Master Ansible: How to Write Your First Playbook on Ubuntu.
Introduction.
Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. It simplifies managing IT infrastructure by defining tasks in YAML-based playbooks. With Ansible, you can automate repetitive tasks across multiple systems, ensuring consistency and efficiency. It works through SSH and doesn’t require agent installation, making it lightweight and easy to use. Playbooks are the heart of Ansible automation, defining a series of tasks to execute on specified hosts. Ansible’s declarative language ensures that tasks are executed in the desired state. It supports various modules for tasks like package installation, service management, and file manipulation. By using Ansible, teams can achieve faster, error-free, and repeatable deployments. It integrates well with cloud platforms and DevOps pipelines. Ansible is popular for its simplicity, scalability, and flexibility, making it a key tool for modern system administration.

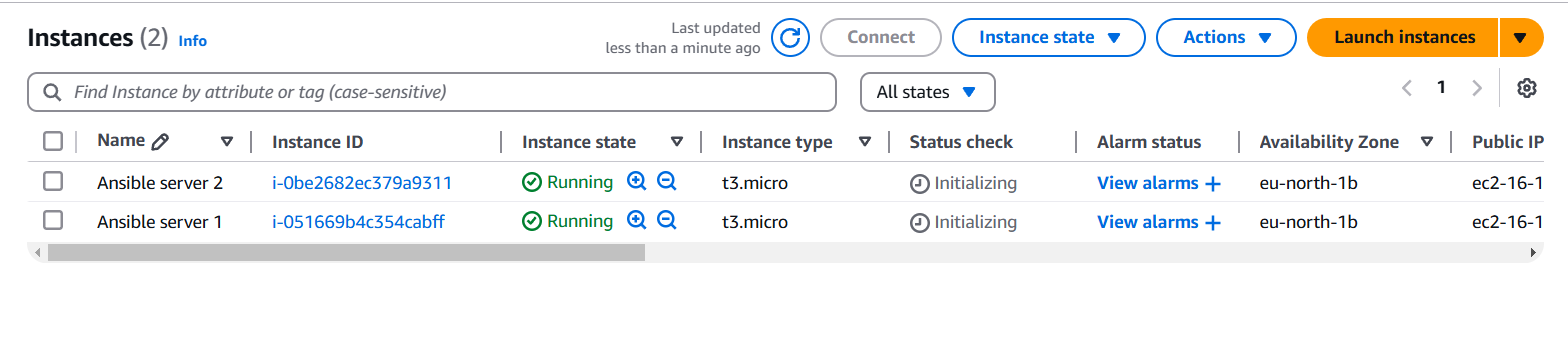
Step 1: Install Ansible
- Update the package index: Open your terminal and update your package list to ensure that you have the latest version of the software.
sudo apt update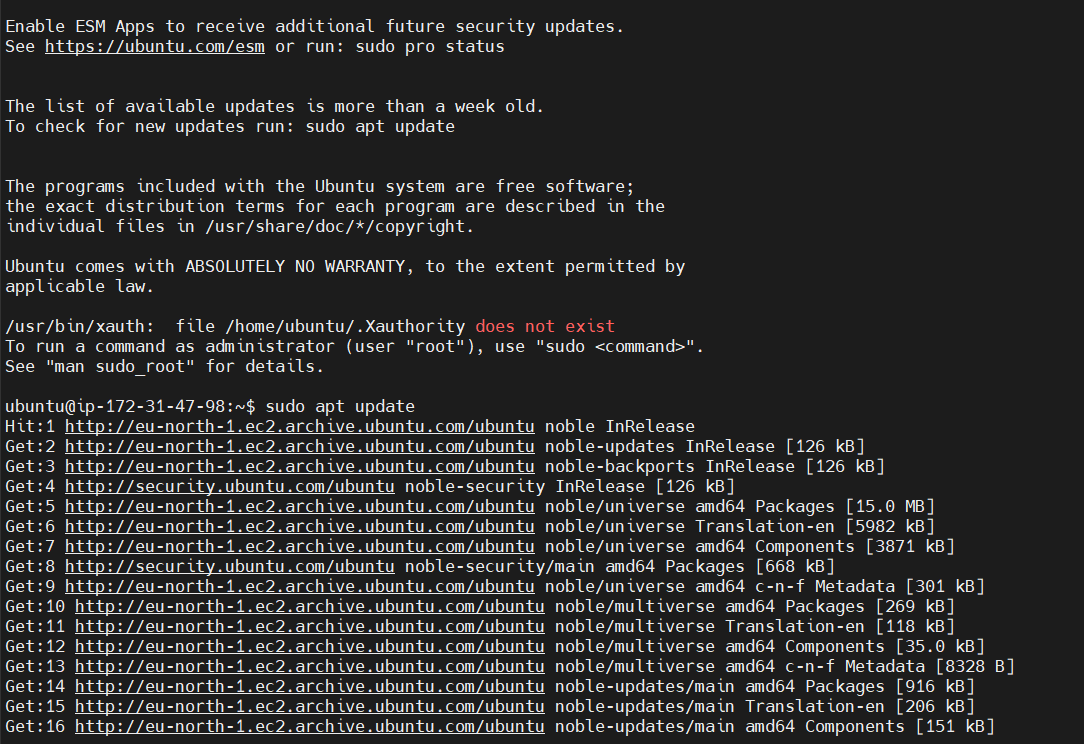
Install Ansible: You can install Ansible by using the following command:
sudo apt install ansible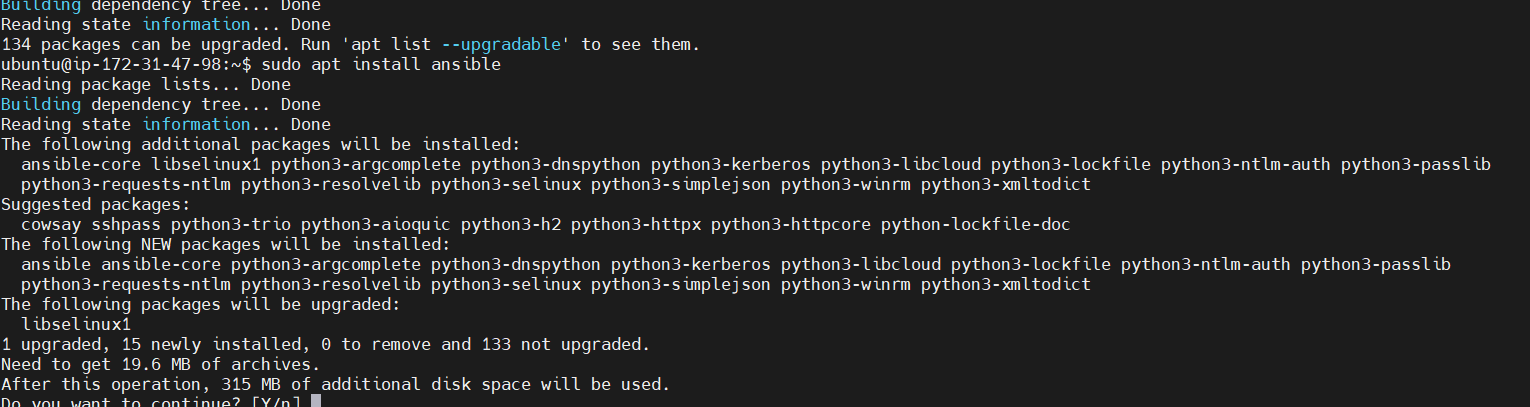
Verify Installation: Check that Ansible has been successfully installed:
ansible --version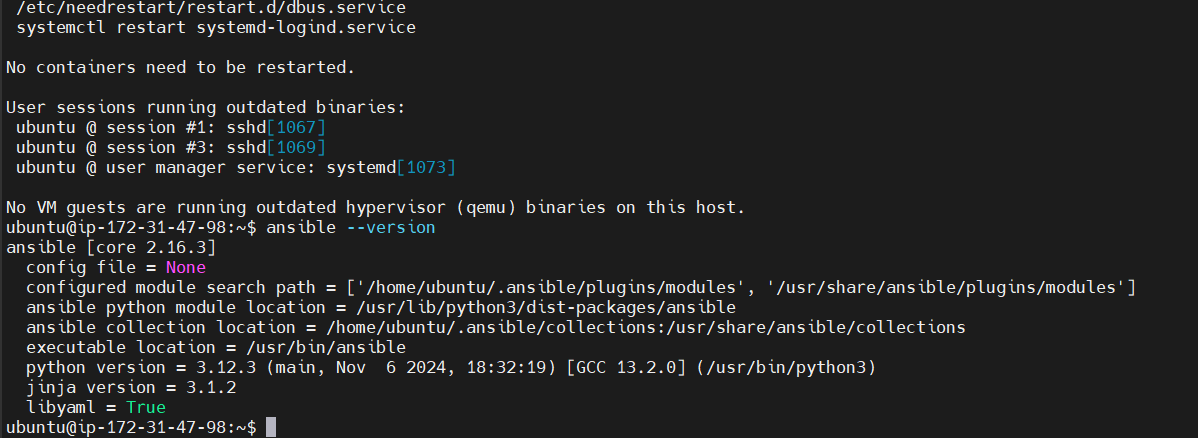
Step 2: Set Up the Inventory File
Ansible requires an inventory file that lists the hosts it will manage. By default, Ansible uses /etc/ansible/hosts, but you can create a custom inventory file if needed.
- Create an inventory file: Create a new inventory file to specify the servers you want to manage.
sudo nano /etc/ansible/hosts
Example hosts file:
[web_servers]
192.168.1.100
192.168.1.101
[db_servers]
192.168.1.200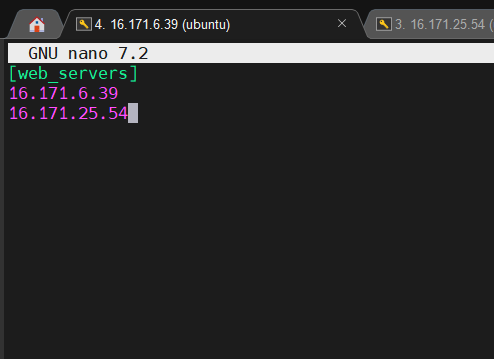
Check your inventory: You can verify the hosts in your inventory file with the following command:
ansible-inventory --list -i /etc/ansible/hosts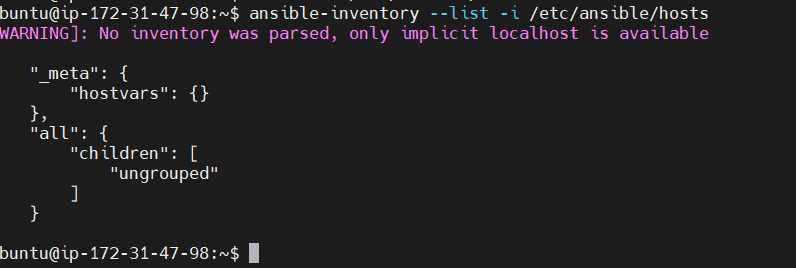
Step 3: Write Your First Ansible Playbook
- Create a playbook file: Playbooks are written in YAML format. Create a new playbook file, for example
first-playbook.yml:
nano first-playbook.yml
Write the playbook: Here’s an example playbook that installs nginx on the web servers.
---
- name: Install nginx on web servers
hosts: web_servers # This specifies the group of servers defined in your inventory file
become: yes # Run tasks with sudo
tasks:
- name: Install nginx package
apt:
name: nginx
state: present
update_cache: yes # Update apt cache before installation
- name: Ensure nginx is running
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: yes # Ensure nginx starts on boot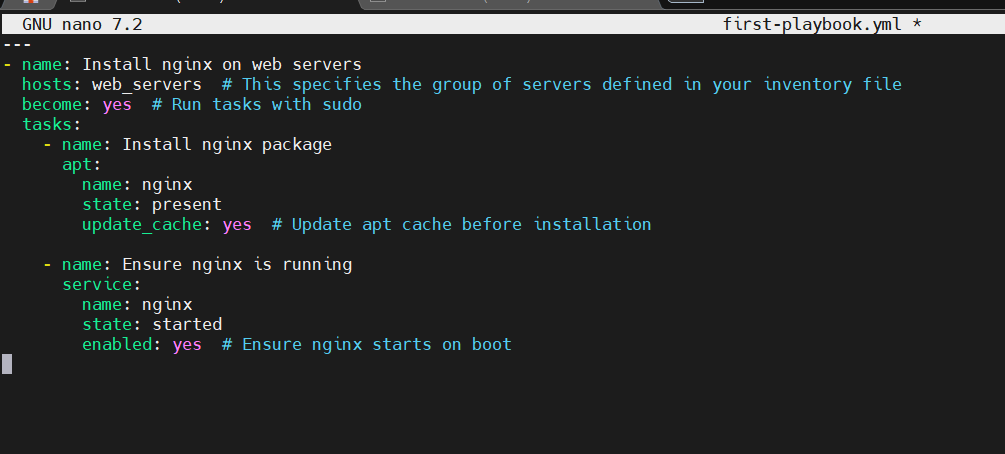
name: Describes what the playbook does.hosts: Specifies which hosts this playbook applies to. In this case, it applies to theweb_serversgroup.become: yes: Indicates that the tasks will be run with elevated privileges (sudo).tasks: A list of tasks to be executed on the remote host. In this example, it installsnginxand starts the service.
Step 4: Run the Playbook
- Execute the playbook: To execute the playbook, run the
ansible-playbookcommand. If you’re using the default inventory file located at/etc/ansible/hosts, you can run:
ansible-playbook -i /etc/ansible/hosts first-playbook.yml
-i /etc/ansible/hosts: This specifies the inventory file to use.first-playbook.yml: This is the playbook you want to execute.
Watch the output: Ansible will connect to the hosts specified in the inventory file and execute the tasks defined in the playbook. The output will look something like this:
PLAY [Install nginx on web servers] ***
TASK [Install nginx package] ***
ok: [192.168.1.100] => (item=None) => {
"changed": false,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "present"
}
TASK [Ensure nginx is running] ***
ok: [192.168.1.100] => (item=None) => {
"changed": false,
"name": "nginx",
"state": "started"
}
PLAY RECAP ***
192.168.1.100 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0Step 5: Verify the Changes
After the playbook finishes running, you can verify the changes:
- Check if nginx is installed: On the target machine (e.g., 192.168.1.100), you can check the status of
nginx:
systemctl status nginx
Check the web server: Open a web browser and navigate to the server’s IP address (e.g., http://192.168.1.100). You should see the default nginx welcome page.

Conclusion.
Congratulations! You’ve written your first Ansible playbook to install and manage Apache on Ubuntu. Playbooks are powerful, and you can expand them by adding more tasks, roles, and configurations to automate even more complex workflows.
Ansible playbooks allow you to define automation tasks that are easy to read and maintain. As you continue learning, you can explore more advanced topics like roles, handlers, and templates to make your playbooks even more flexible and reusable.
An Introduction to Amazon OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards.
Introduction.
Amazon OpenSearch is a fully managed, scalable search and analytics service that allows you to ingest, search, and analyze large volumes of data in real time. Built on the open-source Elasticsearch project, OpenSearch provides powerful search capabilities and is widely used for log analytics, application monitoring, and data exploration. With features like full-text search, filtering, and aggregation, OpenSearch helps organizations gain insights from complex datasets.
OpenSearch Dashboards, the companion visualization tool, enables users to create interactive and customizable visualizations. It allows you to explore your data, create dashboards, and monitor trends in real time. Together, Amazon OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards provide a robust platform for data-driven decision-making.

In this guide, we’ll explore the core features of Amazon OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards, highlighting how they work together to simplify data analysis and visualization.
STEP 1: Navigate Open search services and select managed cluster and click on create.
STEP 2: Enter the domain name.
- Domain Creation Method : Standard Create.
- Templates : Dev/test.
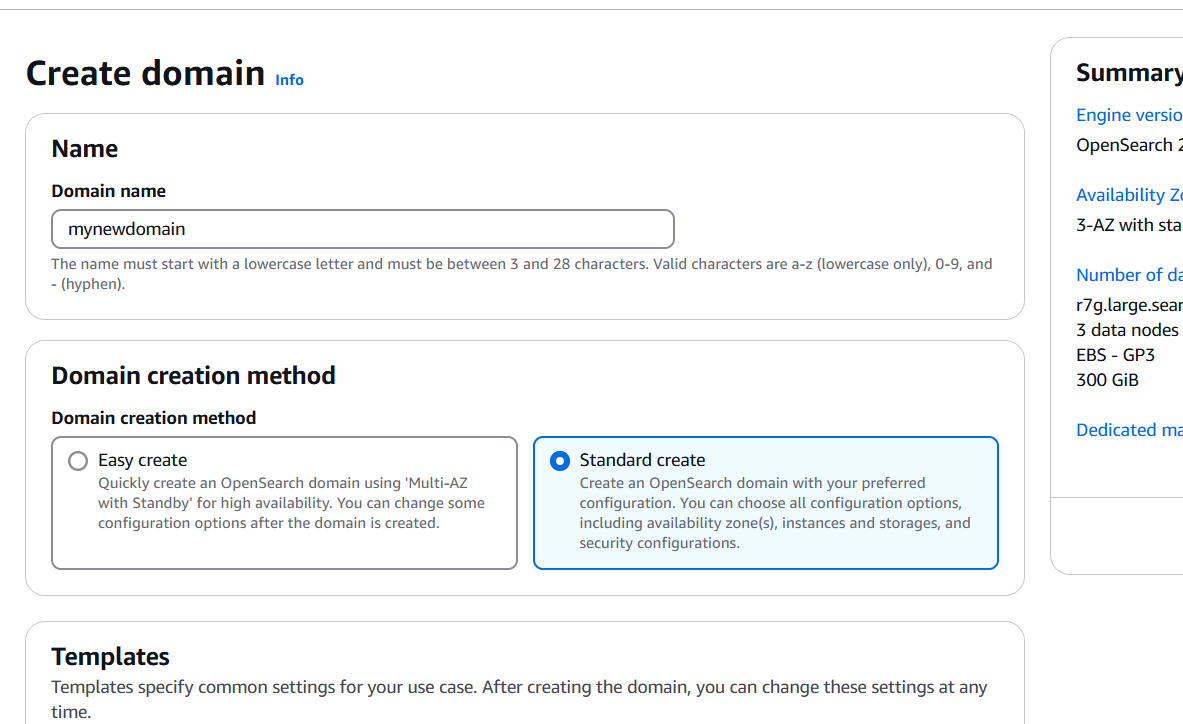
STEP 3: Deployment Option : Domain without standby.
- Select 1-AZ.
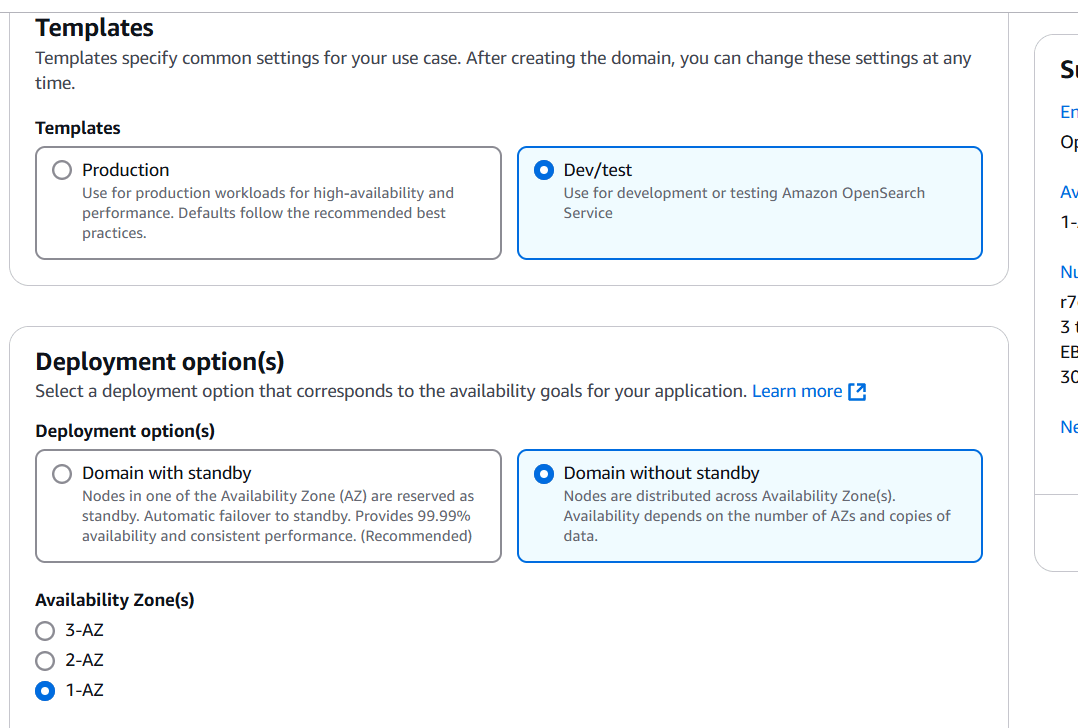
STEP 4: Select the version.
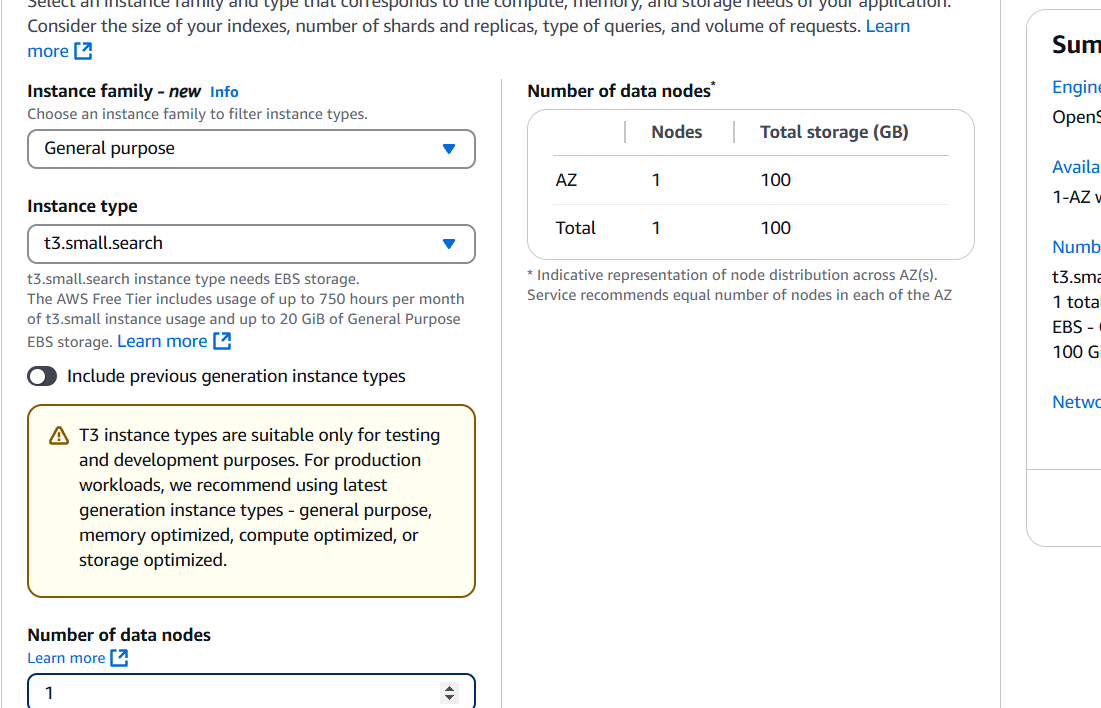
STEP 5: Instance family : General purpose.
Select instance Type.
STEP 6: Select Storage Type.
- EBS Volume type and size.
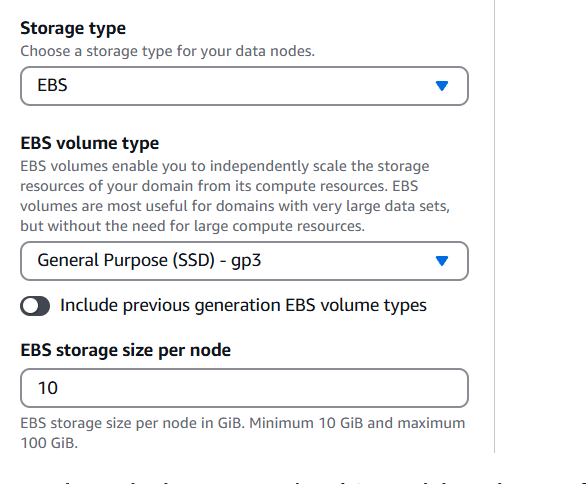
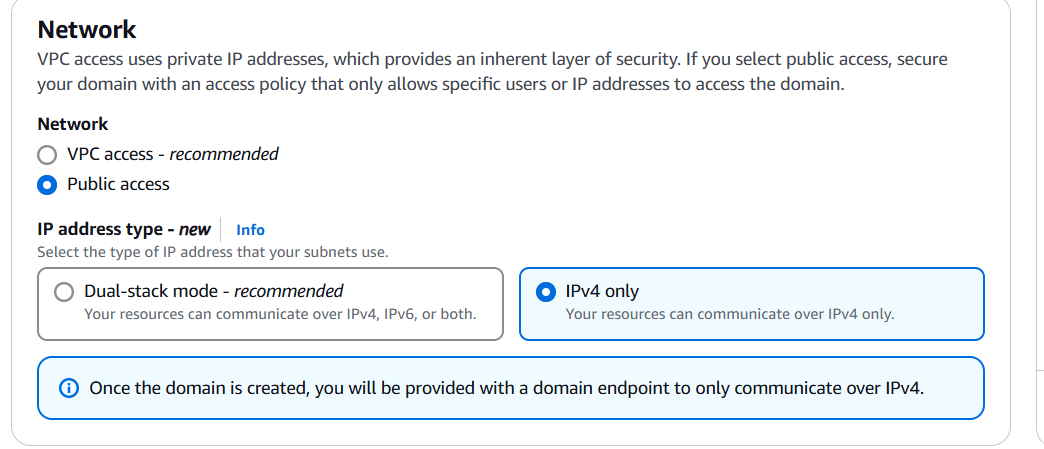
STEP 7: Next go to network and select public access.
- And select Ipv4 only.
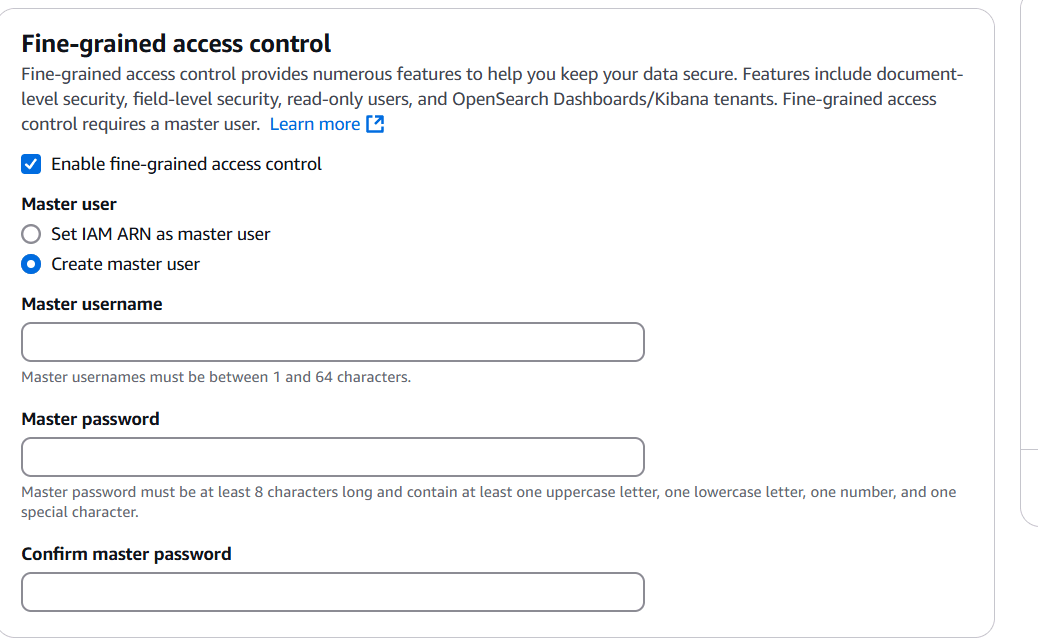
STEP 8: Select enable fine-grained access control.
- And select create master user.
STEP 9: Select domain access policy.

