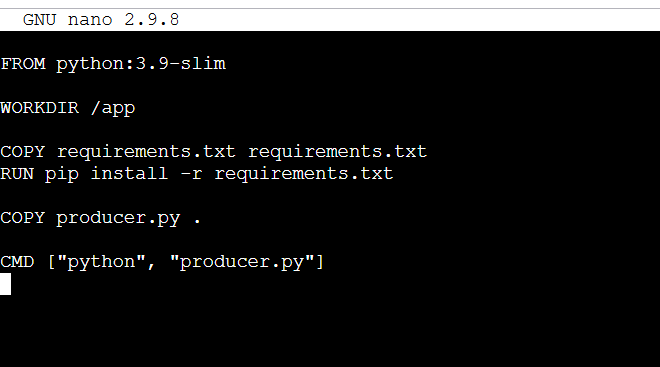
nano producer/DockerfileFROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY producer.py .
CMD ["python", "producer.py"]
STEP 6: create producer requirements.txt file.
nano producer/requirements.txtkafka-python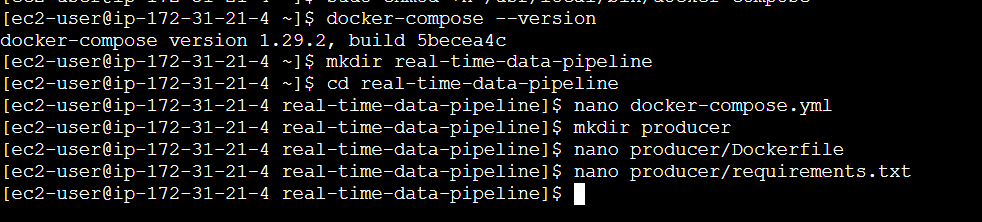

STEP 7: Create the producer.py file.
nano producer/producer.pyfrom kafka import KafkaProducer
import time
import random
import json
producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers='kafka:9092',
value_serializer=lambda v: json.dumps(v).encode('utf-8')
)
while True:
data = {
'sensor_id': random.randint(1, 100),
'temperature': random.uniform(20.0, 30.0)
}
producer.send('sensor_data', data)
print(f'Sent: {data}')
time.sleep(2)
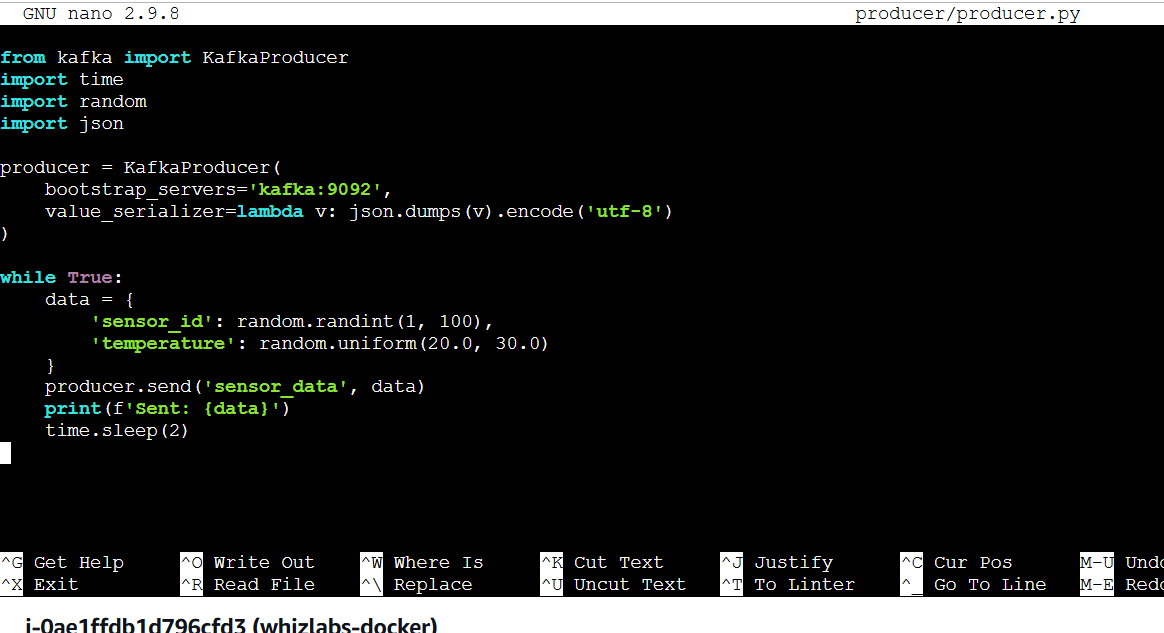
STEP 8: Create a file enter the following command and save the file.
mkdir consumer
nano consumer/DockerfileFROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY consumer.py .
CMD ["python", "consumer.py"]
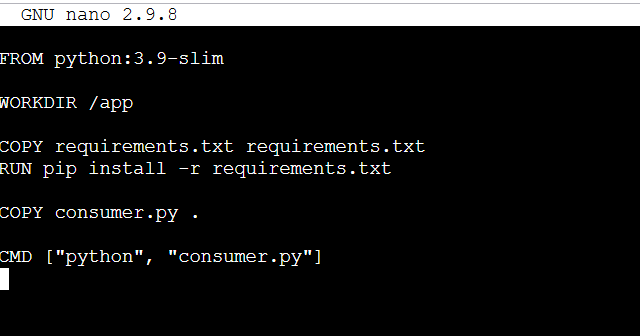
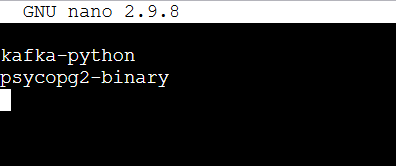
STEP 9: Create consumer requirements.txt file.
nano consumer/requirements.txtkafka-python
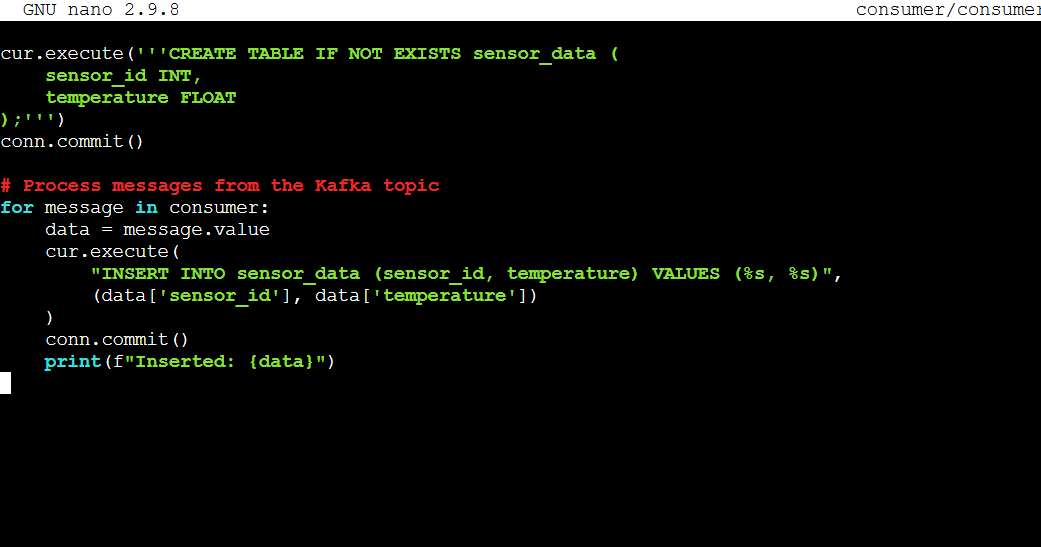
psycopg2-binarynano consumer/consumer.pyfrom kafka import KafkaConsumer
import psycopg2
import json
# Set up the Kafka consumer to listen to the 'sensor_data' topic
consumer = KafkaConsumer(
'sensor_data',
bootstrap_servers='kafka:9092',
value_deserializer=lambda v: json.loads(v)
)
# Establish a connection to the PostgreSQL database
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="postgres",
user="user",
password="password",
host="db"
)
cur = conn.cursor()
# Create the table for storing sensor data if it doesn't exist
cur.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sensor_data (
sensor_id INT,
temperature FLOAT
);''')
conn.commit()
# Process messages from the Kafka topic
for message in consumer:
data = message.value
cur.execute(
"INSERT INTO sensor_data (sensor_id, temperature) VALUES (%s, %s)",
(data['sensor_id'], data['temperature'])
)
conn.commit()
print(f"Inserted: {data}")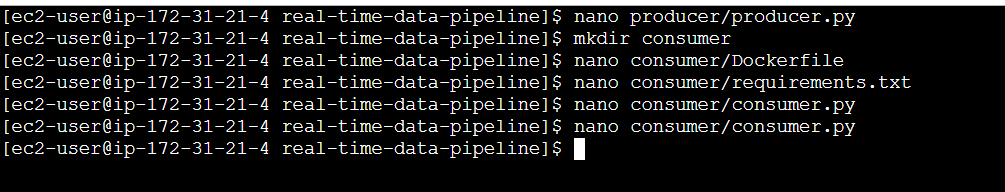
STEP 12: Install PostgreSQL 13 on Amazon Linux 2.
sudo yum update -y
sudo amazon-linux-extras install -y postgresql13
sudo yum install -y postgresql13 postgresql13-server
psql --version
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
docker-compose up -d


STEP 13: Access PostgreSQL Container.
docker ps
docker exec -it <container_id> /bin/bash
psql -U user -d my_database
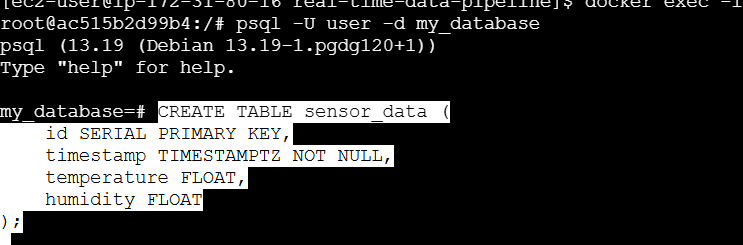
Create a Table inside the Database:
CREATE TABLE sensor_data (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
timestamp TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
temperature FLOAT,
humidity FLOAT
);
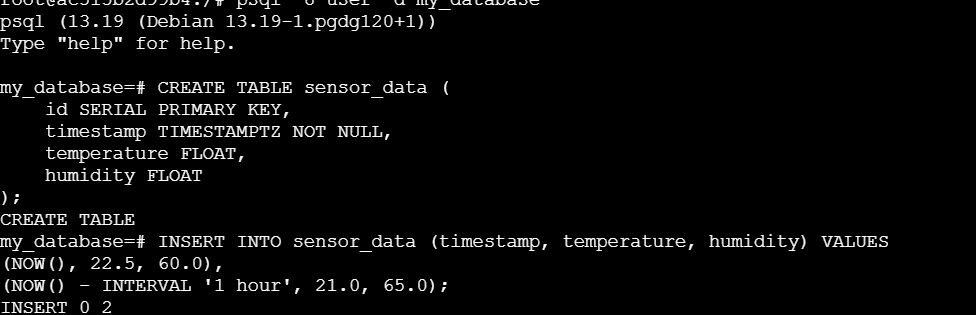
Insert Sample Data to the table:
INSERT INTO sensor_data (timestamp, temperature, humidity) VALUES
(NOW(), 22.5, 60.0),
(NOW() - INTERVAL '1 hour', 21.0, 65.0);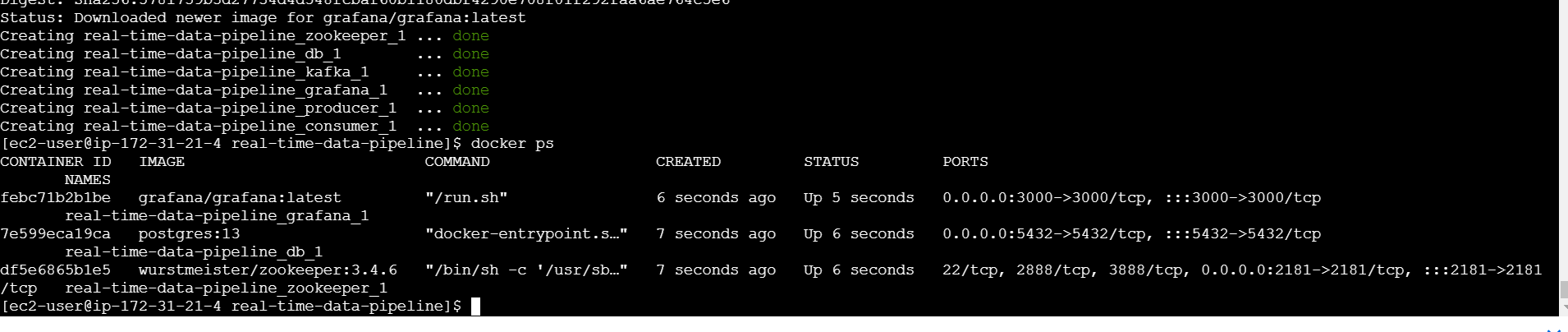

STEP 14: Configure Grafana to connect to this database.
- Enter your browser http://<EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:3000
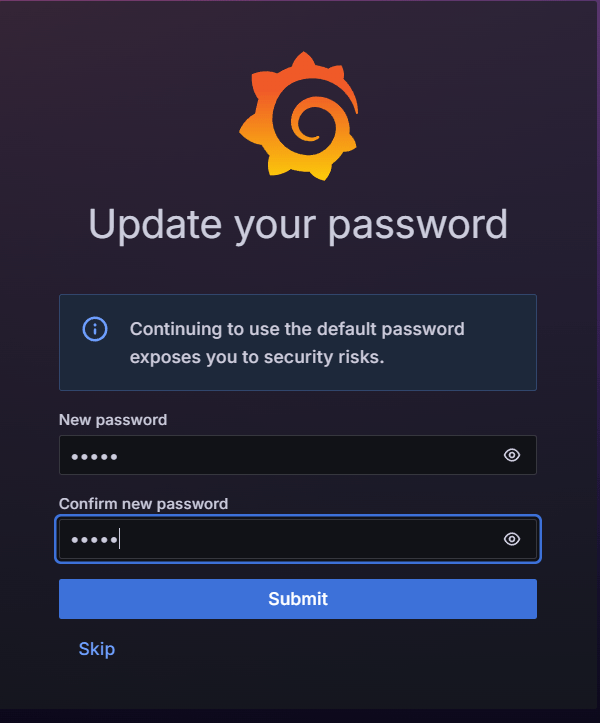
STEP 15: Set a username & password.
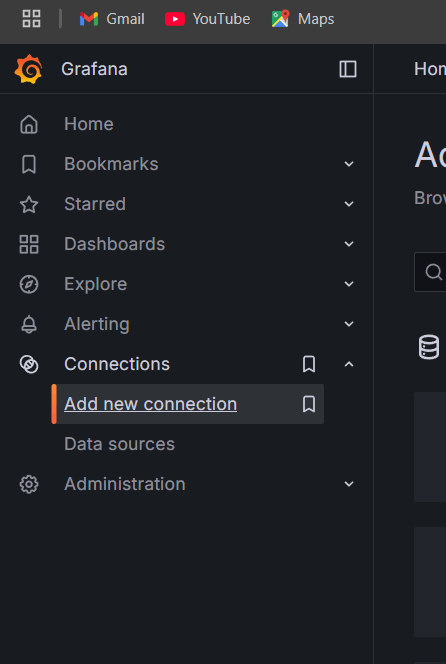
STEP 16: Select connection and click on new connection.
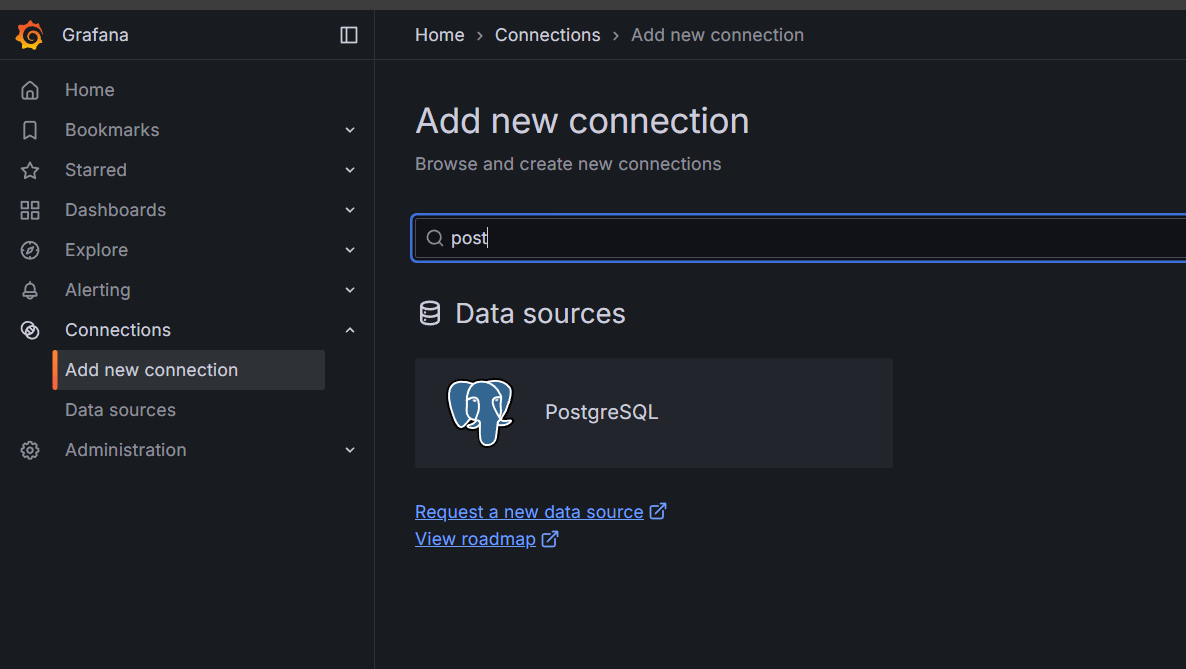
STEP 17: Search for postgresql and select postgreSQL.
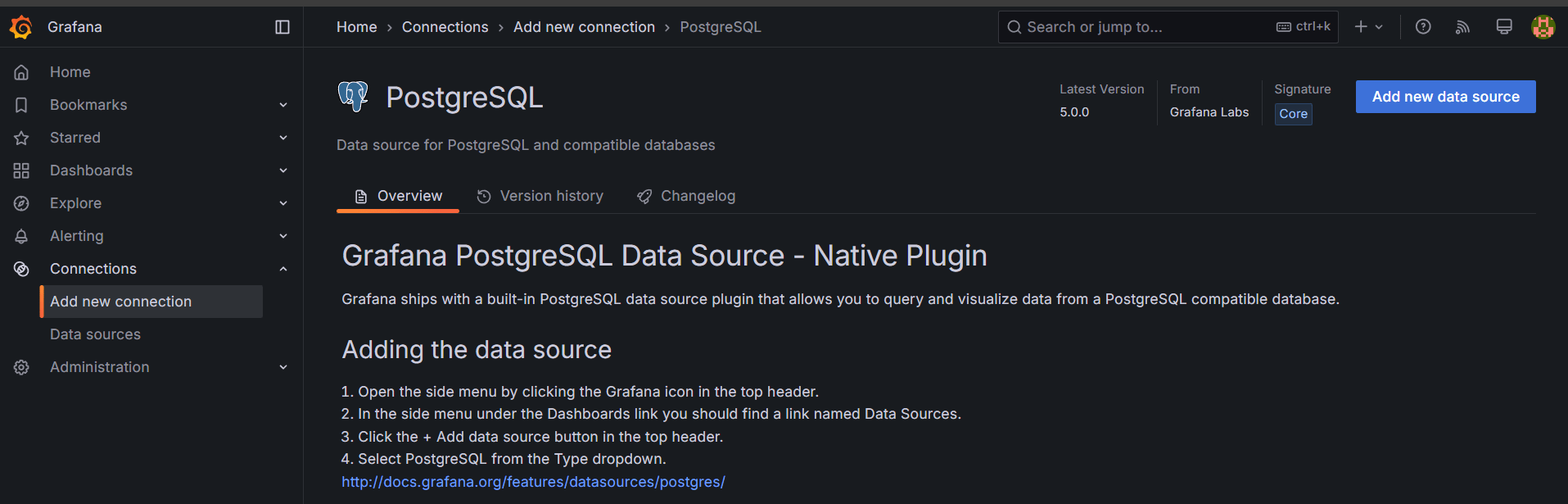
STEP 18: Click on add new data source.
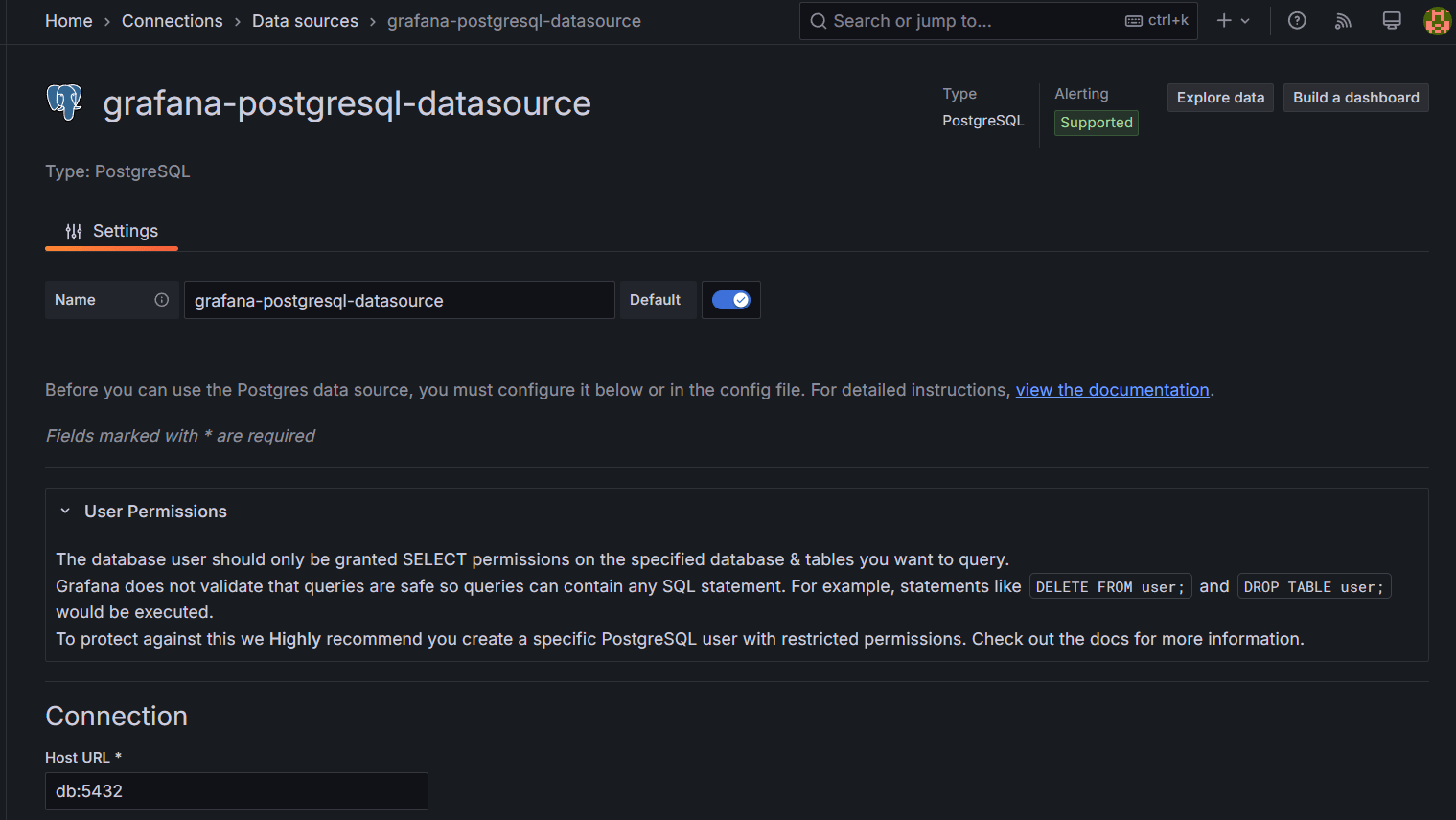
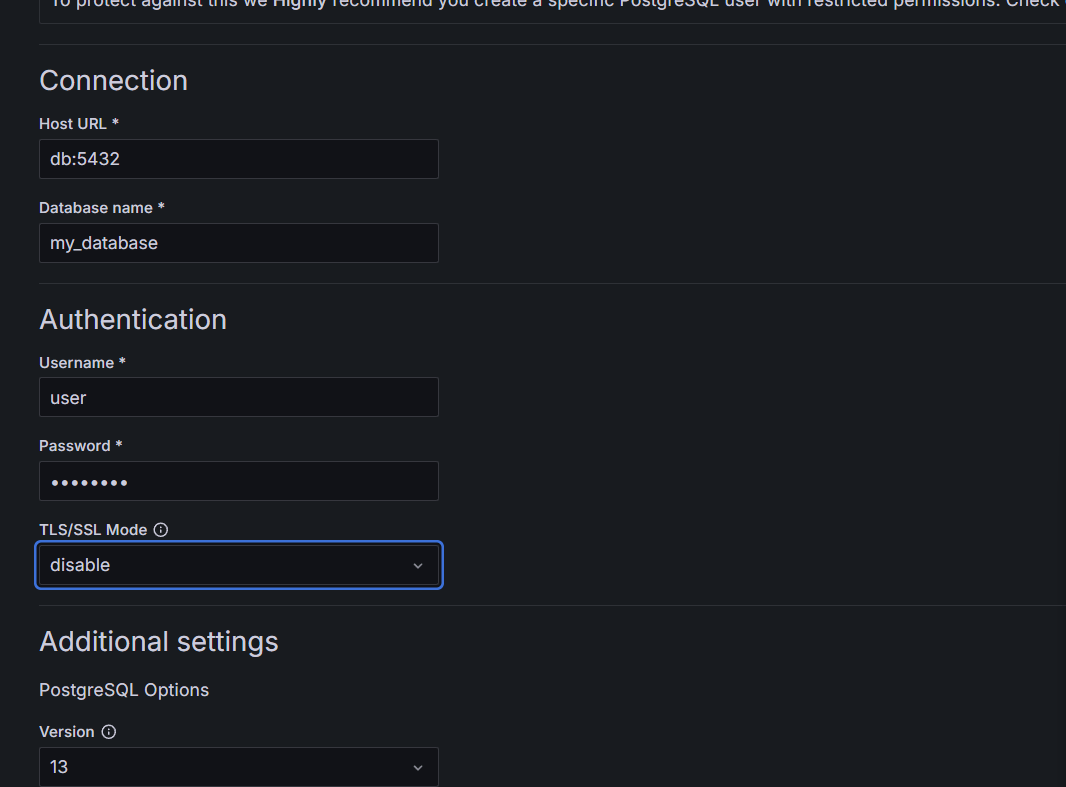
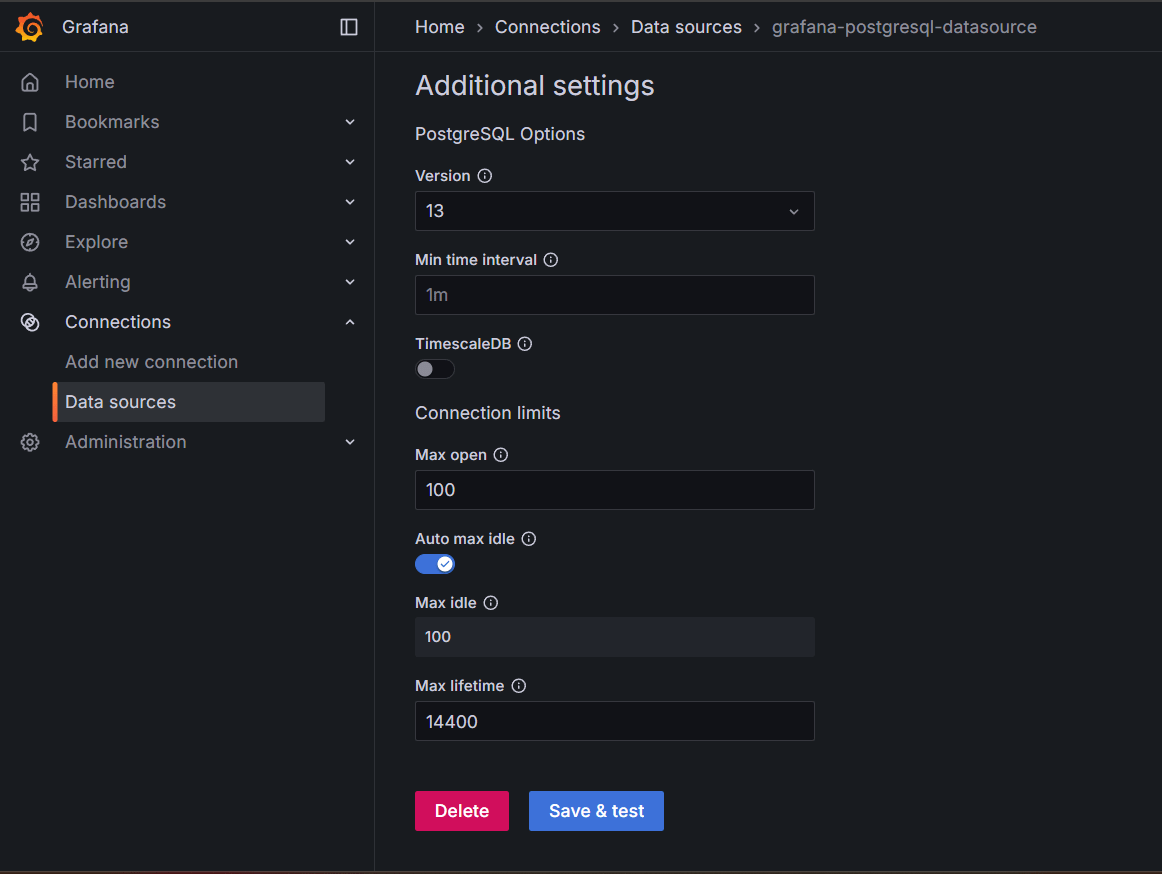
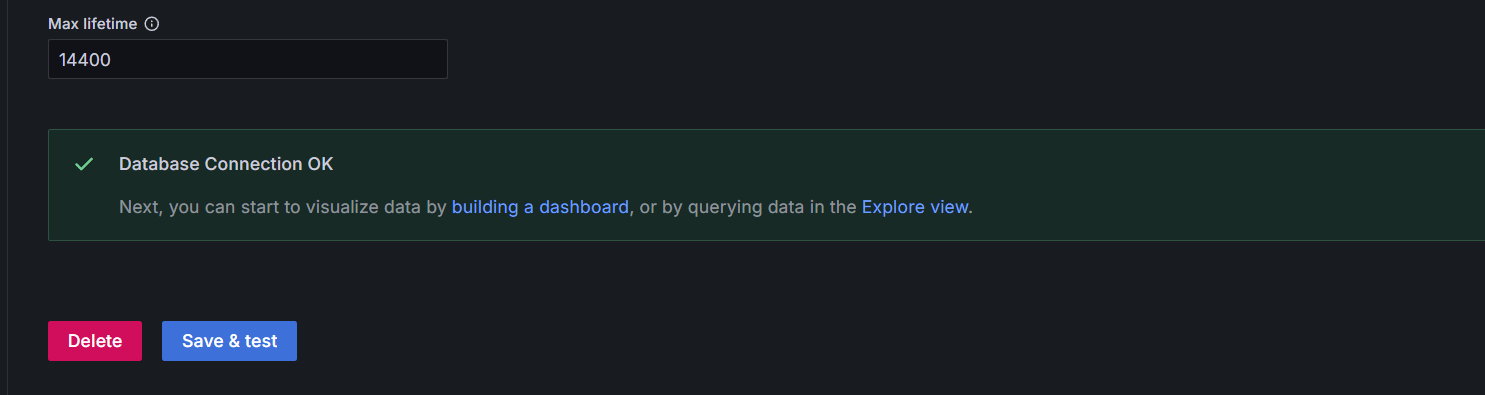
STEP 19: Enter Host URL and Database name Enter Username as “user” and Password as “password”, select TLS/SSL Mode as “Disable”.
- Save & test.
STEP 20: Create Grafana Dashboards.
- 1. Click on + icon on the top left corner and then select New dashboard.
- Select Add vizualization.
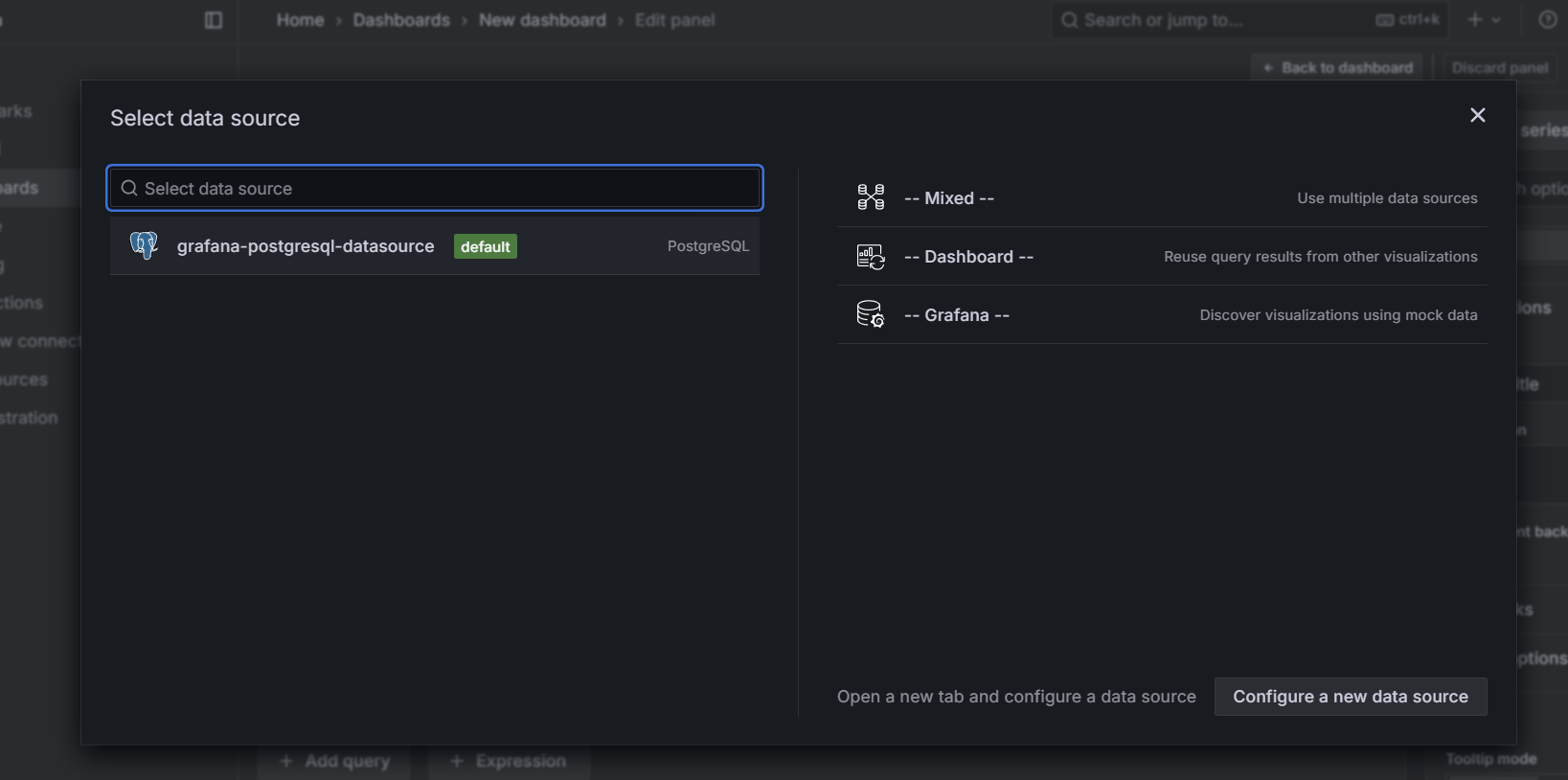
STEP 21: Select data source as PostgreSQL.
STEP 22: Enter the code and title.
SELECT
timestamp AS "time",
temperature,
humidity
FROM
sensor_data
ORDER BY
timestamp DESC
LIMIT 10;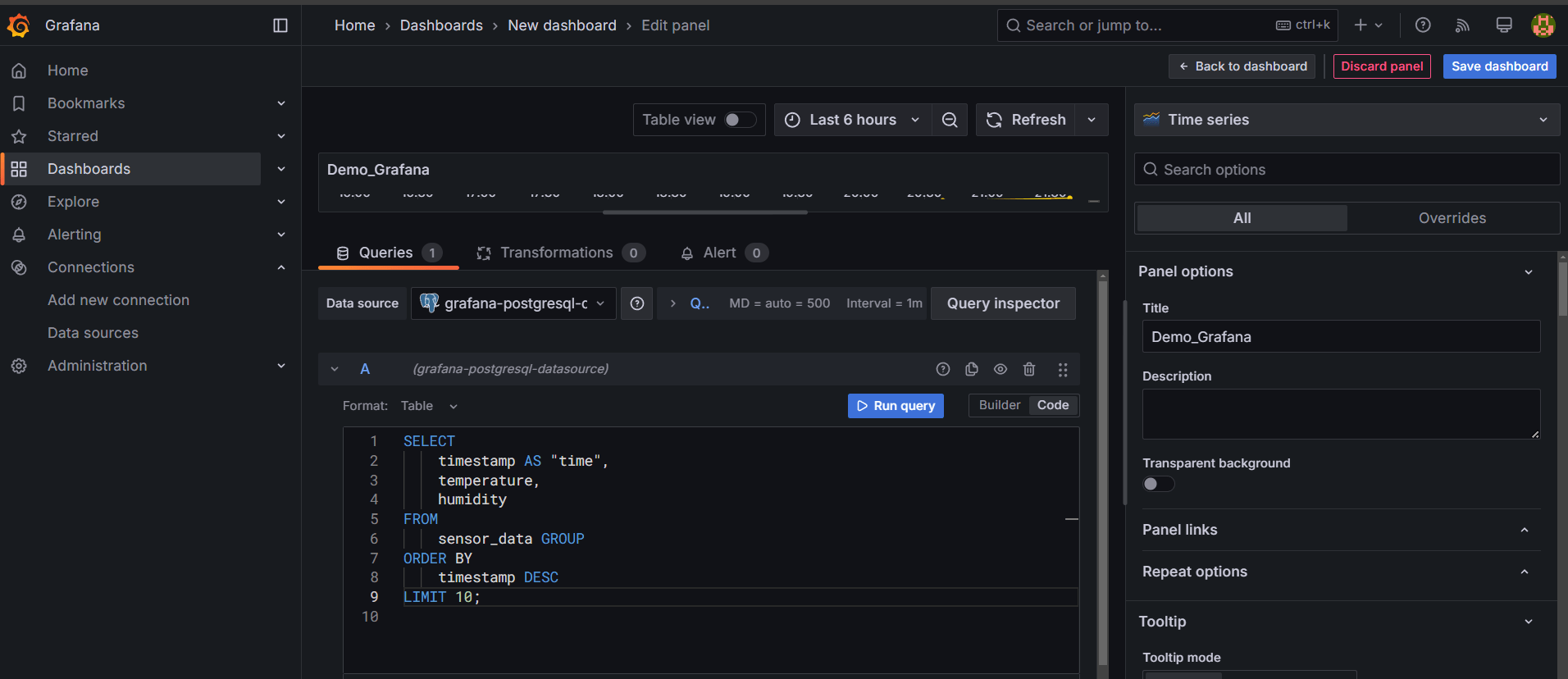
STEP 23: You will see the Dashboard.
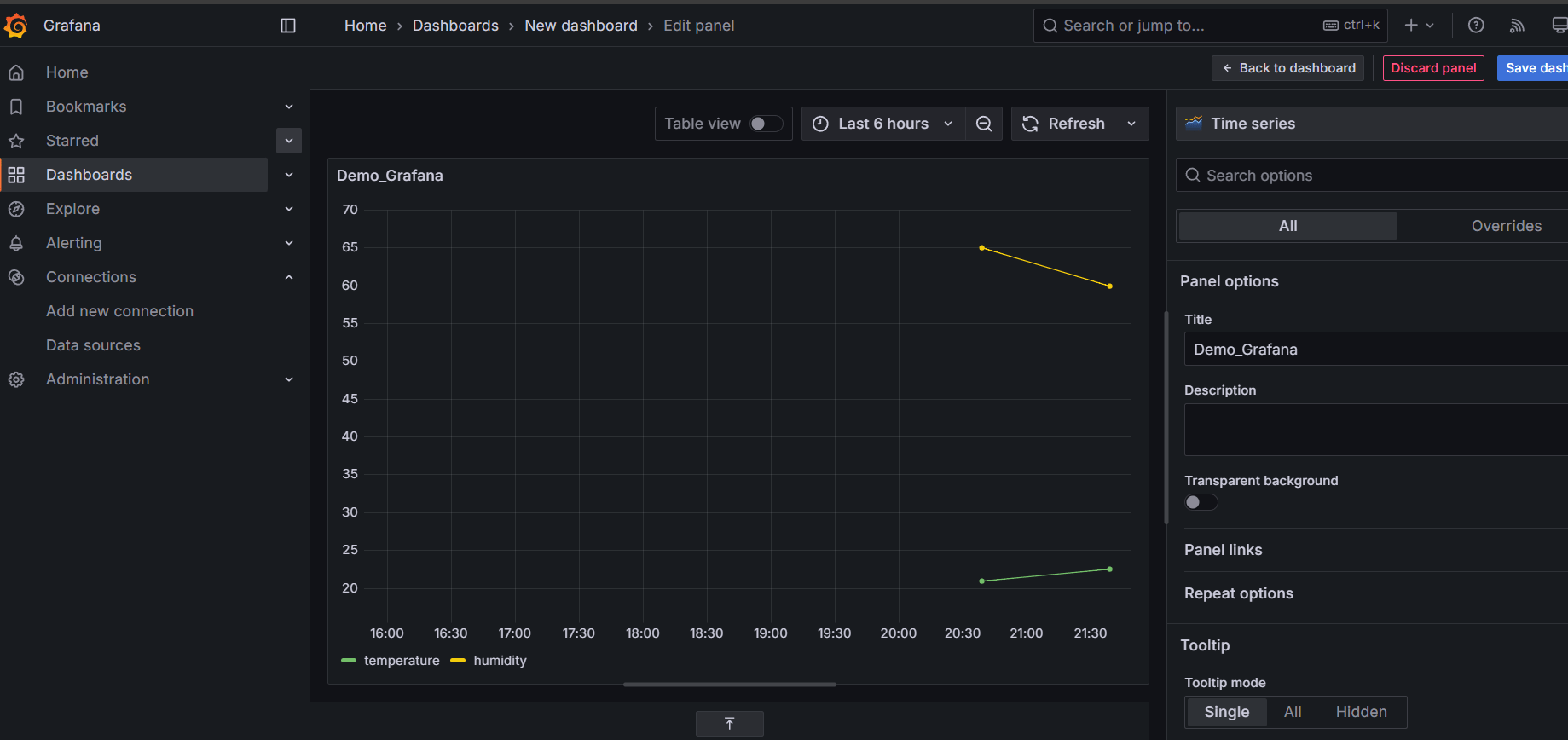

Conclusion.
In conclusion, Docker offers a powerful and efficient way to build and scale real-time data pipelines. By leveraging its containerization capabilities, developers can create isolated, consistent environments for each component, making it easier to manage complex data workflows. Docker’s flexibility and scalability are key when handling large volumes of streaming data, ensuring high performance and reliability.
As we’ve seen, Docker simplifies the deployment of real-time data processing tools, streamlining integration and reducing potential issues related to compatibility and resource management. With the right strategies and best practices in place, Docker can significantly enhance the efficiency of your data pipeline, allowing you to process and analyze data faster than ever before.
Whether you’re building an analytics platform or working with continuous data streams, Docker can empower you to scale your operations smoothly. Embracing containerized environments is a smart step towards optimizing your real-time data pipelines, improving performance, and ensuring seamless scalability as your data needs grow.
Installing JFrog Artifactory on Ubuntu: A Simple Guide.
Introduction.
JFrog Artifactory is a powerful, universal artifact repository manager that enables efficient management of software packages throughout the development lifecycle. It supports all major package formats, including Docker, Maven, Gradle, and more. Whether you’re working with a small team or a large enterprise, Artifactory enhances build automation, promotes best practices, and simplifies version control for software artifacts.
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through the process of installing JFrog Artifactory on an Ubuntu system. Whether you’re new to Artifactory or looking to set it up on a fresh Ubuntu server, this guide will cover everything you need to get started.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a fully functional Artifactory instance running on your machine, ready to manage your software artifacts. We’ll go over the prerequisites, installation steps, and post-installation configuration, ensuring you understand the process at each stage.

Let’s get started with the installation of JFrog Artifactory on Ubuntu and explore how it can benefit your DevOps pipeline. With its robust set of features and easy integration, Artifactory will quickly become an essential tool for your development workflow.
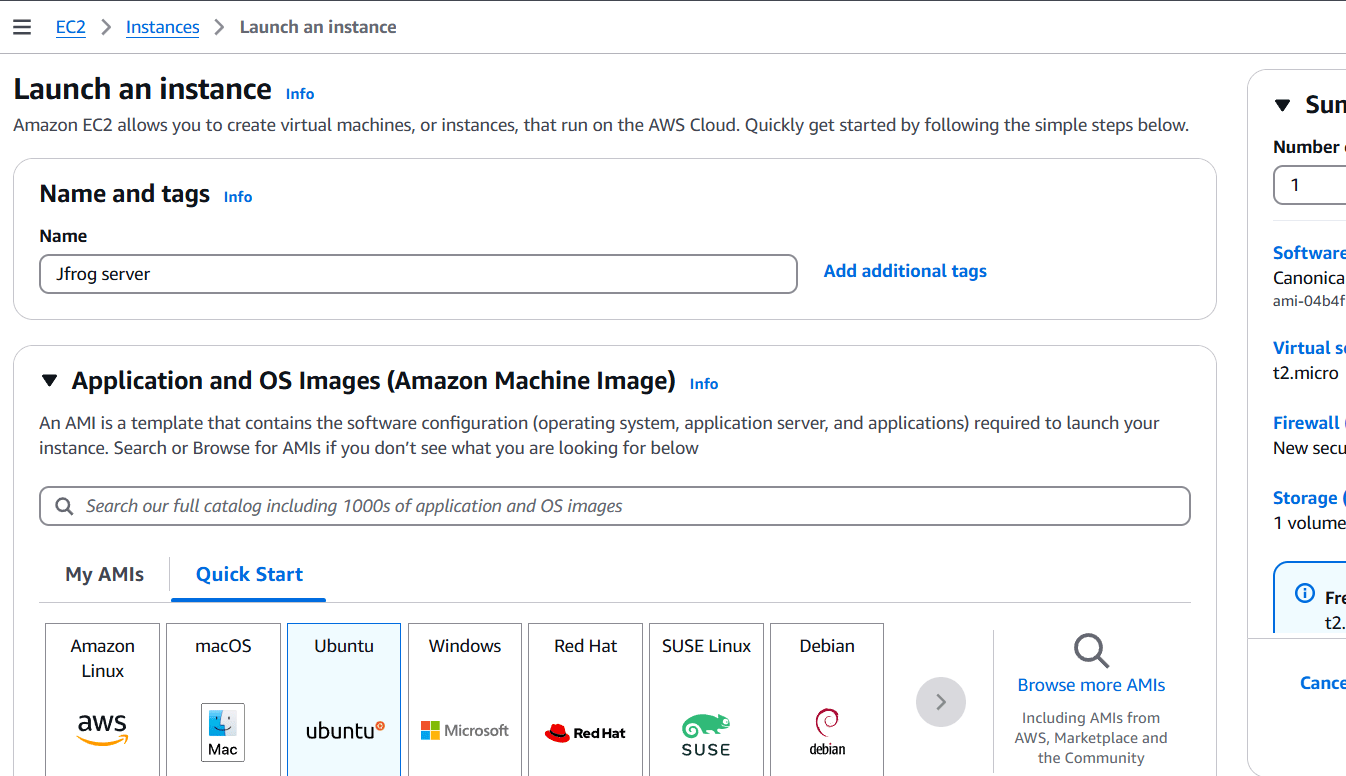
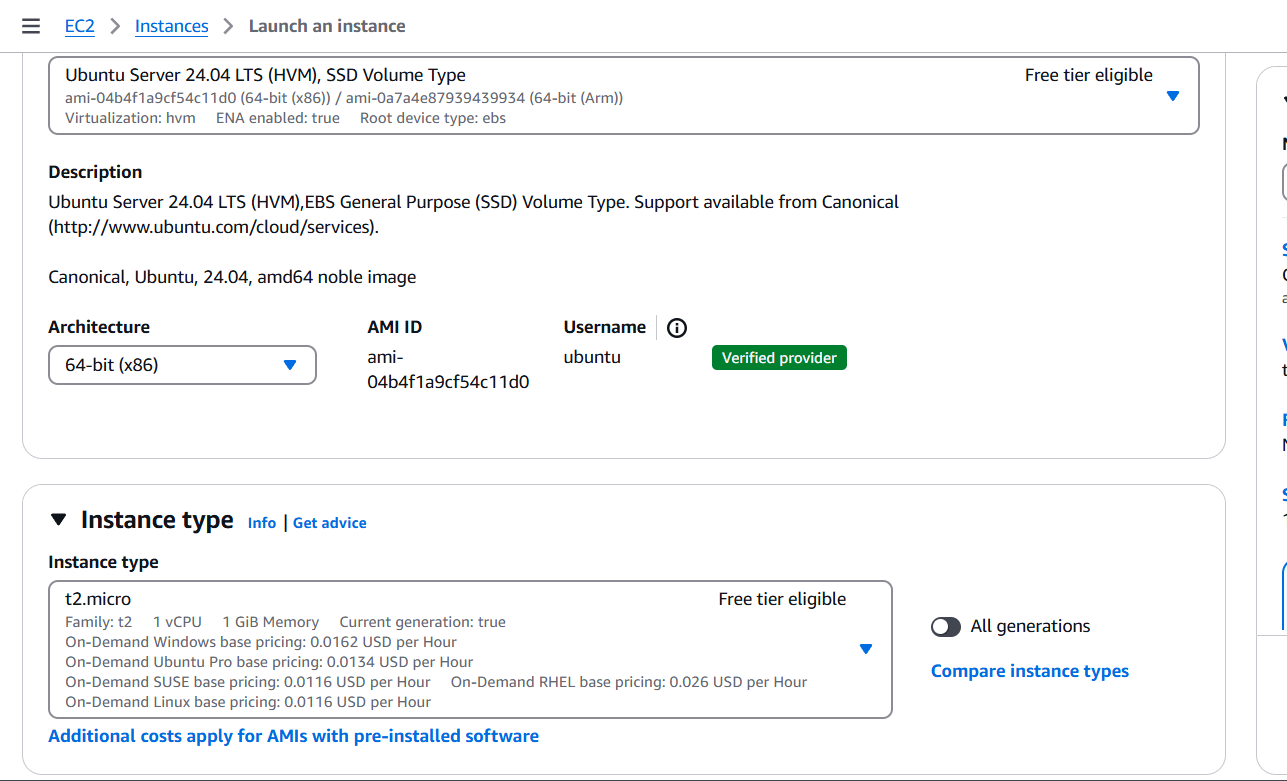
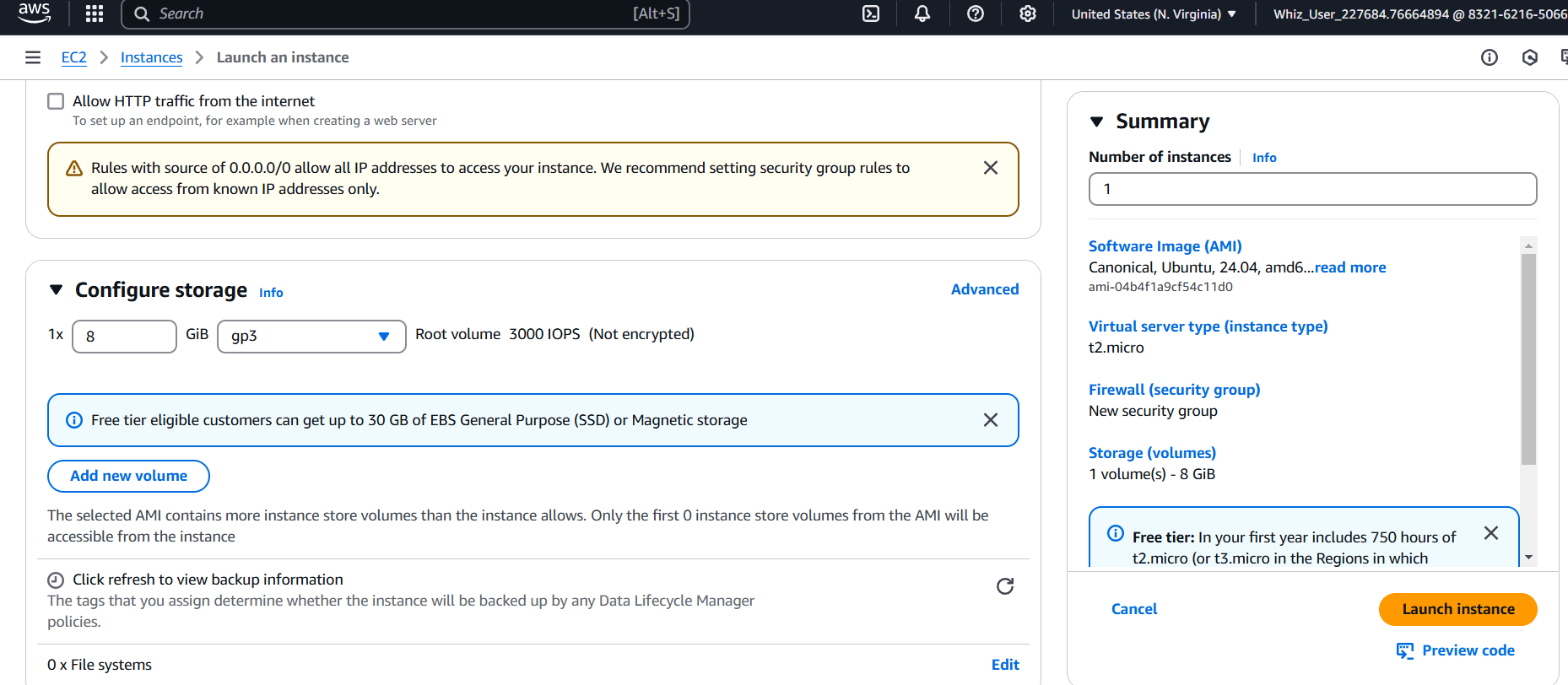
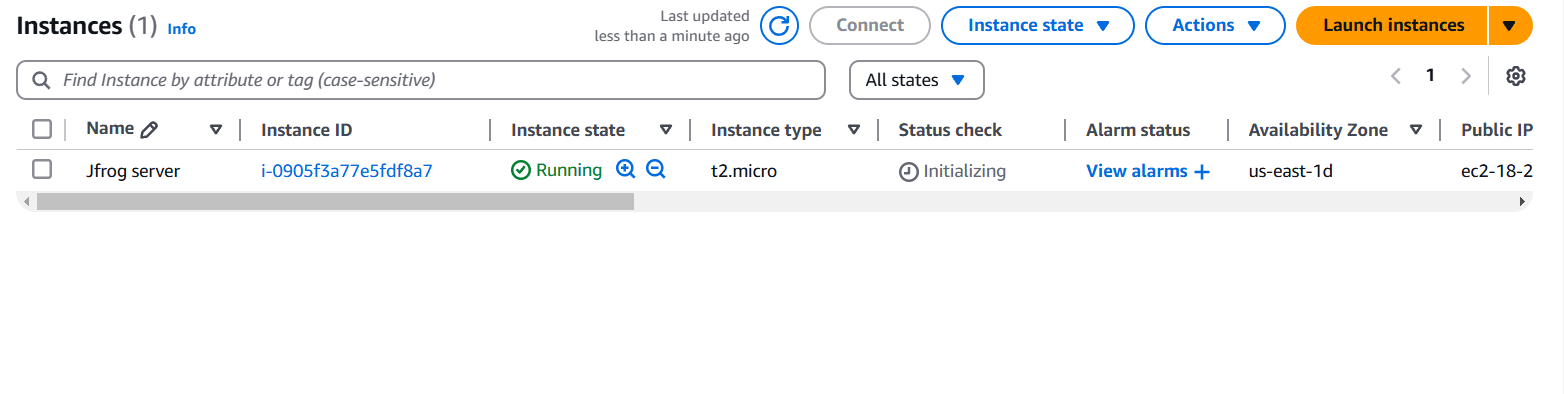
STEP 1: Create EC2 instance.
- Enter the name and AMI(Ubuntu).
- Select t2.micro.
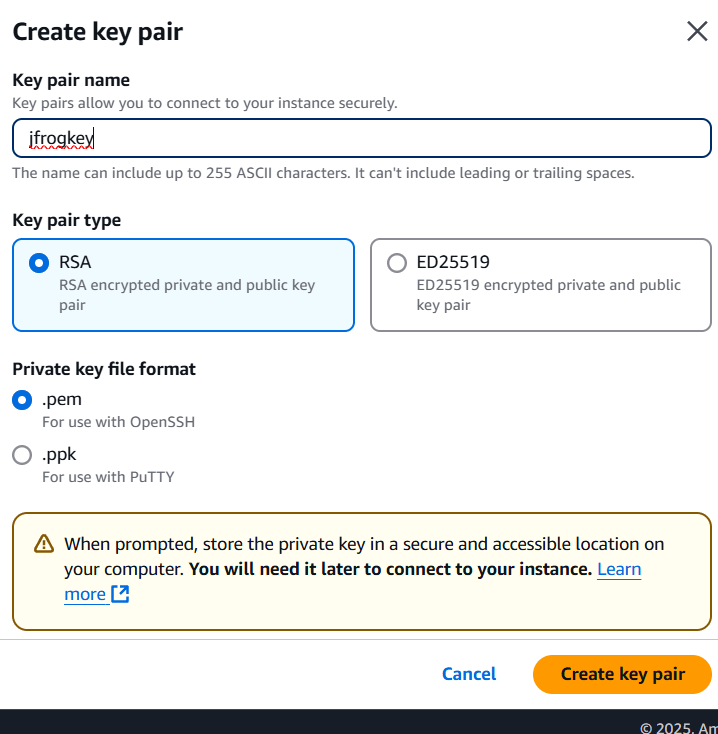
- Create keypair.
- Click on create keypair.
STEP 2: Accessing SSH Connection.
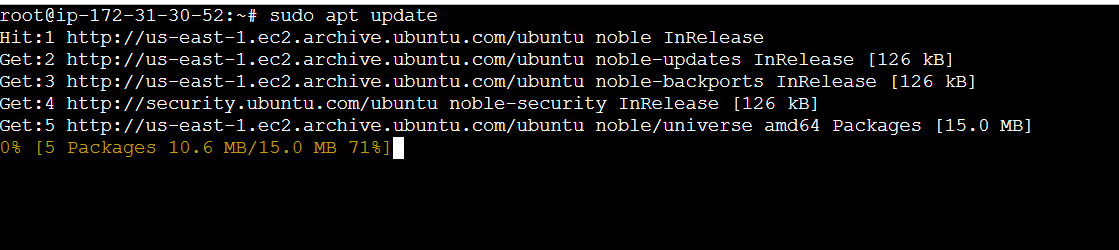
- Install Java JDK Using the following command.
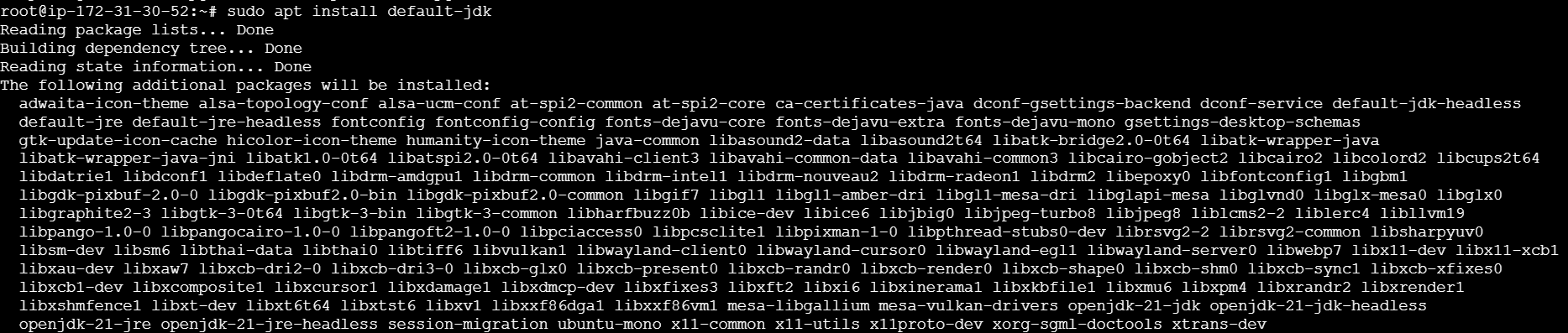
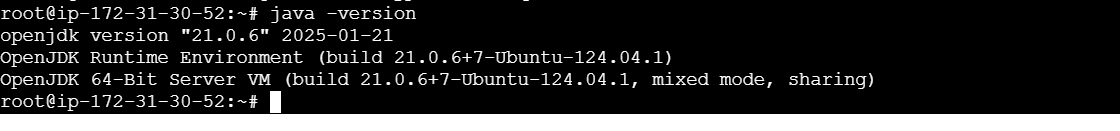
sudo apt update
sudo apt install default-jdk
javac -version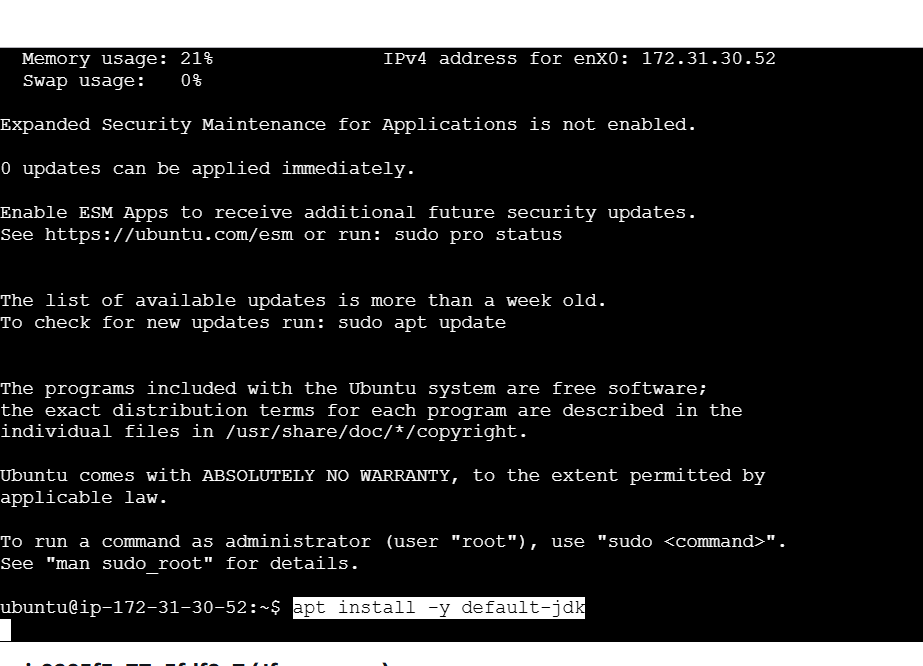
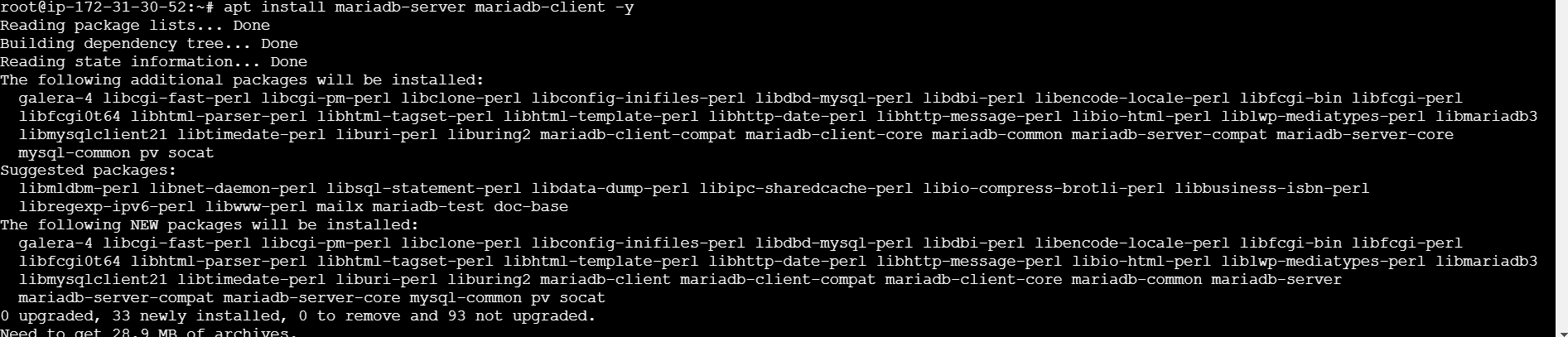
STEP 3: Install mariadb using following command.
curl -LsS https://downloads.mariadb.com/MariaDB/mariadb_repo_setup | bash -s --
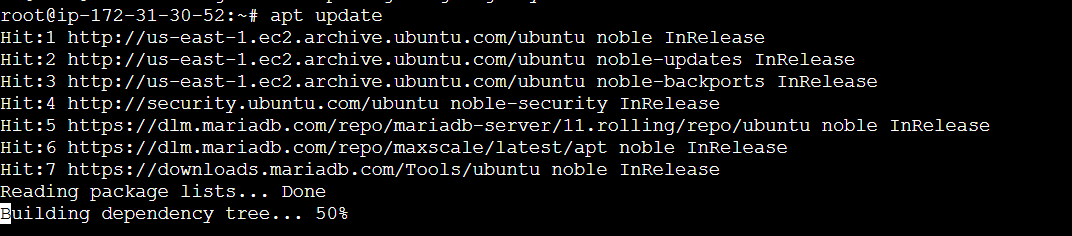
apt update
apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client -y
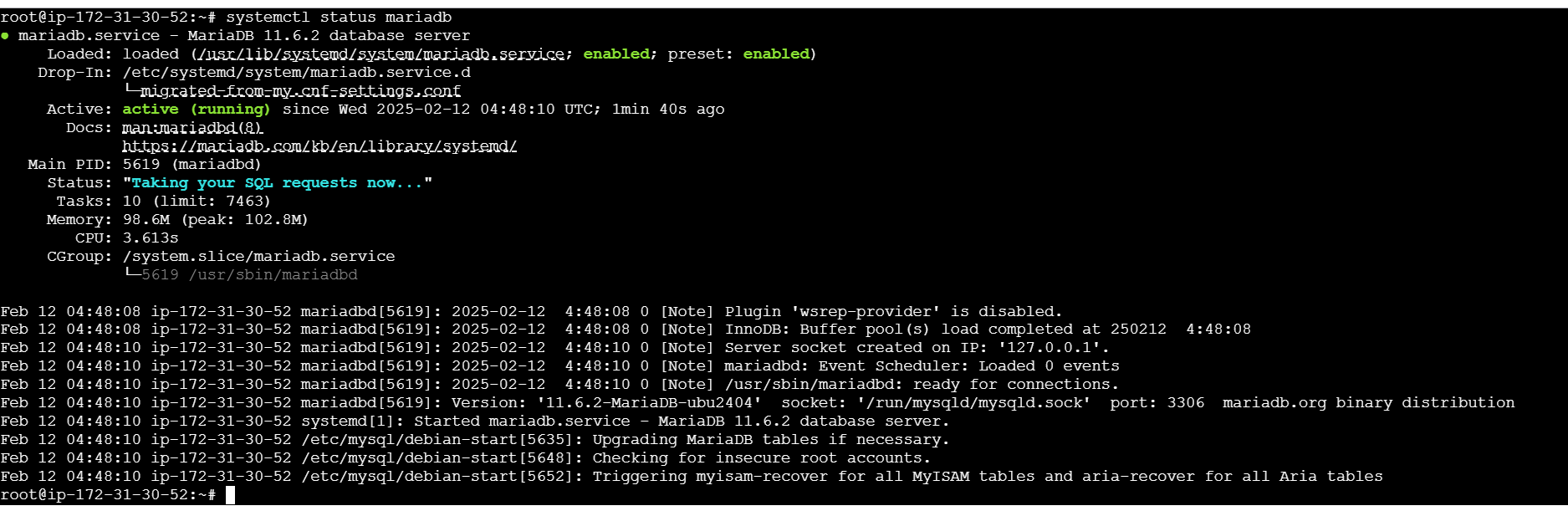
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb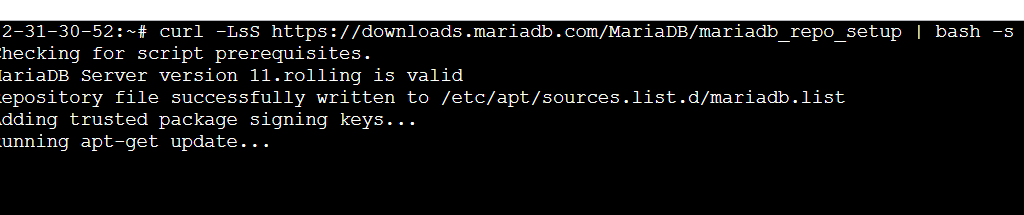