STEP 10: Click on create.
- Wait for the domain to be created, which may take 15-20 minutes, until the Domain Status is Active.
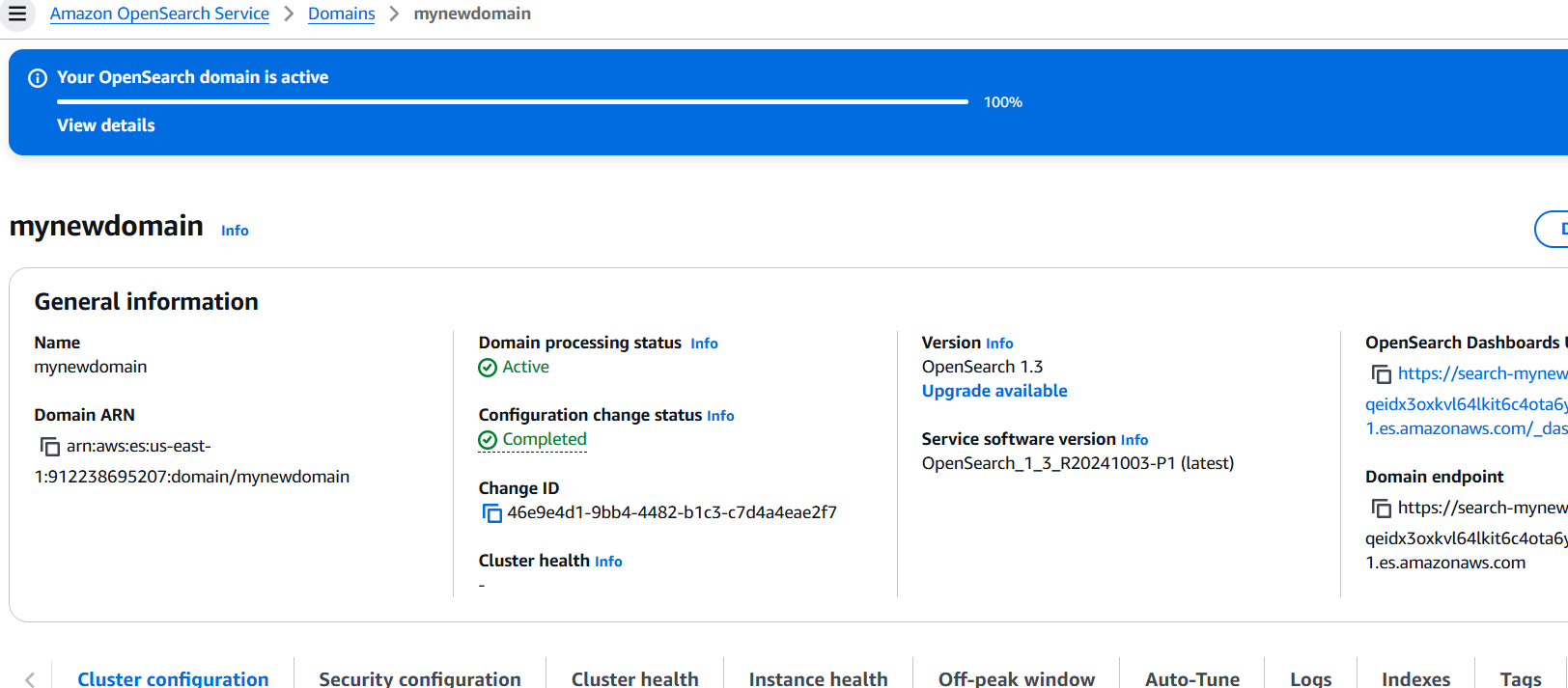
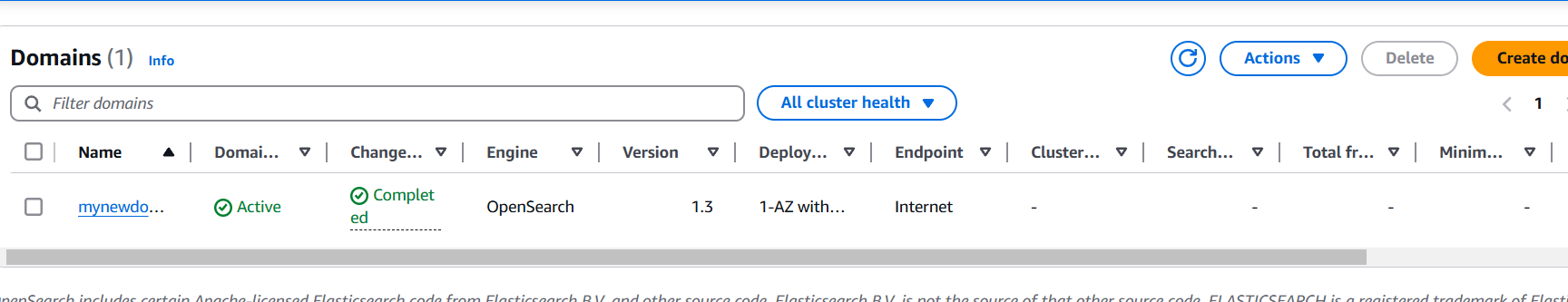
STEP 11: Copy dashboaed URL and enter the browser.
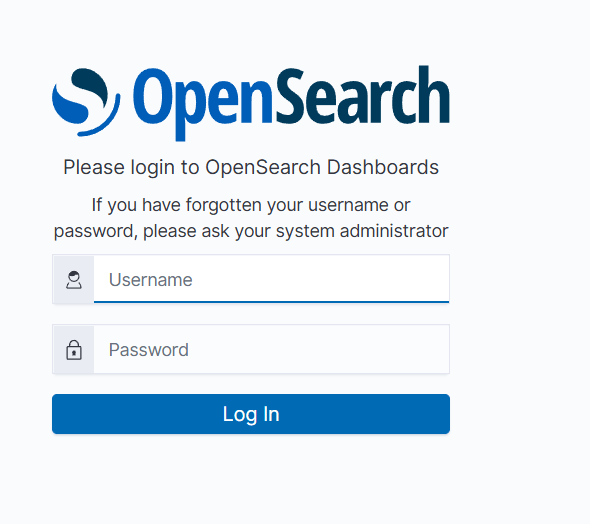
STEP 12: Enter the username and password.

Conclusion.
Amazon OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards offer a powerful, scalable solution for real-time search and analytics. With OpenSearch, you can easily ingest, search, and analyze large datasets, while OpenSearch Dashboards provides an intuitive interface for visualizing and exploring your data. Together, they enable organizations to unlock valuable insights, monitor trends, and make data-driven decisions with ease.
By leveraging these tools, you can enhance your search and analytics capabilities, whether for application monitoring, log analysis, or business intelligence. As an open-source solution, OpenSearch ensures flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making it a go-to choice for many cloud-based data projects.
Step-by-step guide to building a custom VPC and its components using Terraform.
Introduction.
When managing cloud infrastructure, creating a custom Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is one of the first and most crucial steps. A VPC allows you to define your network environment in the cloud, including subnets, IP ranges, routing tables, and more. By using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform, you can automate the process of building and managing a VPC, ensuring consistency, scalability, and easy reproducibility.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of building a custom VPC and configuring its essential components, such as subnets, security groups, and routing, using Terraform. Whether you’re new to Terraform or looking to expand your cloud infrastructure knowledge, this step-by-step tutorial will help you get up and running with a secure and efficient VPC setup.

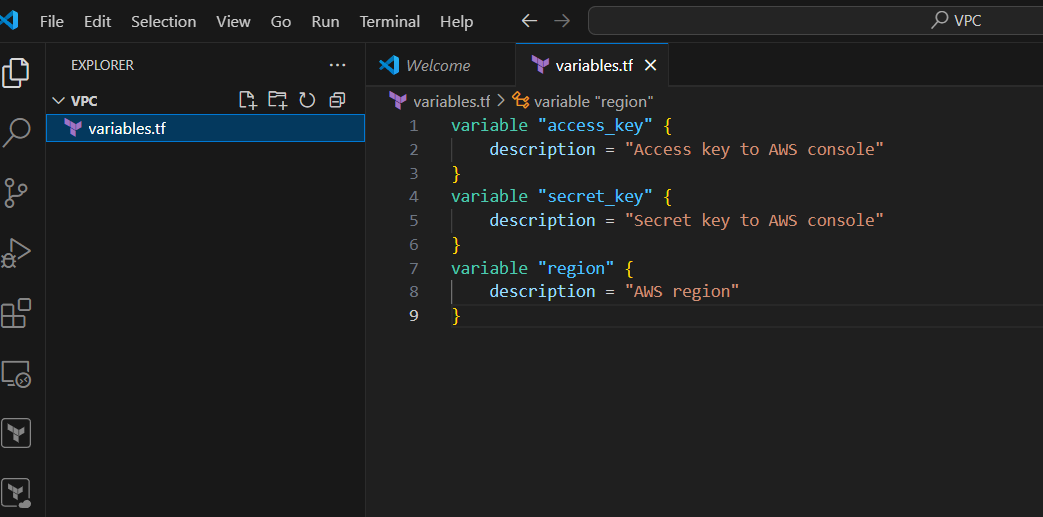
STEP 1: Open the folder and create the variable.tf file.
- Enter the following command and save the file.
variable "access_key" {
description = "Access key to AWS console"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key to AWS console"
}
variable "region" {
description = "AWS region"
}
STEP 2: Next Create terraform.tfvars file.
- Enter the following terrform script and click on save.
- Enter the access key and secret key.
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY"
secret_key = "YOUR_SECRET_KEY"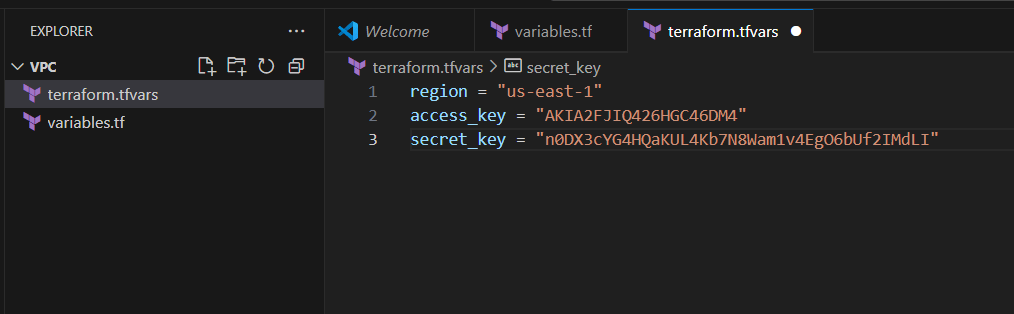
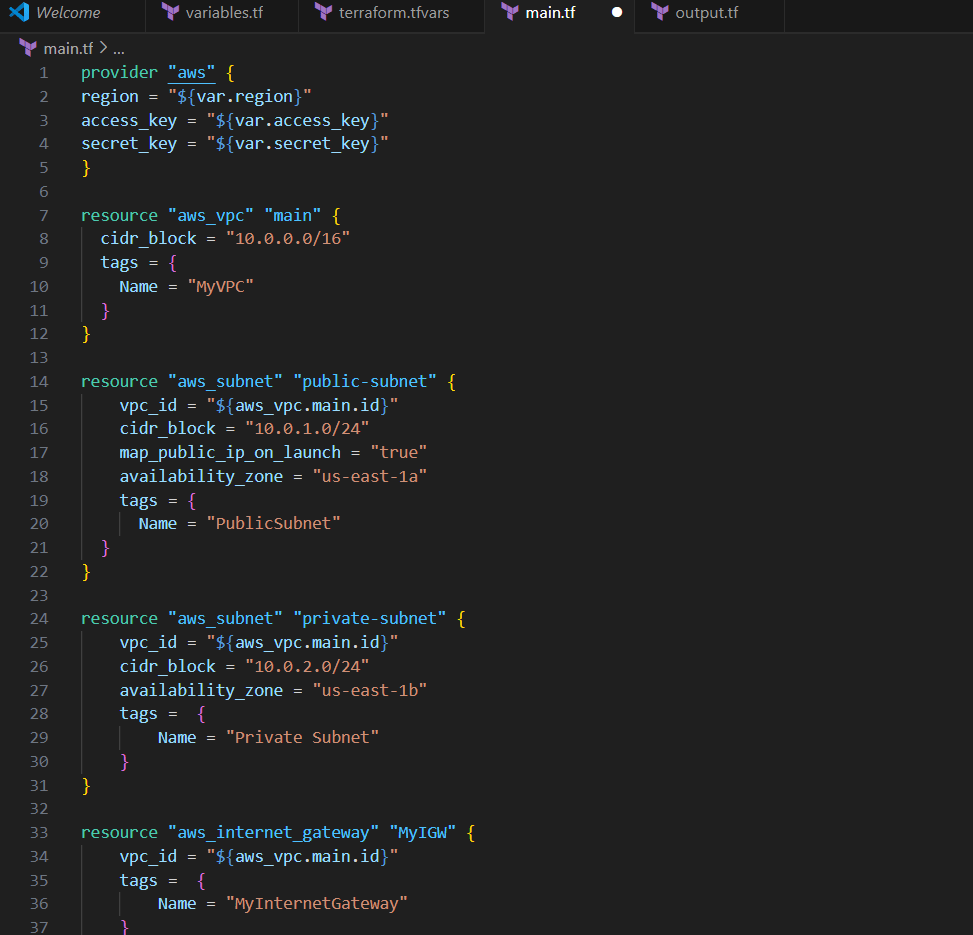
STEP 3: Create main.tf files.
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.region}"
access_key = "${var.access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.secret_key}"
}
resource "aws_vpc" "main" {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
tags = {
Name = "MyVPC"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "public-subnet" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "true"
availability_zone = "us-east-1a"
tags = {
Name = "PublicSubnet"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "private-subnet" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
cidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "us-east-1b"
tags = {
Name = "Private Subnet"
}
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "MyIGW" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
tags = {
Name = "MyInternetGateway"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "publicrt" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = "${aws_internet_gateway.MyIGW.id}"
}
tags = {
Name = "PublicRouteTable"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "publicrt" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = "${aws_internet_gateway.MyIGW.id}"
}
tags = {
Name = "PublicRouteTable"
}
}
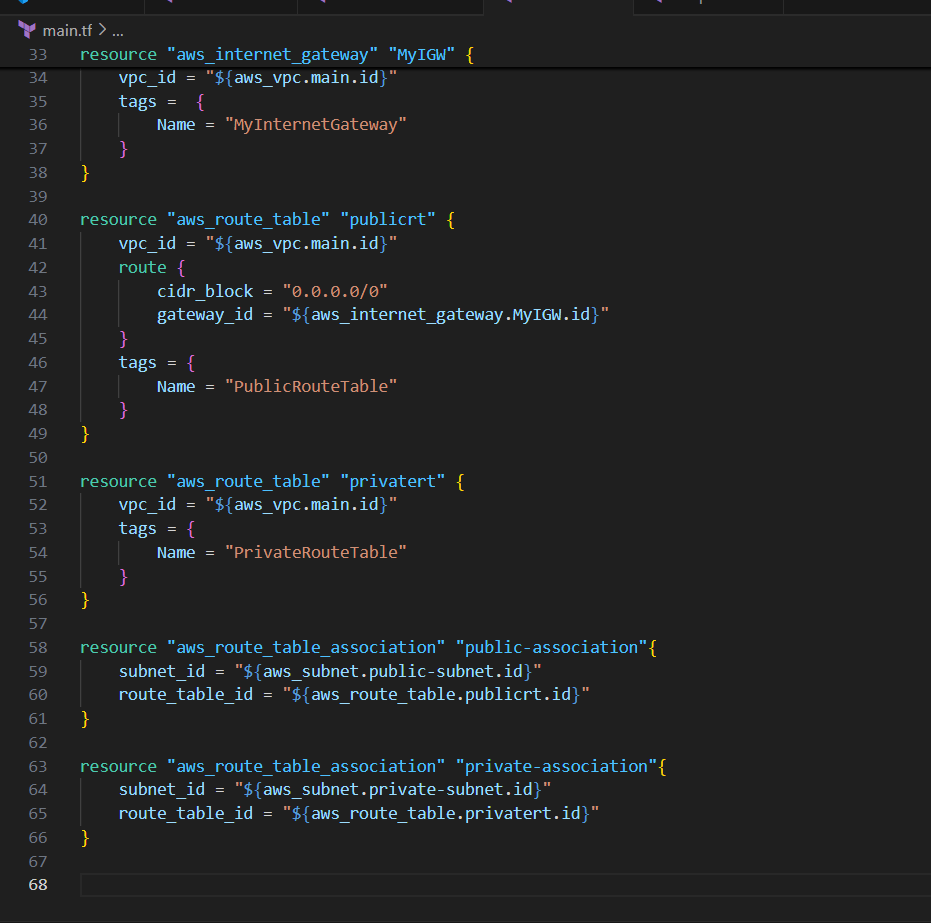
resource "aws_route_table" "privatert" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.main.id}"
tags = {
Name = "PrivateRouteTable"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public-association"{
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.public-subnet.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.publicrt.id}"
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private-association"{
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.private-subnet.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.privatert.id}"
}
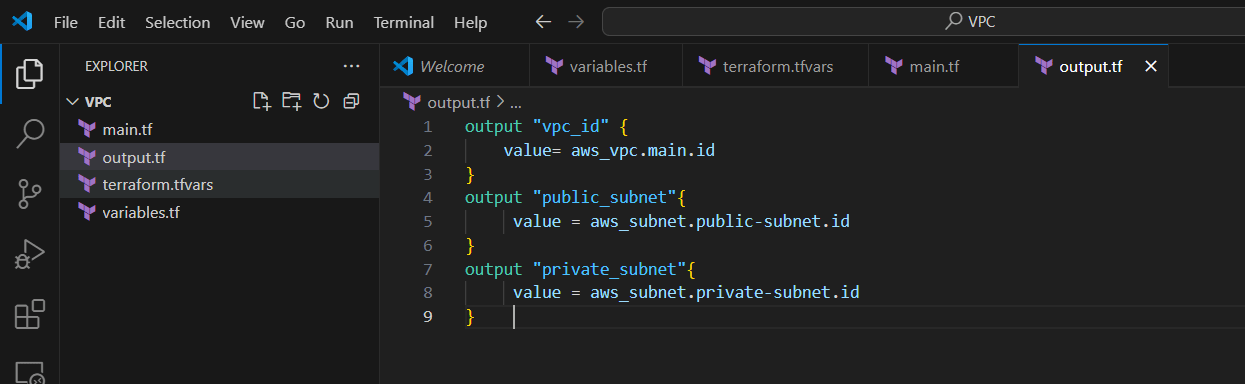
STEP 4: Create an output file.
- Paste the below content into the output.tf file.
output "vpc_id" {
value= aws_vpc.main.id
}
output "public_subnet"{
value = aws_subnet.public-subnet.id
}
output "private_subnet"{
value = aws_subnet.private-subnet.id
} 
STEP 5: Applying terraform configurations.
- Enter terraform init command.
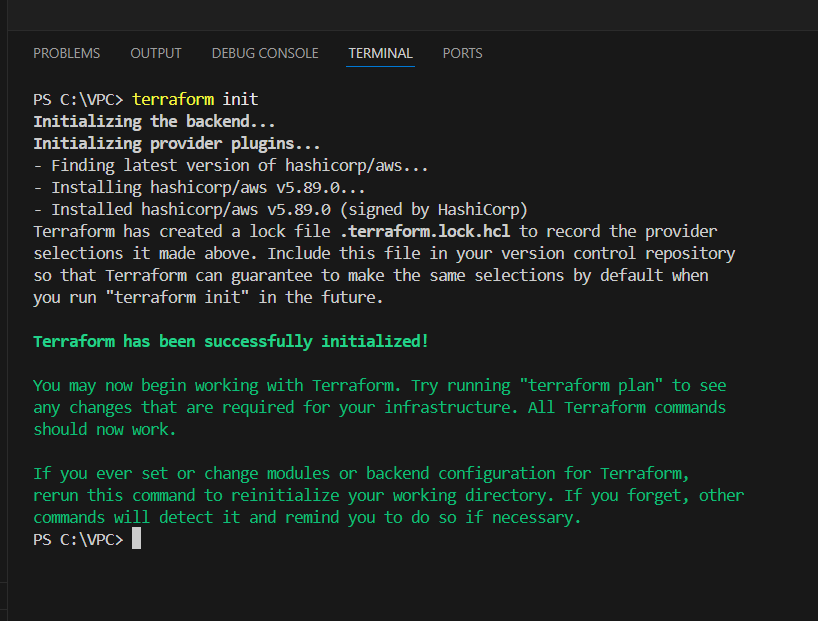
STEP 6: Next enter the terraform plan command.
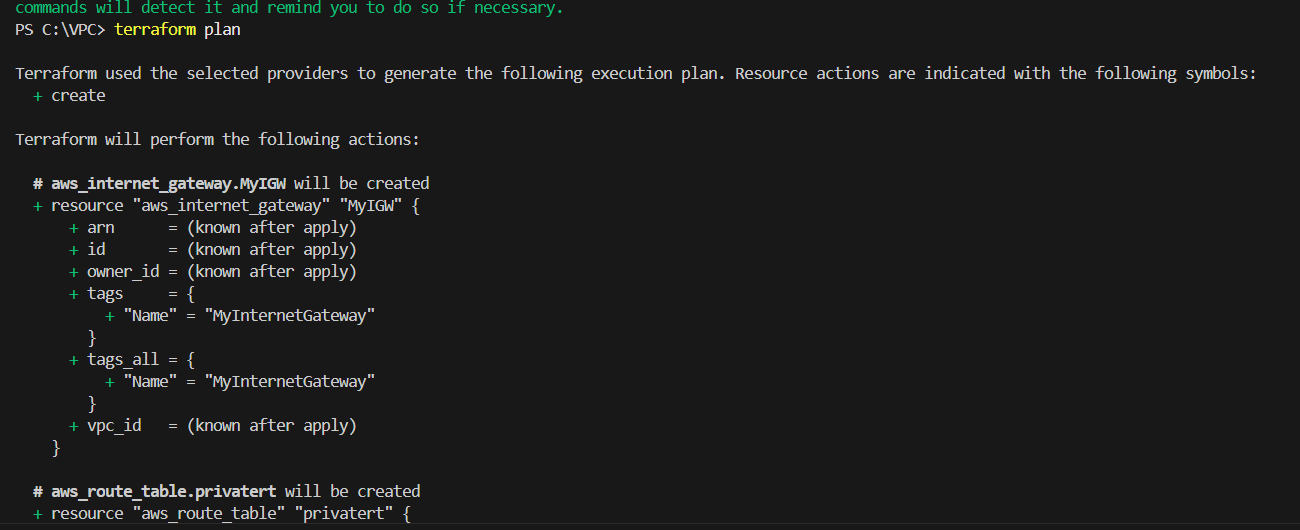
STEP 7: Enter the terraform apply command.
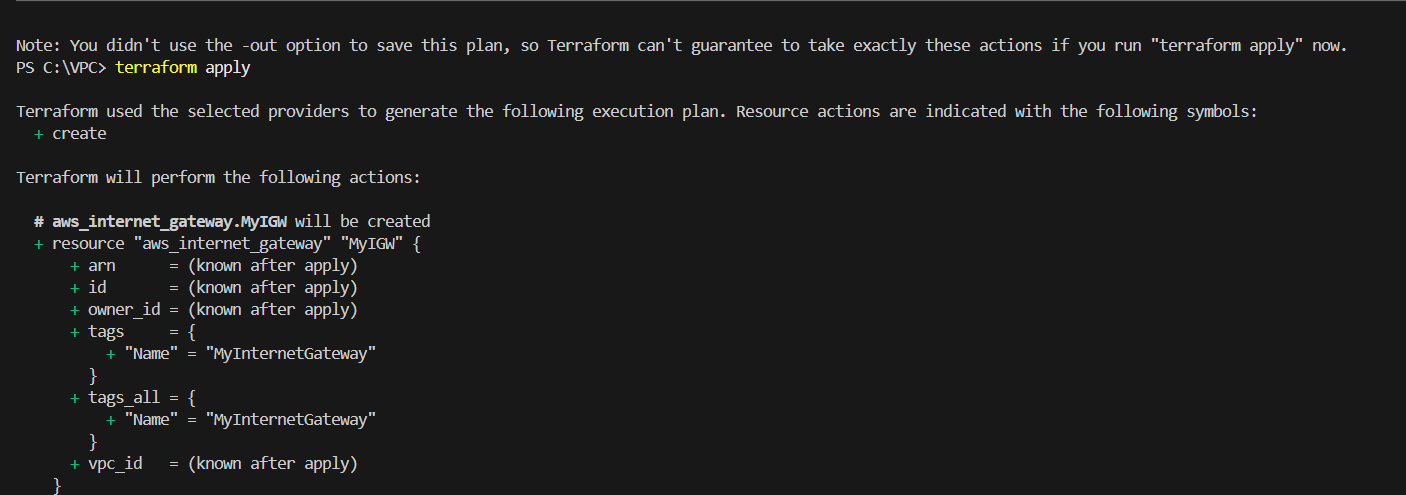
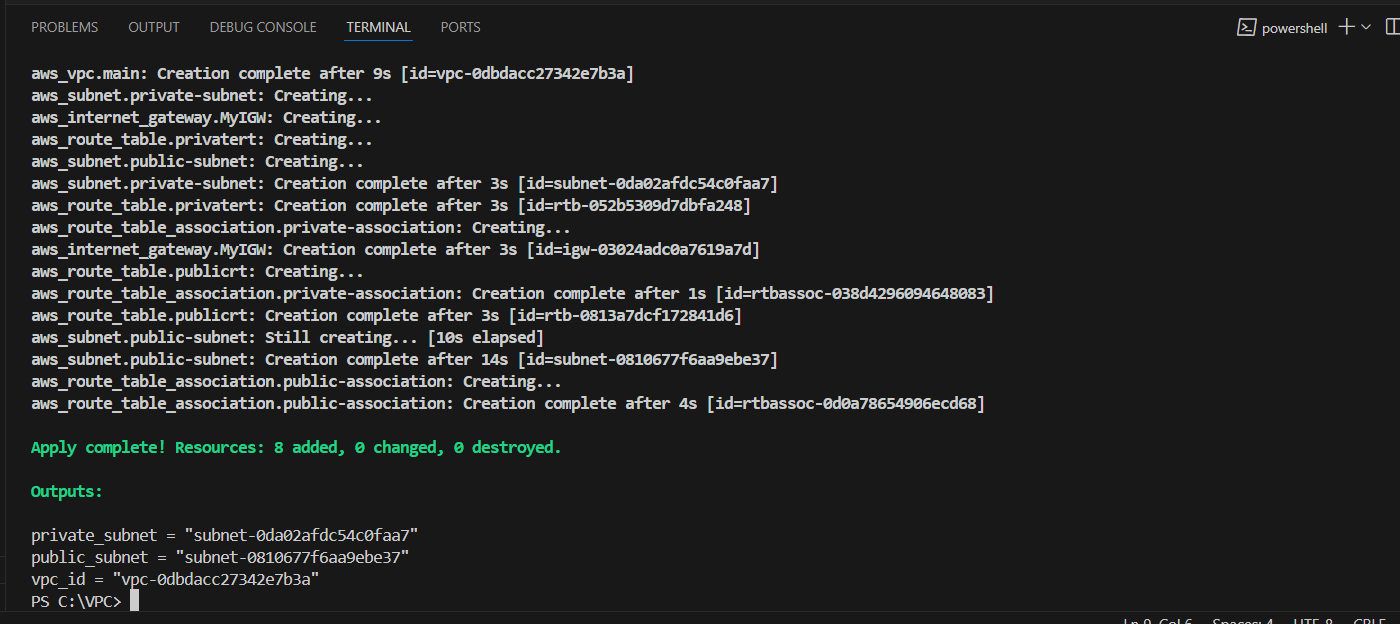
STEP 8: Check the resources in the AWS Console.
- Navigate the vpc.
- You can view that the VPC is created successfully.
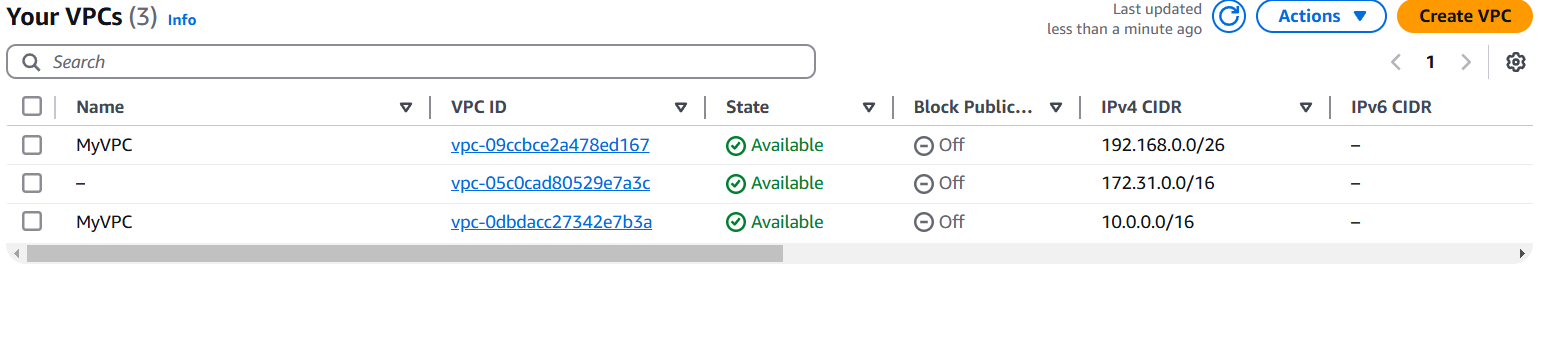
STEP 9: Click on Subnet and verify the new one.
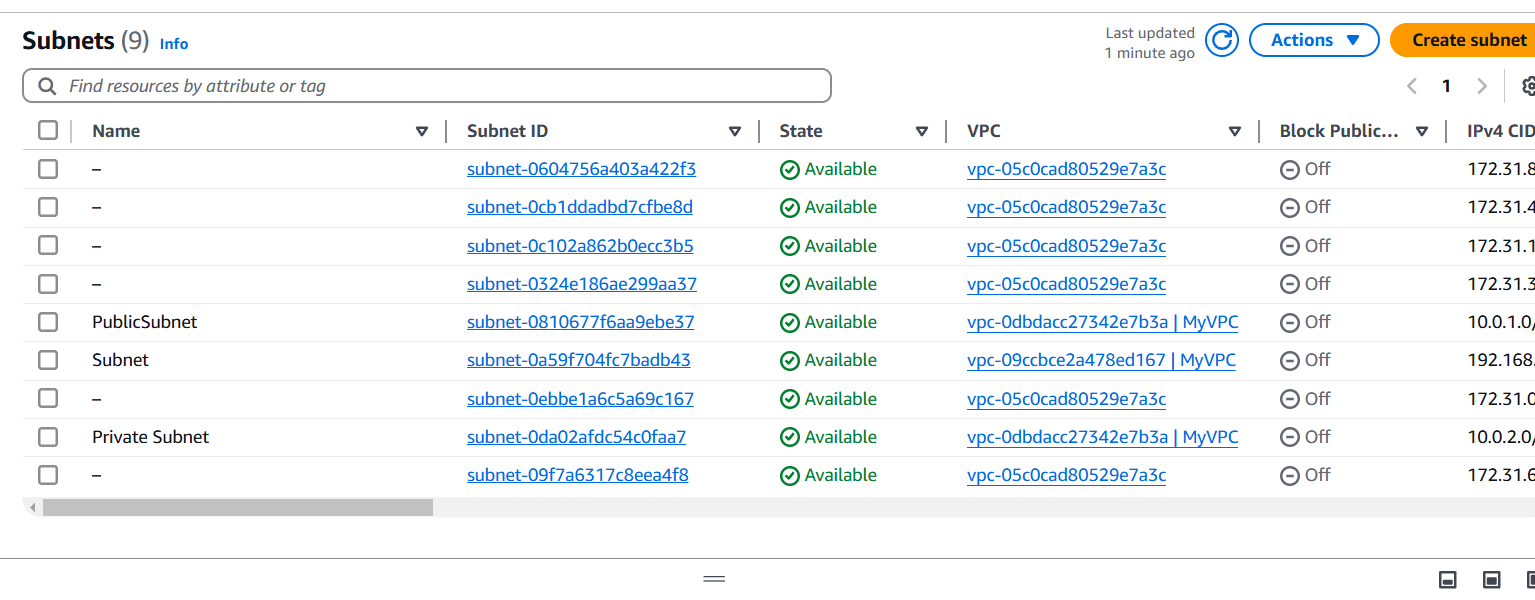
STEP 10: Select routetable and verify the new routetable.
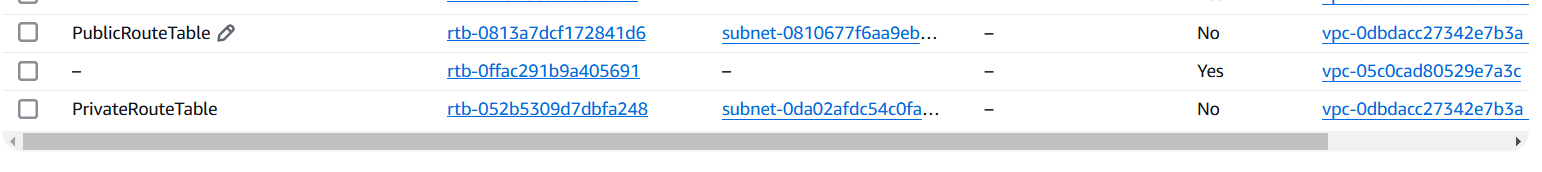
STEP 11: Next, Verify the Internet gateway.


Conclusion.
Building a custom VPC with Terraform is an essential skill for managing cloud infrastructure efficiently. By automating the creation of VPCs and their components, you ensure that your network environment is consistent, secure, and scalable. In this guide, we’ve walked through the key steps to configure subnets, security groups, and routing tables, helping you set up a robust VPC tailored to your needs.
With Terraform, you can easily modify, version control, and scale your infrastructure, making it easier to manage in the long run. Whether you’re working on a small project or managing complex cloud architectures, mastering Terraform for VPC creation is a valuable step toward optimizing your cloud infrastructure management.
Automating AWS Auto Scaling Deployment with Terraform.
Introduction.
AWS Auto Scaling is a service that automatically adjusts the number of compute resources in your environment to meet changing traffic demands. It helps maintain application performance while optimizing costs by scaling resources up or down based on predefined conditions. Terraform, a popular Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool, enables users to define and provision cloud resources using declarative configuration files. By using Terraform to manage AWS Auto Scaling, you can automate the creation and management of scaling policies, launch configurations, and scaling groups. This approach provides consistency, repeatability, and version control for your infrastructure. In this guide, we will explore how to leverage Terraform to manage AWS Auto Scaling efficiently, ensuring your applications are always prepared to handle varying workloads while minimizing costs.

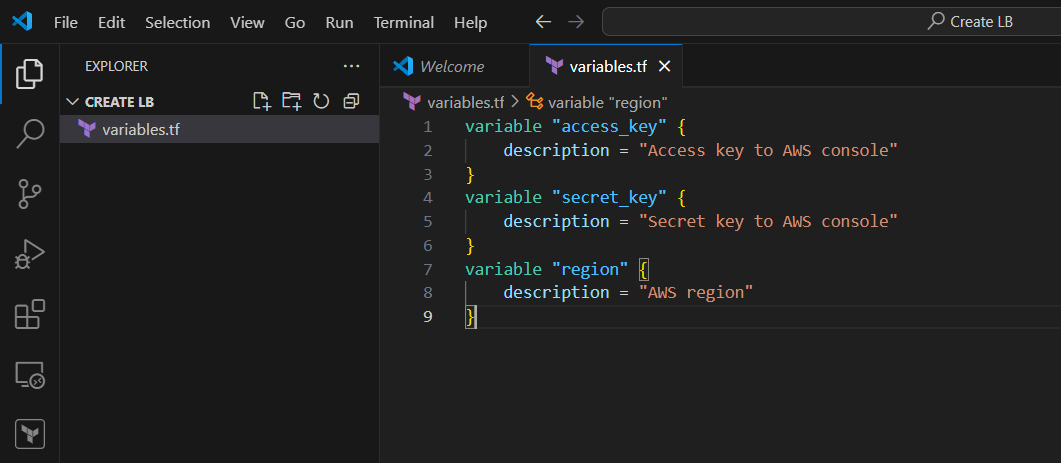
STEP 1: Create variable.tf file and enter the following terraform script.
variable "access_key" {
description = "Access key to AWS console"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key to AWS console"
}
variable "region" {
description = "AWS region"
}
STEP 2: Next, create terraform.tfvars file.
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "<YOUR_ACCESS_KEY>"
secret_key = "<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"
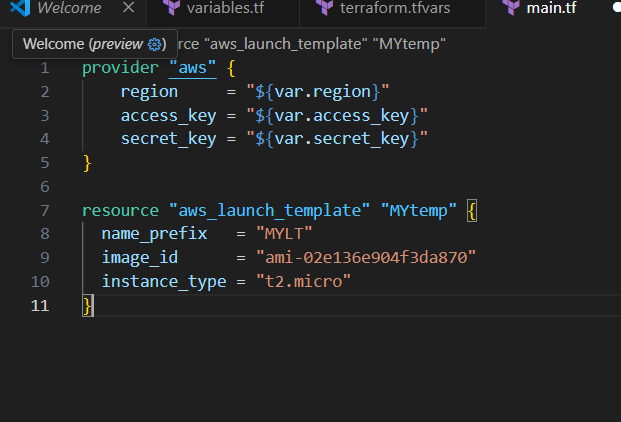
STEP 3: Create main.tf file.
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.region}"
access_key = "${var.access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.secret_key}"
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "MYgroup" {
name= "ASG1"
availability_zones = ["us-east-1a","us-east-1b"]
desired_capacity = 2
max_size = 2
min_size = 2
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.MYtemp.id
version = "$Latest"
}
}
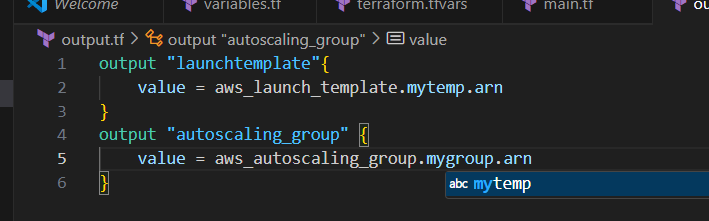
STEP 4: Create an Output file.
resource "aws_launch_template" "mytemp" {
name_prefix = "myLT"
image_id = "ami-02e136e904f3da870"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
STEP 5: Apply terraform configurations.
Enter terraform init command, terraform plan and terraform apply commands.
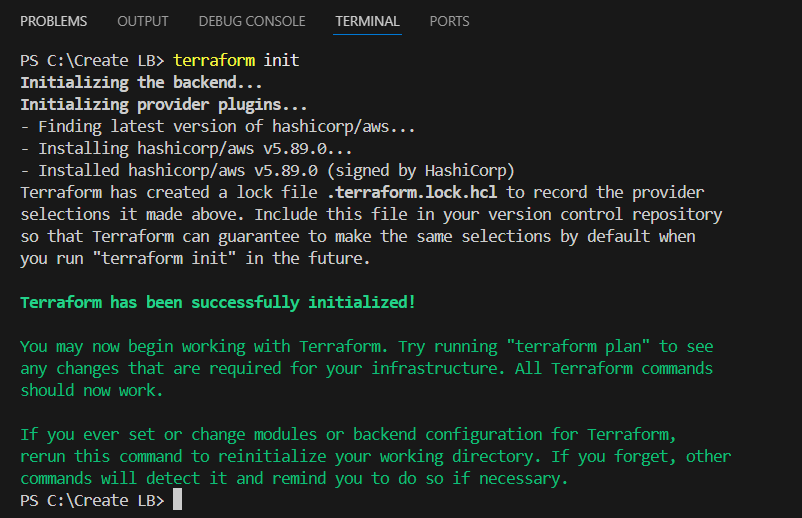

Check the resources in AWS Console.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, managing AWS Auto Scaling with Terraform offers significant benefits in terms of automation, consistency, and scalability. By using Terraform to define and manage Auto Scaling groups, policies, and configurations, you can automate resource scaling in response to fluctuating traffic demands, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This approach not only reduces manual intervention but also enables version-controlled infrastructure, making it easier to maintain and update your scaling configurations. With Terraform’s declarative syntax and AWS Auto Scaling’s powerful features, you can create a highly resilient and cost-effective environment, ensuring your applications scale seamlessly as needed.
Guide to Installing ArgoCD on Amazon Linux.
Introduction.
ArgoCD is a powerful, open-source GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes that enables developers to automate the deployment and management of applications using Git repositories. It allows for version-controlled application deployment, ensuring consistency and traceability of application states. Installing ArgoCD on Amazon Linux is a straightforward process that involves setting up the necessary prerequisites like kubectl, the ArgoCD CLI, and configuring ArgoCD in your Kubernetes cluster. By doing so, you can leverage ArgoCD’s intuitive web UI and CLI to manage your Kubernetes applications efficiently. This installation guide will walk you through the necessary steps to set up ArgoCD on an Amazon Linux instance, enabling you to streamline your application deployment and improve the overall management of your Kubernetes environment.

Step 1: Update the System
Make sure your system packages are up to date before starting the installation process.
sudo yum update -y
Step 2: Install kubectl
ArgoCD requires kubectl to interact with your Kubernetes cluster. If you don’t have kubectl installed, follow these steps:
- Add the Kubernetes repository.
echo "[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg" | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
Install kubectl.
sudo yum install -y kubectl
kubectl version --client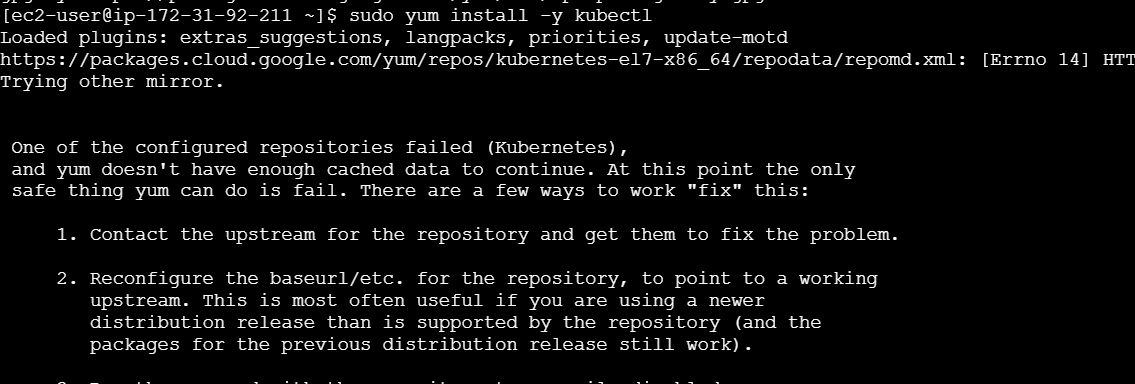
Step 3: Install ArgoCD CLI
To install the ArgoCD command-line tool (CLI), follow these steps:
- Download the latest version of the ArgoCD CLI.
curl -sSL -o argocd-linux-amd64 https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/download/v2.7.7/argocd-linux-amd64- Make the binary executable:
chmod +x argocd-linux-amd64
sudo mv argocd-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argocd
argocd version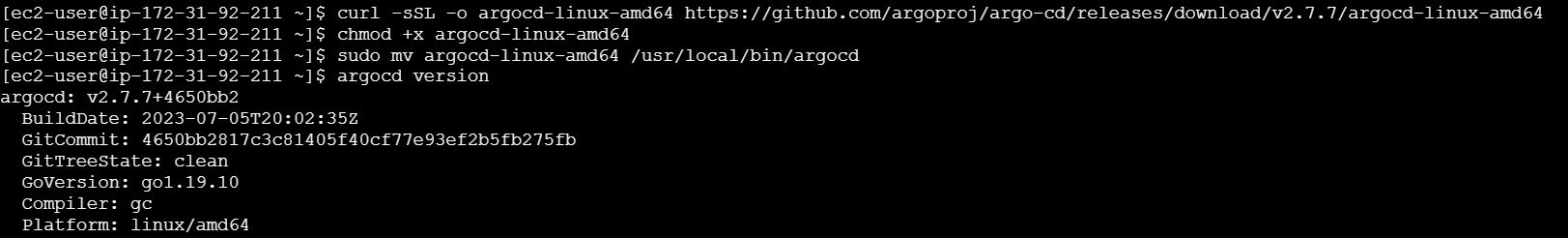
Step 4: Install ArgoCD on Kubernetes Cluster
- Create the ArgoCD namespace.
kubectl create namespace argocdInstall ArgoCD components using kubectl.
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
Step 5: Access the ArgoCD Web UI
To access the ArgoCD UI, follow these steps:
- Get the initial admin password.
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' | base64 -d
Forward the ArgoCD server port to your local machine:
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443
STEP 6: Open the ArgoCD Web UI:
- Go to
https://localhost:8080in your web browser. - Login with the username
adminand the password retrieved earlier.
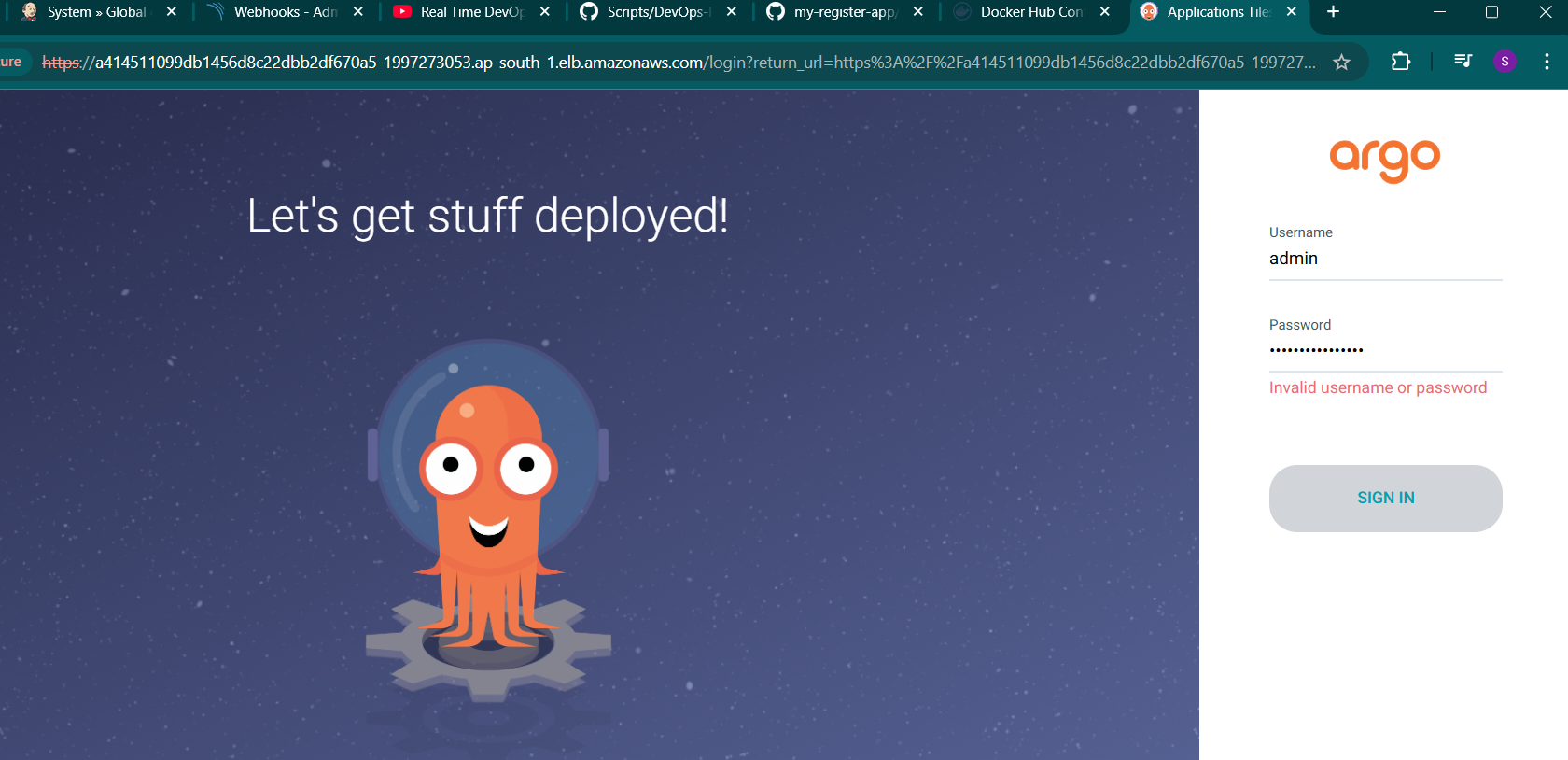

Conclusion.
In conclusion, installing ArgoCD on Amazon Linux allows you to easily manage and deploy applications on your Kubernetes clusters using GitOps principles. By following the outlined steps, you can set up ArgoCD CLI and access the ArgoCD Web UI, which provides an intuitive interface for managing your application lifecycle. With kubectl and the installation of ArgoCD on your Kubernetes cluster, you can automate and simplify the deployment of applications, ensuring streamlined updates and greater scalability. Whether you choose to expose ArgoCD via a LoadBalancer or use it locally with port-forwarding, ArgoCD significantly enhances the efficiency and control of your CI/CD pipeline.
Setting up DNS with Route 53 for a Custom URL.
Introduction.
Configuring DNS with Amazon Route 53 is an essential part of managing domain names and directing traffic to your web applications. Route 53 is a scalable, highly available Domain Name System (DNS) web service provided by AWS, enabling users to route end-user requests to applications running on AWS or elsewhere. By configuring DNS with Route 53, users can create, update, and manage DNS records, such as A records, CNAME, or MX records, for domain names. This process ensures that traffic is directed to the right resources, whether it’s an Elastic Beanstalk environment, an EC2 instance, or an external server. Route 53 also integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, offering additional features like health checks and routing policies for optimized performance. With Terraform, this entire process can be automated, ensuring repeatable, version-controlled infrastructure deployment, making DNS management efficient and scalable.