STEP 4: Install JFrog Artifactory.
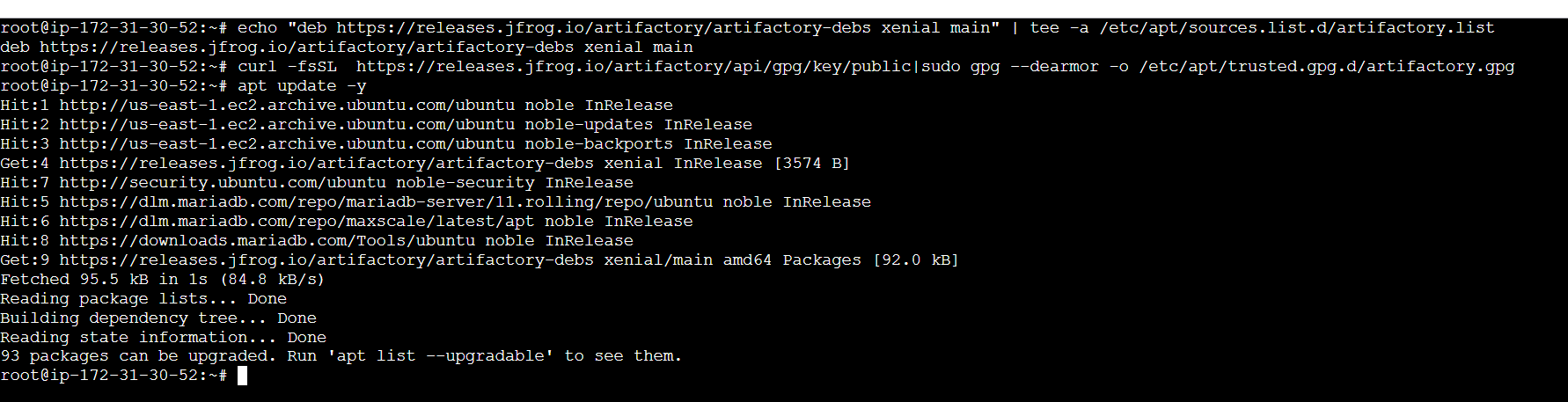
echo "deb https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/artifactory-debs xenial main" | tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/artifactory.list
curl -fsSL https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/api/gpg/key/public|sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/artifactory.gpg
apt update -y
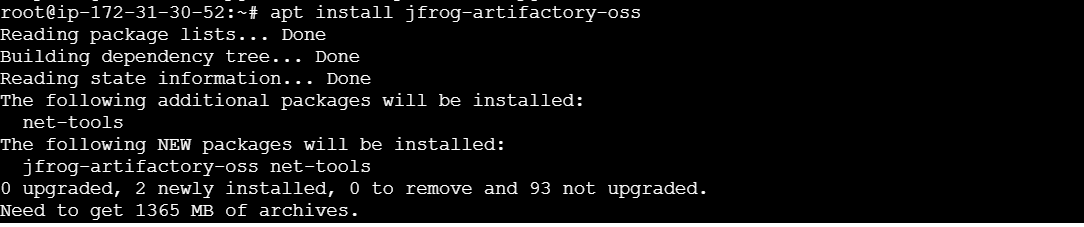
apt install jfrog-artifactory-oss
systemctl start artifactory.service
systemctl enable artifactory.service
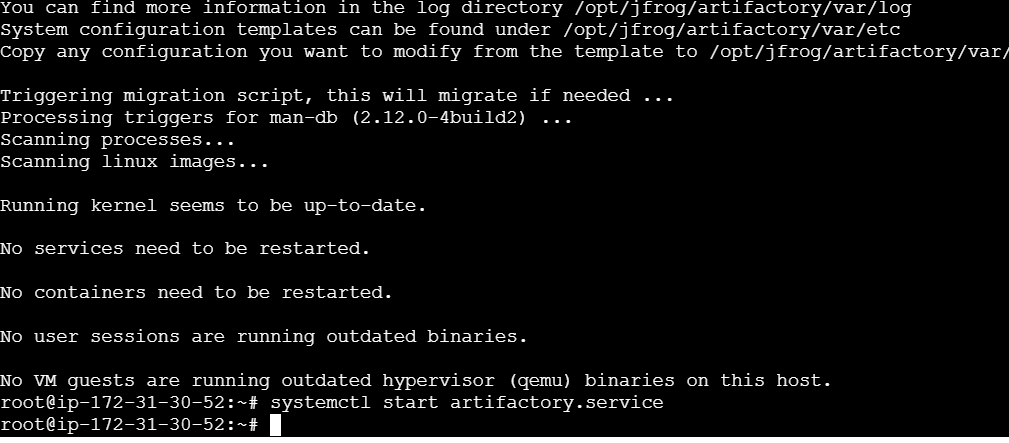
systemctl status artifactory.service 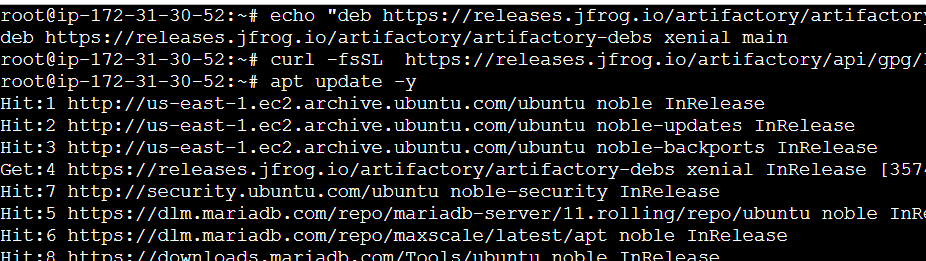
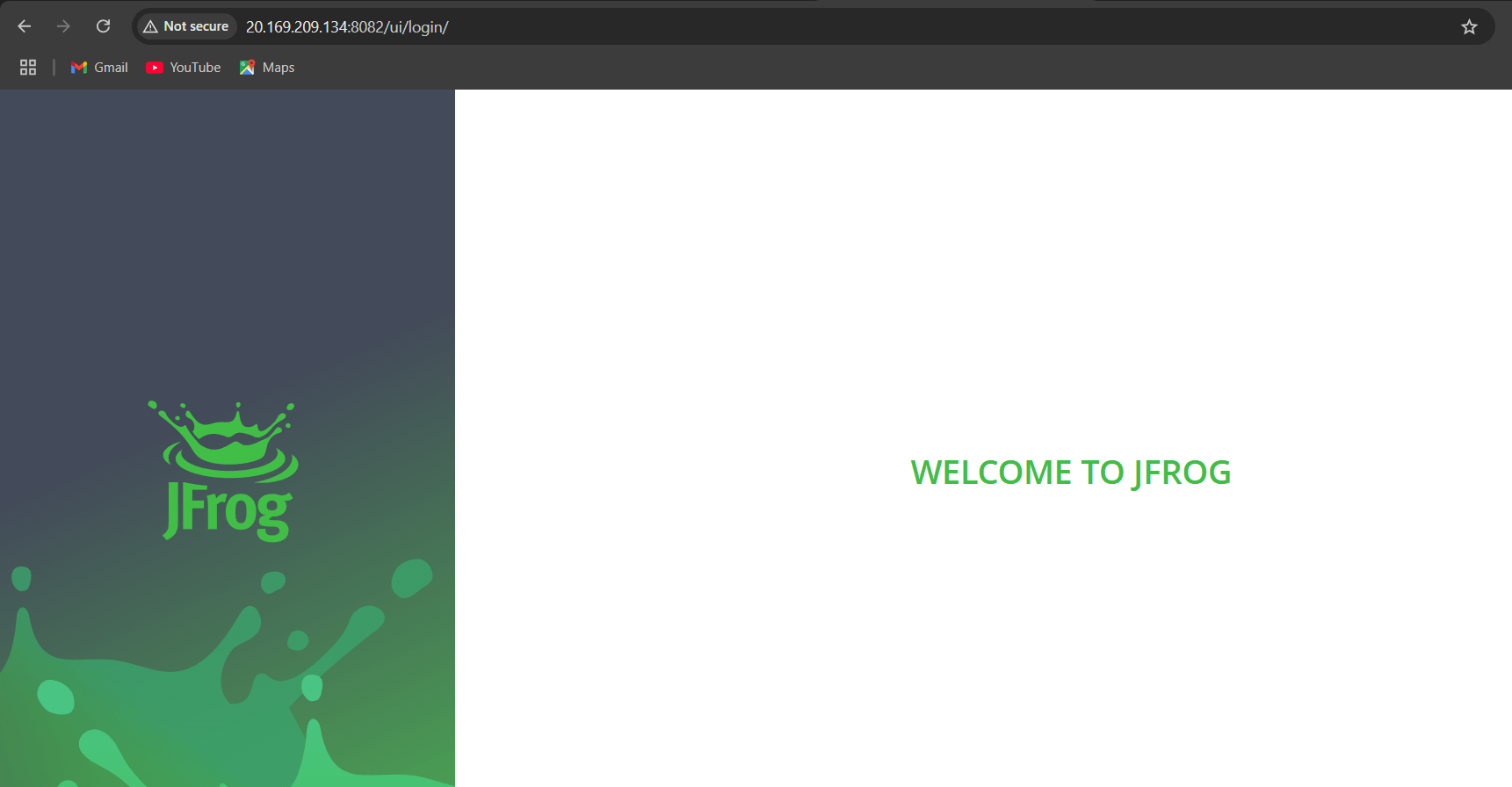
STEP 5: Copy your IP and paste in your browser with port like: http<Public IP>:9200.
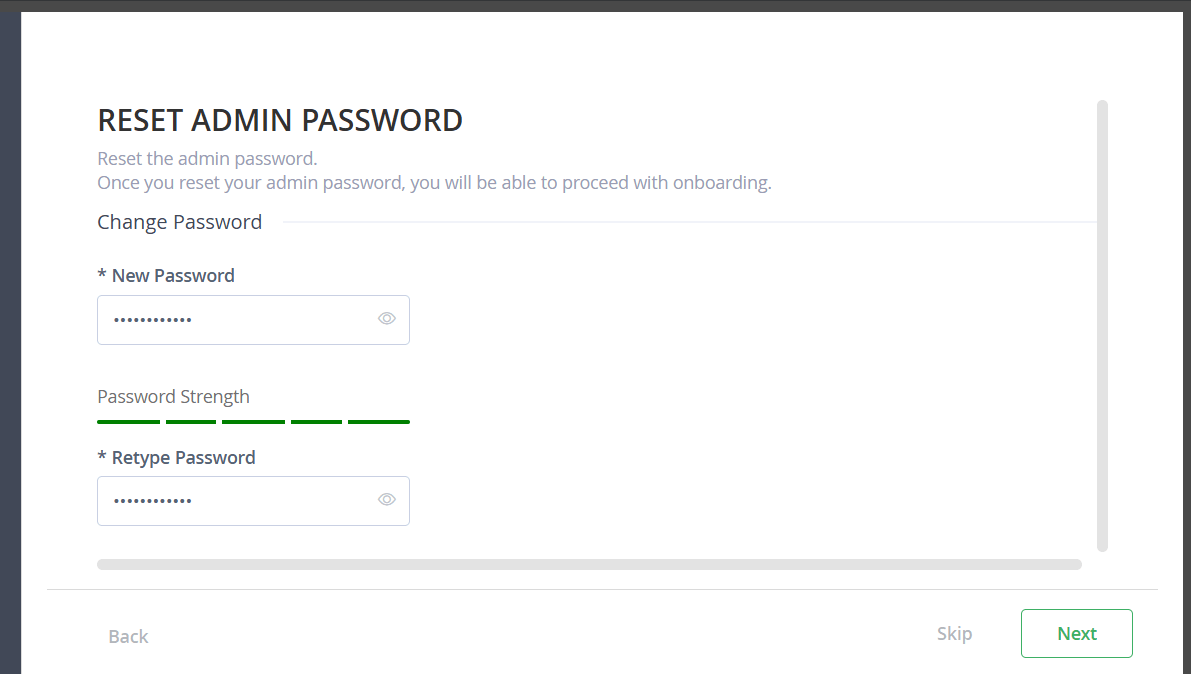
STEP 6: Click on get started and set the password.

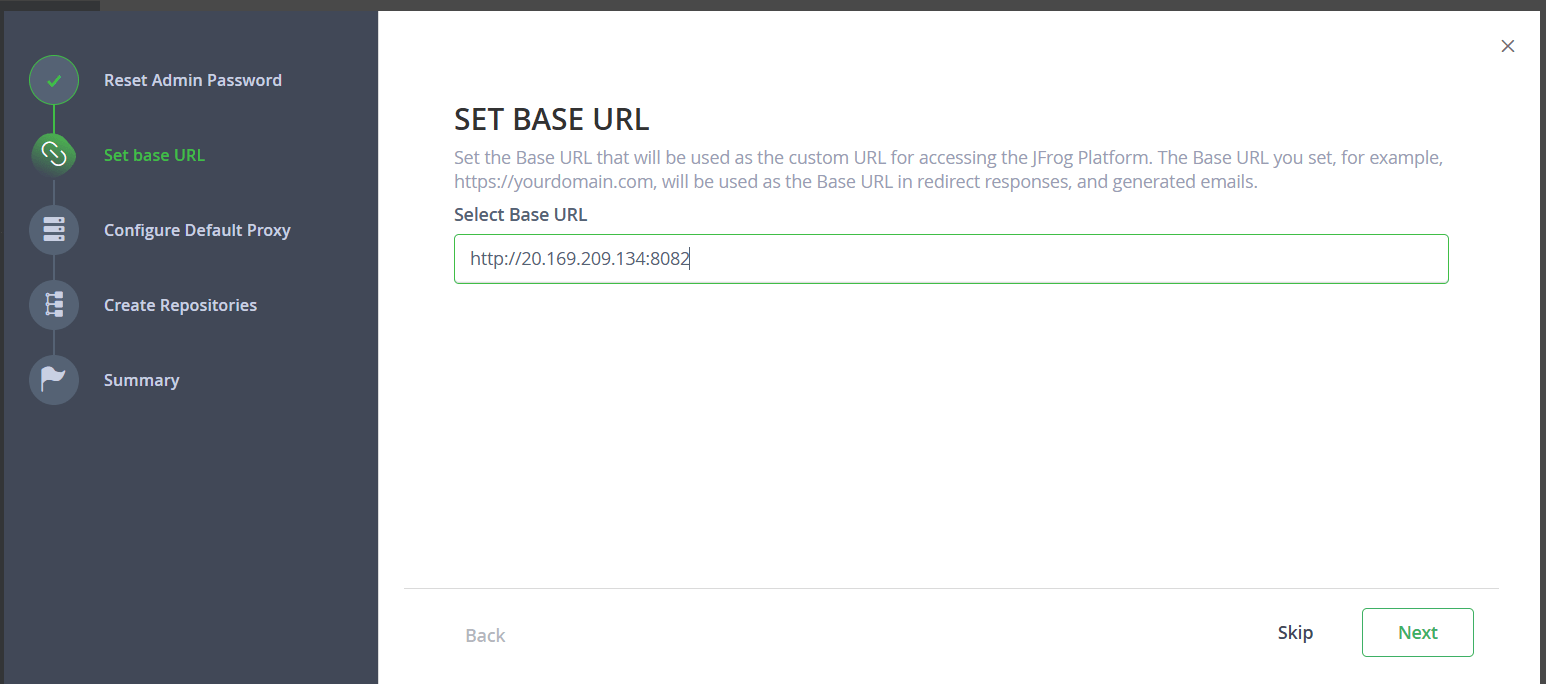

Conclusion.
In this guide, we’ve successfully walked through the steps to install JFrog Artifactory on an Ubuntu system. By setting up Artifactory, you’ve unlocked a powerful tool for managing your software artifacts and improving your development pipeline. With its support for various package formats and seamless integration with build tools, Artifactory helps streamline the process of storing, versioning, and distributing artifacts.
Now that you have Artifactory up and running, you can begin configuring repositories, managing dependencies, and optimizing your CI/CD workflows. As your projects scale, Artifactory will continue to be a vital resource for enhancing collaboration and ensuring consistency across your development and deployment environments.
With the basics covered in this tutorial, you’re ready to explore more advanced features, including security controls, remote repositories, and advanced integration options. JFrog Artifactory is designed to grow with your needs, providing an enterprise-grade solution for managing the artifacts that power your applications.
Feel free to experiment, explore the documentation, and fine-tune your setup to best fit your development process. Happy coding!
A Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Maven on Ubuntu.
Introduction.
Maven is a popular build automation and project management tool primarily used in Java-based software development. It simplifies the process of building, compiling, and managing dependencies in a project.
Here’s a breakdown of what Maven does:
- Build Automation: Maven automates the process of compiling code, running tests, packaging applications, and deploying them. This helps developers save time and avoid errors associated with manual processes.
- Dependency Management: One of Maven’s key features is its ability to handle dependencies. If your project depends on external libraries (like JAR files), Maven can automatically download and manage them from a central repository. It also keeps track of versioning and ensures compatibility.
- Project Structure: Maven promotes standardization by encouraging a consistent project directory structure. This makes it easier for developers to collaborate and maintain projects over time.
- Centralized Repositories: Maven uses a central repository (usually Maven Central) where commonly used libraries and tools are stored. Developers can access these repositories directly without manually downloading and configuring dependencies.
- Plugins: Maven supports numerous plugins that help extend its functionality, such as for code analysis, documentation generation, deployment, and more.
- Lifecycle Management: Maven follows a defined lifecycle with phases like “clean,” “validate,” “compile,” “test,” and “install.” Each phase has a specific task and ensures that the build process runs smoothly and consistently.