STEP 1: Navigate The EC2 and Select the instance click on create instance.
- Enter the instance name.
- Select the AMI and Instance type.
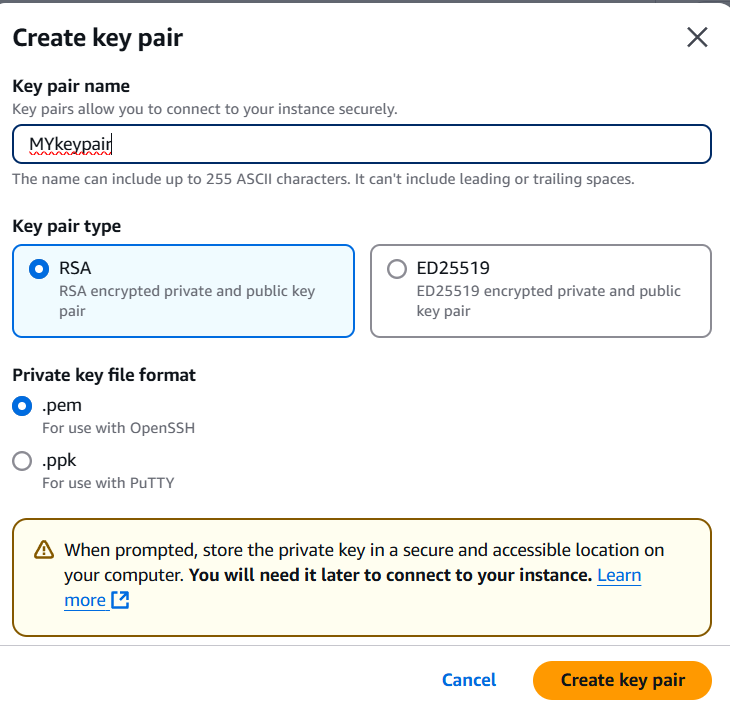
- Create the keypair.
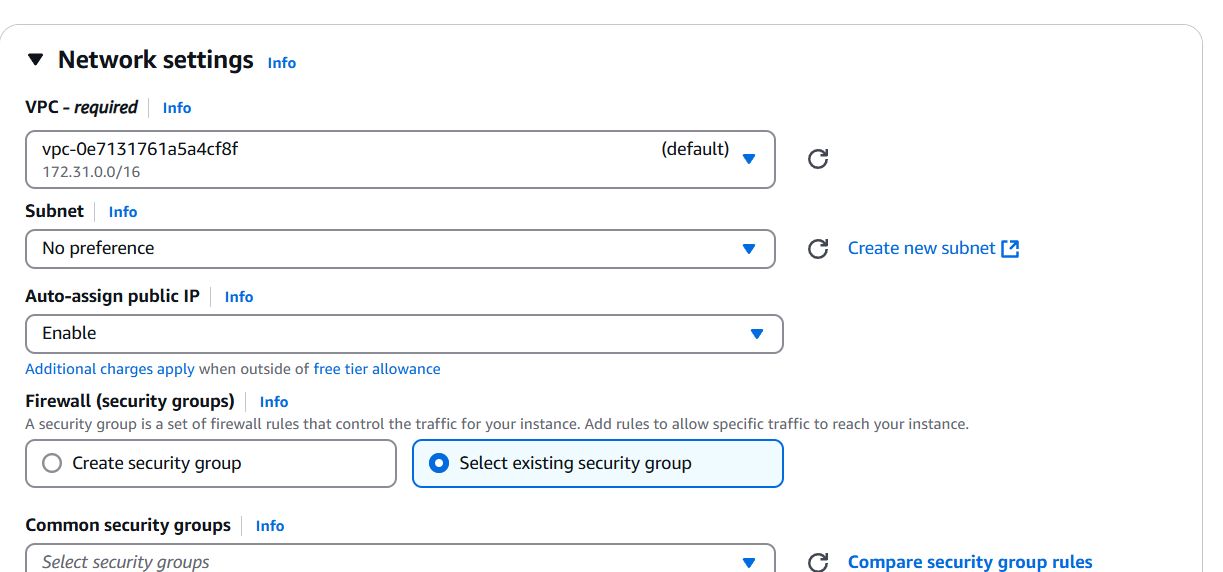
STEP 2: Edit the network settings.
- Enable the auto assign public IP.
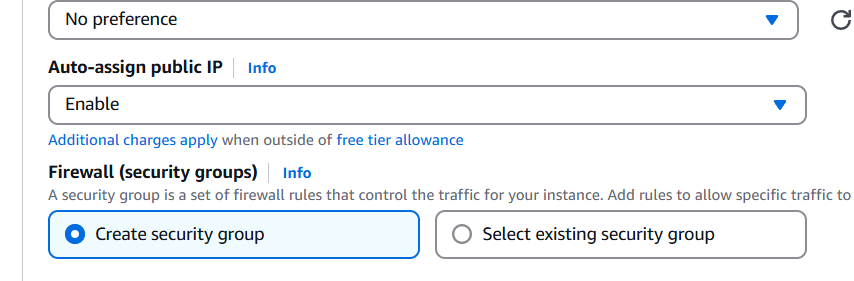
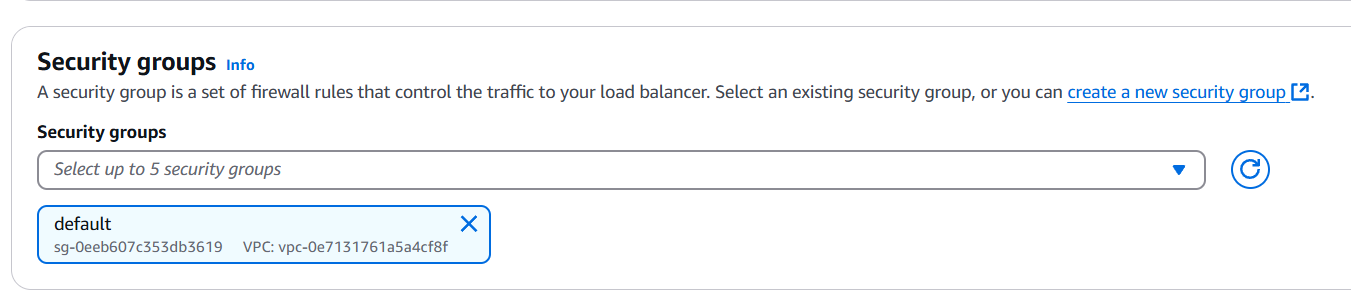
- Create security gropu.
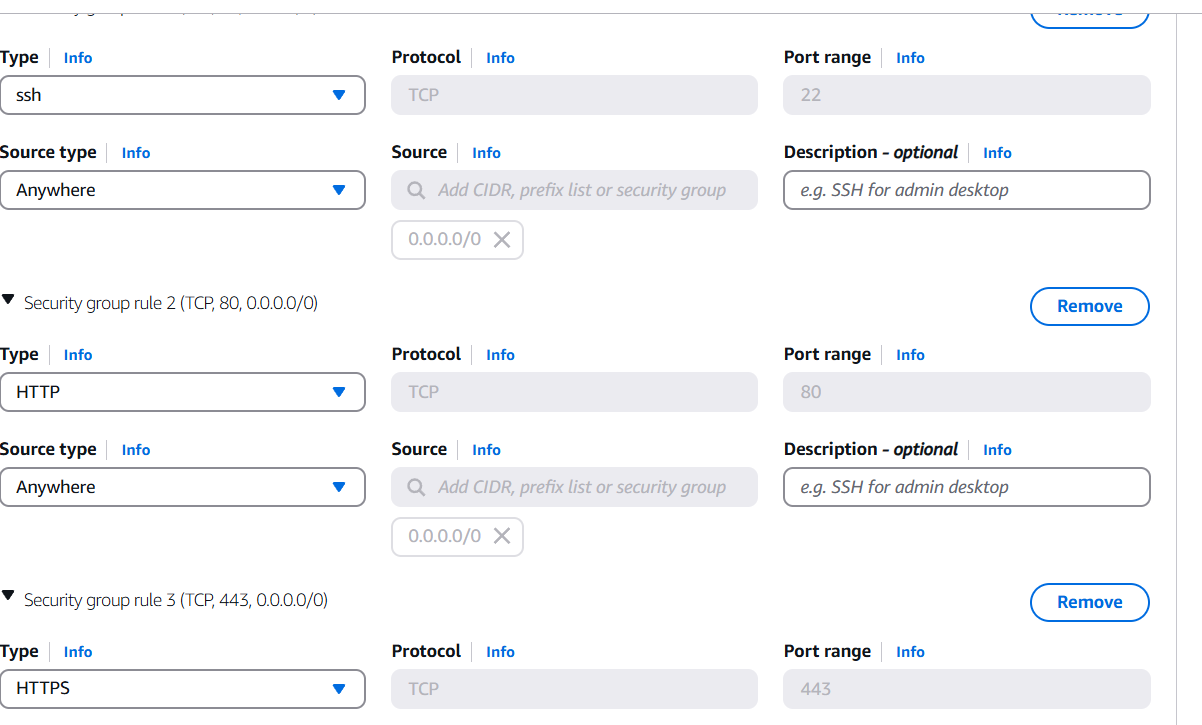
- To add the SSH, HTPP, HTPPS.
STEP 3: Go to additional and enter the lines in the user data box.
#!/bin/bash
sudo su
yum update -y
yum install httpd -y
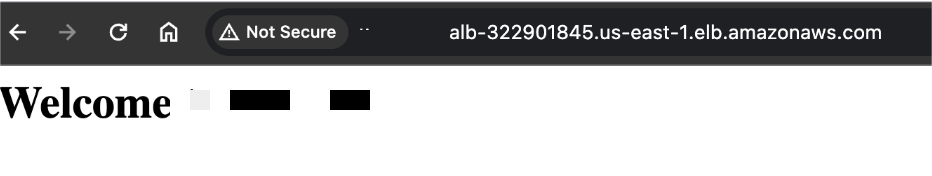
echo "<html><h1> Welcome </h1></html>" >> /var/www/html/index.html
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
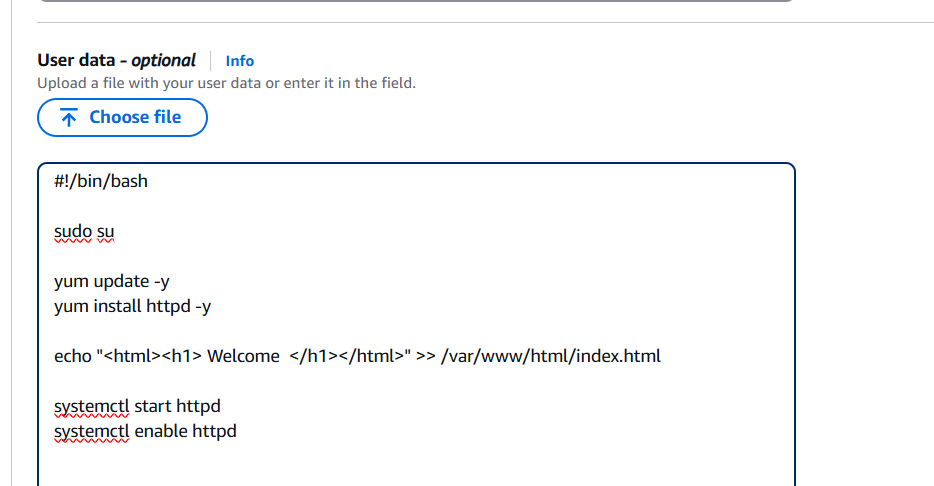
STEP 4: Click on launch instance.
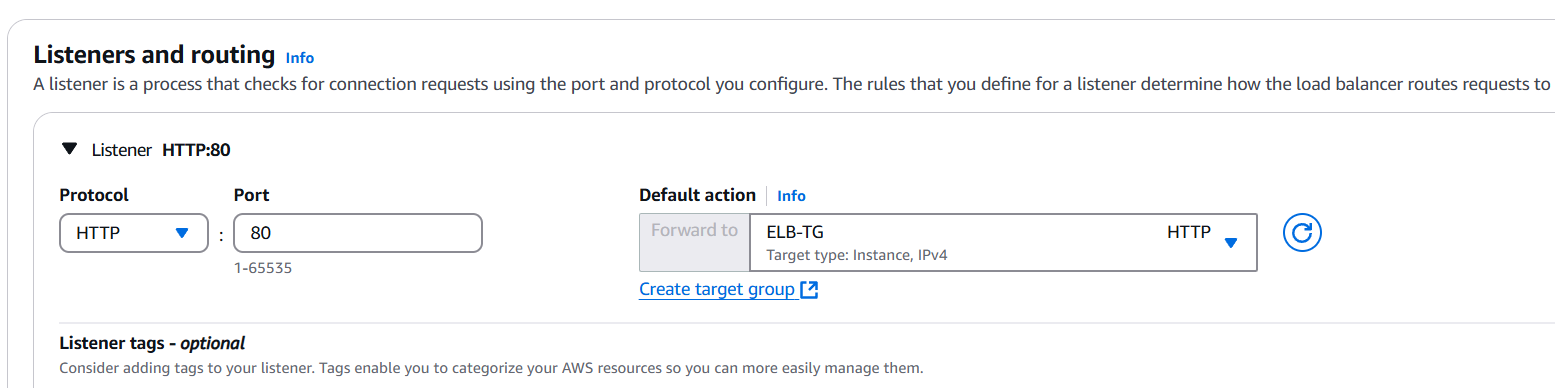
STEP 5: Go target groups and click on create.

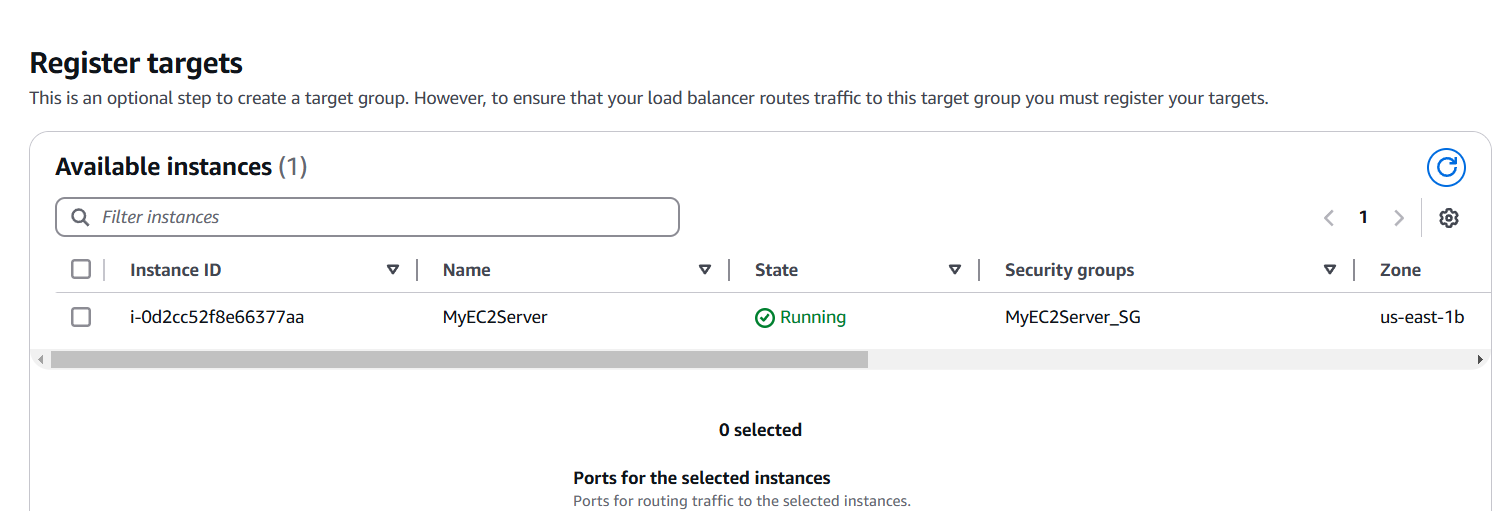
STEP 6: Enter the name and select the instance.
- Click on next and select your created instance.
STEP 7: Click on create loadbalancer.
- Select application loadbalancer.

STEP 8: Copy your DNS and enter the browser.
STEP 9: Go route53 and select hosted zones.
- Click on Create Record button.
- Keep the record name as default.
- In Value/Route traffic to, choose Alias to Application and Classic Load Balancer.
- Choose the Region : us-east-1.
- Choose the load balancer, For Evaluate target health, choose No and click on Create record button.
- Copy the record name of Type A, Open a web browser and paste the record name.

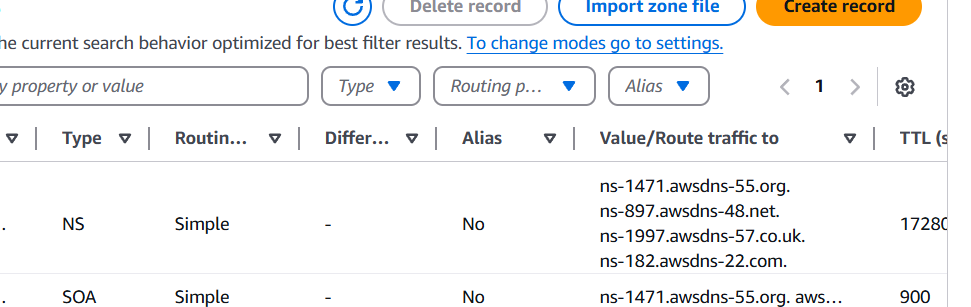

Conclusion.
In conclusion, configuring DNS with Amazon Route 53 is a crucial step in managing web traffic and ensuring that domain names correctly point to the right resources. By leveraging Route 53, businesses can achieve reliable, scalable, and highly available DNS management. Integrating Route 53 with AWS services and automating the configuration with tools like Terraform ensures consistency, reduces manual errors, and streamlines the deployment process. This setup enhances the overall performance, availability, and flexibility of web applications, allowing developers to focus on building their applications while leaving the complexity of DNS management to AWS Route 53.
Create an Elastic Beanstalk Application using Terraform.
Introduction.
Elastic Beanstalk is a fully managed service from AWS that allows developers to easily deploy and manage applications. With Elastic Beanstalk, users can focus on writing code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It supports various programming languages and frameworks, including Java, Python, .NET, Node.js, and more. Terraform is an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that allows users to define and provision infrastructure using declarative configuration files. Using Terraform to create an Elastic Beanstalk application involves defining resources like the application itself and the environment in which it runs. This approach enables version-controlled, repeatable deployments and simplifies infrastructure management. By leveraging Terraform’s automation and Elastic Beanstalk’s managed environment, developers can streamline deployment processes, scale applications, and ensure high availability. The integration of both tools makes it easy to set up and maintain complex application environments in the cloud.

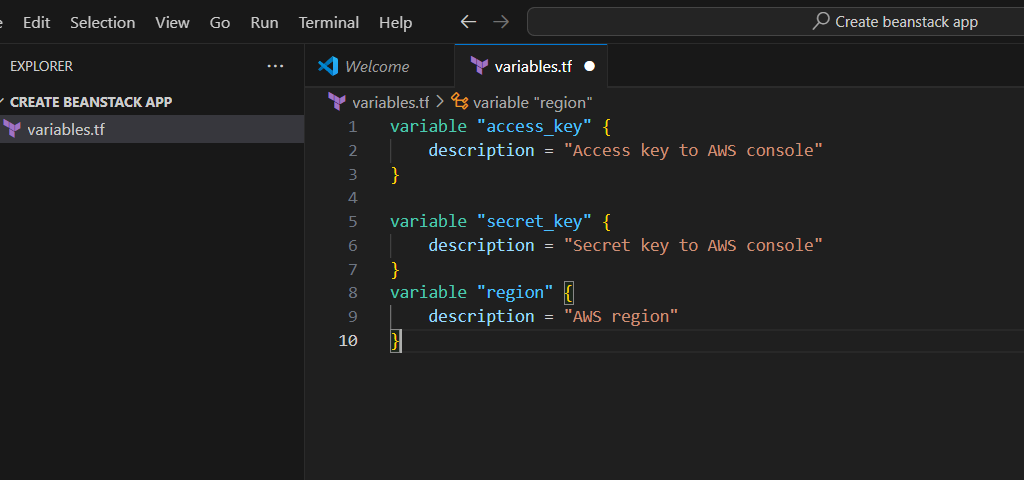
STEP 1: Go to vscode and Open your Folder and create a variable.tf file.
- Enter the following Script.
variable "access_key" {
description = "Access key to AWS console"
}
variable "secret_key" {
description = "Secret key to AWS console"
}
variable "region" {
description = "AWS region"
}
STEP 2: Click on create a terraform.tfvars file.
- Enter the following command.
region = "us-east-1"
access_key = "<YOUR_ACCESS_KEY>"
secret_key = "<YOUR_SECRET_KEY>"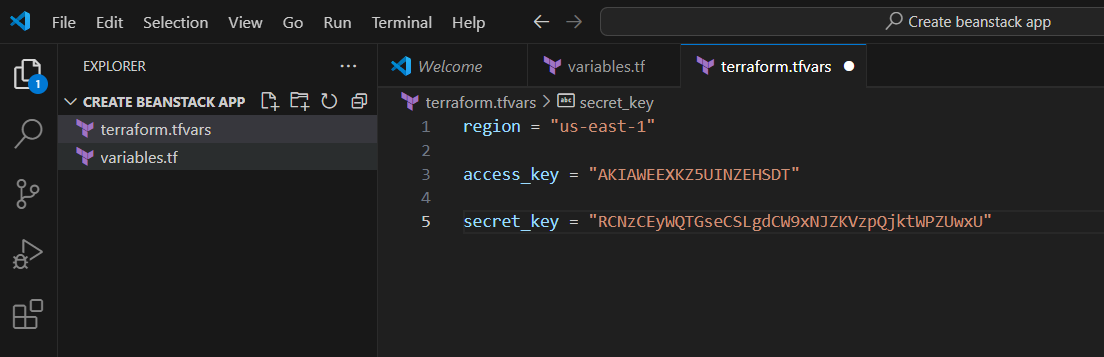
STEP 3: Next, Create a main.tf file.
provider "aws" {
region = "${var.region}"
access_key = "${var.access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.secret_key}"
}
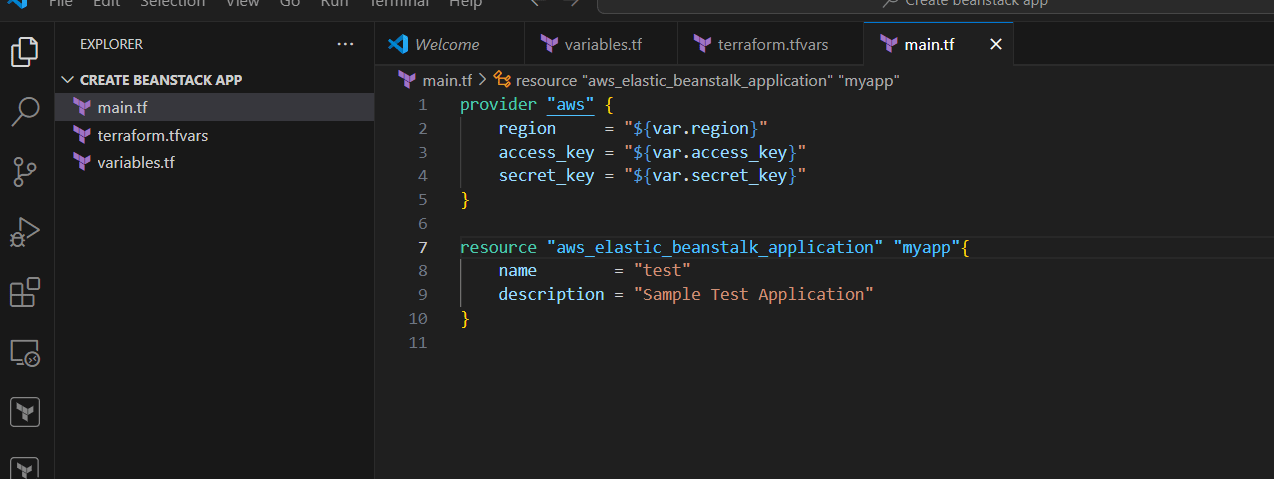
resource "aws_elastic_beanstalk_application" "myapp"{
name = "test"
description = "Sample Test Application"
}
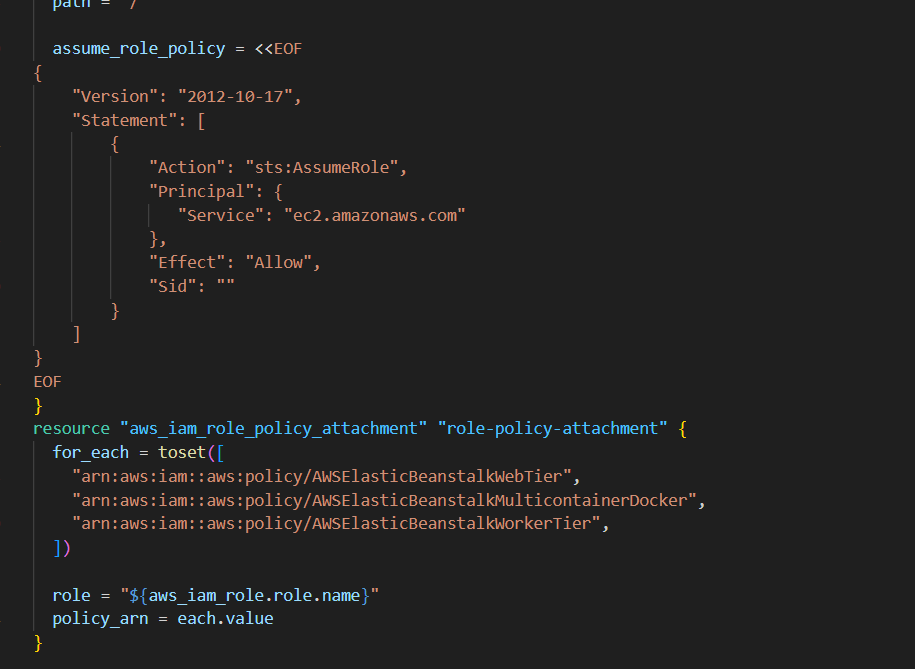
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "subject_profile" {
name = "test_role_new"
role = aws_iam_role.role.name
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "role" {
name = "test_role_new"
path = "/"
assume_role_policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": ""
}
]
}
EOF
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "role-policy-attachment" {
for_each = toset([
"arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSElasticBeanstalkWebTier",
"arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSElasticBeanstalkMulticontainerDocker",
"arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSElasticBeanstalkWorkerTier",
])
role = "${aws_iam_role.role.name}"
policy_arn = each.value
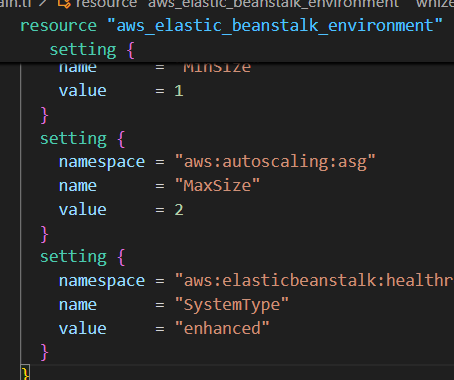
}STEP 4: To create an elastic environment for the application, paste the below code in the main.tf
resource "aws_elastic_beanstalk_environment" "env" {
name = "environment"
application = aws_elastic_beanstalk_application.whizapp.name
solution_stack_name = "64bit Amazon Linux 2 v3.4.1 running Corretto 17"
setting {
namespace = "aws:autoscaling:launchconfiguration"
name = "IamInstanceProfile"
value = "${aws_iam_instance_profile.subject_profile.name}"
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:elasticbeanstalk:environment:process:default"
name = "MatcherHTTPCode"
value = "200"
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:elasticbeanstalk:environment"
name = "LoadBalancerType"
value = "application"
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:autoscaling:launchconfiguration"
name = "InstanceType"
value = "t2.micro"
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:autoscaling:asg"
name = "MinSize"
value = 1
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:autoscaling:asg"
name = "MaxSize"
value = 2
}
setting {
namespace = "aws:elasticbeanstalk:healthreporting:system"
name = "SystemType"
value = "enhanced"
}
}
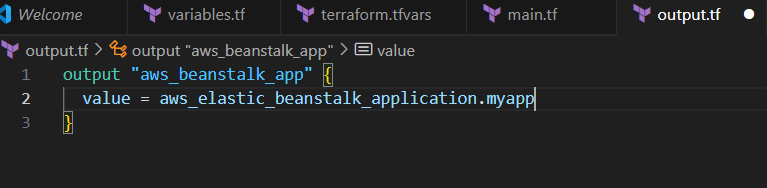
STEP 5: Create output.tf file.
output "aws_beanstalk_app" {
value = aws_elastic_beanstalk_application.myapp.arn
}
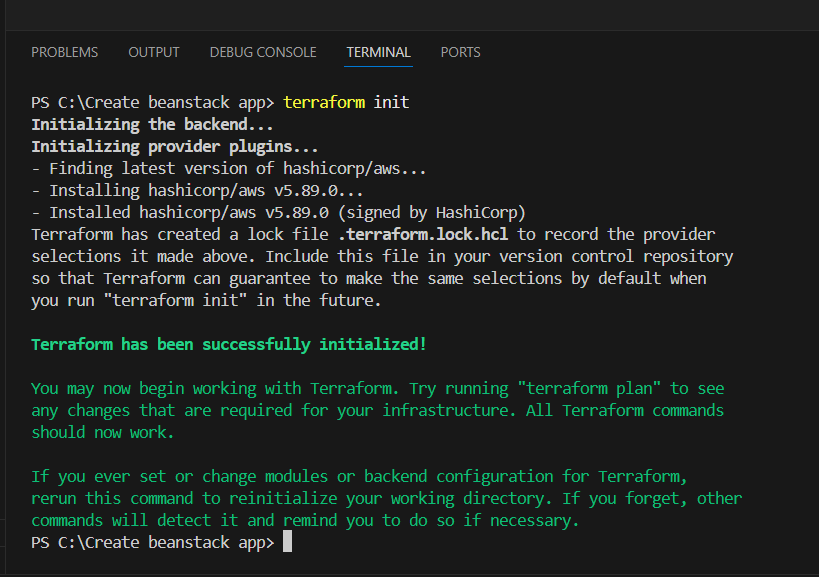
STEP 6: Go to terminal and enter the terraform init command.
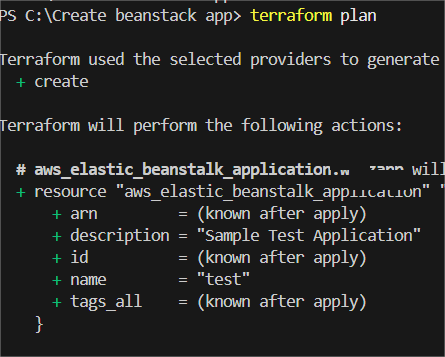
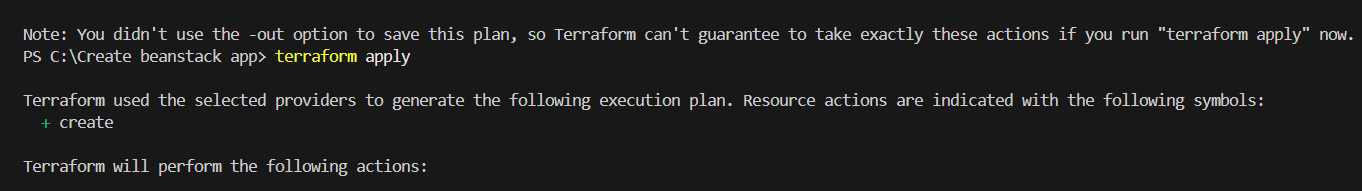
STEP 7: Next, Enter the terraform plan and terraform apply command.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, using Terraform to create and manage an Elastic Beanstalk application offers numerous benefits, including infrastructure automation, scalability, and ease of management. By defining your Elastic Beanstalk application and environment in code, you can ensure consistent deployments, streamline updates, and minimize the risk of manual errors. Terraform’s declarative approach to infrastructure management allows for version control and collaboration, which enhances the flexibility and reliability of your application deployment pipeline. Leveraging both AWS Elastic Beanstalk’s managed environment and Terraform’s powerful provisioning capabilities creates a seamless workflow for developers, enabling faster, more efficient development cycles while maintaining full control over the infrastructure.
Introduction to IoT Greengrass.
Introduction.
In today’s world of interconnected devices, managing and processing data locally at the edge has become a key factor in improving efficiency and reducing latency. AWS IoT Greengrass is a powerful service that extends AWS’s cloud capabilities to edge devices, allowing them to run applications, process data, and even act autonomously. In this post, we’ll explore what IoT Greengrass is, how it works, and how you can leverage it to create smarter, more responsive IoT solutions.