In short, Maven helps Java developers efficiently manage projects, dependencies, and build processes, making the development process more organized and scalable.
Method 1: Install Maven on Ubuntu with APT.
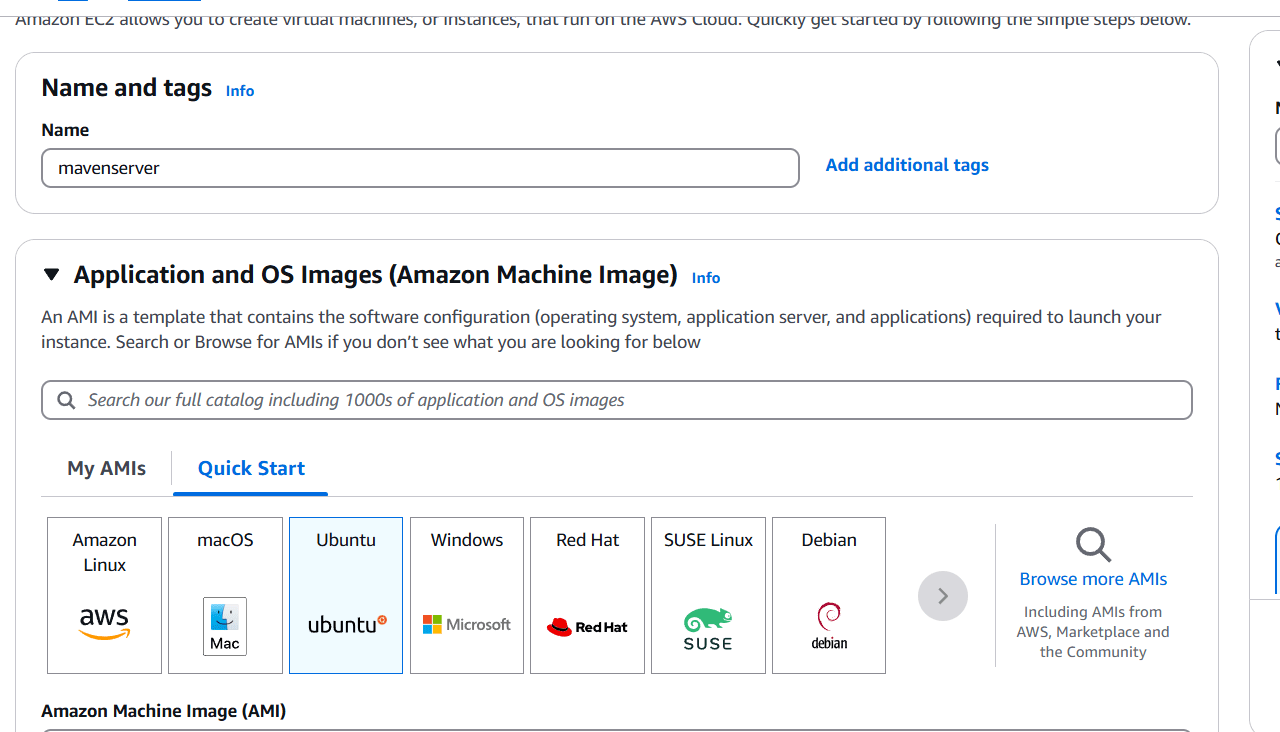
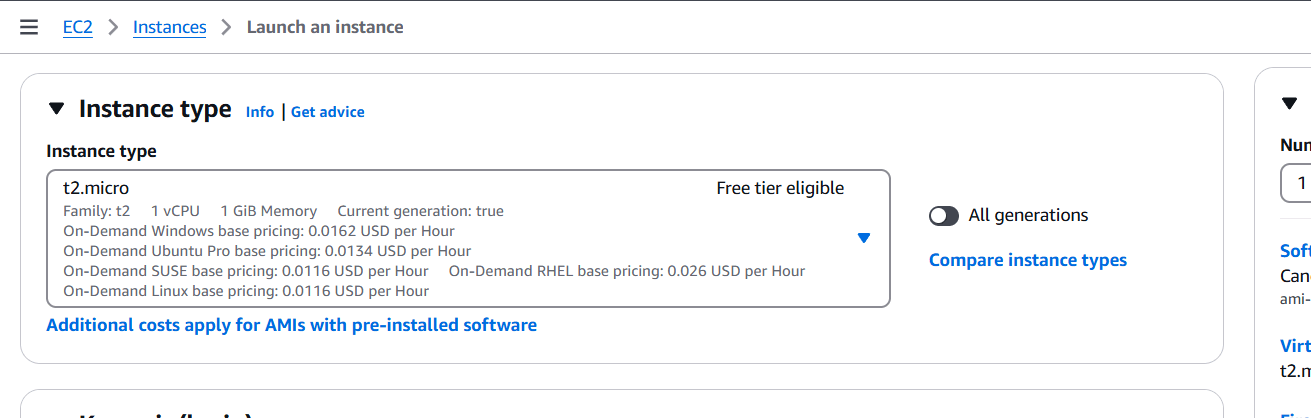
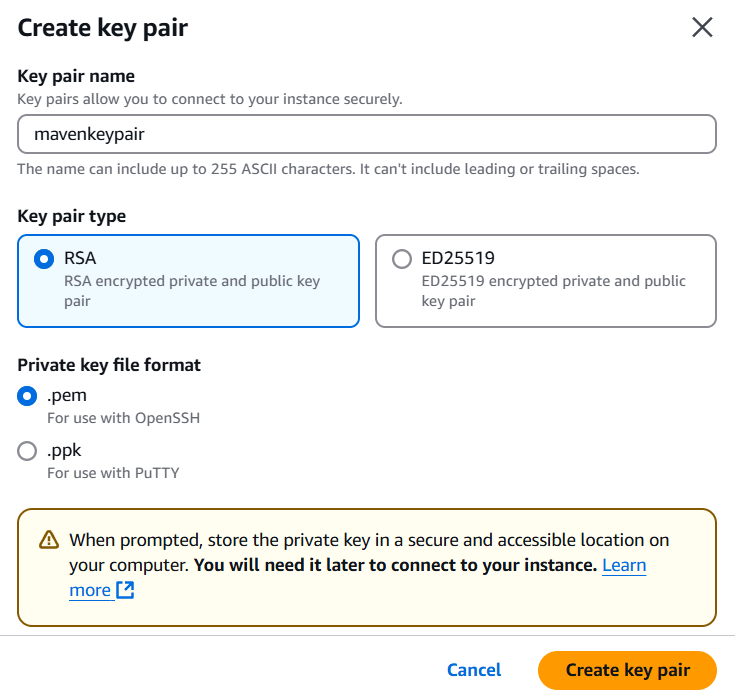
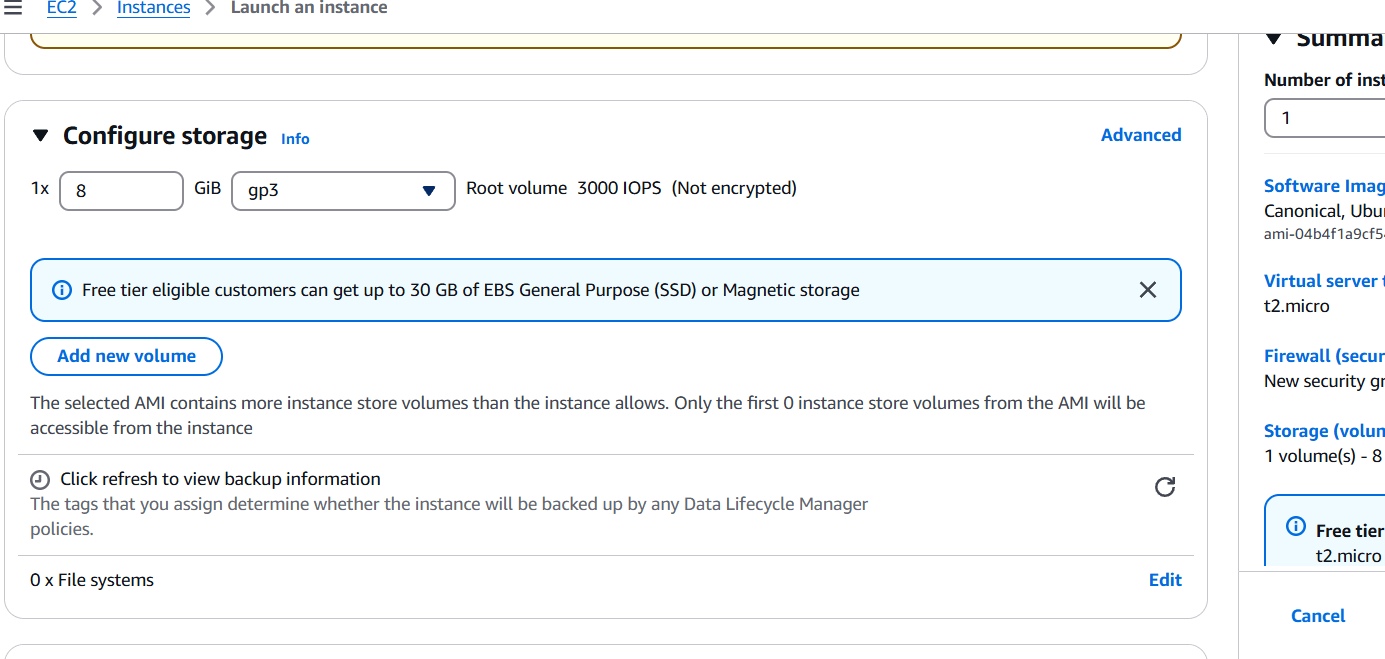
STEP 1: Create a EC2 instance.
- Enter the name.
- Select AMI.
- Create keypair.
- Click on create instance.
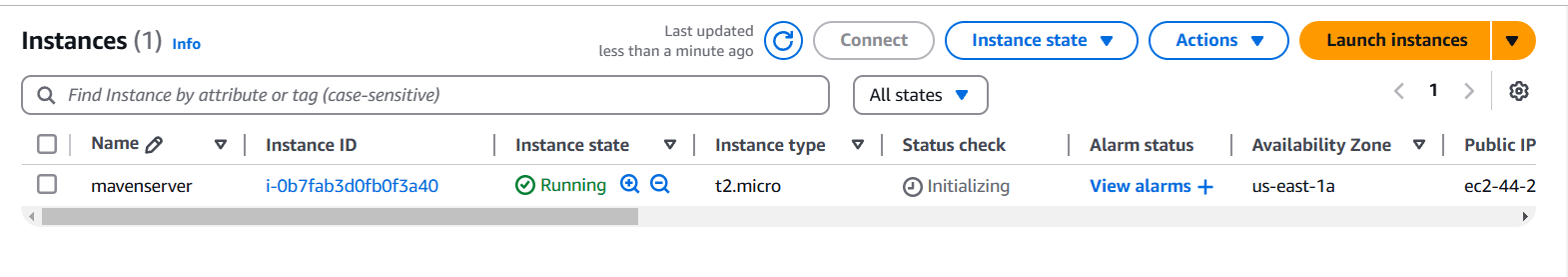
STEP 2: Accessing SSH Connection.
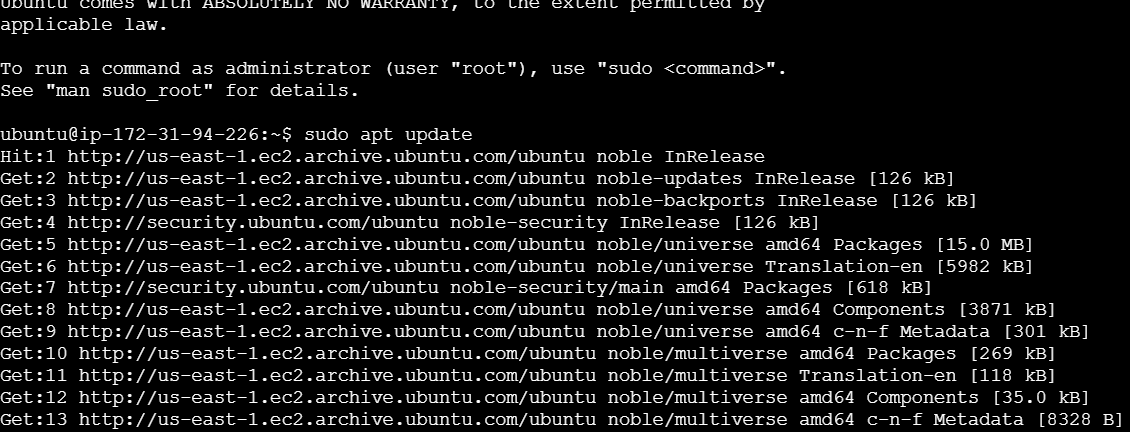
- Follow these steps to install Maven with APT.
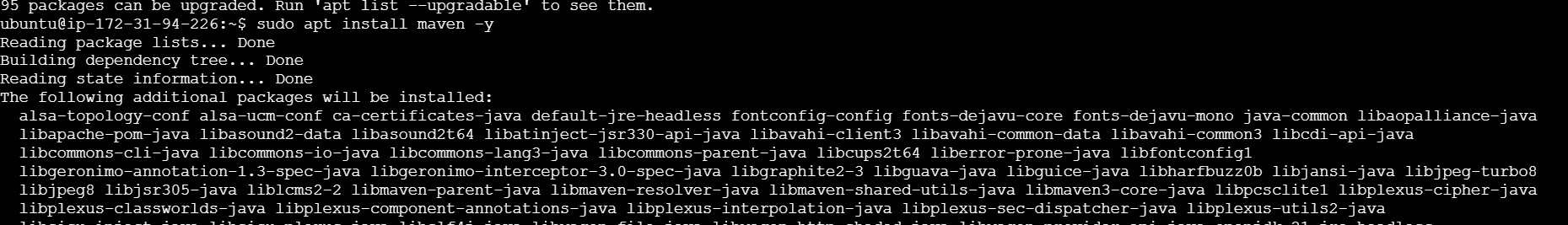
sudo apt update
sudo apt install maven -y
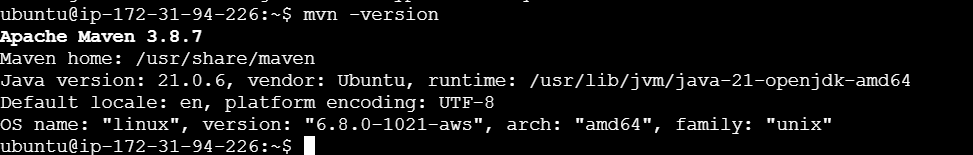
mvn -version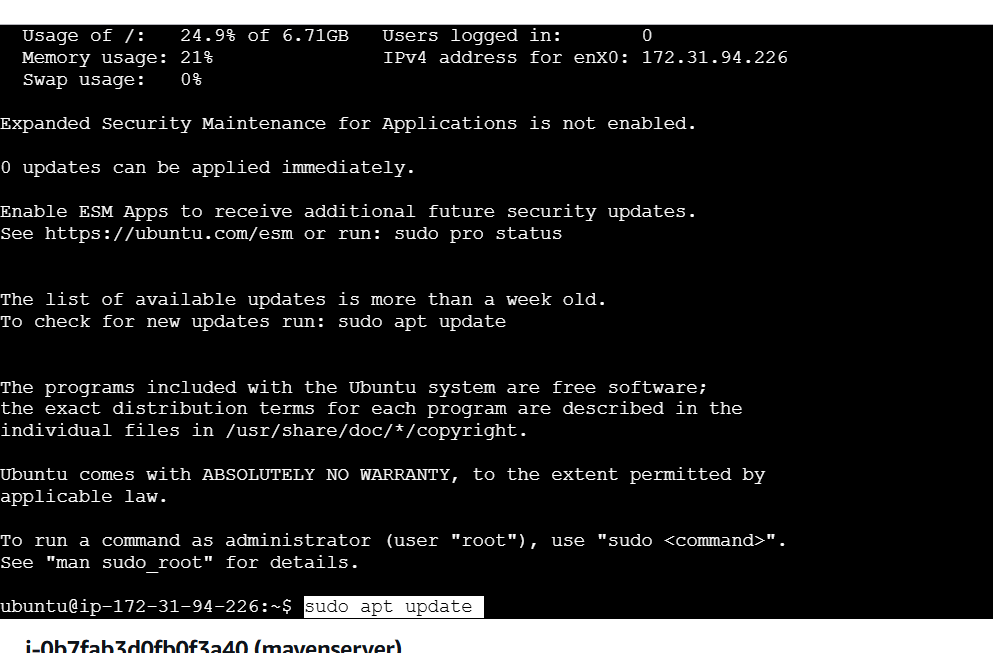
Method 2: Download and Install Maven’s Recent Version on Ubuntu.
STEP 1: Install OpenJDK.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install default-jdk -y
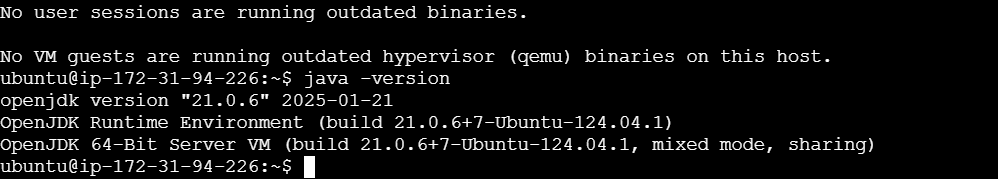
java -version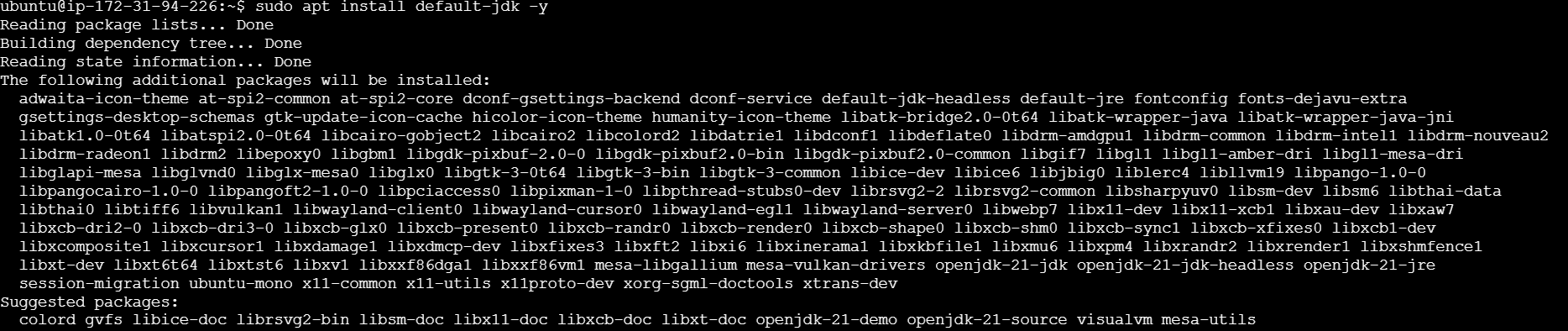
STEP 2: Download and Install Maven.
- Install maven.
- Copy the 1st link.
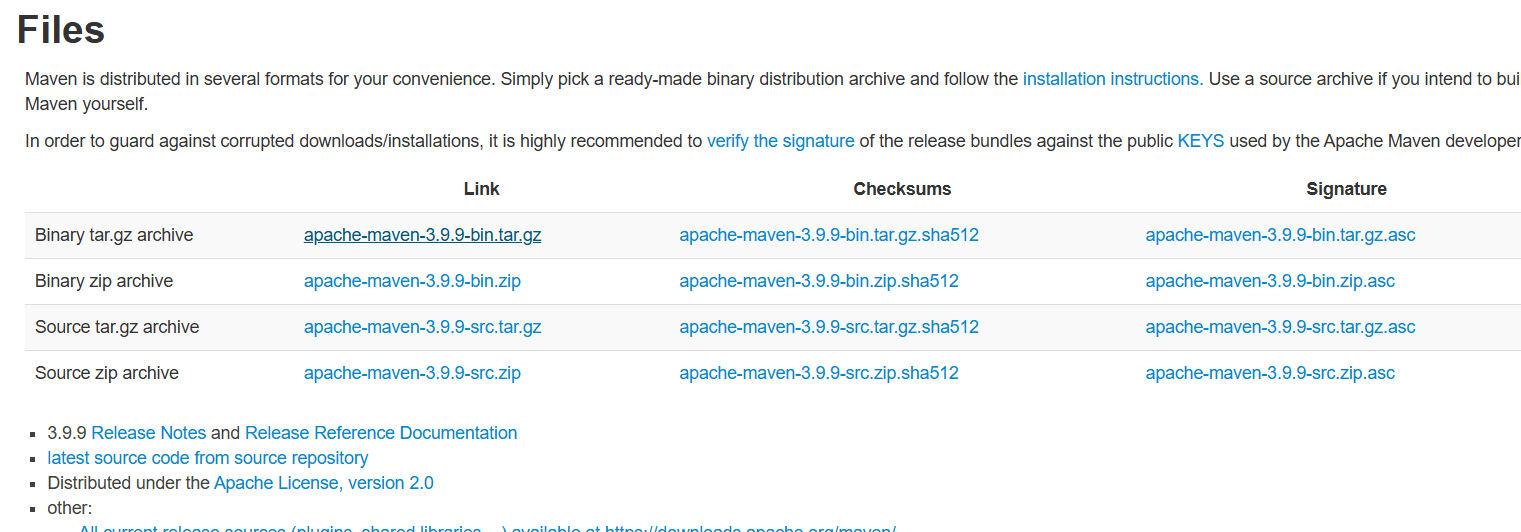
- Paste the link in following method.
wget [link] -P /tmp
sudo tar xf /tmp/apache-maven-*.tar.gz -C /opt
sudo ln -s /opt/apache-maven-3.9.6 /opt/maven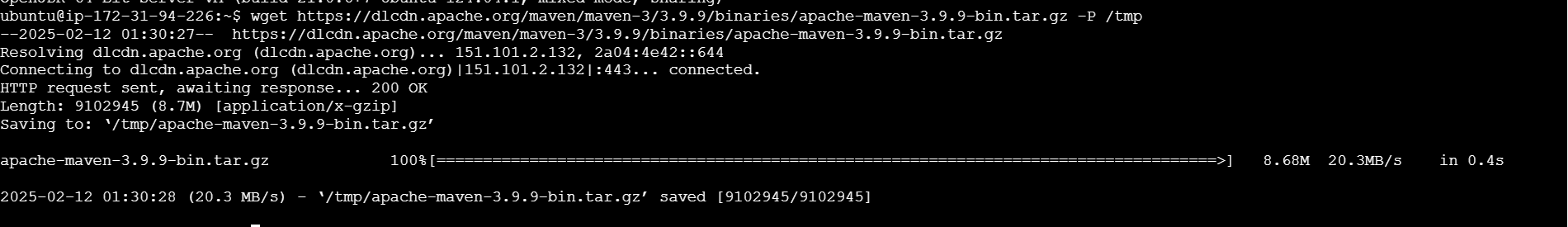
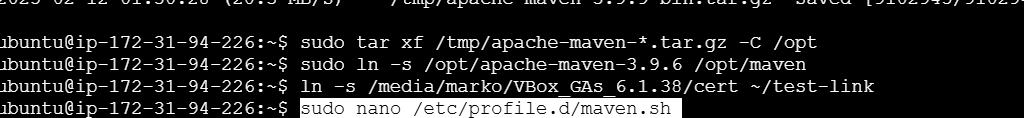
STEP 3: Set Up Environment Variables.
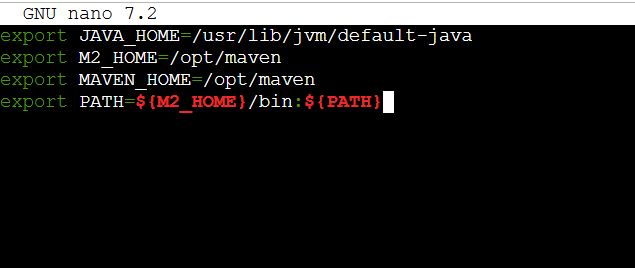
sudo nano /etc/profile.d/maven.sh- Enter the following command.
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/default-java
export M2_HOME=/opt/maven
export MAVEN_HOME=/opt/maven
export PATH=${M2_HOME}/bin:${PATH}- Save the file.
STEP 4: Verify Maven Installation.
sudo chmod +x /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
source /etc/profile.d/maven.sh
mvn -version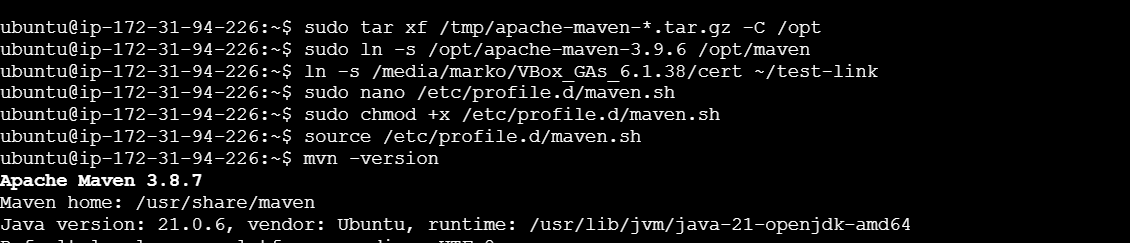

Conclusion.
In conclusion, Maven is an essential tool for Java developers, offering powerful features that streamline the build, dependency management, and project organization processes. By automating tedious tasks, ensuring consistent project structures, and facilitating smooth collaboration, Maven helps developers focus more on coding and less on manual configuration. Whether you’re working on a small project or a large enterprise application, Maven’s simplicity and flexibility make it an invaluable tool for managing the complexities of modern software development.
Step-by-Step Guide to Deploying a Sample WordPress Application Using AWS CodeDeploy.
Introduction.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the process of deploying a sample WordPress application using AWS CodeDeploy. AWS CodeDeploy is a fully managed deployment service that automates application updates and minimizes downtime, making it an ideal solution for managing the deployment lifecycle of your applications. Whether you are new to CodeDeploy or looking to optimize your deployment workflows, this guide will provide you with the necessary steps to set up and deploy a simple WordPress application with minimal effort. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a robust deployment pipeline that streamlines the process of delivering your WordPress application to production.

STEP 1: Create a instance Enter the instance name and Select AMI.
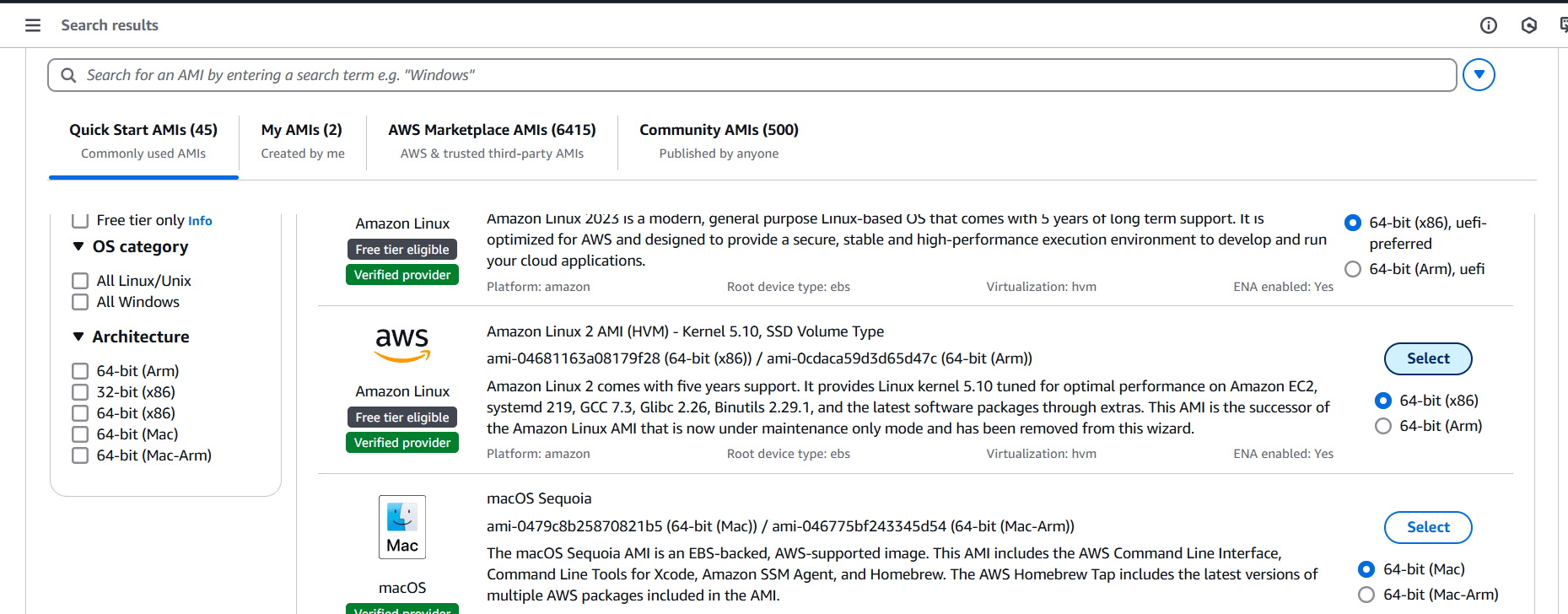
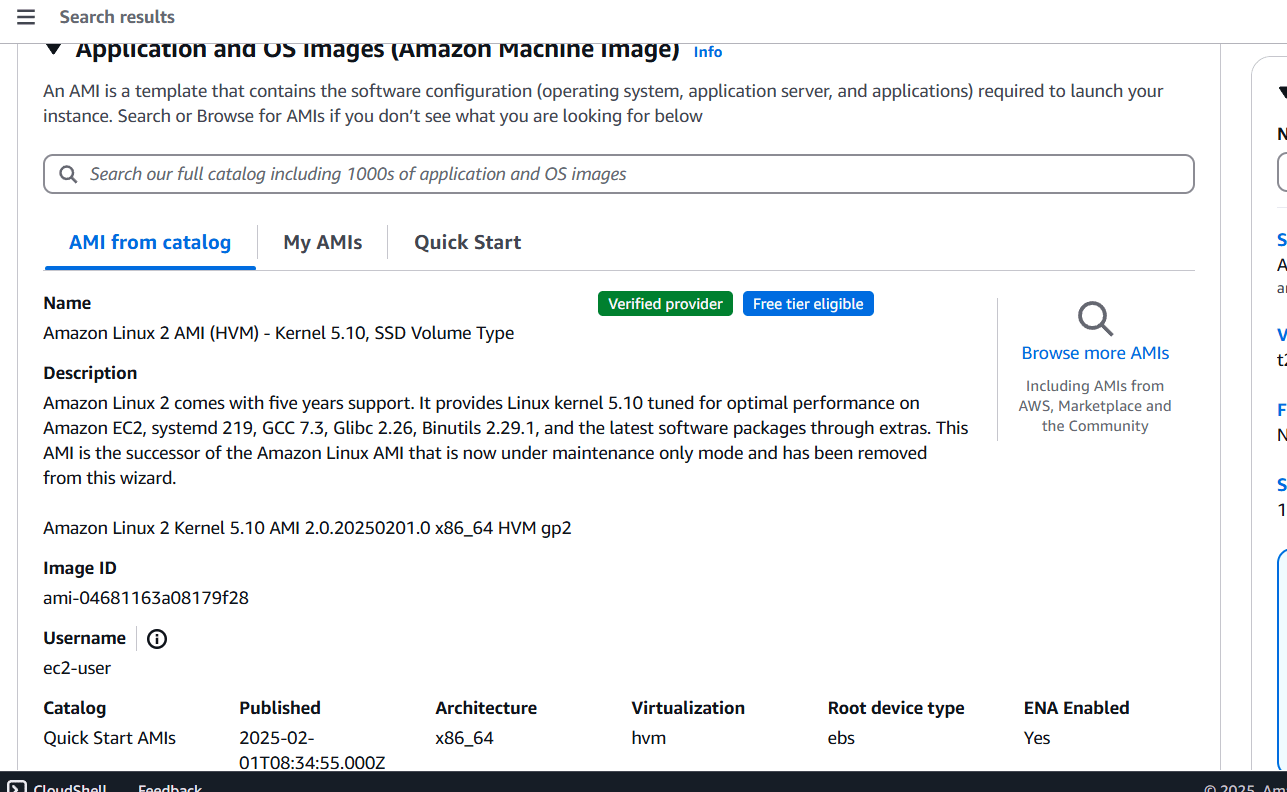
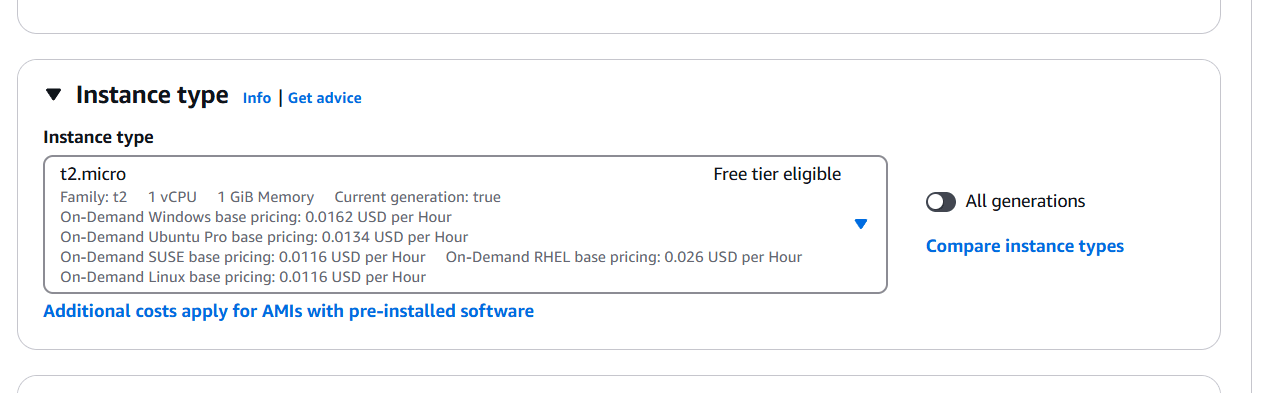
STEP 2: Create Keypair and select the instance type (t2micro).
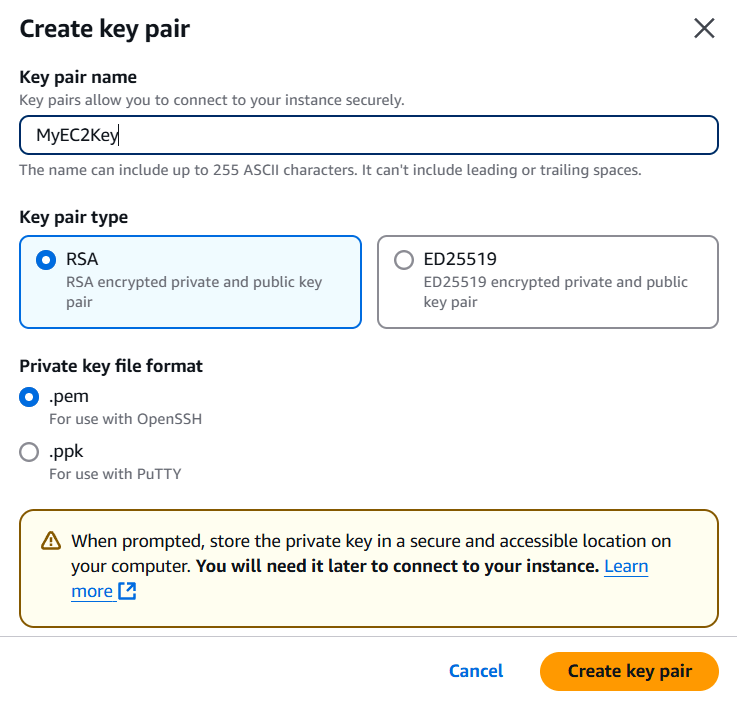
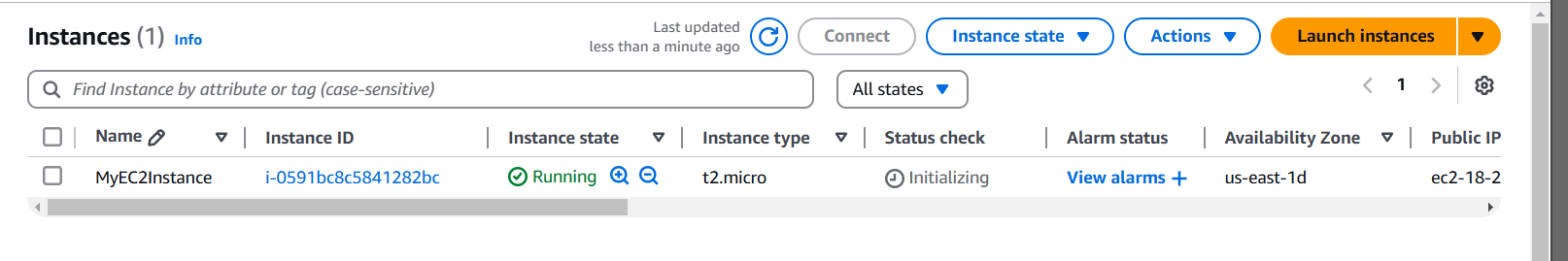
STEP 4: Click on create instance.
STEP 5: Accessing SSH Connection.
- Enter the following commands.
sudo su
yum -y update
yum install awscli git -y
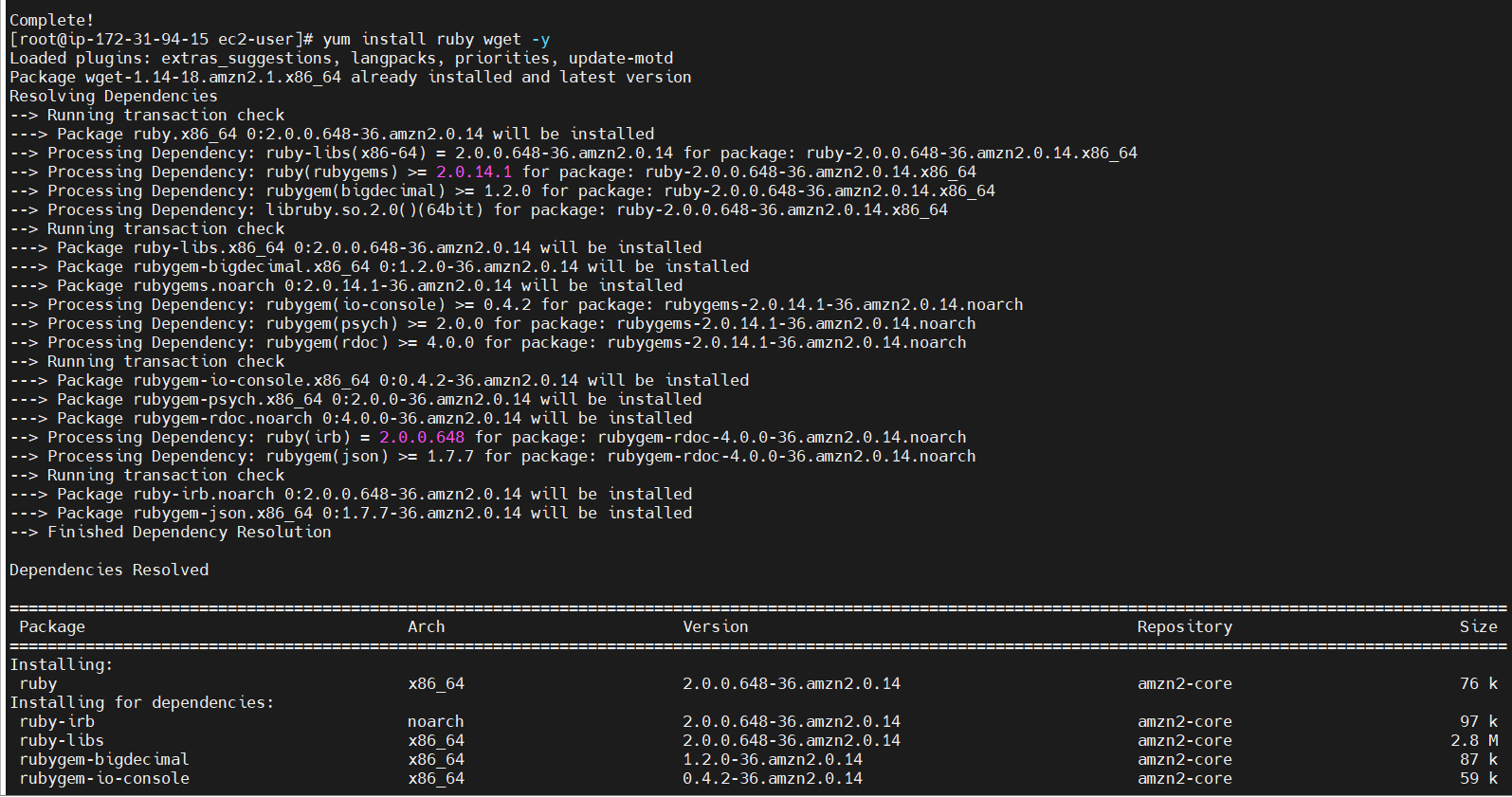
yum install ruby wget -y
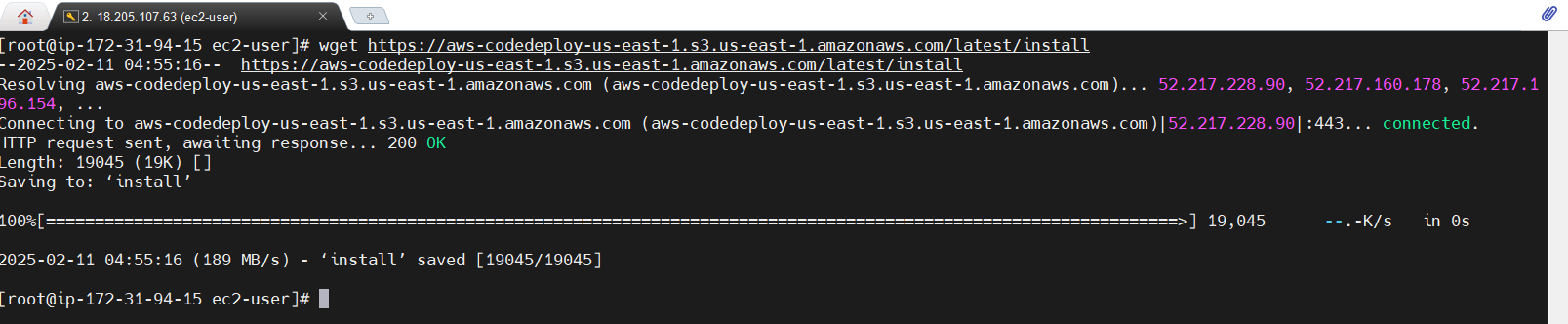
wget https://aws-codedeploy-us-east-1.s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/latest/install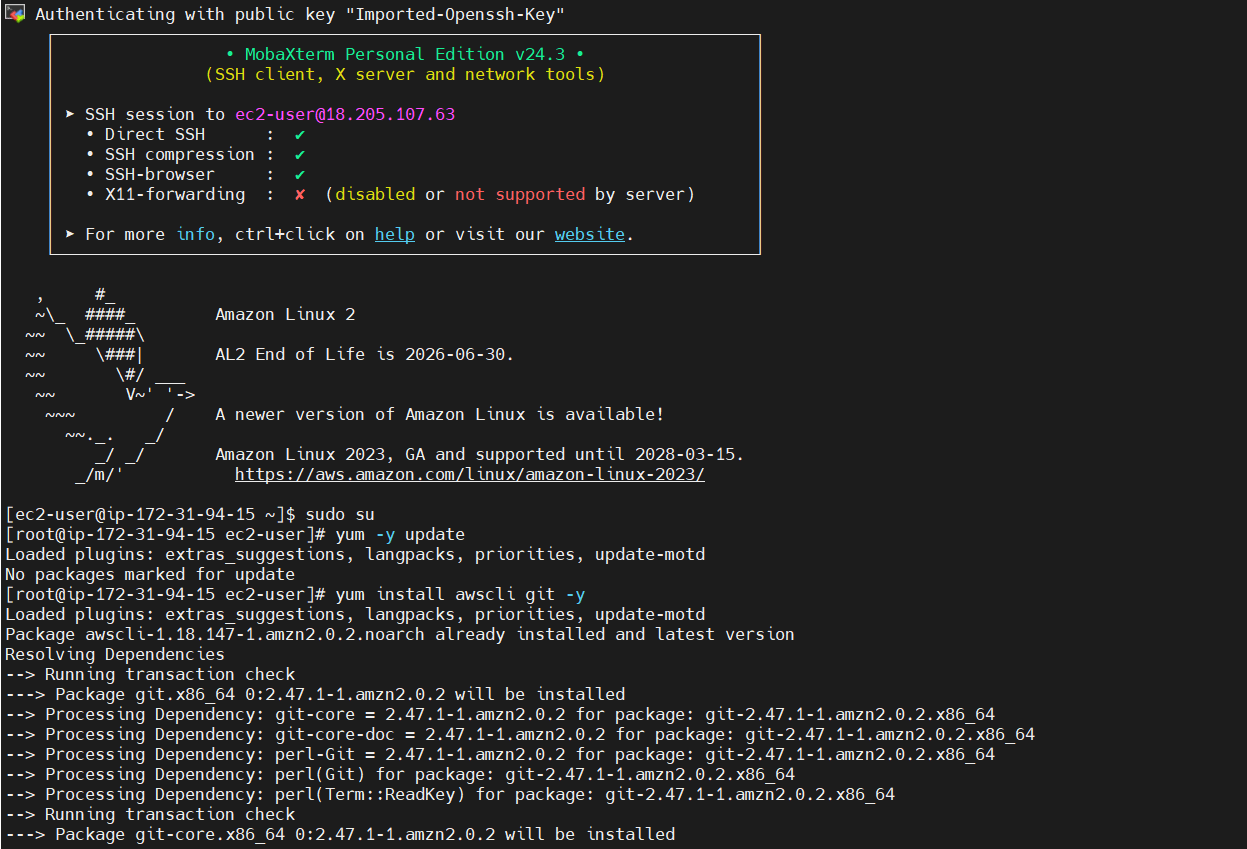
STEP 6: Change the permission of the installer.
chmod +x ./install
sudo ./install auto
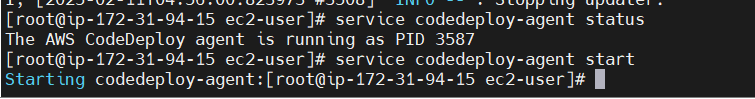
service codedeploy-agent status
service codedeploy-agent start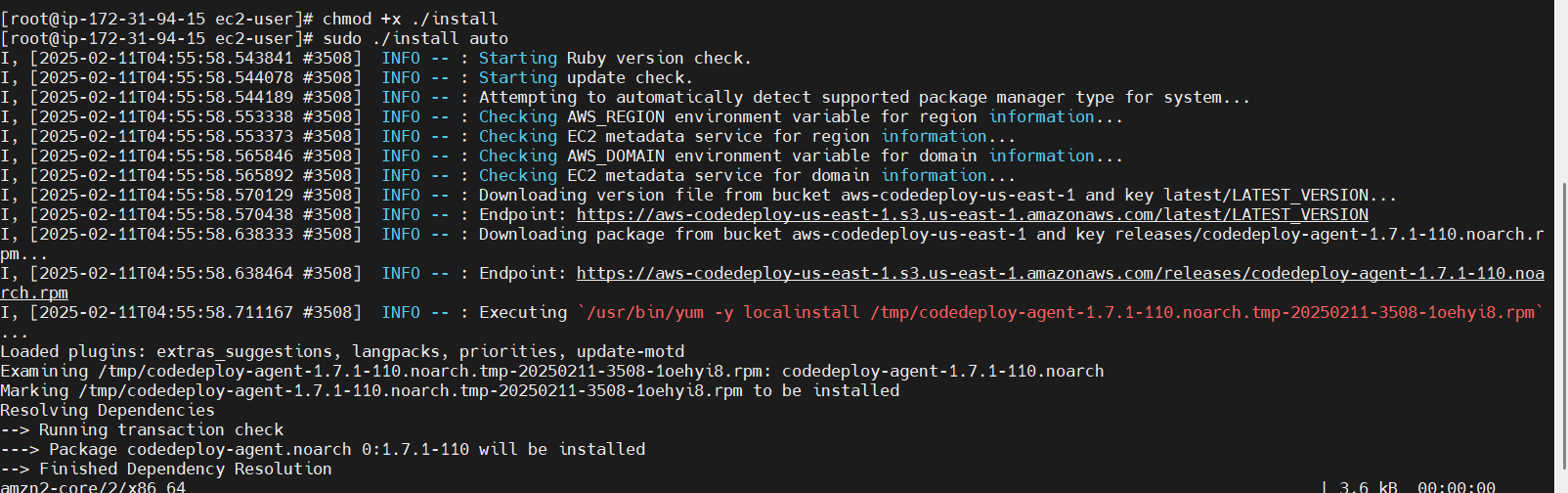
STEP 7: Clone the application and copy application files from S3 Bucket.
git clone https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress.git /home/ec2-user/WordPress
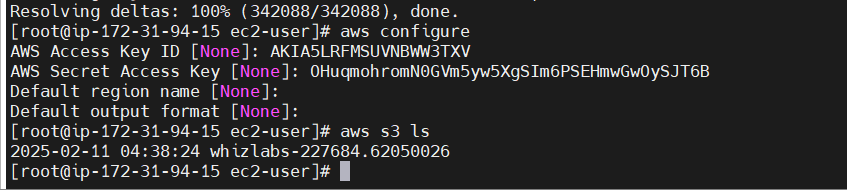
aws configure- Enter the Secret key and access key.
aws s3 ls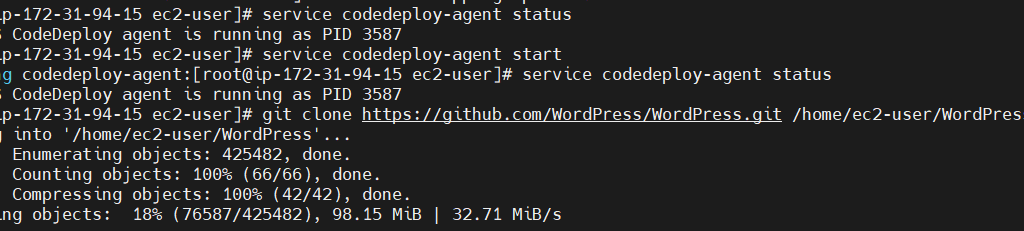
STEP 8: Copy the script files to /tmp/WordPress/scripts folder
aws s3 cp s3://{Bucket-name}/ /home/ec2-user/WordPress --recursive
cd /home/ec2-user/WordPress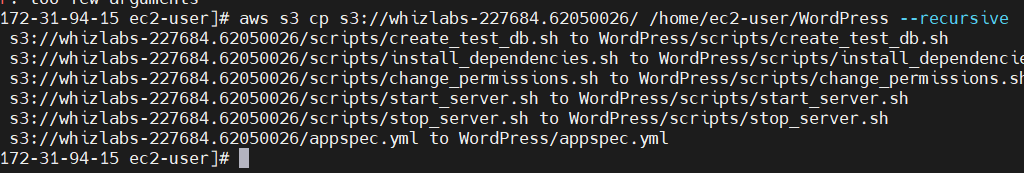
STEP 9: Enter the following command.
aws deploy create-application --application-name WordPress_App --region us-east-1