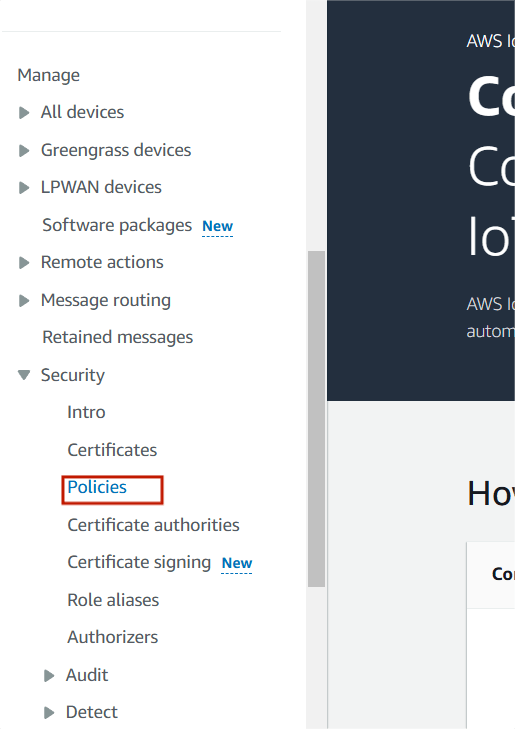
STEP 1: Navigate IoT Core, Select the policies under security.
STEP 2: Click on create policy.
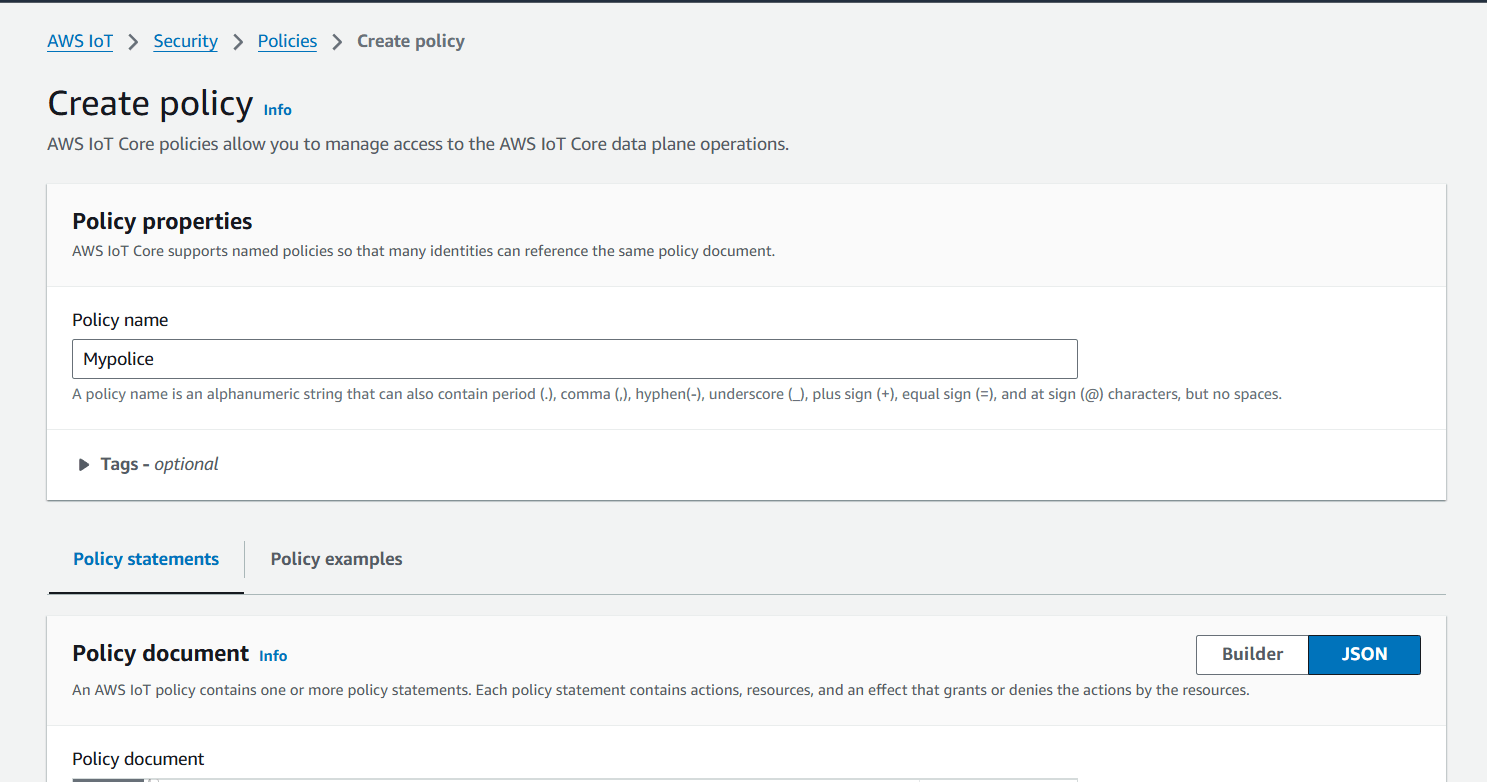
STEP 3: Enter the policy name.
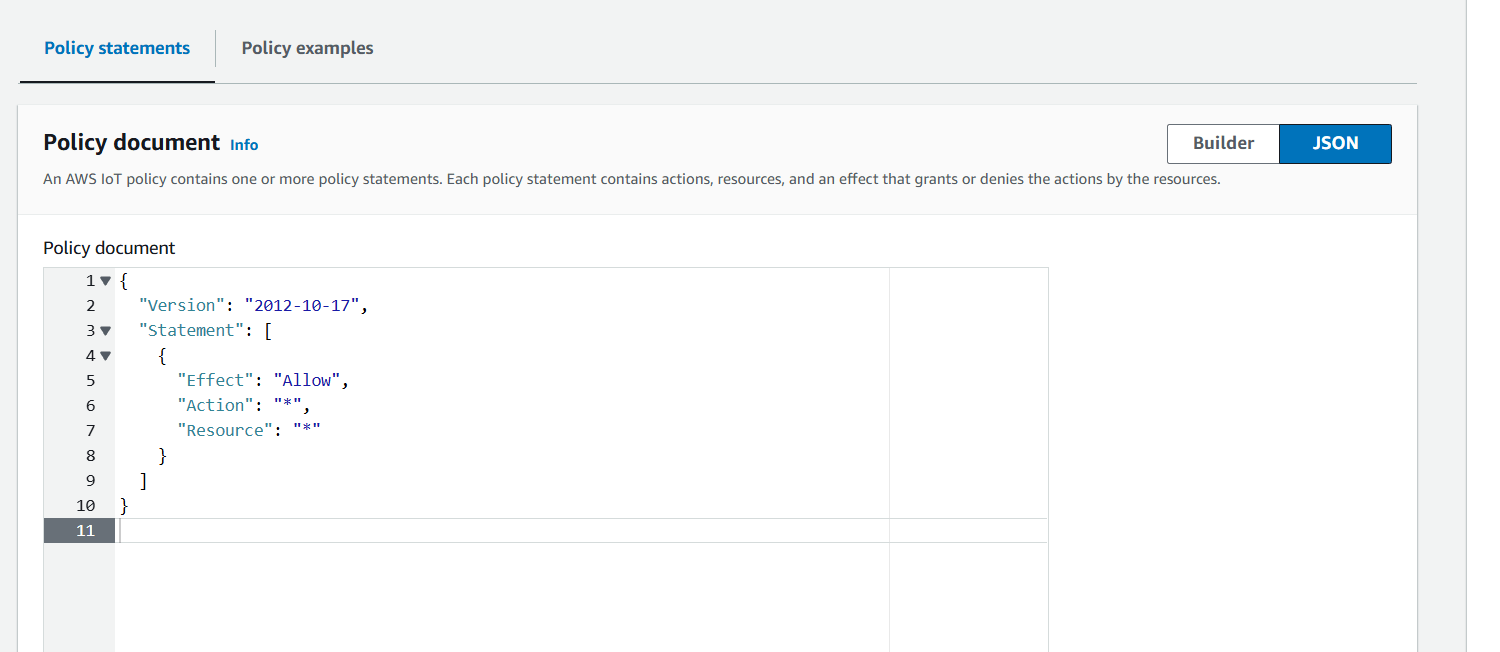
- Policy Document Select JSON remove the existing and copy paste the below policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
STEP 4: Select Things under All devices.
- Click on Create things.
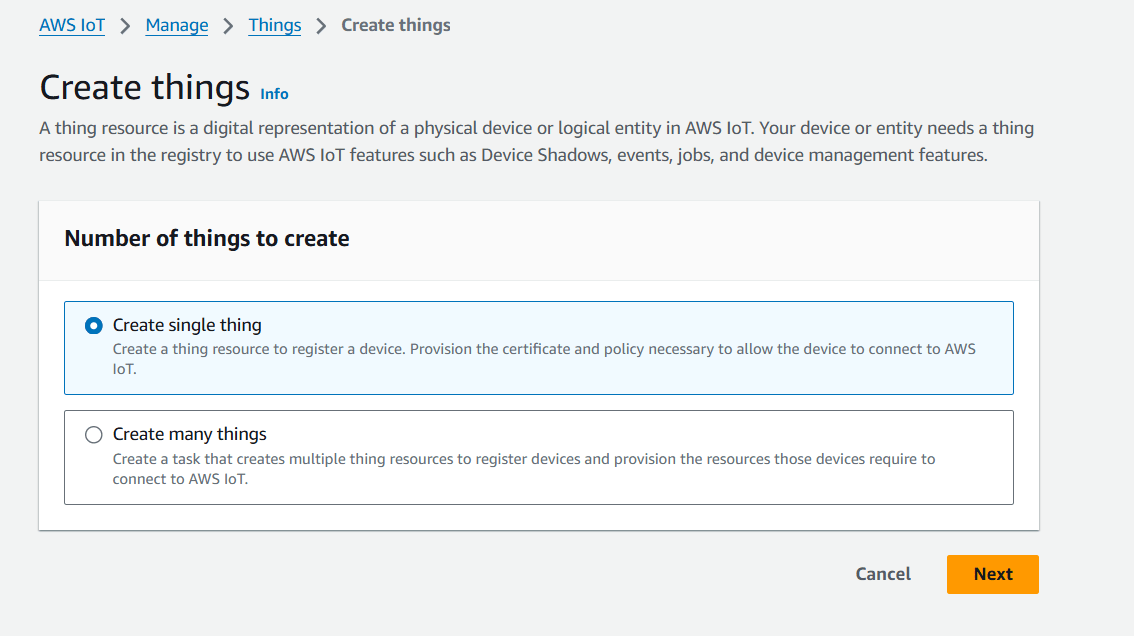
- Select single things and click on next.
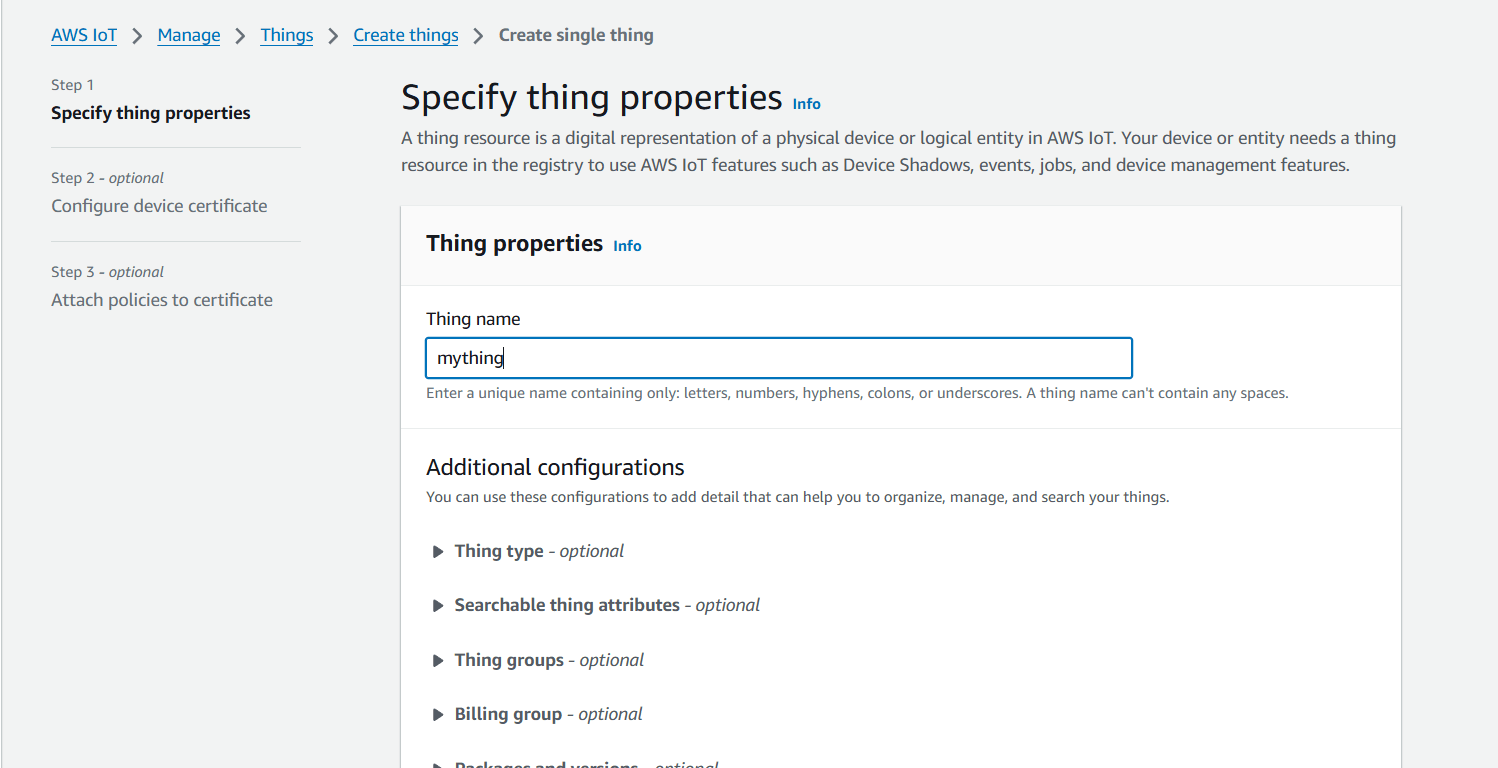
STEP 5: Enter Things name.
- Select a certificate click on next.
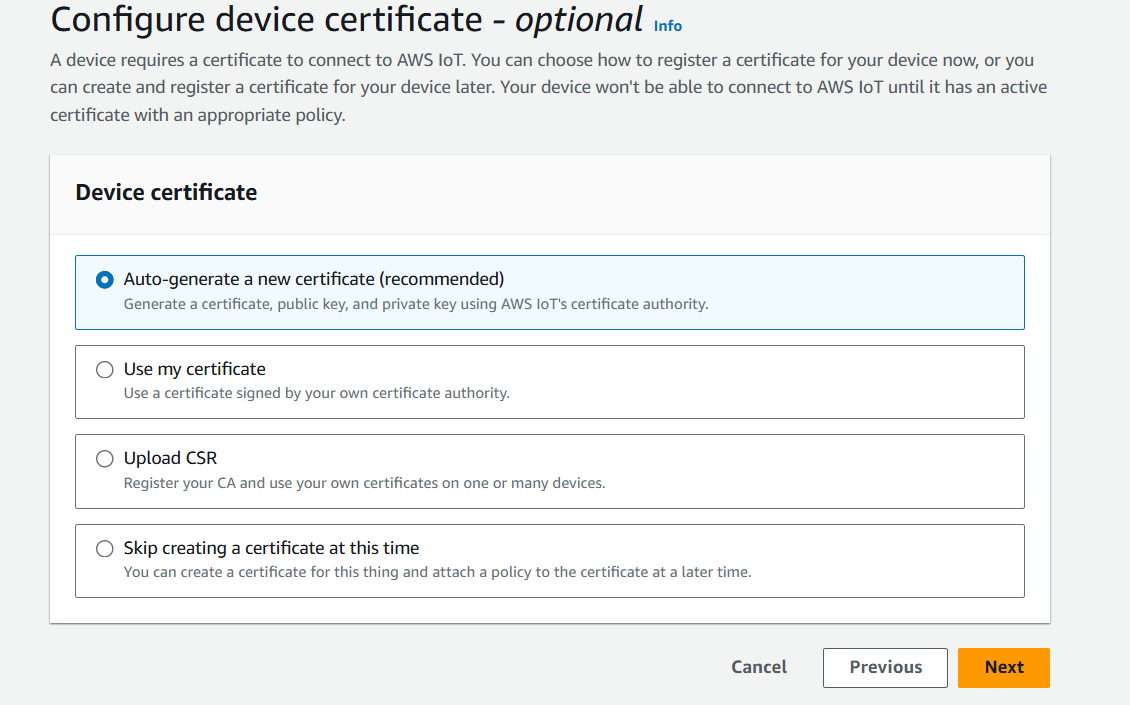
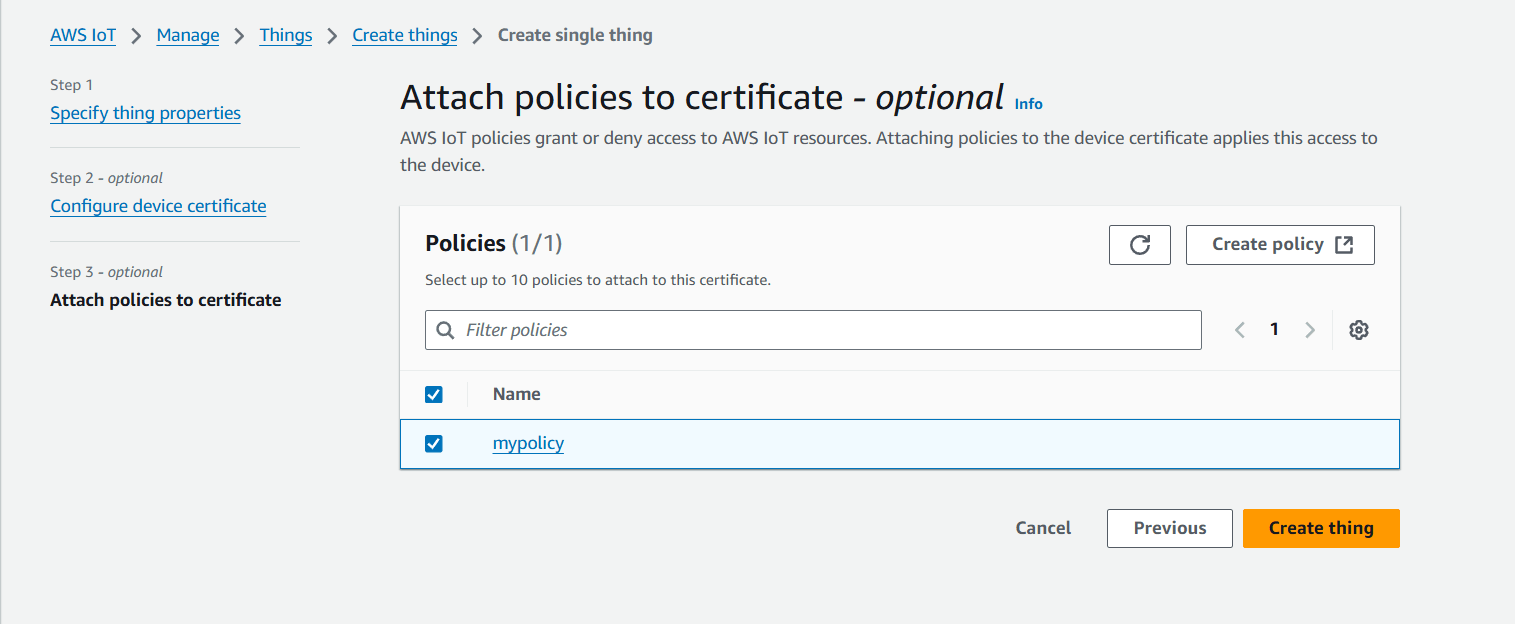
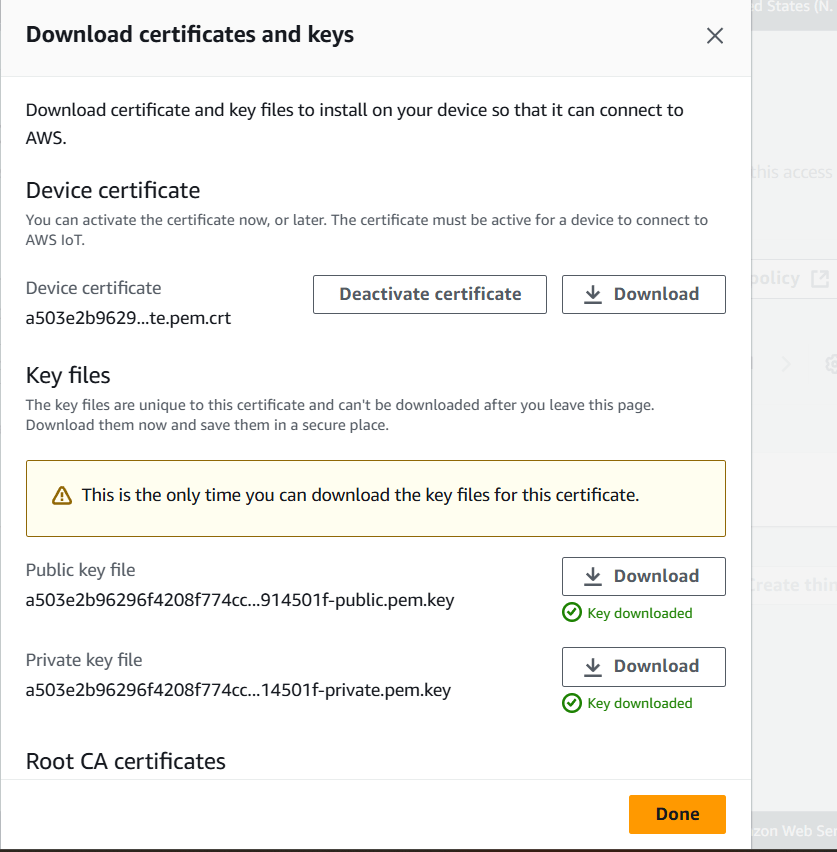
STEP 6: Download all the 5 certificates and keys in your local and click on Done.
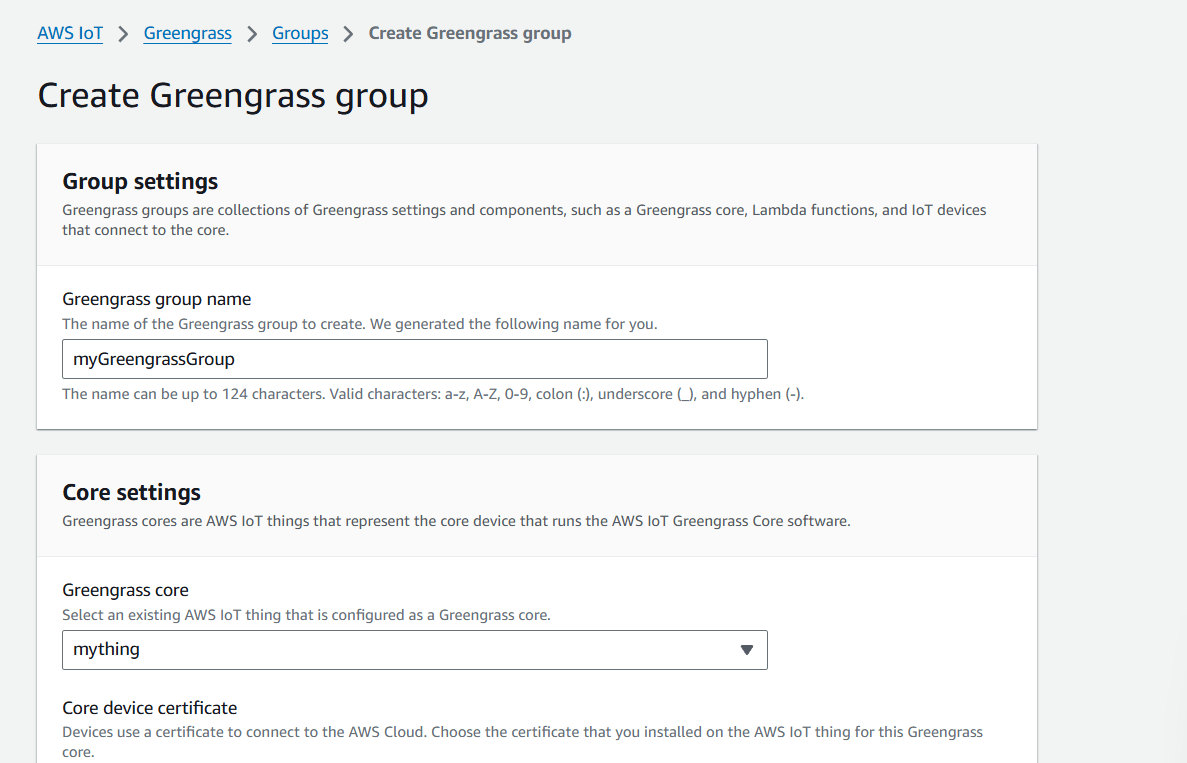
STEP 7: Create a greengrass group.
- Enter name and select you created thing.
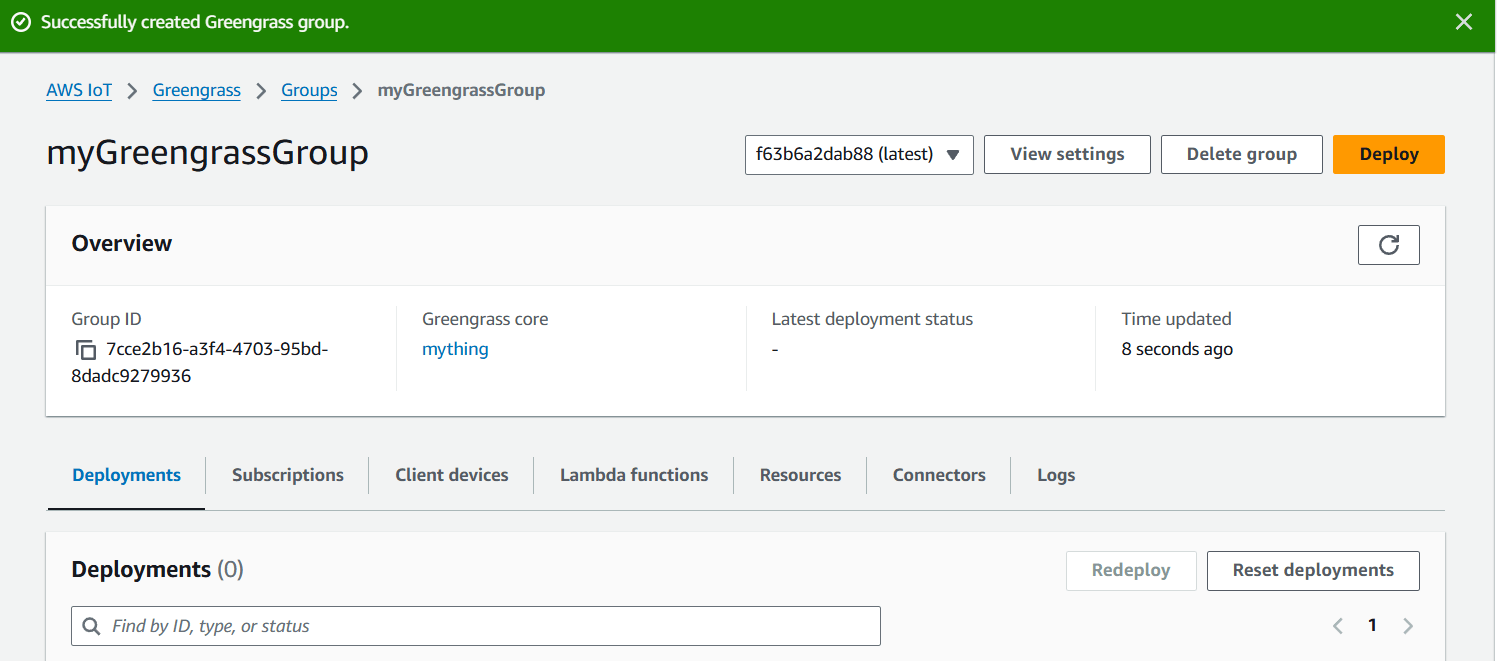
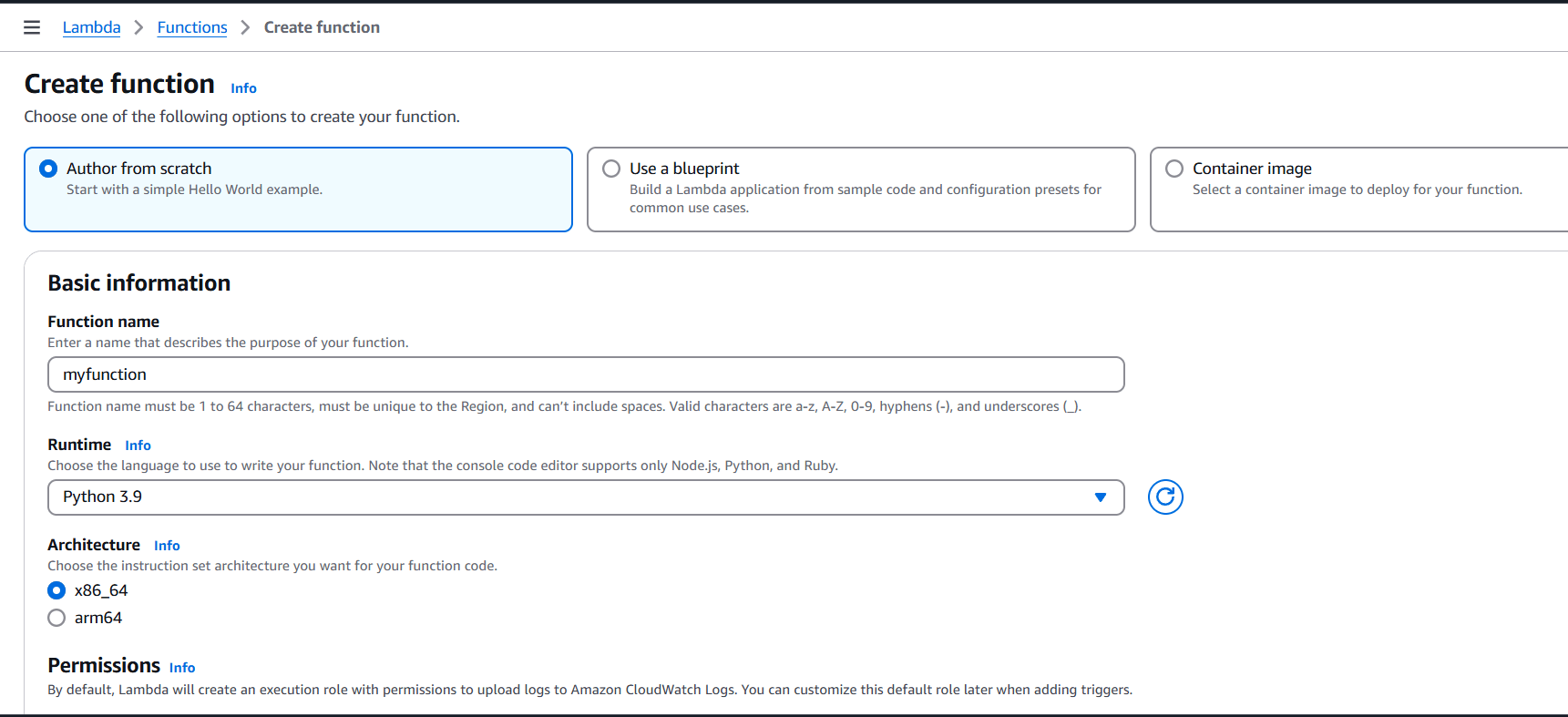
STEP 8: Navigate the lambda services and click on create a function.
- Author from scratch.
- Enter the name.
- Run time.
- Click on create.
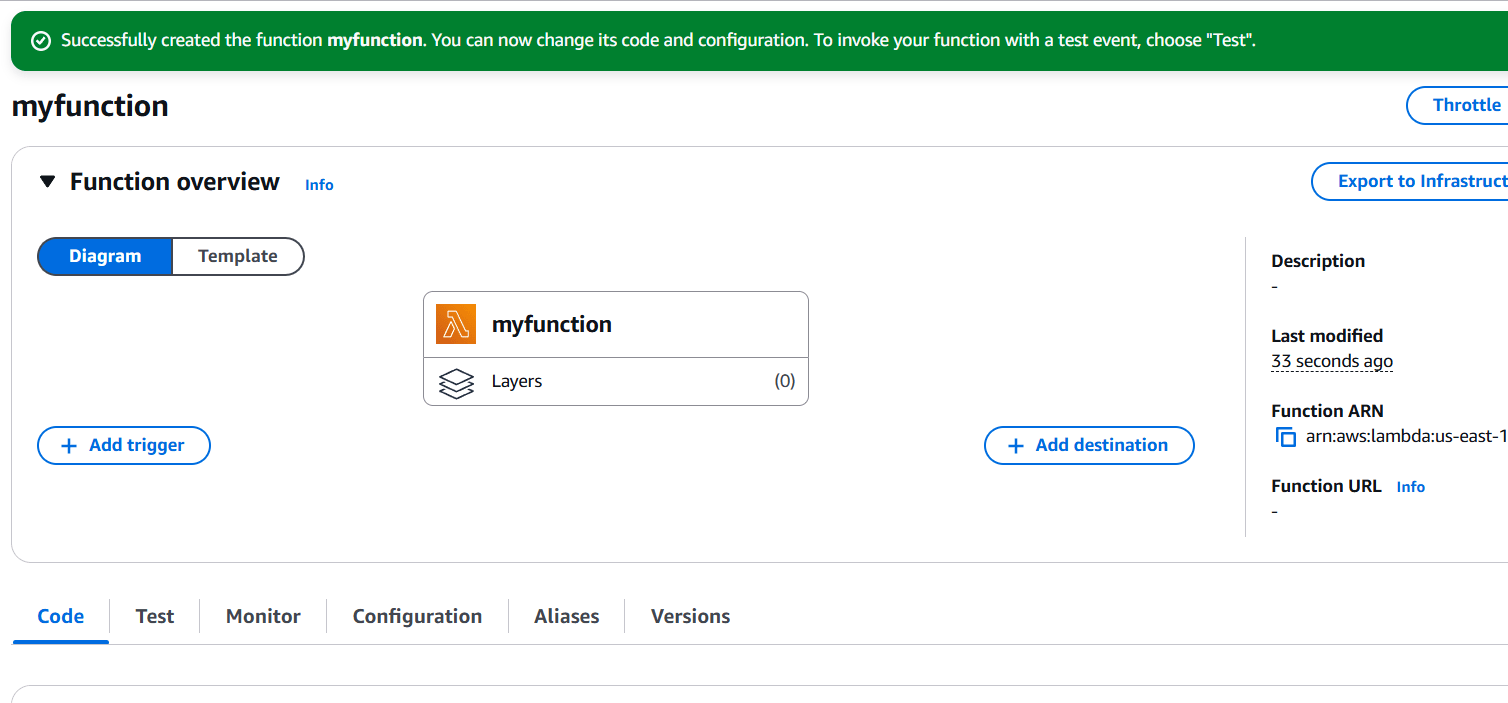
STEP 9: Scroll down.
- Enter the following command and click on deploy.
def function_handler(event, context):
print("Hello from AWS IoT Greengrass!")
return "Function executed successfully"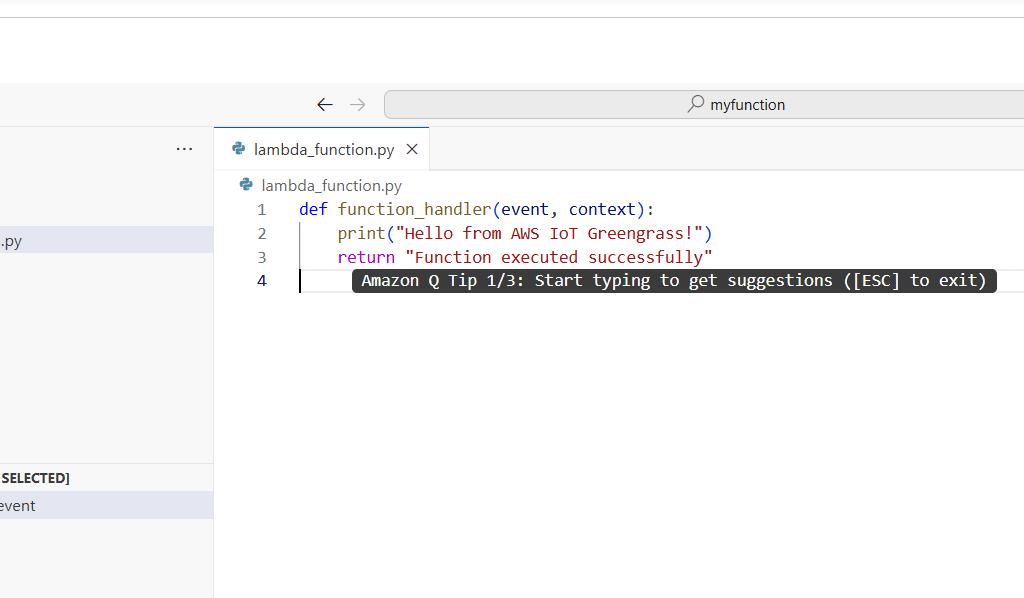
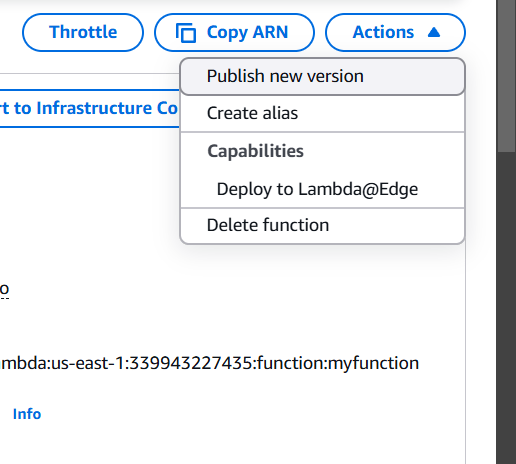
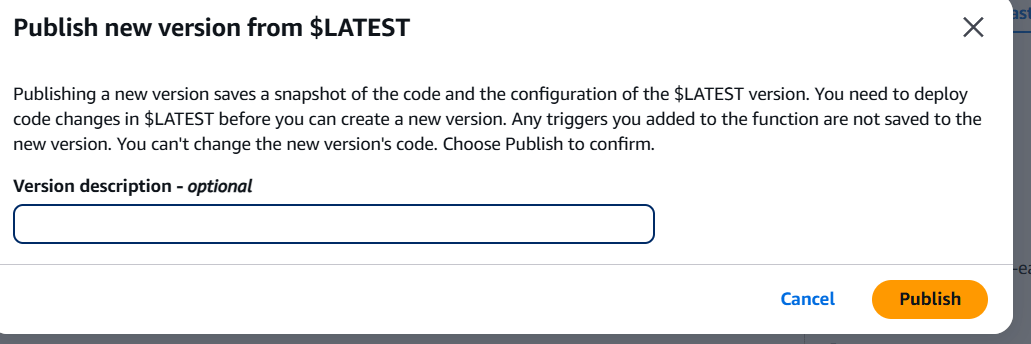
STEP 9: Click on version and select publish new version.
- Click on publish.
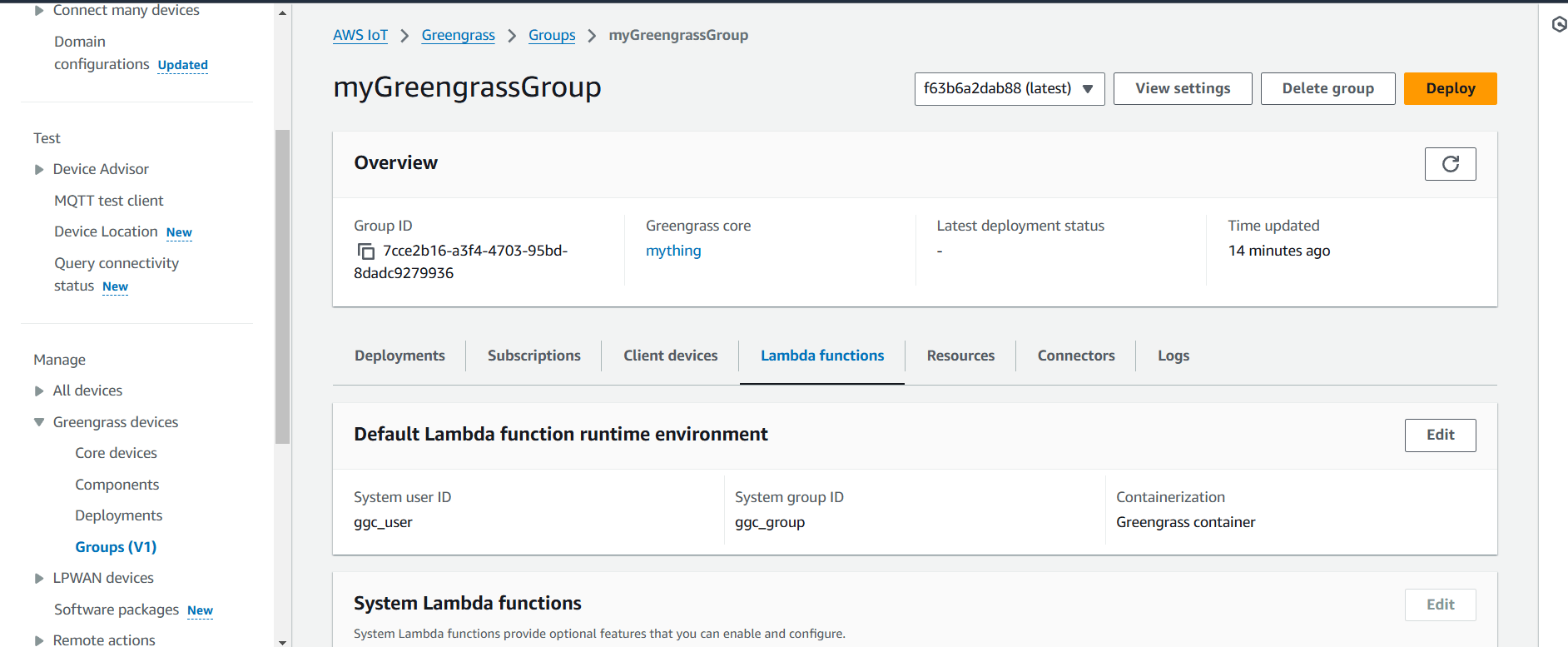
STEP 10: Go to AWS Iot core select greengrass and click on groups.
- Go to lambda function.
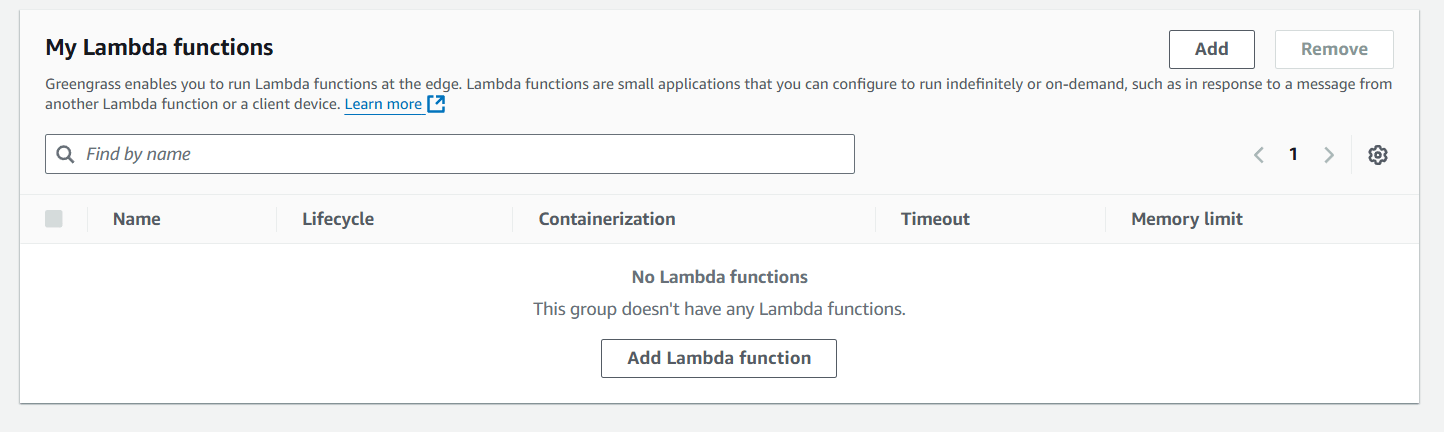
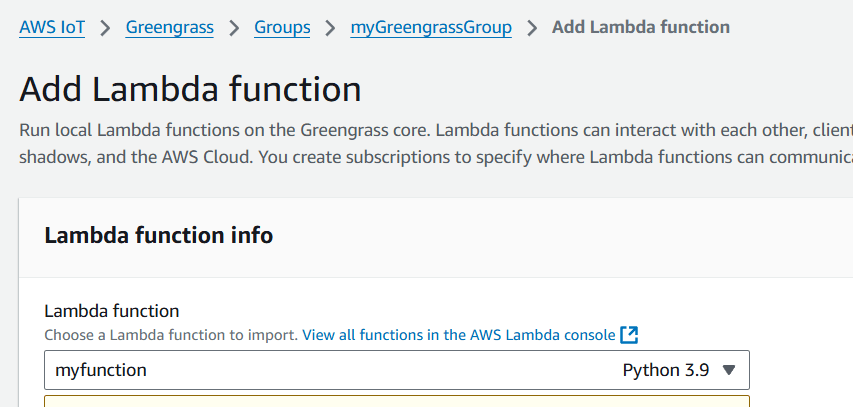
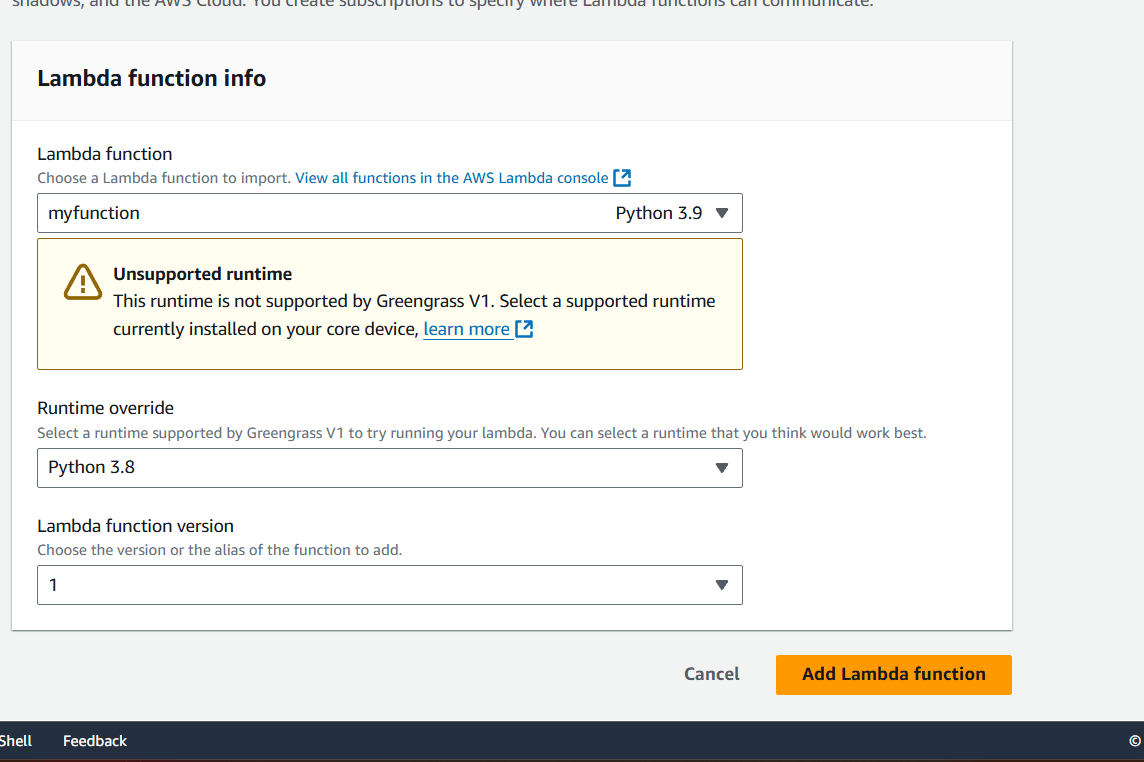
- Click on add lambda.
- Create a lambda function.