STEP 10: Create a Deployment group.
- Navigate the code deploy.
- Select developer tools and click on codedeploy.
- Click on Applications.
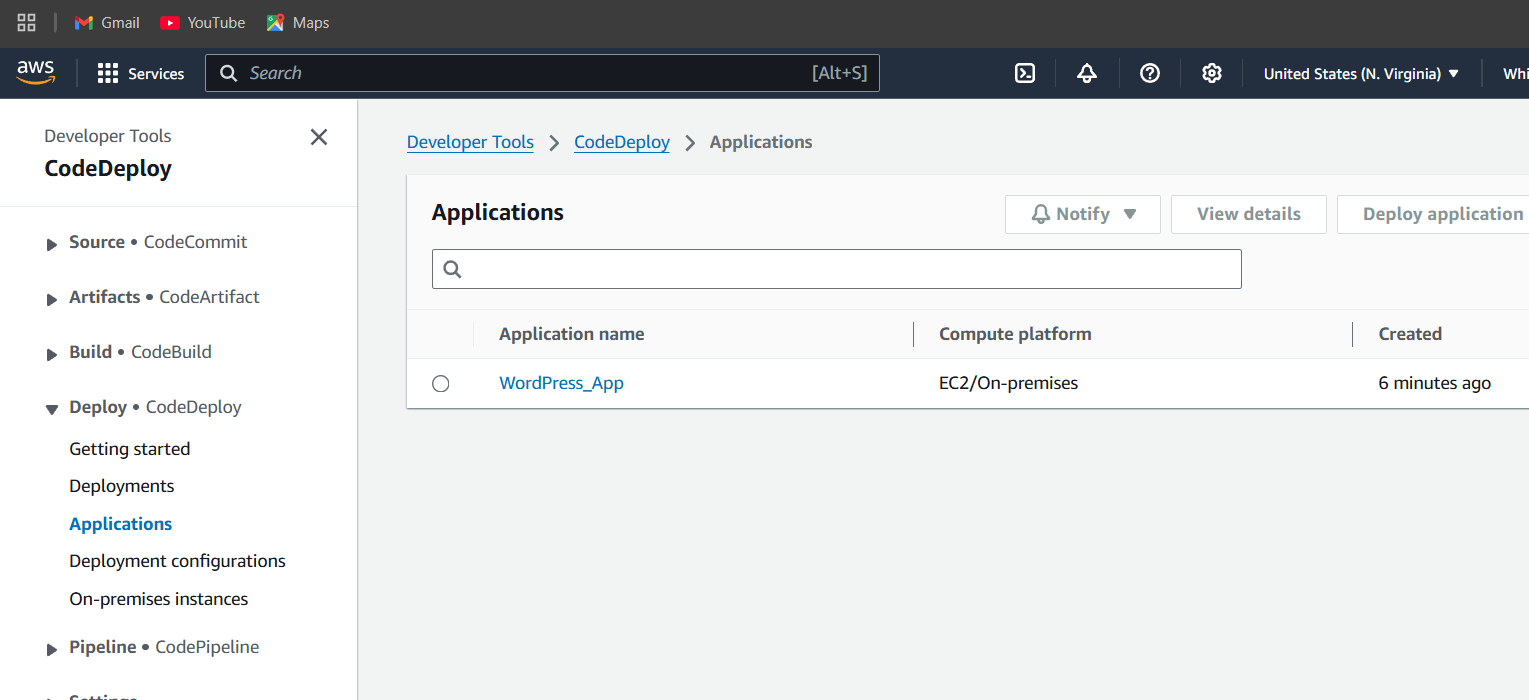
STEP 11: You will see a created applications.
- Click on your application name.
- Next, Click on Create deployment group.
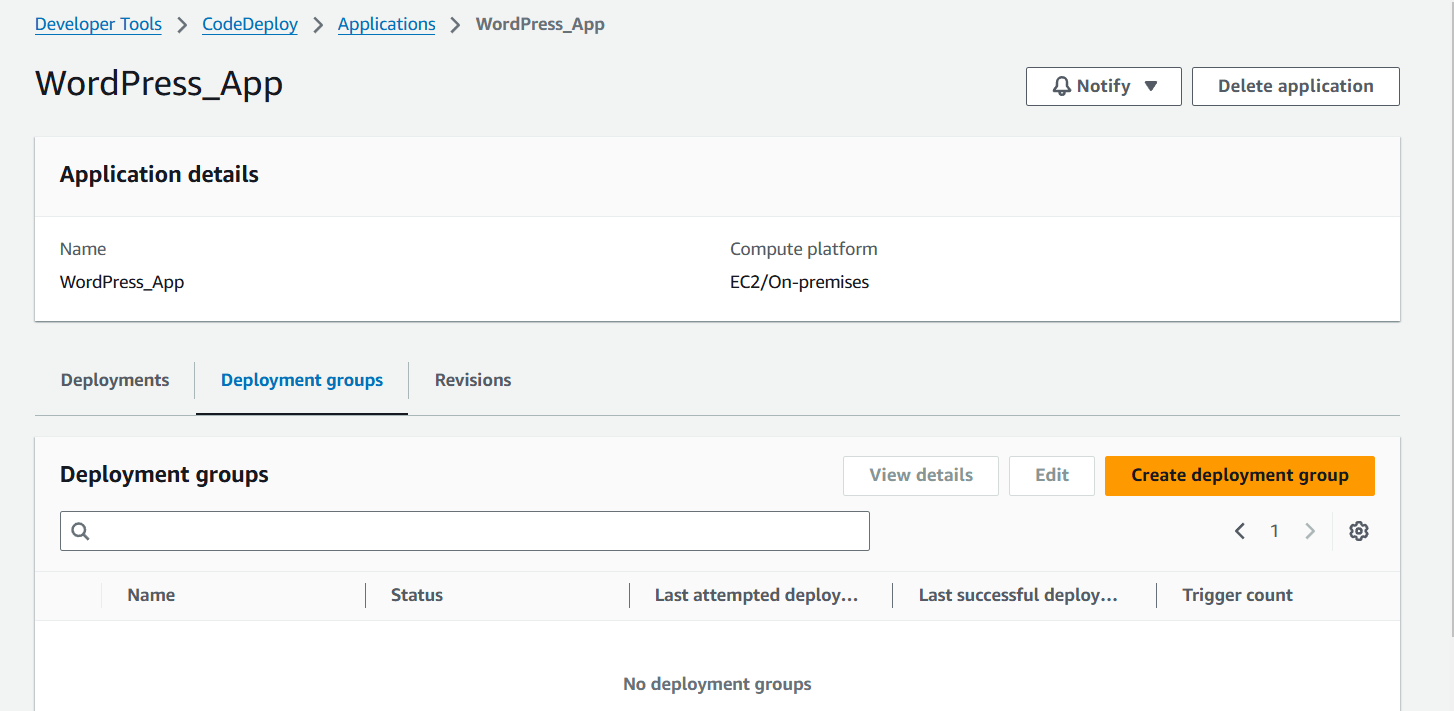
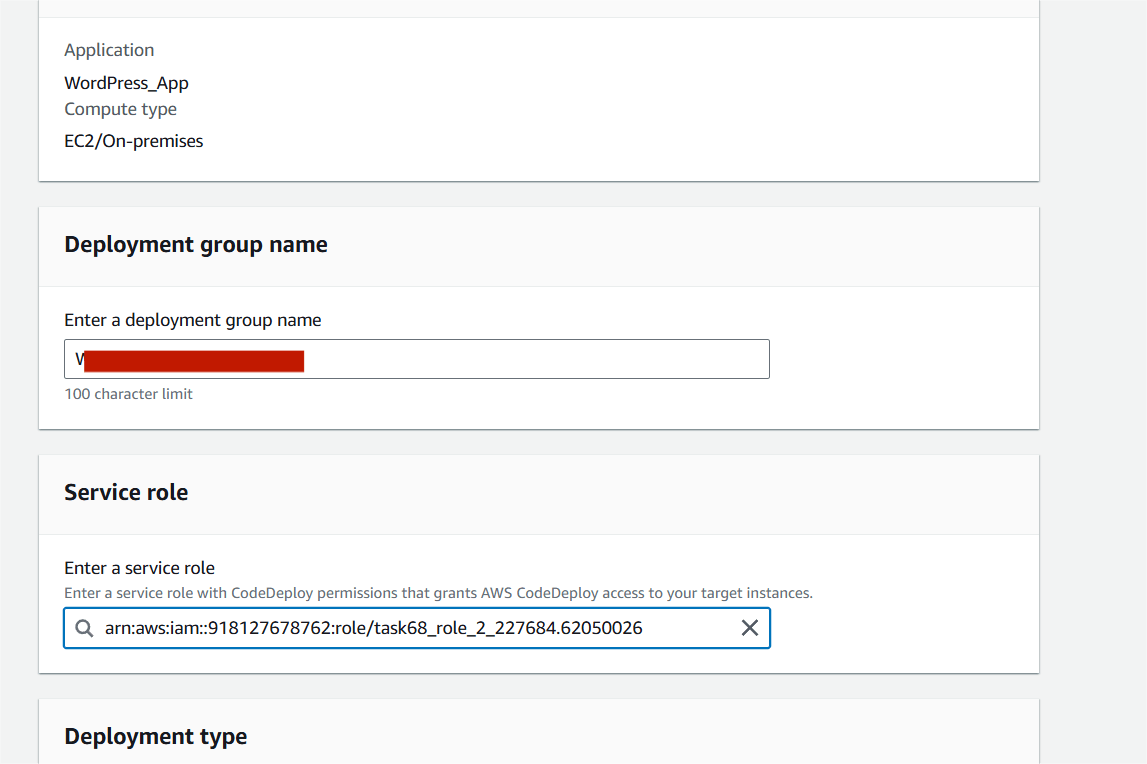
STEP 12: Enter the group name.
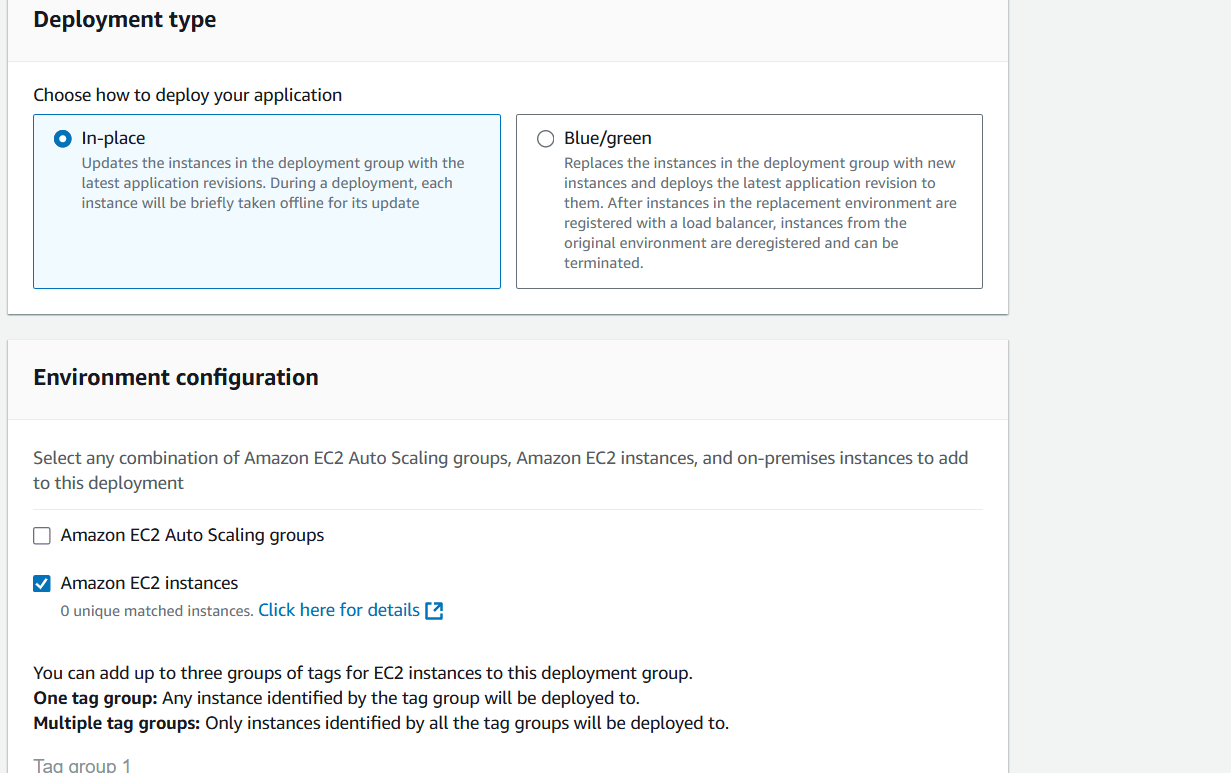
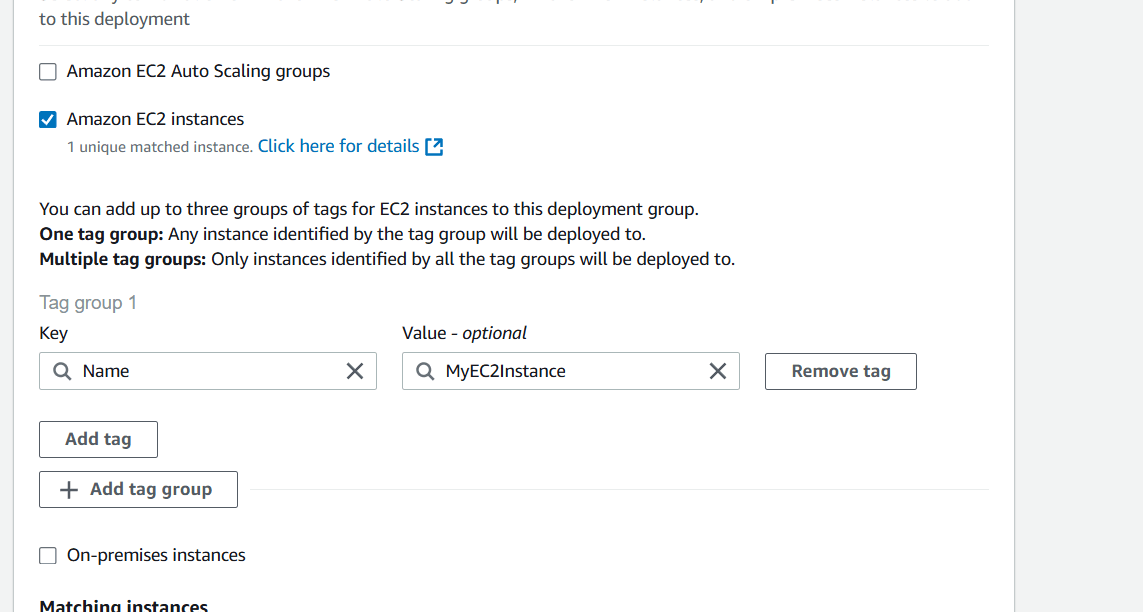
- Select your role.
- Select deployment type and EC2 instance.
- Click on create.
STEP 13: Click on create deployment.
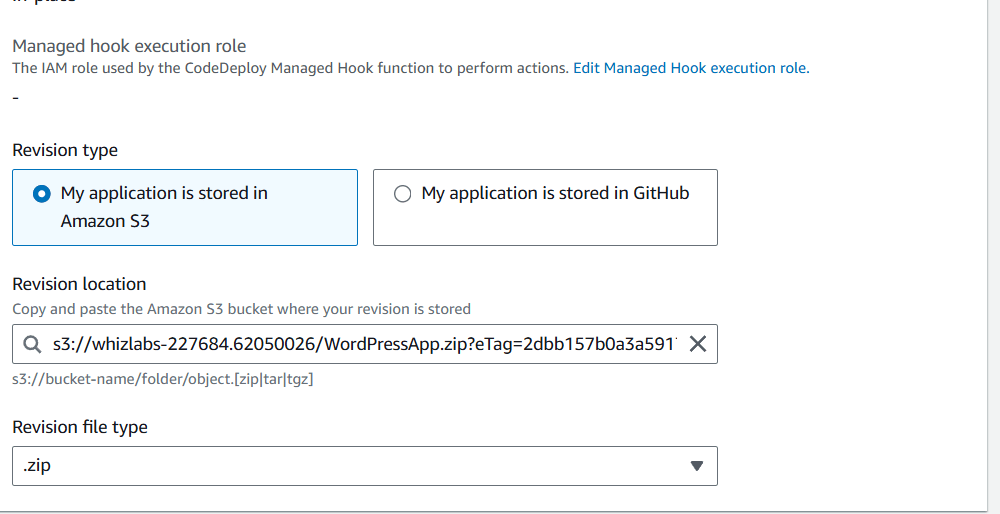
STEP 14: Select revision type.
- Select revision location.
- Click on create.
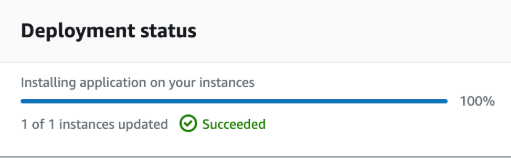
STEP 15: Deployment status shows succeed if everything is done correctly.
STEP 16: Copy the Public IPv4 DNS of the Instance.
- Enter the browser like this : http://ec2-18-205-155-113.compute-1.amazonaws.com/WordPress/
- The application is ready to do the setup.
- Fill in the below details.
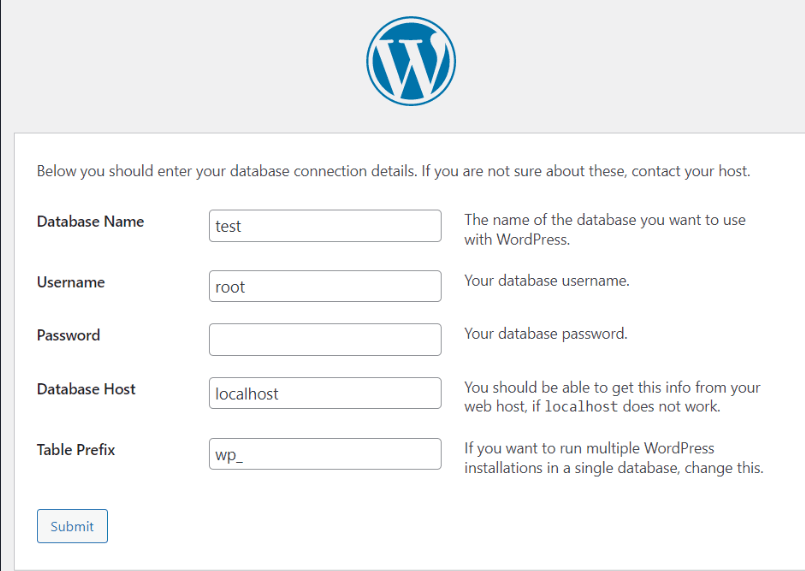
STEP 17: Access the WordPress site.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, deploying a sample WordPress application using AWS CodeDeploy offers a scalable and efficient solution for automating application updates and ensuring smooth, consistent deployments. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you have set up a reliable deployment pipeline that simplifies managing your WordPress application in the cloud. With CodeDeploy, you can automate rollbacks, handle complex deployments, and maintain uptime, all while reducing manual intervention. As you continue to scale your infrastructure, leveraging AWS services like CodeDeploy will help streamline your deployment processes, ensuring faster, more reliable delivery of new features and updates to your users.
Mastering Amazon GuardDuty Setup Using Terraform.
Overview.
Amazon GuardDuty is a managed threat detection service offered by AWS, designed to monitor your AWS accounts and workloads for potential security threats. It continuously analyzes and processes data from various AWS sources, such as CloudTrail logs, VPC Flow Logs, and DNS logs. GuardDuty uses machine learning, anomaly detection, and integrated threat intelligence to identify suspicious activity and potential security risks.
It provides real-time alerts on unauthorized behavior, like unusual API calls, compromised instances, or malicious network traffic. The service is easy to set up, requiring no additional infrastructure or management. Once activated, GuardDuty automatically starts analyzing your AWS environment, offering actionable findings for security teams to respond to.

GuardDuty is scalable and integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like CloudWatch and Lambda. With its cost-effective pay-as-you-go model, it is suitable for businesses of all sizes. This service helps reduce the complexity of security monitoring, making it an essential tool for maintaining a secure AWS environment.
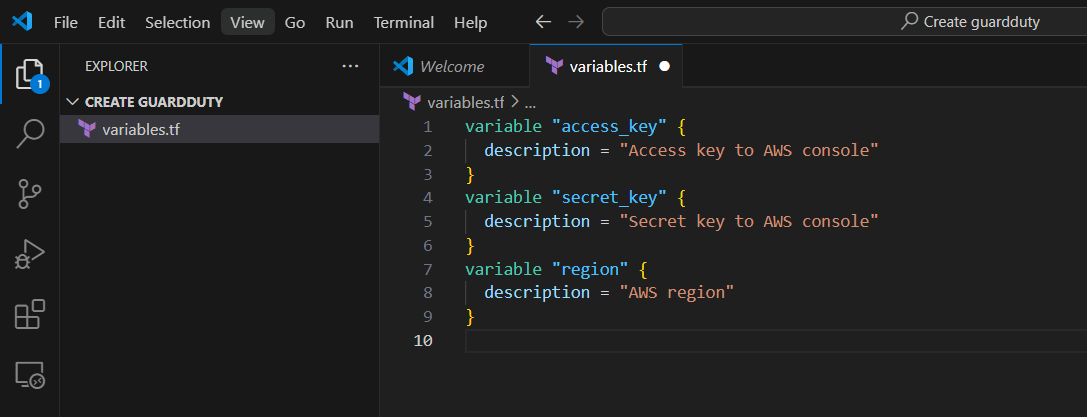
STEP 1: Create variables.tf file.
- Enter the following terraform script and save the file.
variable "access_key" {
description = "Access key to AWS console"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key to AWS console"
}
variable "region" {
description = "AWS region"
}
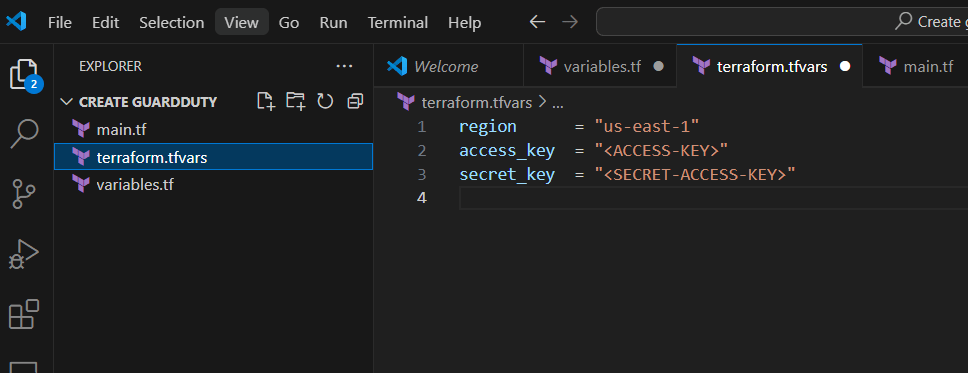
STEP 2: Next Create Terraform.tfvars file.
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "<ACCESS-KEY>"
secret_key = "<SECRET-ACCESS-KEY>"- Save the file.
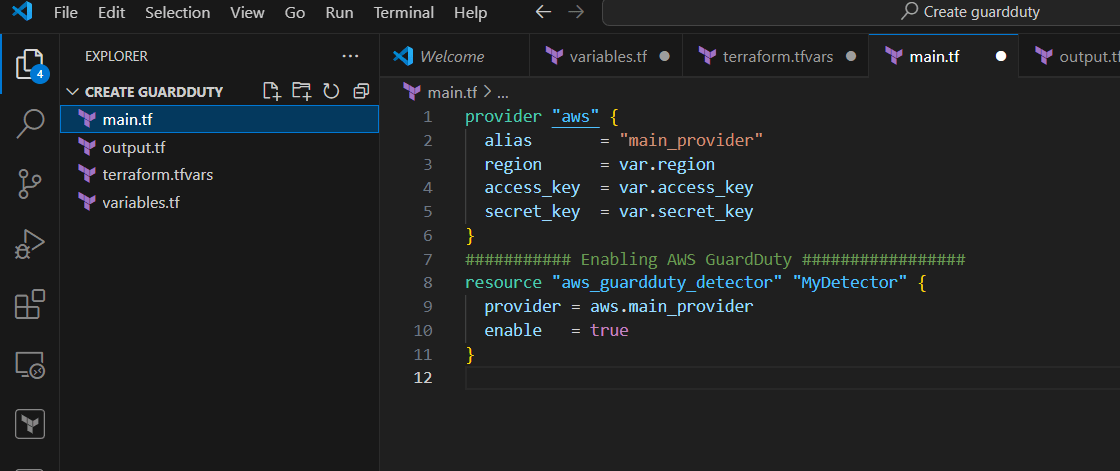
STEP 3: Create main.tf file.
provider "aws" {
alias = "main_provider"
region = var.region
access_key = var.access_key
secret_key = var.secret_key
}
########### Enabling AWS GuardDuty #################
resource "aws_guardduty_detector" "MyDetector" {
provider = aws.main_provider
enable = true
}
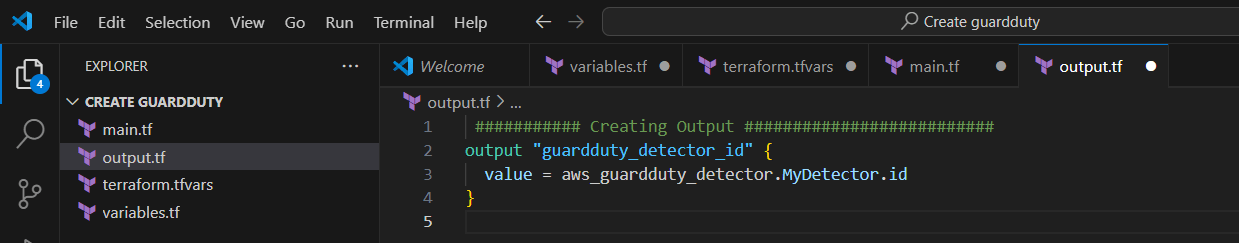
STEP 4: Create output.tf file.
- Enter the following Script and save the file.
########### Creating Output ##########################
output "guardduty_detector_id" {
value = aws_guardduty_detector.MyDetector.id
}
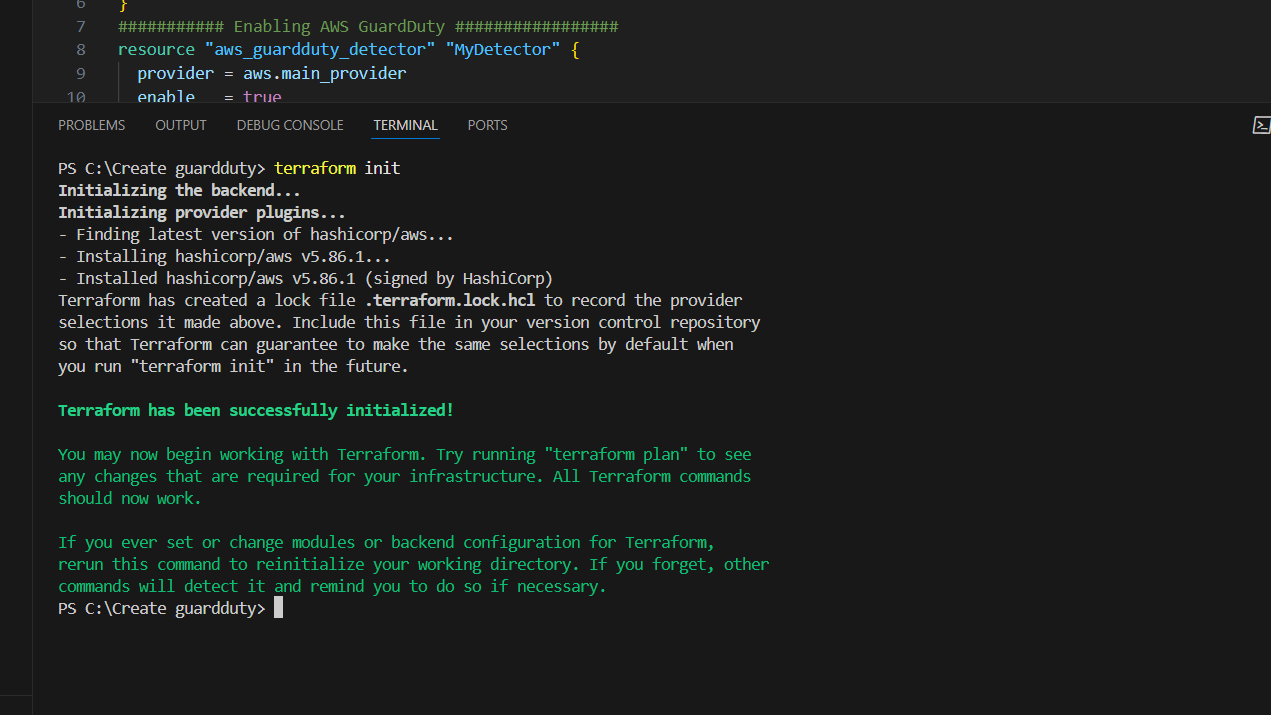
STEP 5: Go to the terminal and enter the terraform init.
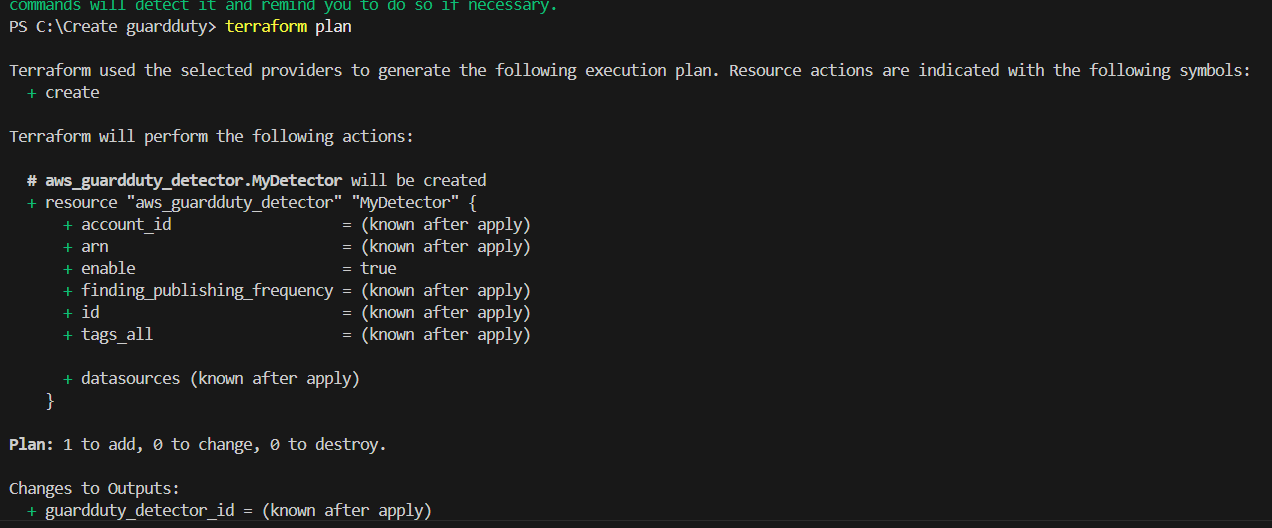
STEP 6: Next Enter the terraform plan command.
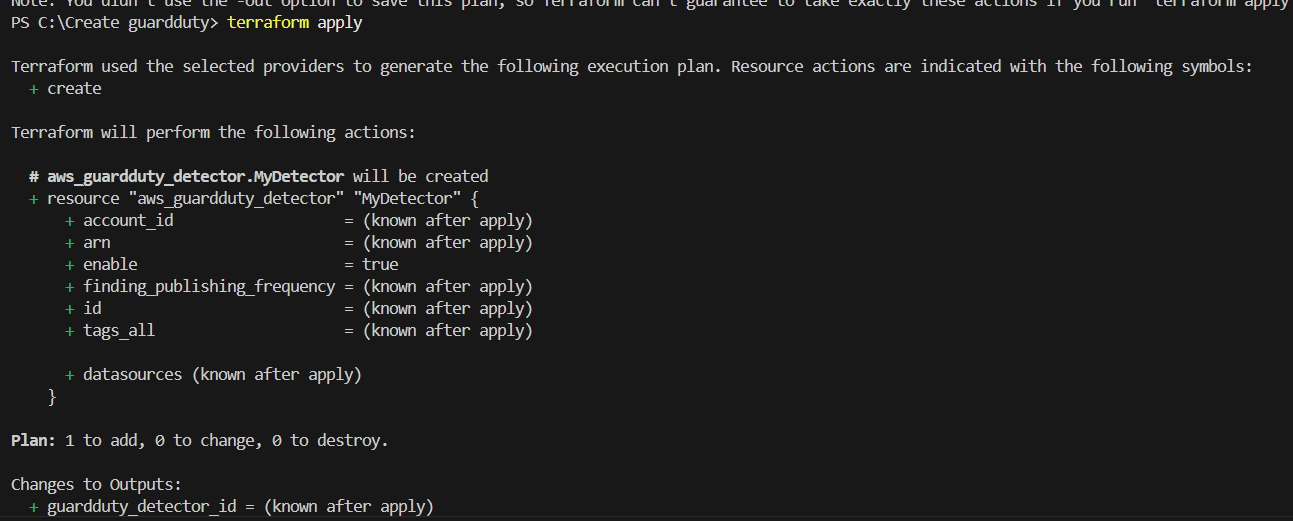
STEP 7: Enter the terraform apply command.
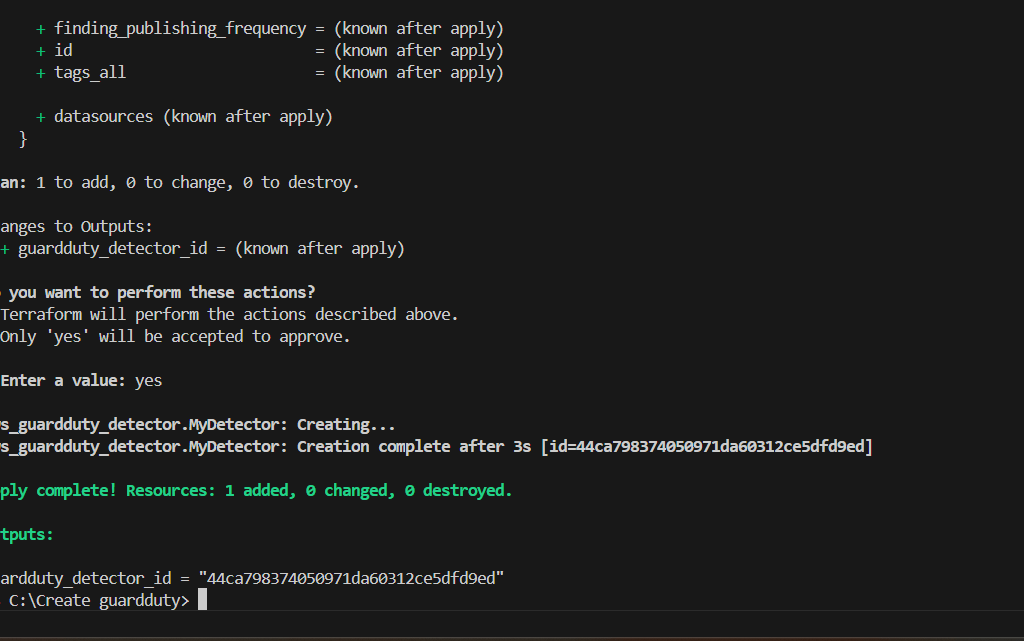
STEP 8: Verify the resources in AWS Console.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, setting up Amazon GuardDuty using Terraform offers a streamlined and automated approach to enhance your AWS security posture. By leveraging Terraform’s infrastructure-as-code capabilities, you ensure that GuardDuty is consistently and efficiently deployed across your AWS environment, with minimal manual intervention. This process not only simplifies the initial setup but also facilitates easy management, scaling, and adjustments to your security configuration as your infrastructure evolves.
By following the steps outlined, you gain a deeper understanding of integrating GuardDuty with other AWS services, enhancing threat detection and response times. Moreover, Terraform’s version control and infrastructure management make it possible to maintain a repeatable and auditable security setup. As cloud environments grow in complexity, automating and codifying security services like GuardDuty is critical for maintaining a robust defense against potential threats.
In the long term, adopting this approach improves both operational efficiency and security reliability, making Terraform a powerful tool in securing your AWS infrastructure.
Build Your Own WordPress Website Using Terraform.
Introduction.
Building a WordPress website using Terraform involves automating the provisioning and configuration of the infrastructure needed to run WordPress on AWS (or any other cloud provider you choose). Terraform is an Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tool that allows you to define your infrastructure in code and manage it consistently and efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of setting up a WordPress site using Terraform to automate infrastructure provisioning on AWS.

Prerequisites:
- Terraform: Make sure Terraform is installed on your machine. You can download it from Terraform’s official website.
- VS Code: Visual Studio Code should be installed, and you should have the Terraform extension installed.
- AWS Account: An active AWS account for deploying resources.
- AWS CLI: Make sure the AWS CLI is configured to use your credentials.
TASK 1: Set up Terraform Configuration
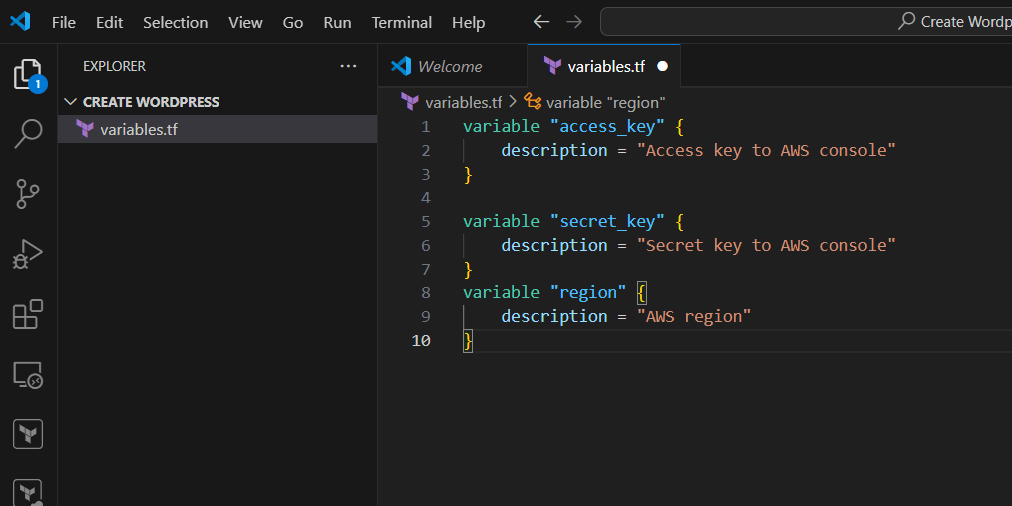
STEP 1: Create variables.tf file.
- Enter the following command.
- And save the file.
variable "access_key" {
description = "Access key to AWS console"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key to AWS console"
}
variable "region" {
description = "AWS region"
}
STEP 2: Next, Create terraform.tf file.
- Enter the following command and save the file.
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "<YOUR AWS CONSOLE ACCESS ID>"
secret_key = "<YOUR AWS CONSOLE SECRET KEY>"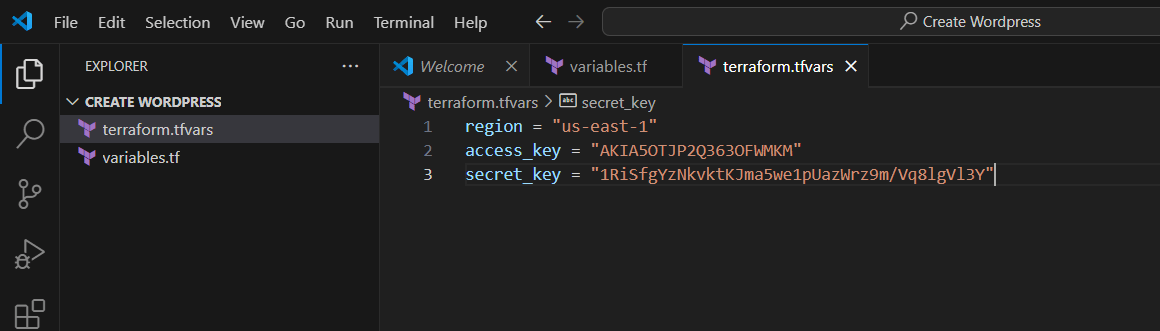
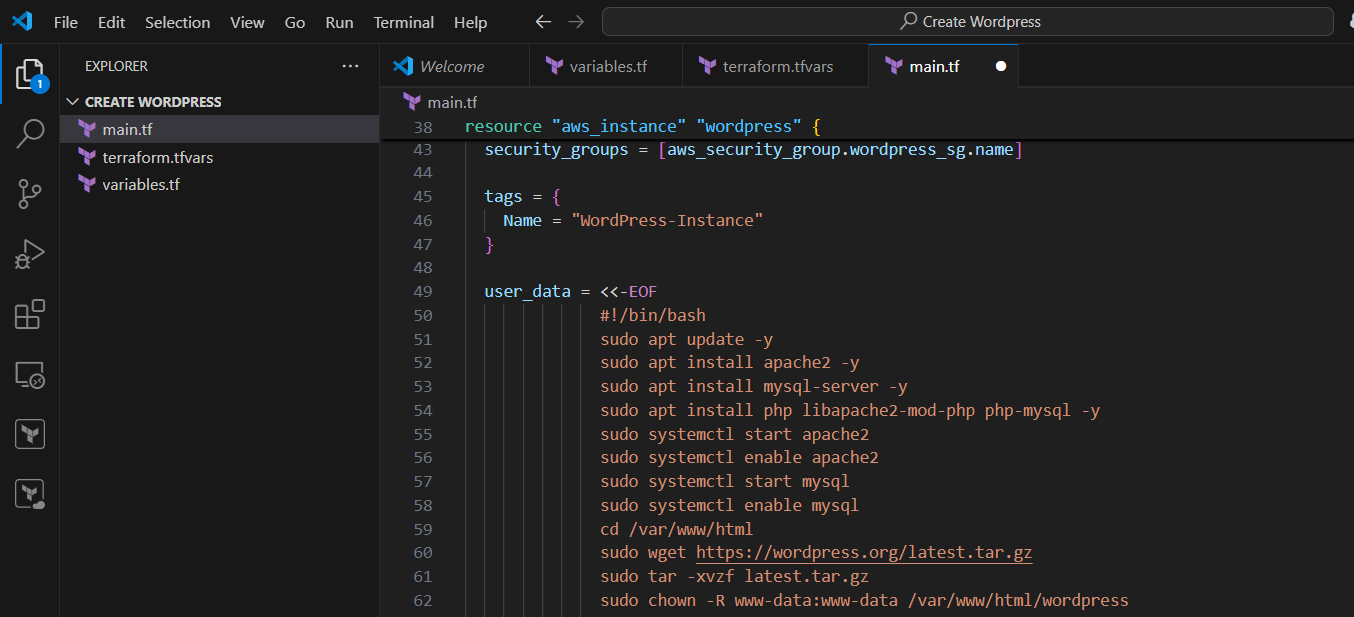
STEP 3: Create main.tf file.
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1" # Change region as per your preference
}
resource "aws_security_group" "wordpress_sg" {
name = "wordpress_sg"
description = "Security group for WordPress"
ingress {
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "wordpress" {
ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0" # This should be the latest Ubuntu AMI (update as per region)
instance_type = "t2.micro"
key_name = "your-key-pair" # Ensure you have an existing key pair
security_groups = [aws_security_group.wordpress_sg.name]
tags = {
Name = "WordPress-Instance"
}
user_data = <<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install apache2 -y
sudo apt install mysql-server -y
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql -y
sudo systemctl start apache2
sudo systemctl enable apache2
sudo systemctl start mysql
sudo systemctl enable mysql
cd /var/www/html
sudo wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
sudo tar -xvzf latest.tar.gz
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/wordpress
EOF
}
resource "aws_eip" "wordpress_ip" {
instance = aws_instance.wordpress.id
}
output "website_url" {
value = "http://${aws_eip.wordpress_ip.public_ip}"
}
TASK 2: Apply terraform configurations.
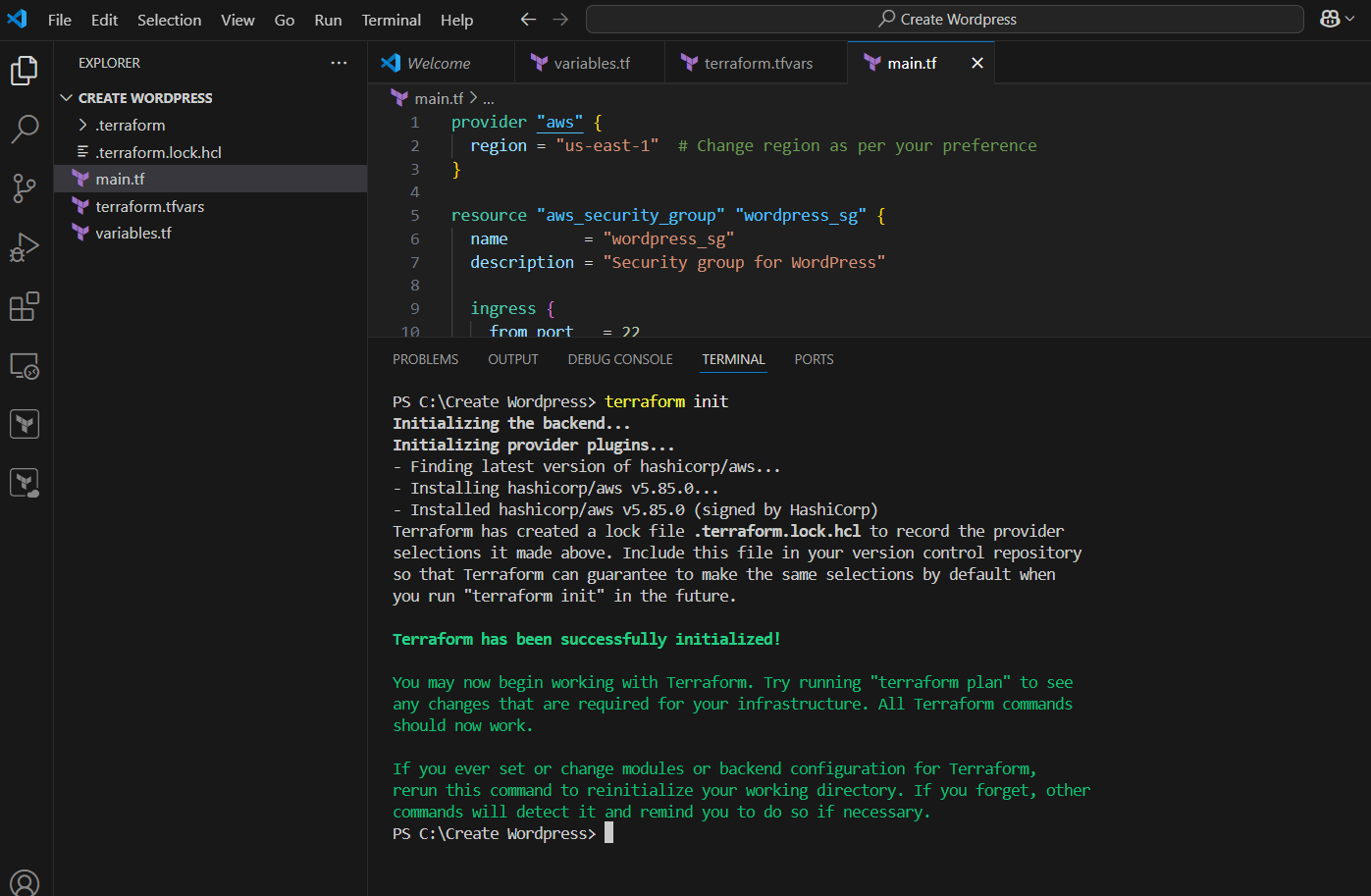
STEP 1: Go to terminal enter terraform init command.
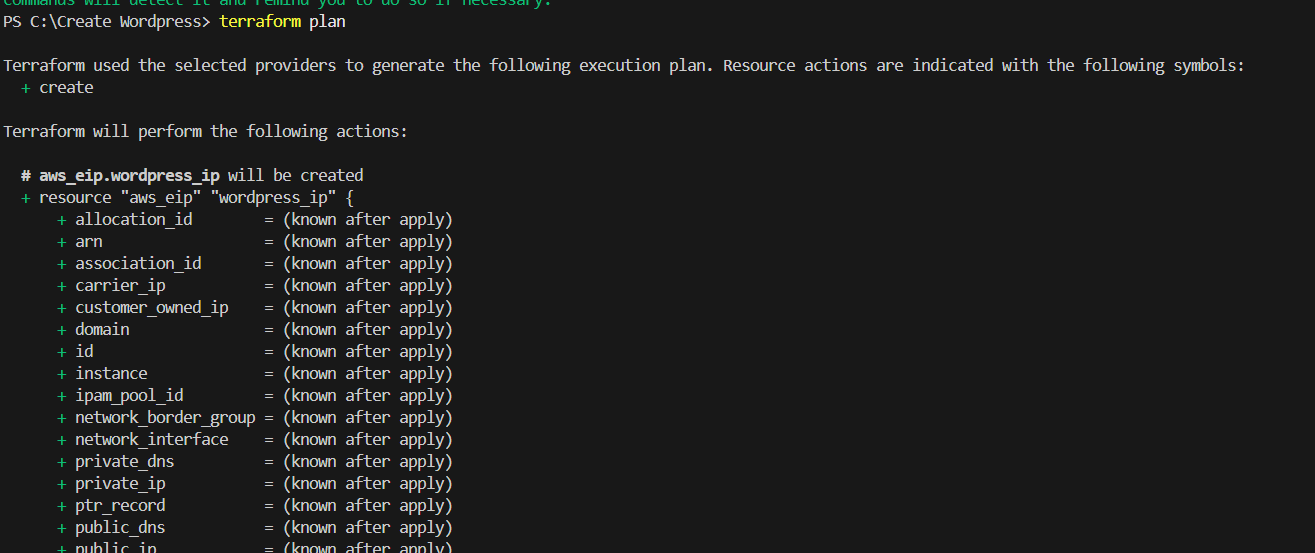
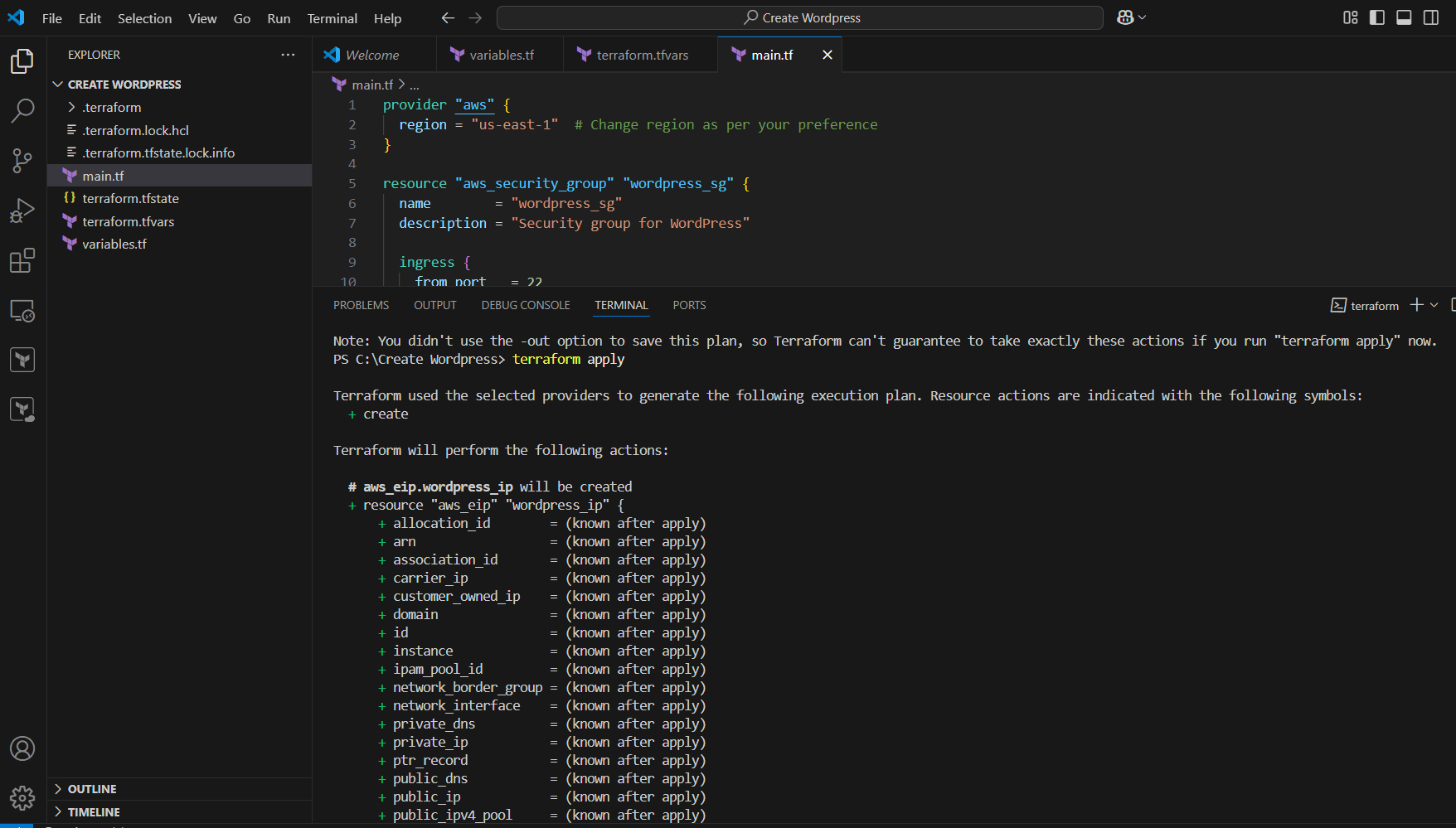
STEP 2: Next, Enter terraform plan and terraform apply command.
TASK 3: Open the WordPress Dashboard.
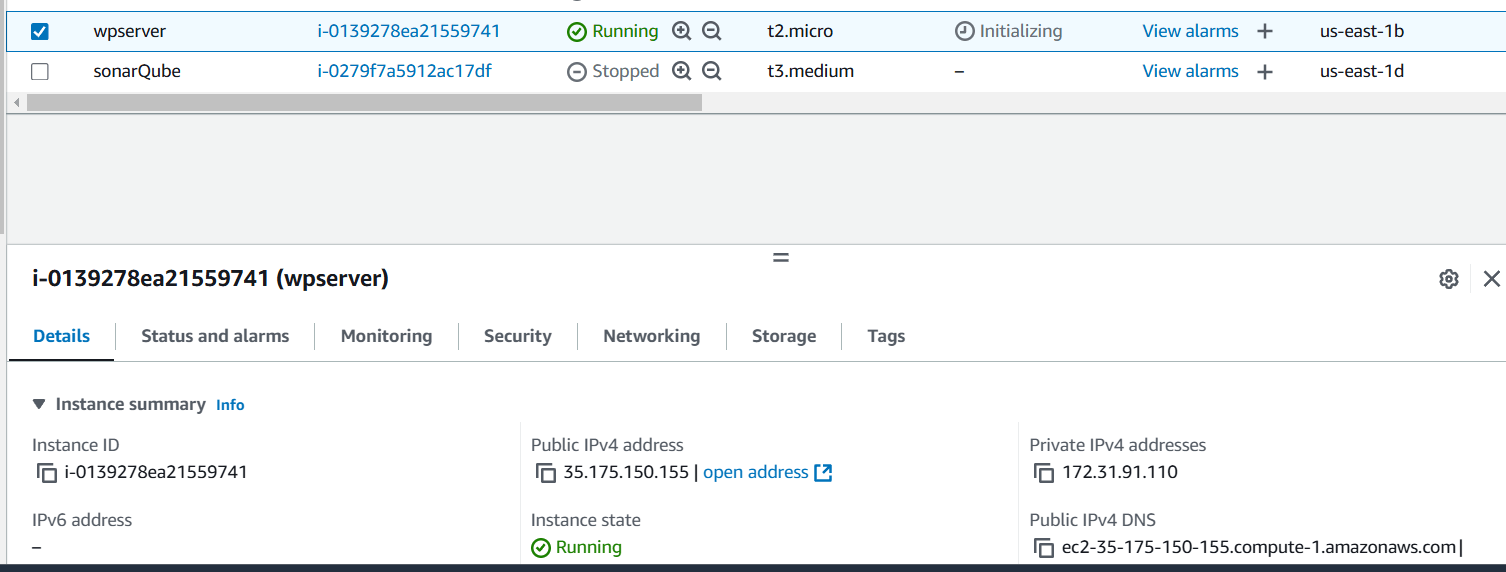
STEP 1: Go to aws console verify created the instance.
- Select the public IP and paste your browser.
STEP 2: Select English and click continue.
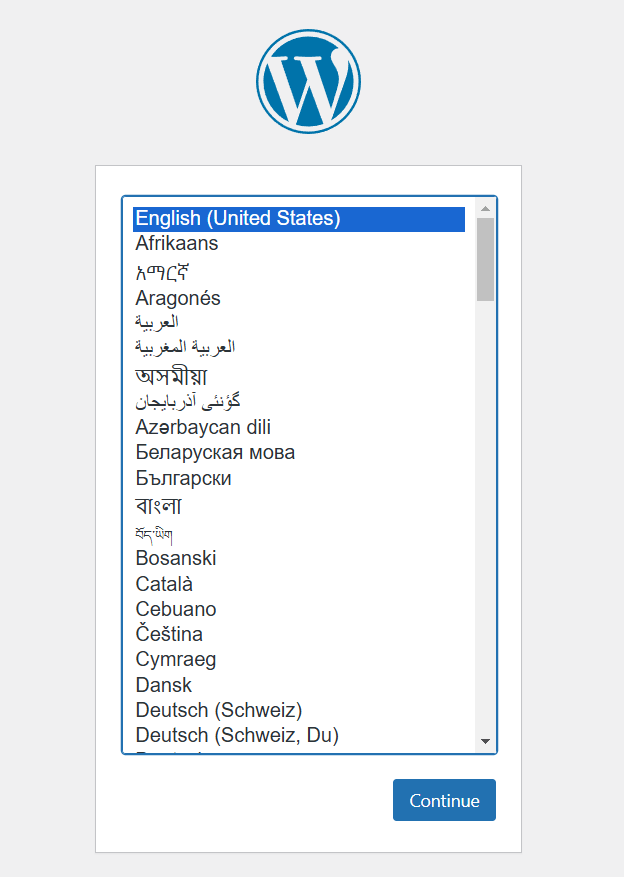
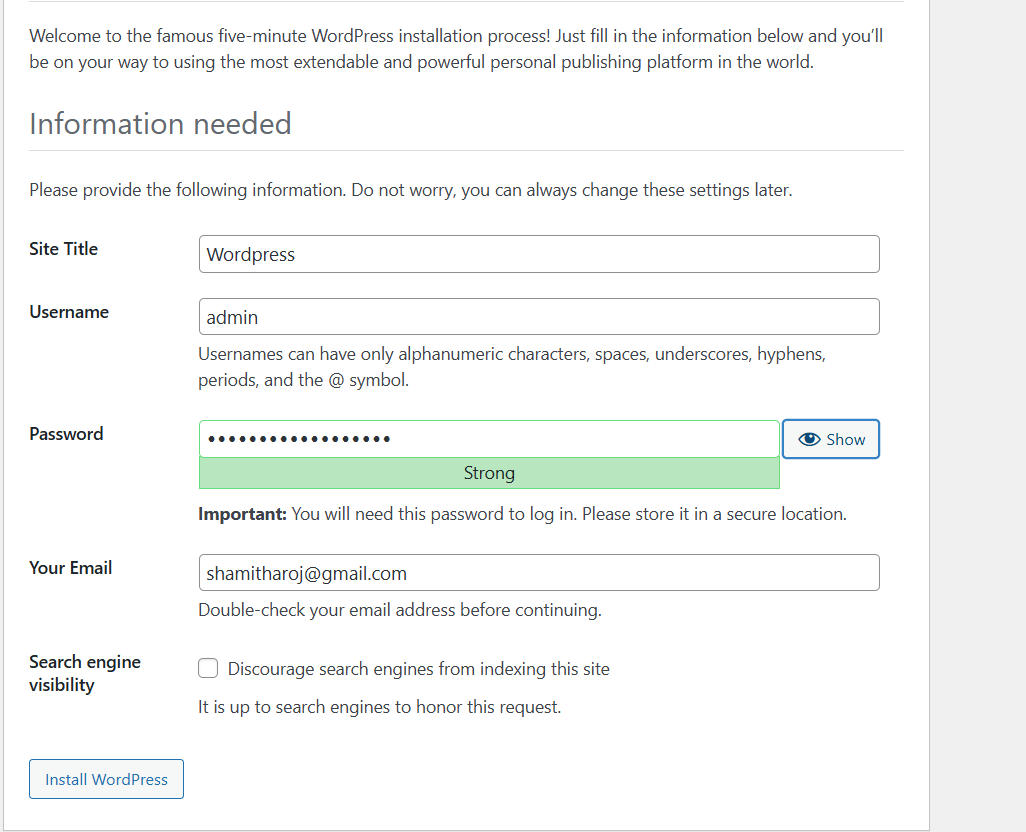
STEP 3: Enter the Title , Username , Email.
- Click on WordPress.
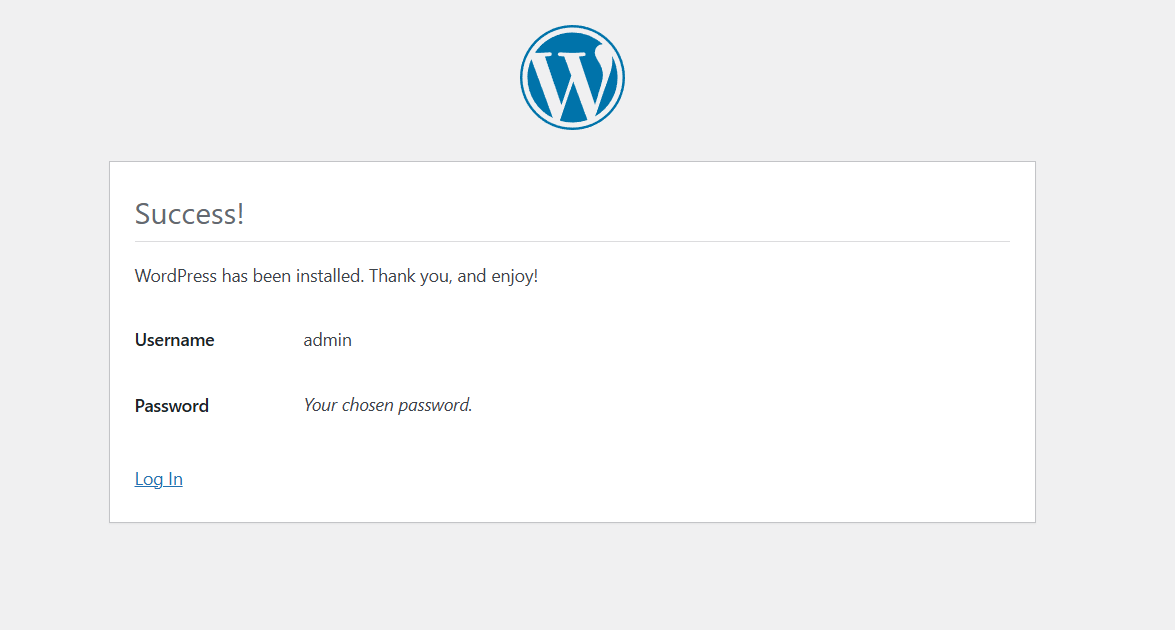
Step 4 : Click on Log In button.
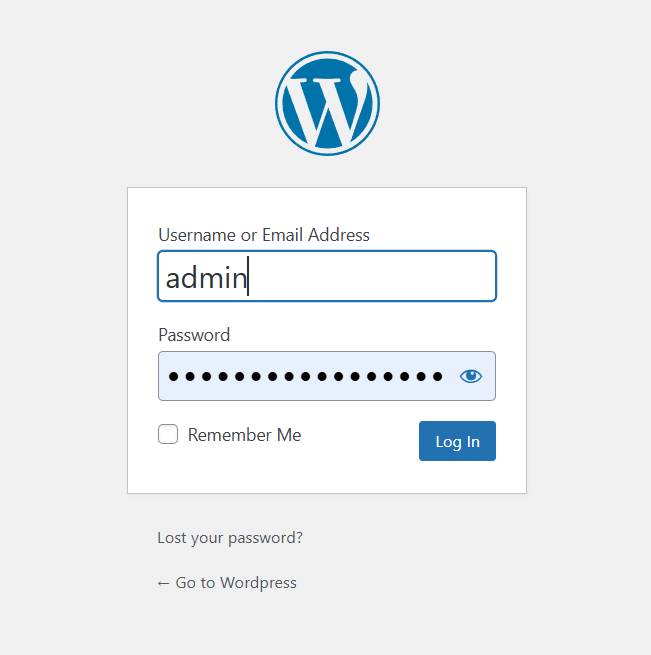
STEP 5 : Now you will see wordpress dashboard.
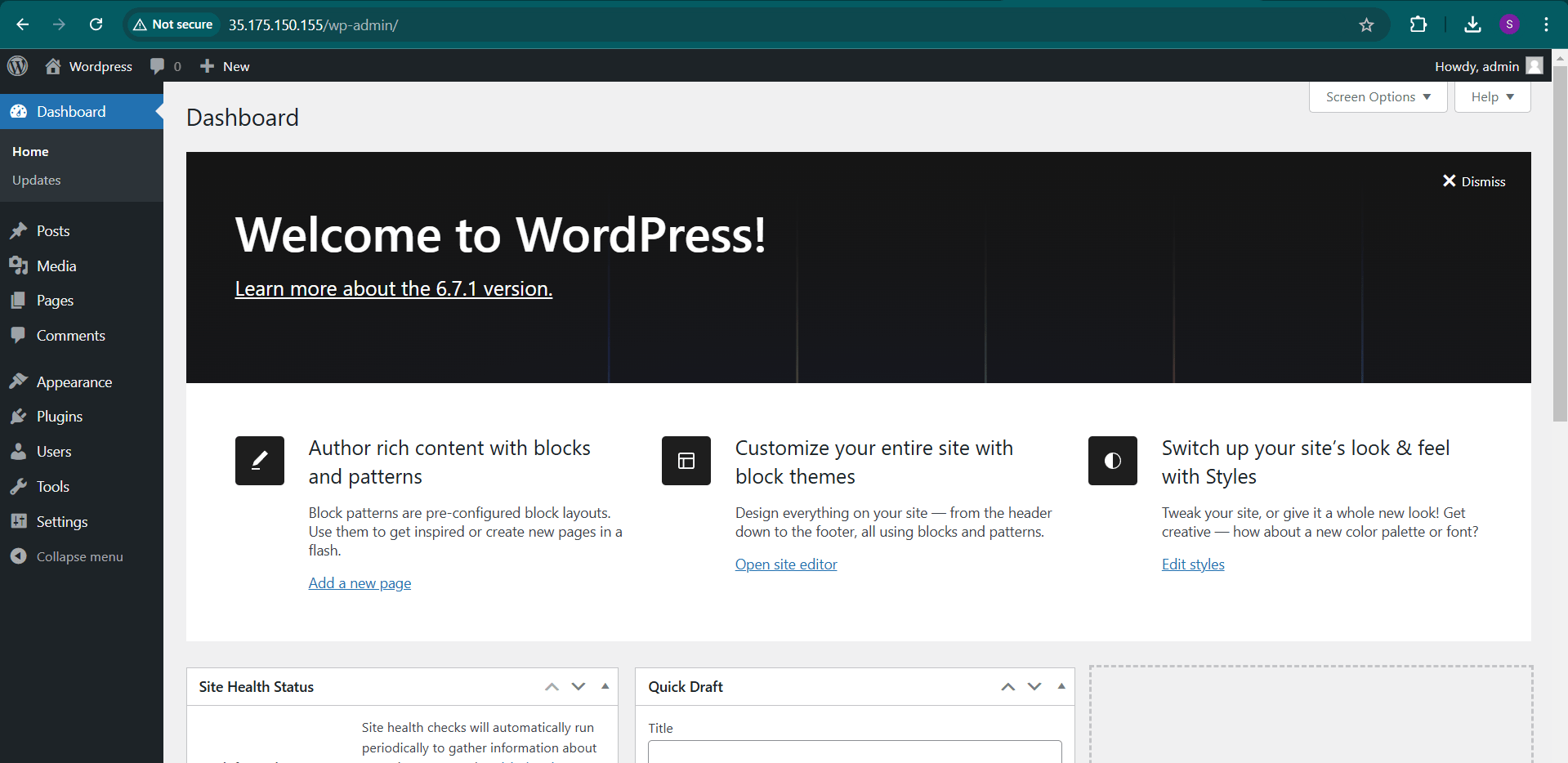

Conclusion.
Building a WordPress website using Terraform in Visual Studio Code is an excellent way to automate the infrastructure deployment process, especially when working in a cloud environment like AWS. By leveraging Terraform, you can ensure that your WordPress setup is repeatable, scalable, and easily manageable.
Quick Guide: Installing Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (Elastic Stack) on Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Introduction.
The Elastic Stack (formerly known as the ELK Stack) is a set of tools commonly used for searching, analyzing, and visualizing large amounts of data in real-time. It consists of three components: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the steps to install and configure the Elastic Stack on an Ubuntu 22.04 server.