Conclusion.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, IoT Greengrass is a powerful edge computing service that enables efficient data processing, device management, and local execution of AWS Lambda functions on IoT devices. By allowing devices to function independently of the cloud and handle tasks like data filtering, machine learning inference, and offline operation, it enhances scalability, reduces latency, and optimizes resource usage. With seamless integration with AWS services, IoT Greengrass empowers businesses to deploy smarter, more responsive IoT applications that are both reliable and cost-effective. As IoT adoption continues to grow, solutions like Greengrass are essential in enabling more intelligent, responsive, and scalable edge computing systems.
Understanding the Jenkins REST API: A Comprehensive Guide.
Introduction.
In today’s fast-paced software development world, automation is a crucial part of improving efficiency and reducing errors. Jenkins, a popular open-source automation server, plays a significant role in this by providing continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) services. To further enhance its capabilities, Jenkins offers a powerful REST API that allows developers to integrate Jenkins with other applications, monitor jobs, trigger builds, and manage configurations programmatically. In this blog, we’ll dive into the concept of the Jenkins REST API, explore its key features, and discuss how you can leverage it to automate workflows and improve your DevOps practices. Whether you’re looking to build custom integrations or automate repetitive tasks, understanding Jenkins’ REST API is a valuable skill for modern developers.

STEP 1: Go to jenkins dashboard.
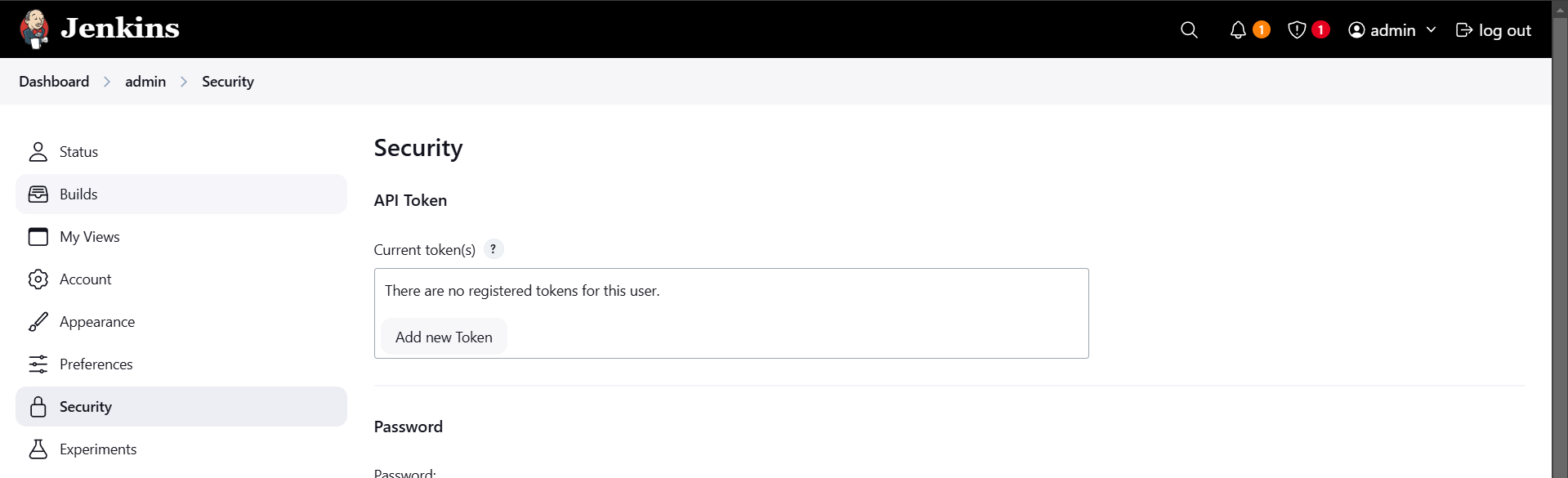
STEP 2: Click on your user name.
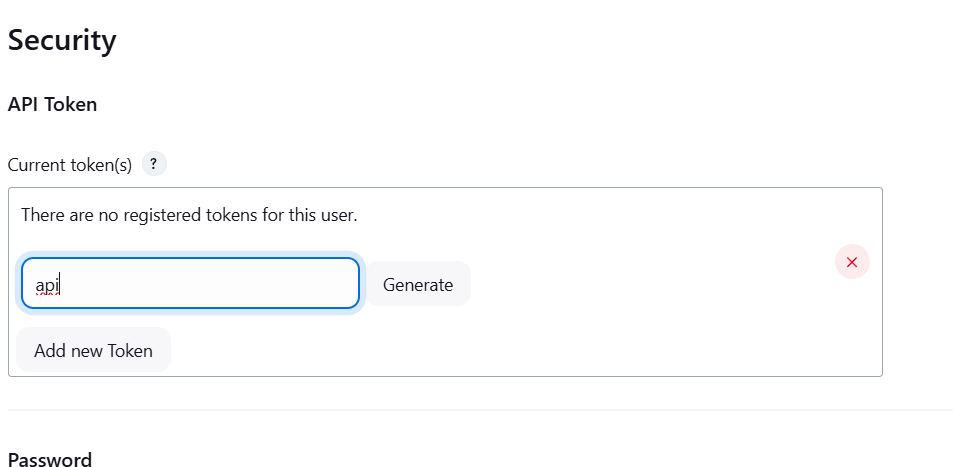
- Select security create API Token.
- Click on Add new token.
- Enter the name and click on generate.
- Copy your token.
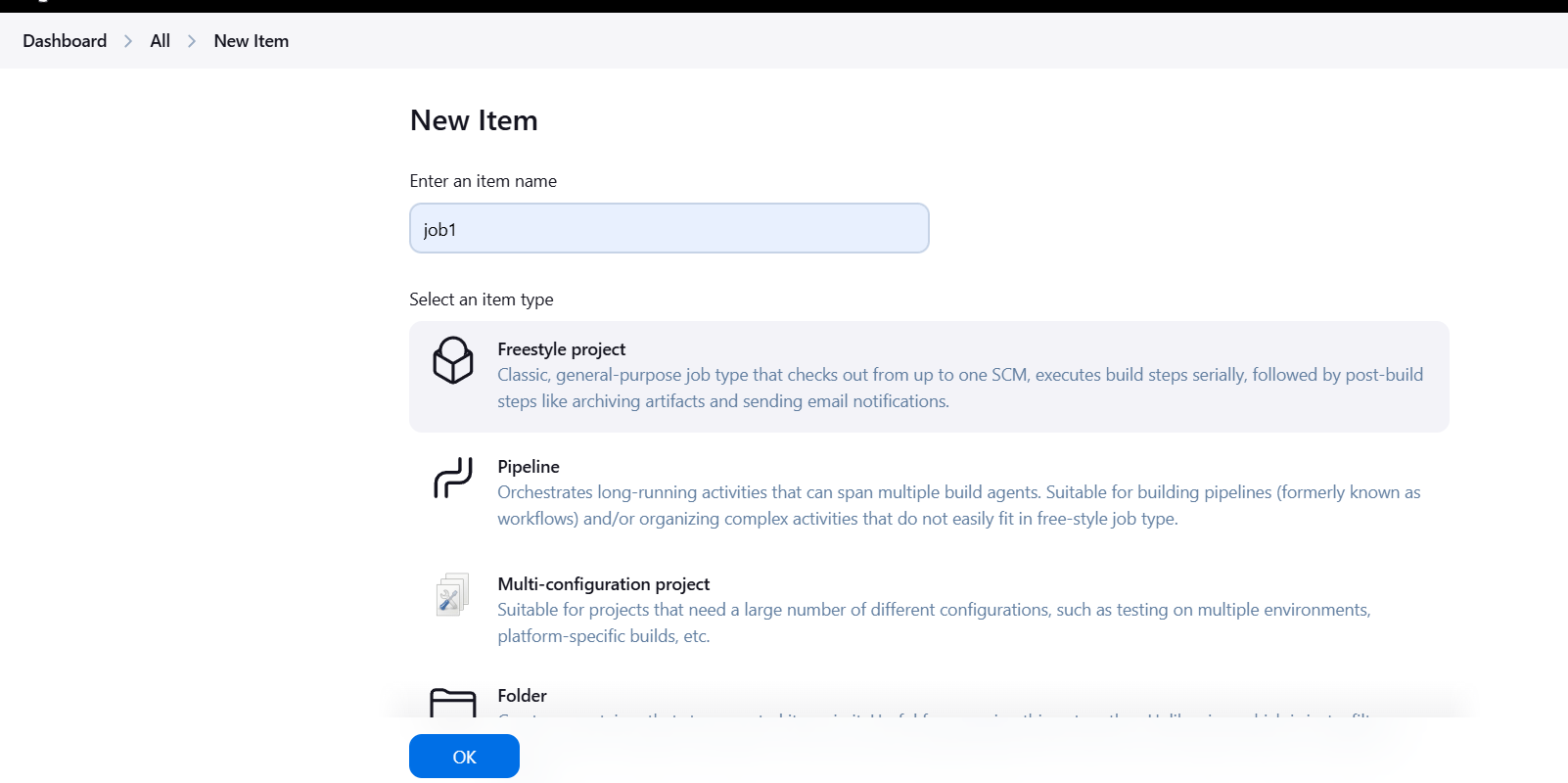
STEP 3: Next, Go to dashboard create new item.
- Enter the Job name and select the freestyle project.
- Click on ok.
- Configure the Job.
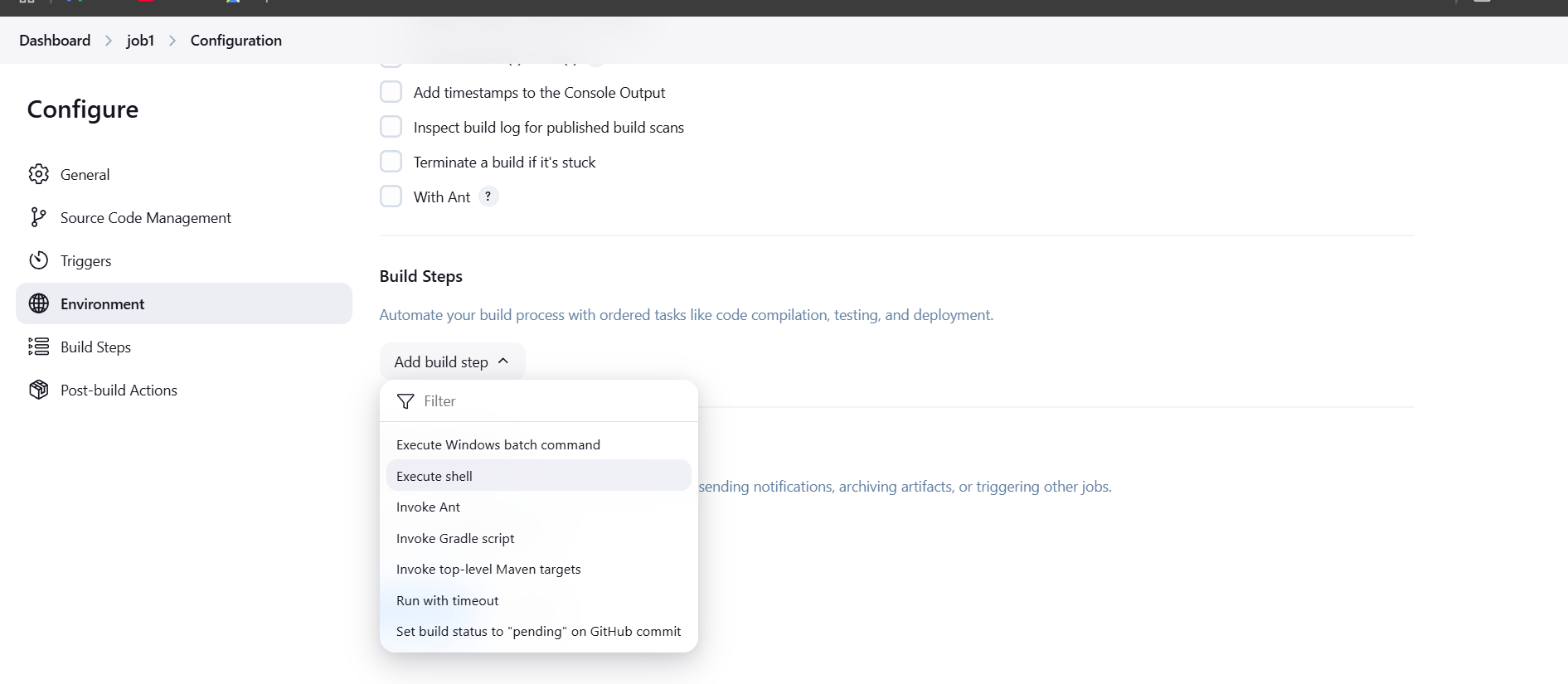
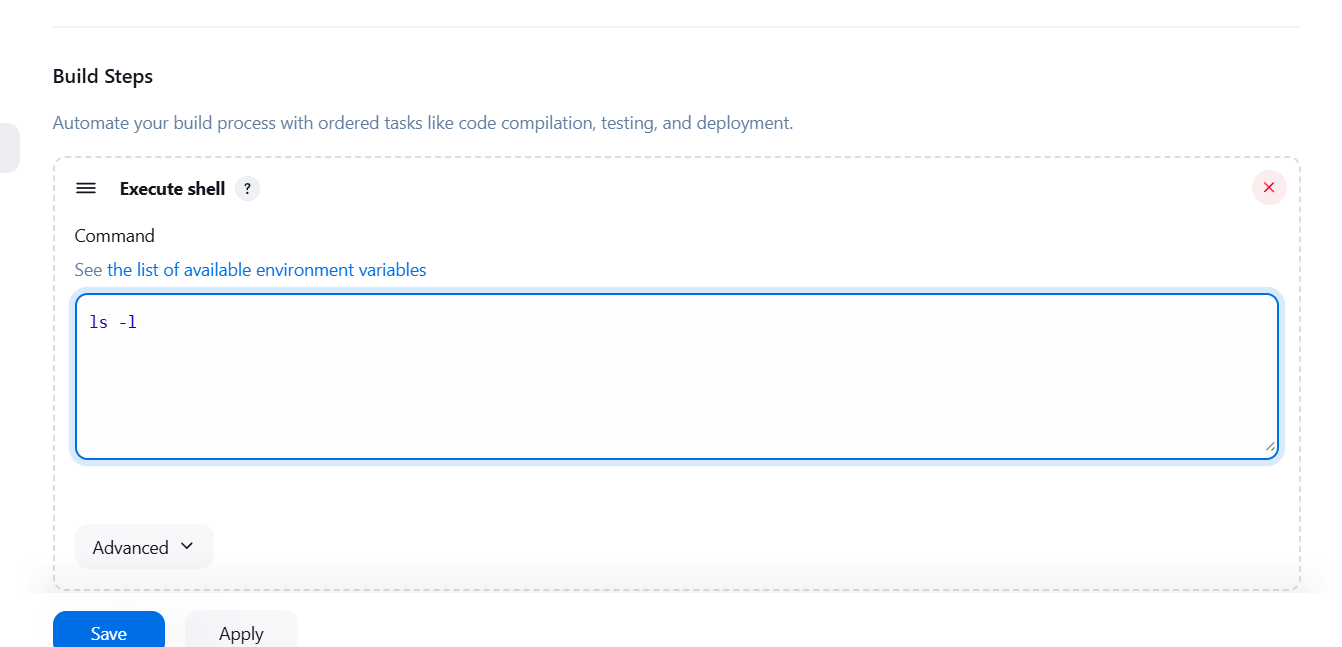
- Scroll down Click on Add build and select execute shell.
- Enter the ls -l command.
- Apply and save.
STEP 4: Accessing the SSH Connection.
- Enter the following command.
echo "<API_TOKEN>" > APITOKEN
cat APITOKEN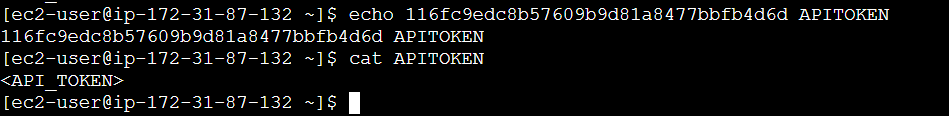
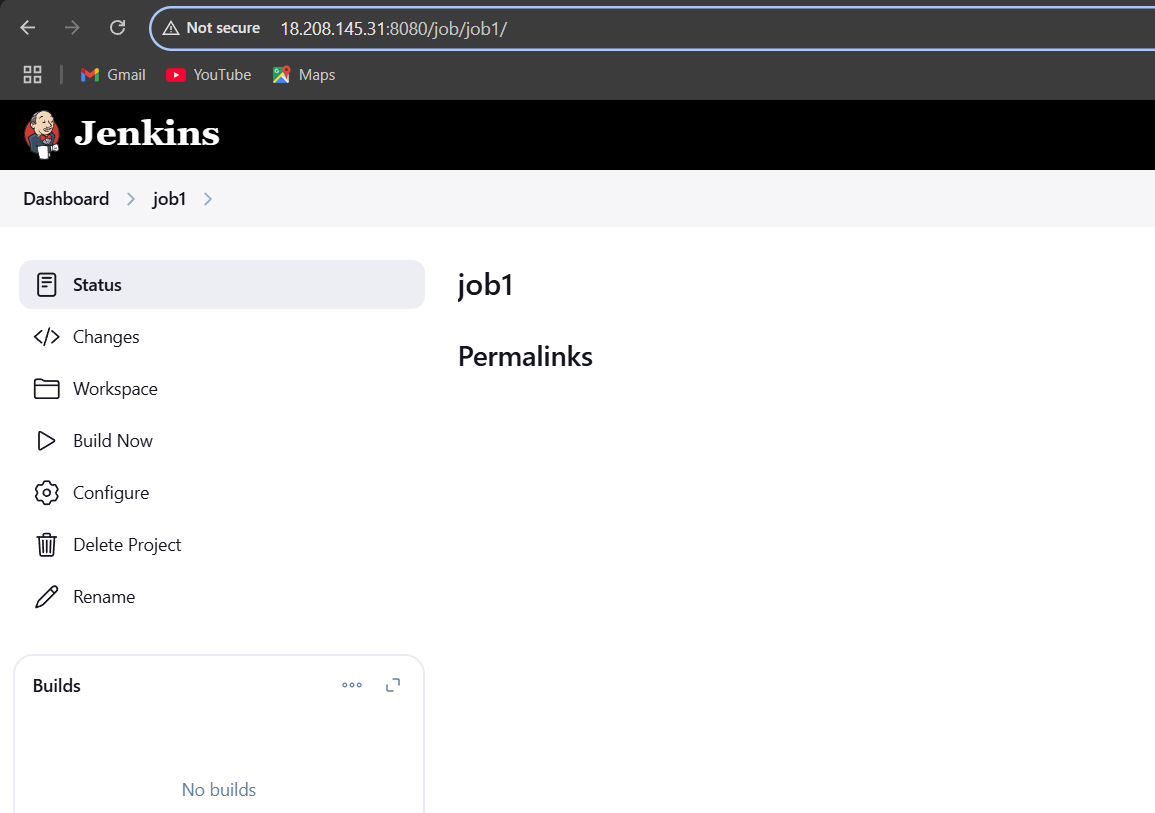
STEP 5: Go to jenkins dashboard.
- Re-write the URL of Jenkins by adding /crumbIssuer/api/xml then hit Enter:
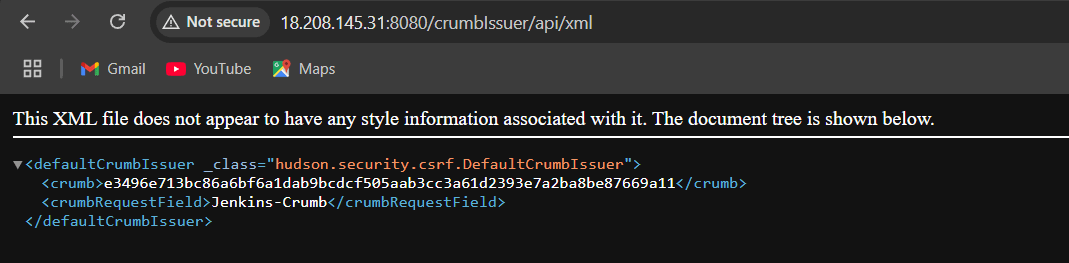
STEP 6: Execute the following command in the shell to retrieve the Jenkins crumb token. Replace username and password with the credentials Used in SSH Connection, and <jenkins-server-url> with the public IPv4 address of the EC2 instance.
crumb=$(curl -u "username:password" -s "http://<jenkins-server-url>/crumbIssuer/api/xml?xpath=concat(//crumbRequestField,\":\",//crumb)")
echo $crumb
cat APITOKEN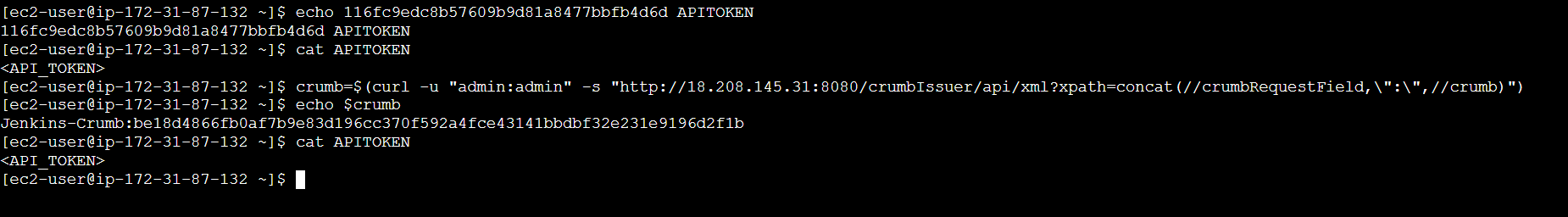
STEP 7: Run below command to start the build on Job1, replace “USERNAME:APITOKEN” with the username that you set initially and APITOKEN from previous step.
curl -X POST -u USERNAME:APITOKEN "JOB_URL/build" -H "crumb"STEP 8: Go to dashboard and verify the job build.
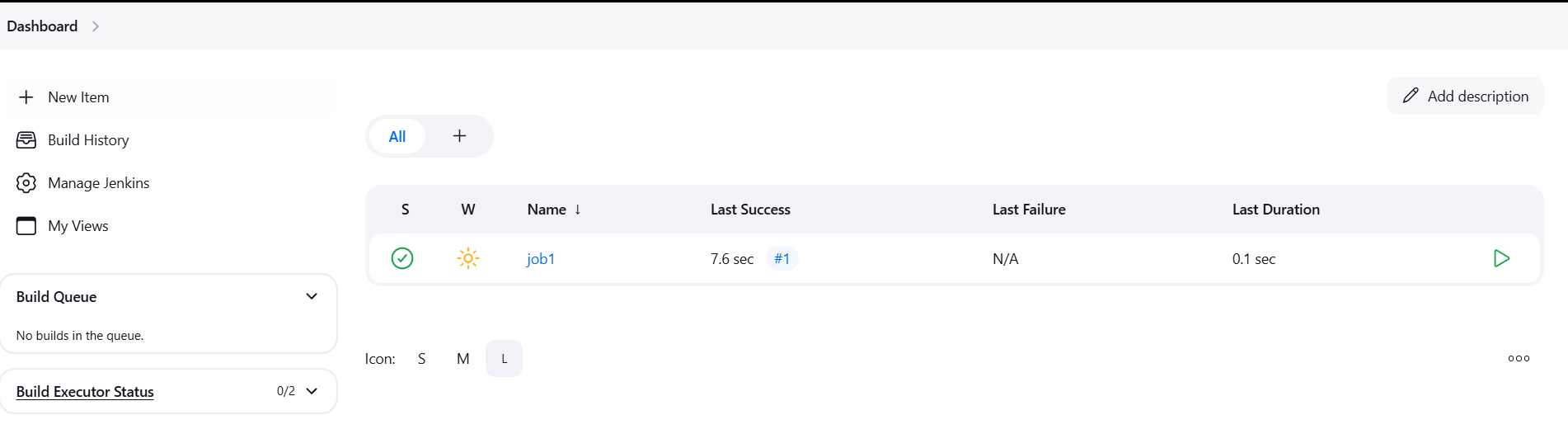
STEP 9: Run the below command to retrieve the configuration of a Jenkins job and save it locally, replace JobURL with the URL of Job1 from previous step, USER_NAME.
curl -X GET JobURL/config.xml -u USER_NAME:API_TOKEN -o mylocalconfig.xml
ls -l
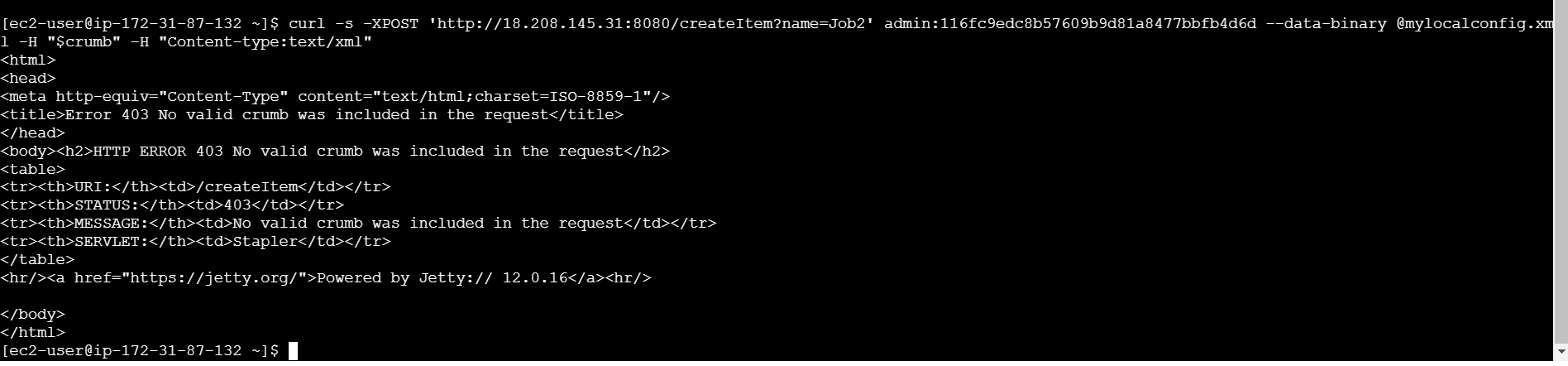
curl -s -XPOST 'JENKINS_HOST/createItem?name=JOB_NAME' -u USERNAME:API_TOKEN --data-binary @mylocalconfig.xml -H "$crumb" -H "Content-type:text/xml"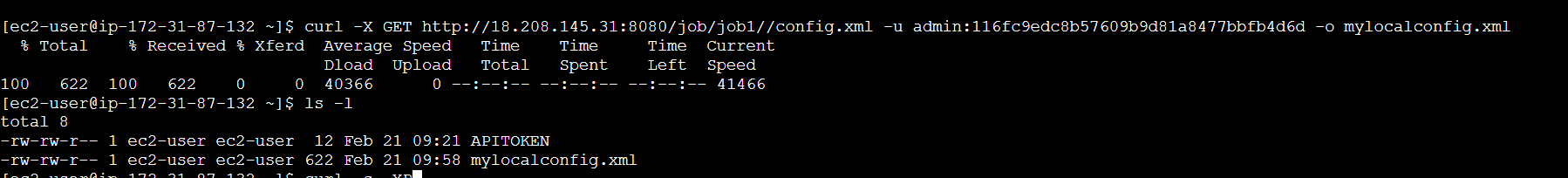
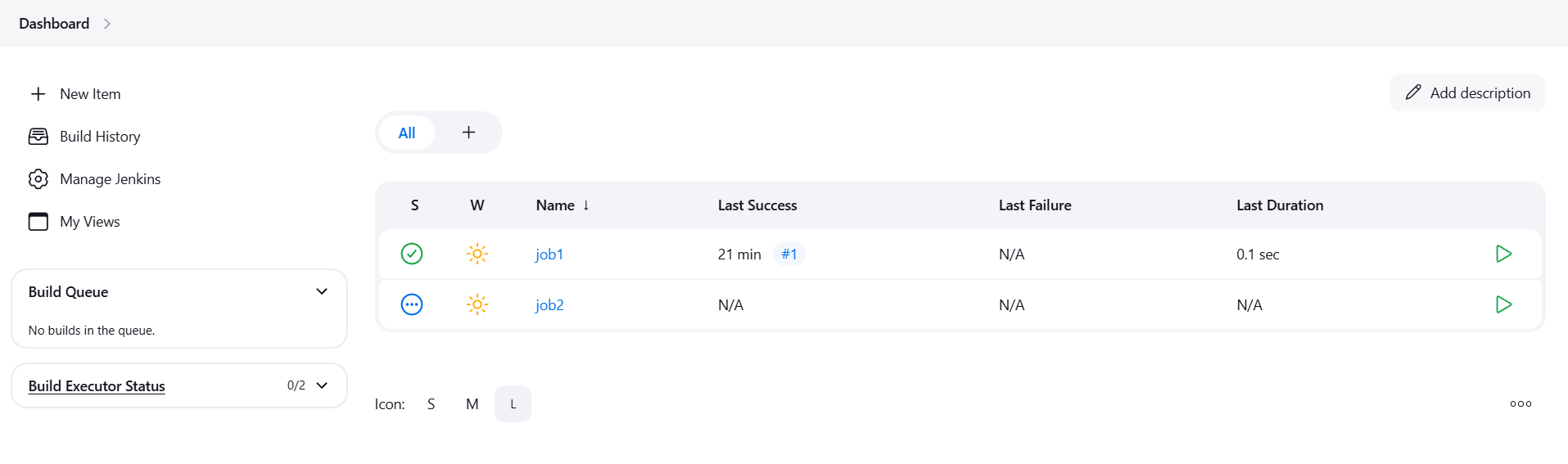
STEP 10: Go to jenkins dashboard and verify the created the job2 like job1.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, the Jenkins REST API enhances the flexibility of Jenkins by providing a means for developers and system administrators to automate processes, monitor builds, and manage Jenkins configurations without directly interacting with the Jenkins UI. It’s a valuable resource for DevOps teams looking to streamline their workflows and integrate Jenkins into a broader automation pipeline.
Introduction to Amazon Artifact.
Introduction.
Amazon Artifact is a security and compliance service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that offers customers access to a comprehensive set of compliance reports and security documentation. It is designed to help organizations meet their regulatory, security, and compliance requirements when using AWS cloud services. Amazon Artifact simplifies the process of obtaining relevant documentation needed for audits and compliance reviews.
Key features include access to AWS’s third-party audit reports, security certifications, and agreements, such as SOC, ISO, PCI-DSS, and GDPR. Users can download and view these reports to ensure they meet industry standards and regulations.
The platform is tailored for both internal and external auditors, security officers, and compliance teams, enabling them to quickly access necessary documentation. Artifact helps reduce the burden of manually requesting reports, offering a self-service interface to download documents and ensure up-to-date compliance status.