Elastic Search.
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine designed for handling large amounts of data quickly and efficiently. It is commonly used for full-text search, logging, and real-time analytics. Elasticsearch is built on top of Apache Lucene and is the core component of the Elastic Stack (often referred to as the ELK Stack, which includes Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana).
Logstash.
Logstash is an open-source data processing pipeline that helps you collect, transform, and transport data from various sources to different destinations. It is part of the Elastic Stack (formerly known as the ELK Stack), which also includes Elasticsearch and Kibana. Logstash is particularly useful for processing logs and event data, although it can handle a wide range of data formats and use cases.
Kibana.
Kibana is an open-source data visualization and exploration tool that is part of the Elastic Stack (formerly the ELK Stack, which includes Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana). Kibana allows users to visualize, explore, and analyze data stored in Elasticsearch in an interactive, intuitive way. It is often used to display logs, metrics, and other types of data collected and indexed by Elasticsearch.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure your system meets the following prerequisites:
- Ubuntu 22.04 server.
- At least 4 GB of RAM and 20 GB of free disk space.
- A non-root user with sudo privileges.
- An active internet connection.
TASK 1: Install Java And Nignx.
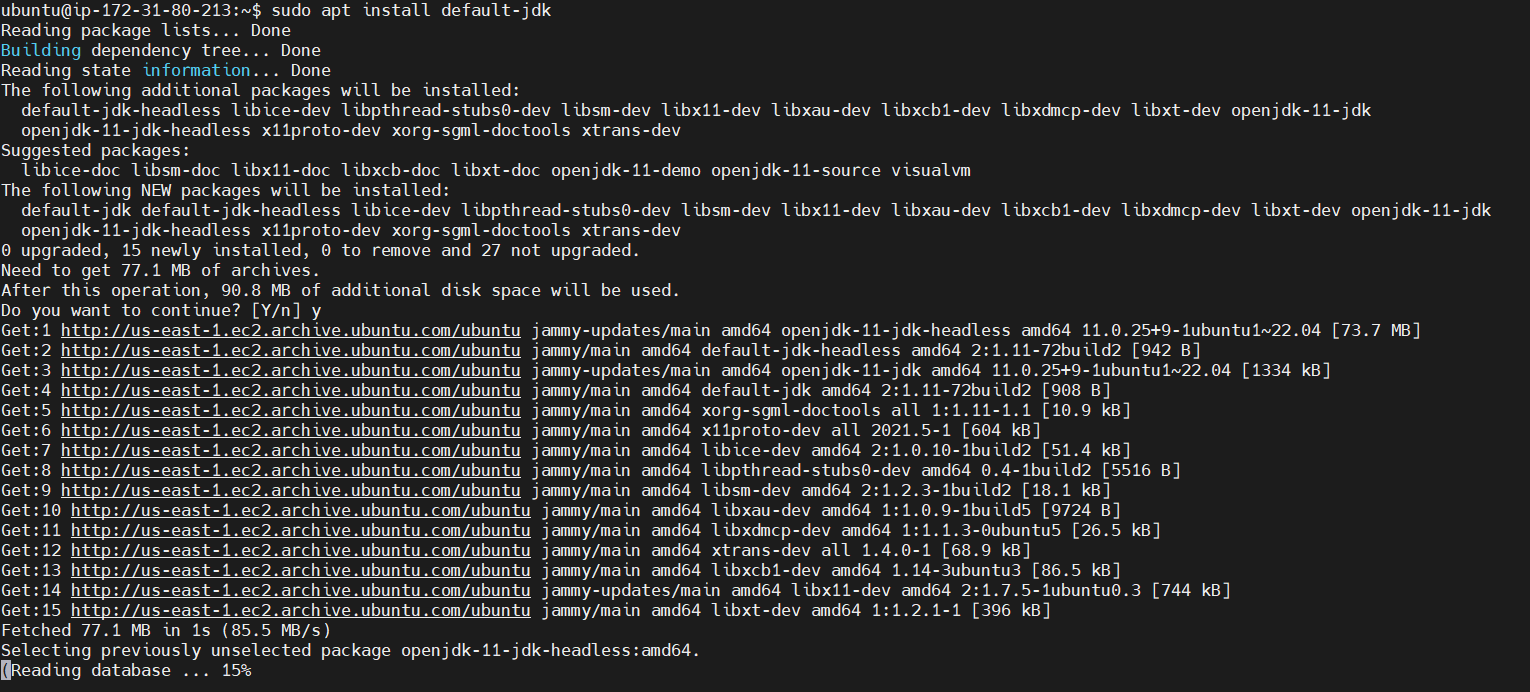
STEP 1: Install java using following commands.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install default-jdk
java -version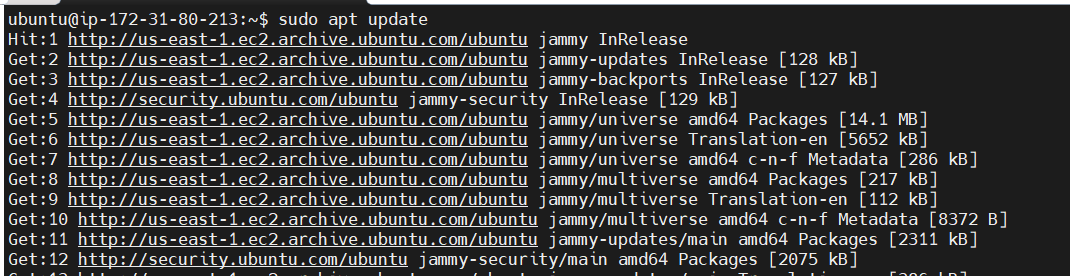

STEP 2: Nginx installed Using the below command.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
sudo ufw app list
sudo ufw allow 'Nginx HTTP'
sudo ufw status
systemctl status nginx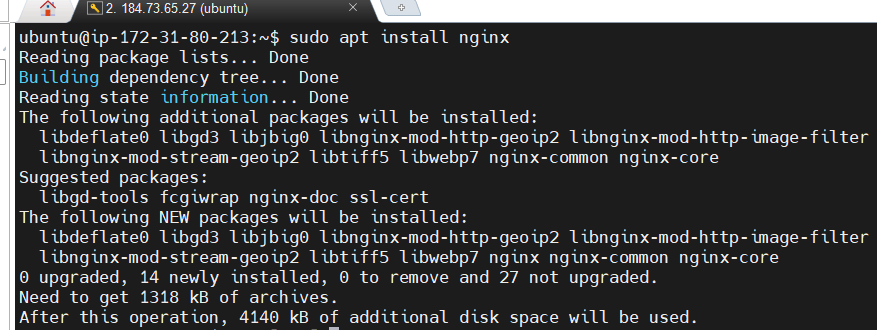
TASK 2: Install ElasticSearch.
STEP 1: Install elastic search using the following command.
curl -fsSL https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch |sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elastic.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elastic.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install elasticsearch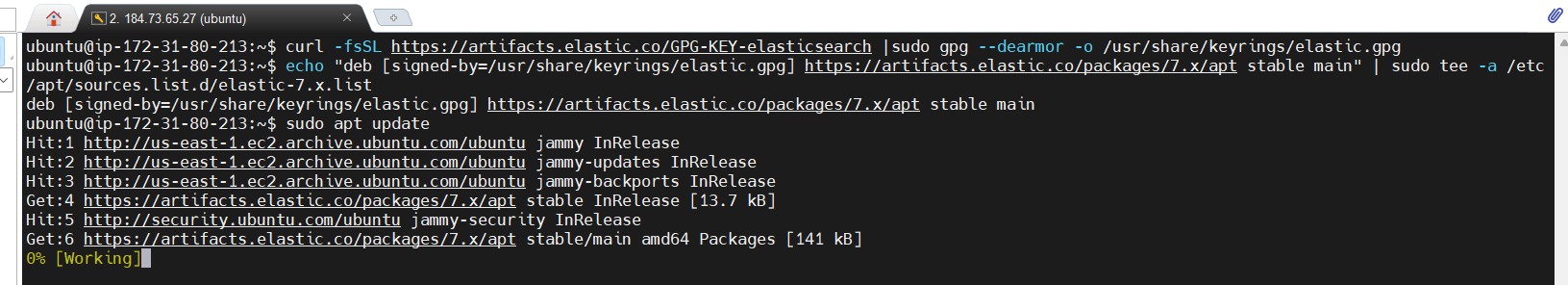
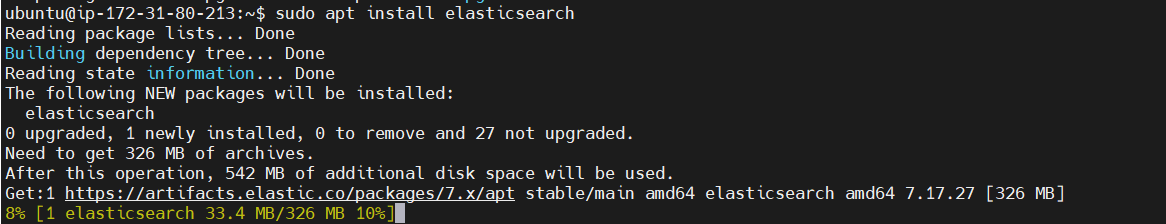
STEP 2: configuration file, elasticsearch.yml.
sudo nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlSTEP 3: Edit the Network host : Local Host.
- Save the file.
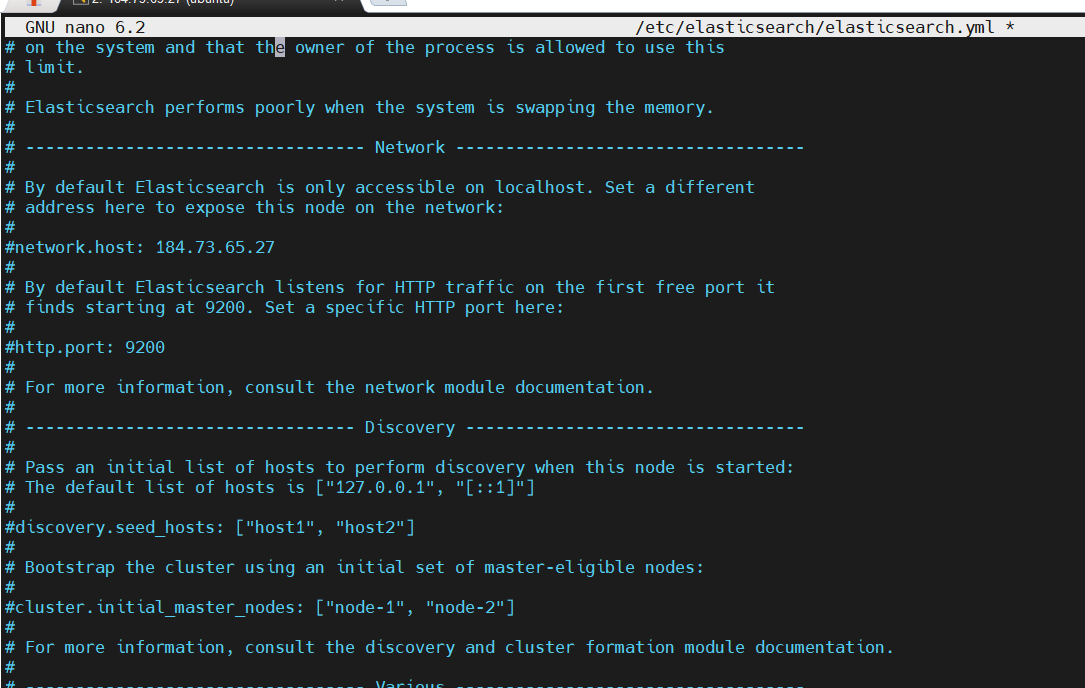
STEP 4: Start the elasticsearch.
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
curl -X GET "localhost:9200"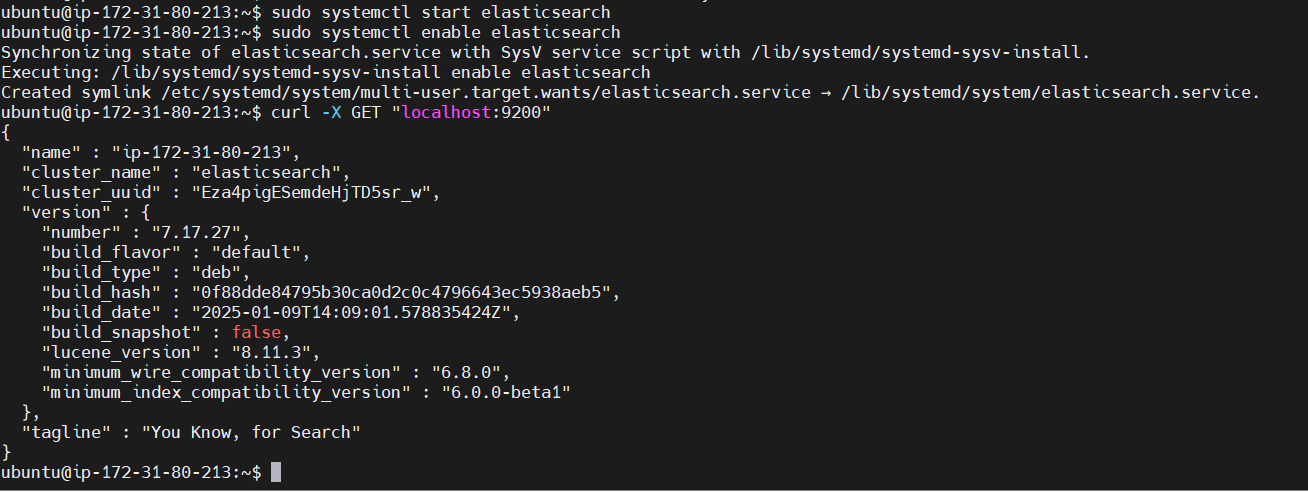
TASK 3: Install logstash.
STEP 1: Install loogstash package, Using the following command.
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elastic-keyring.gpg
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elastic-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list
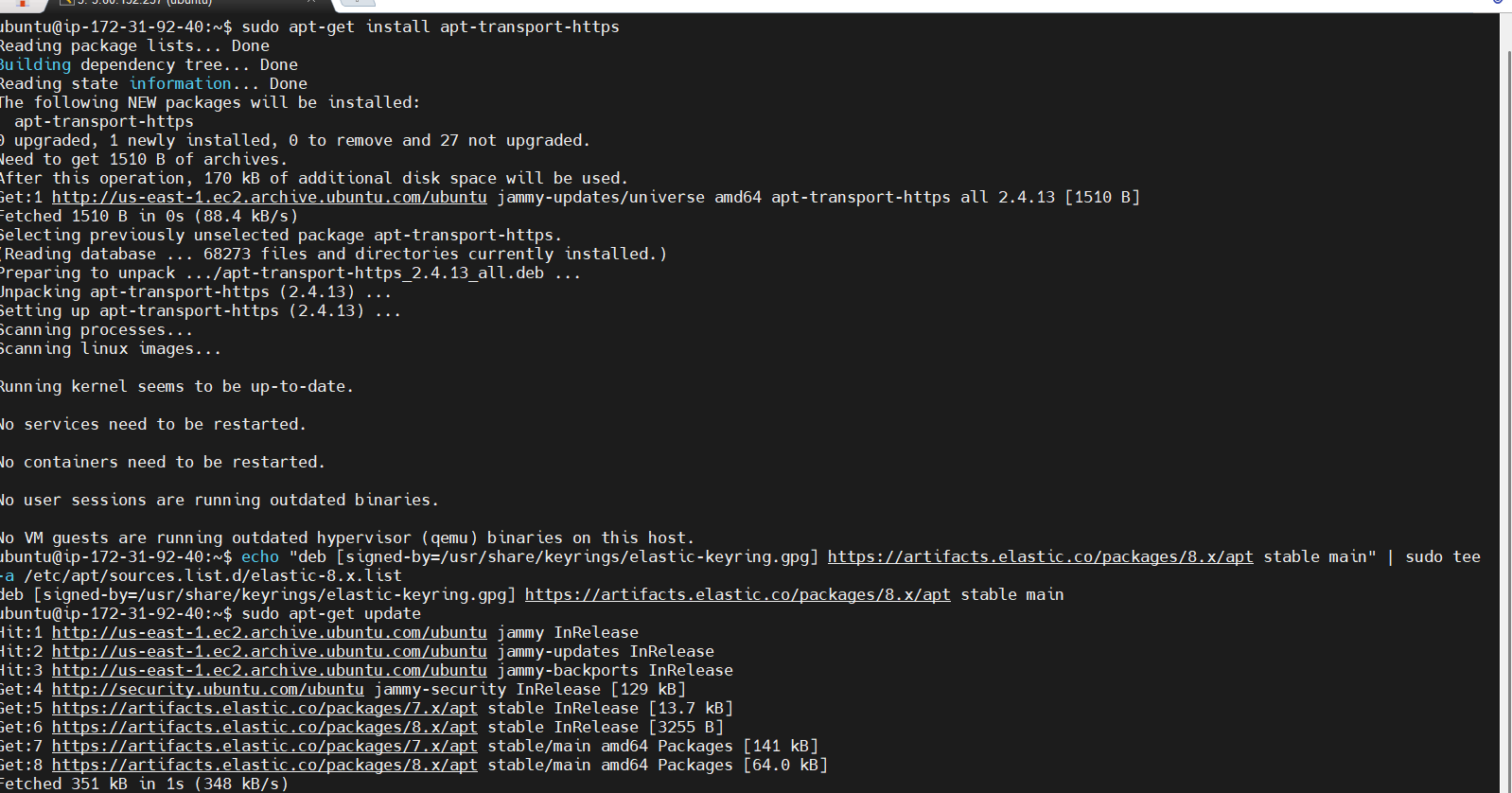
STEP 2: Enter the command.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install logstash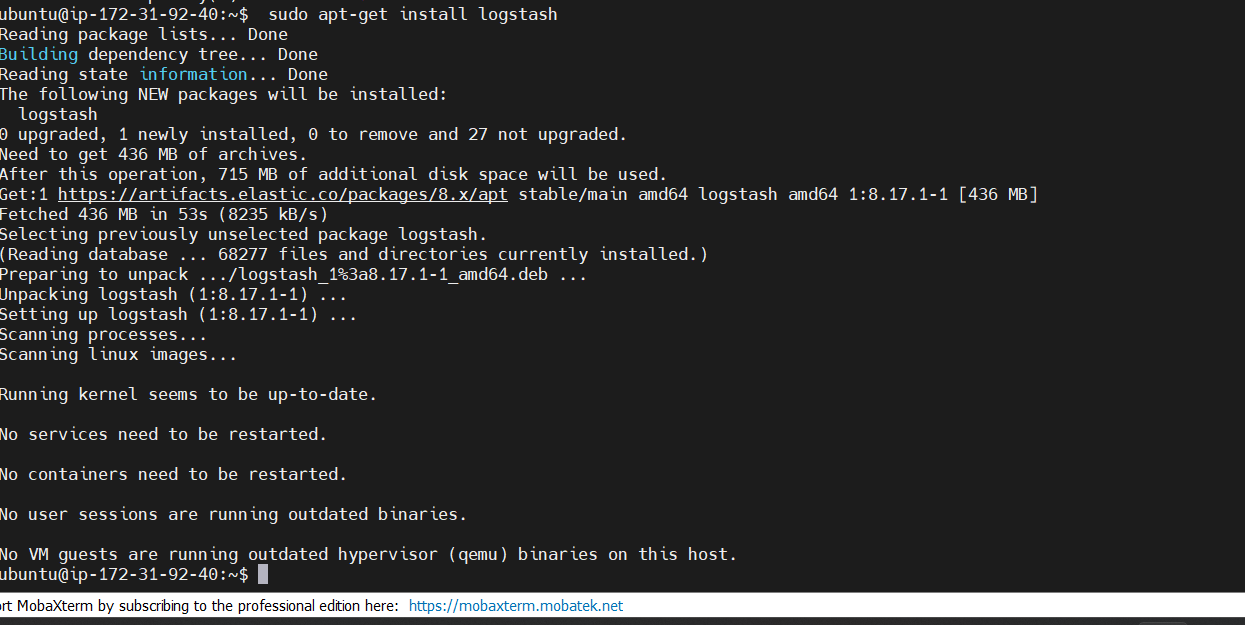
STEP 3: Start the logstash.
sudo systemctl start logstash
sudo systemctl enable logstash
sudo systemctl enable logstash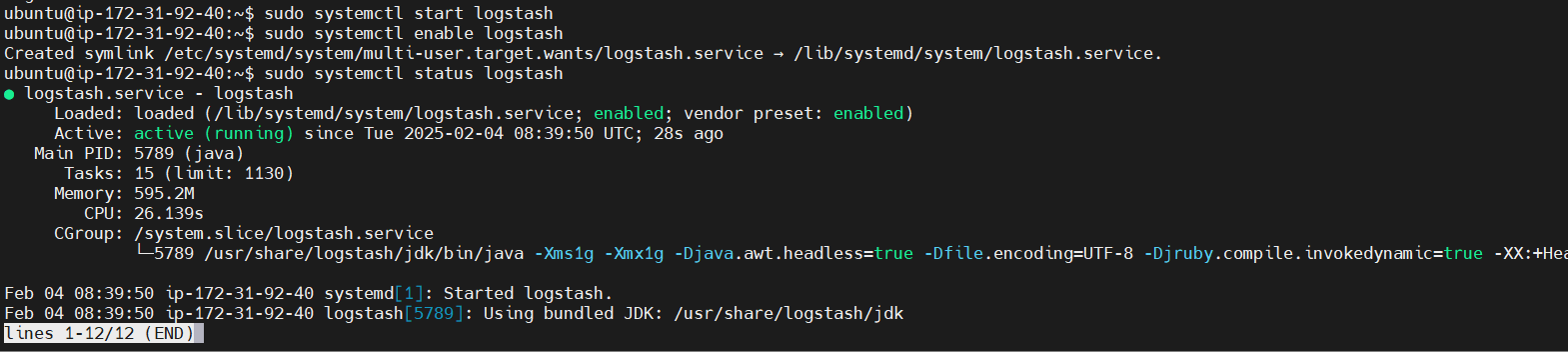
TASK 4: Install Kibana.
STEP 1: Enter the following command.
sudo apt install kibana
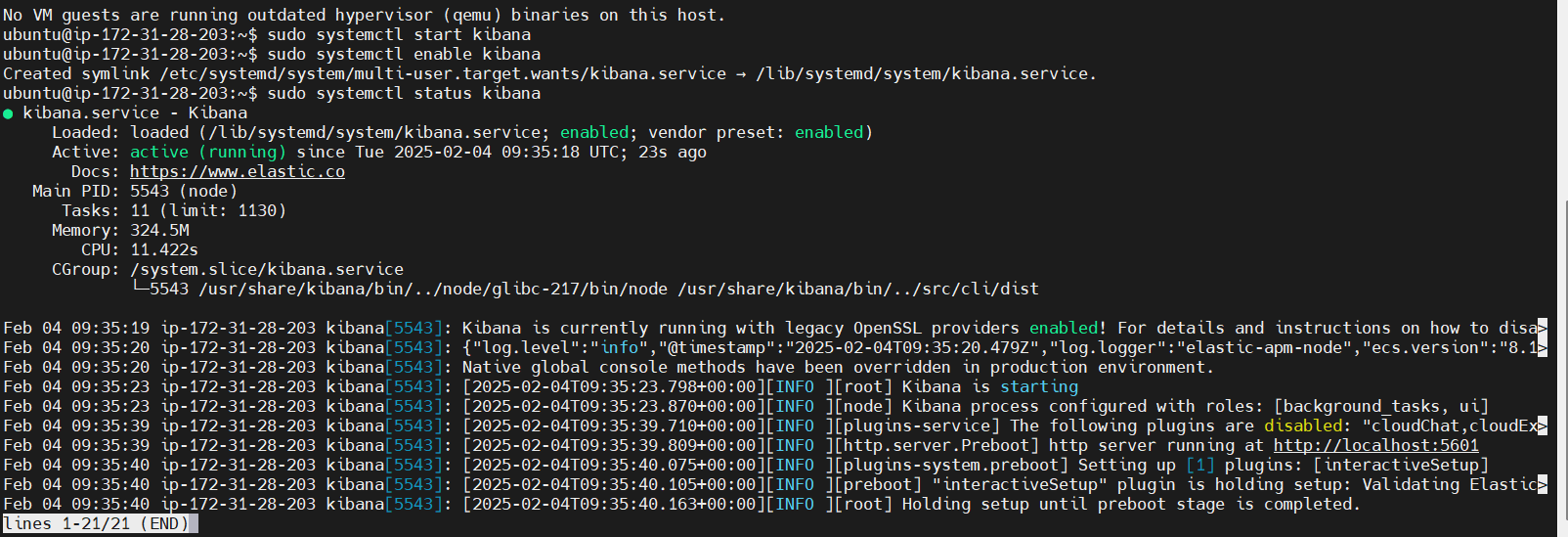
sudo systemctl enable kibana
sudo systemctl start kibana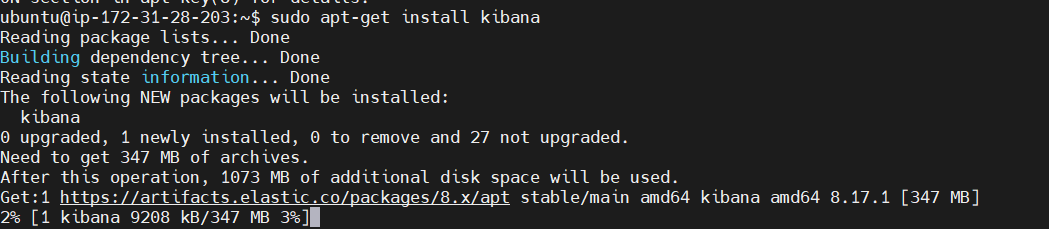

Conclusion.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed the Elastic Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) on your Ubuntu 22.04 server. You can now start ingesting, processing, and visualizing data in real time. With the flexibility and power of the Elastic Stack, you’ll be able to build robust data processing pipelines and create insightful visualizations for your data.