Amazon Artifact also supports transparency by allowing customers to gain insight into AWS’s infrastructure, data protection practices, and security controls. It ensures that businesses can maintain trust and accountability when using AWS services.
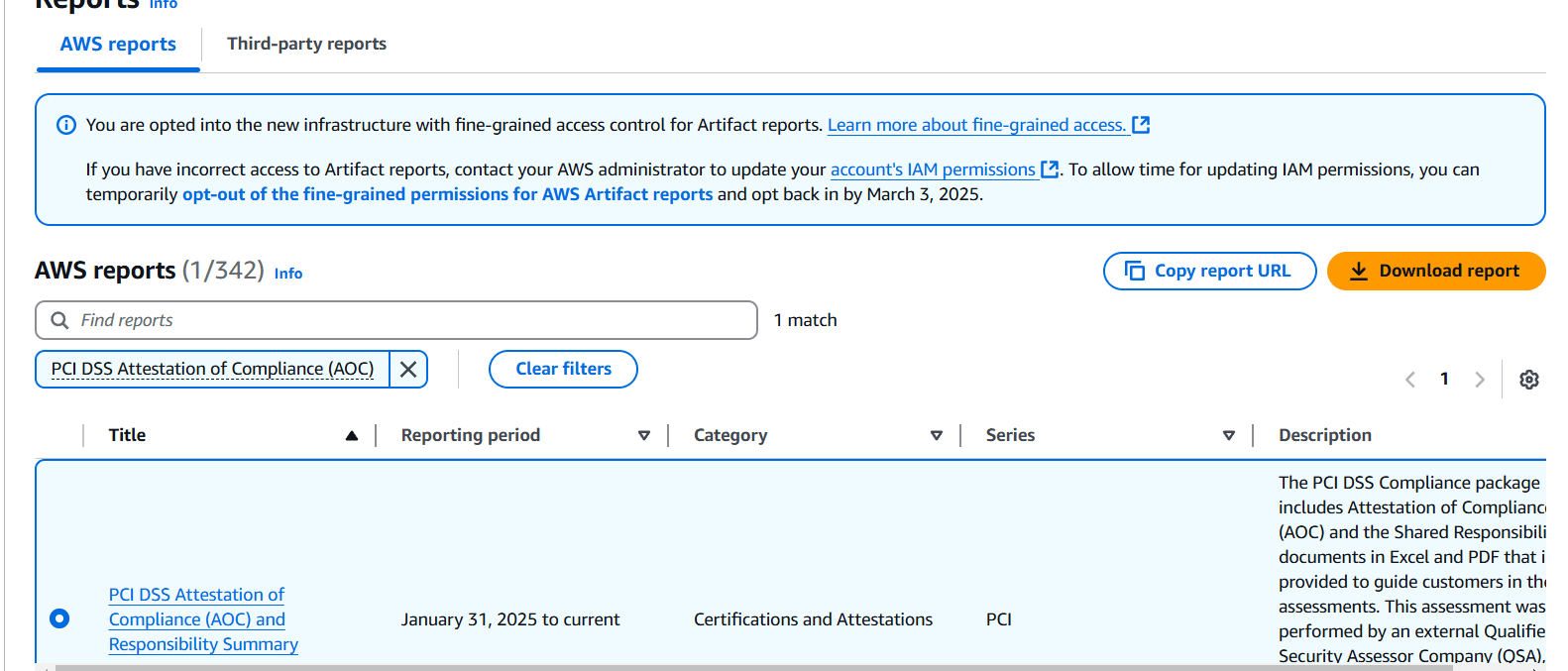
STEP 1: Navigate the AWS artifact and select the reports.
- Select the PCI DSS Attestation of Compliance (AOC) and download the report.
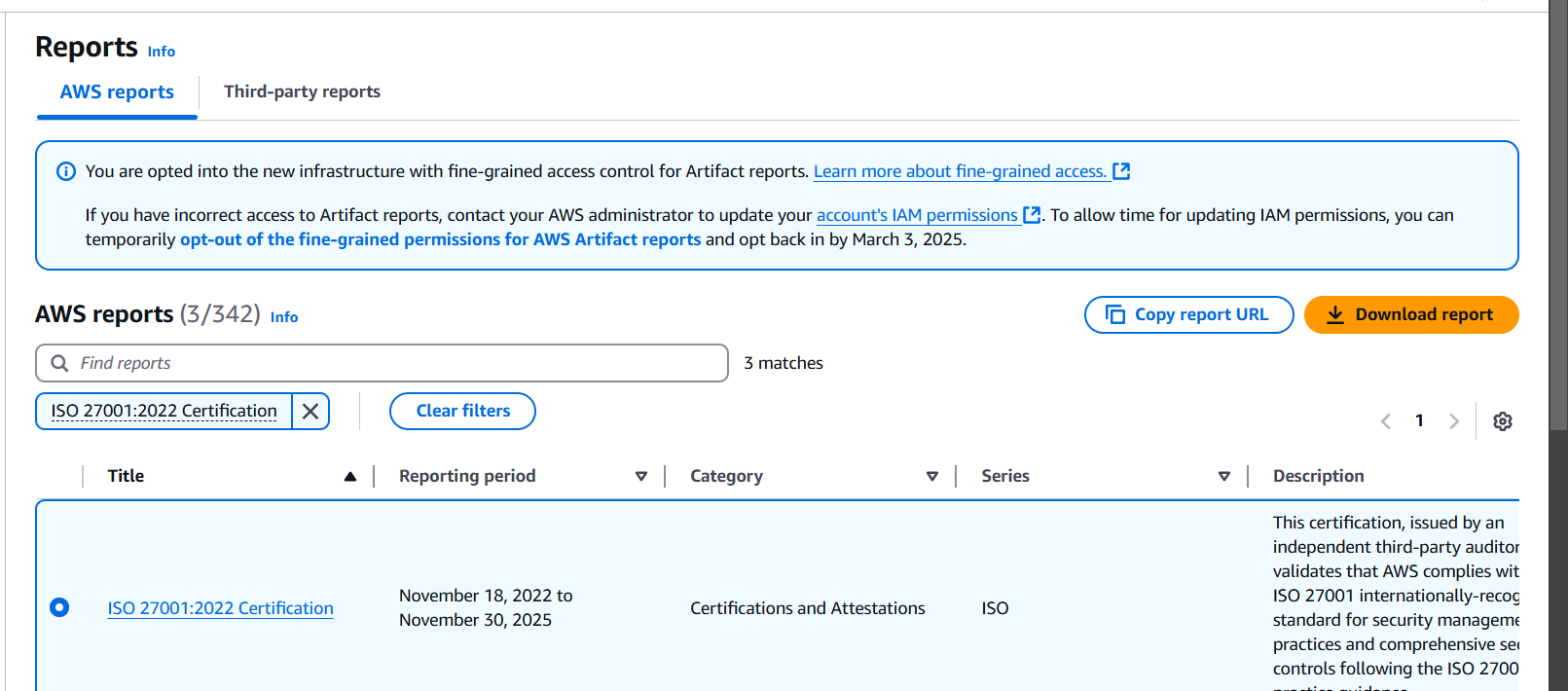
STEP 2: Select the ISO 27001:2022 Certification and download the report.
STEP 3: Select the SOC Continued Operations Letter and Click on download report.
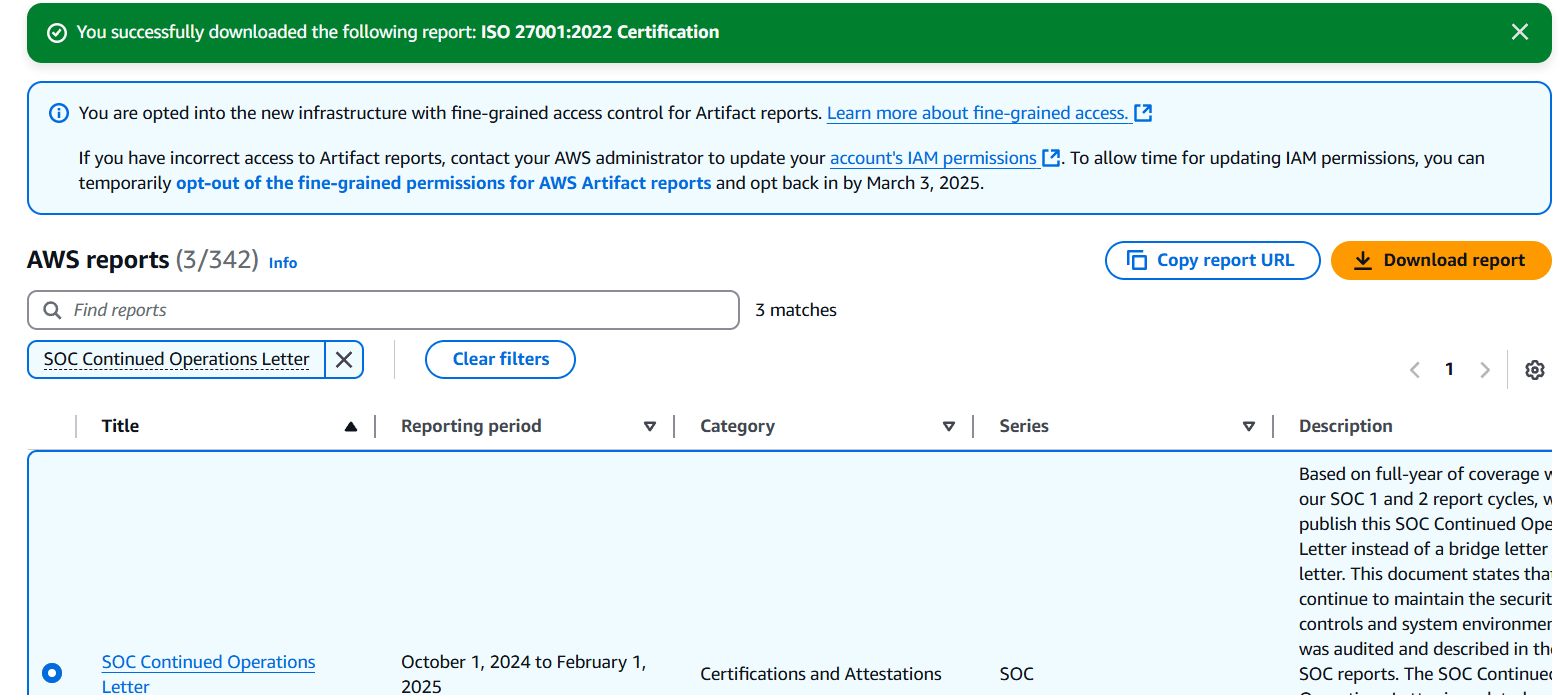
STEP 4: Click on Accept terms and download report.
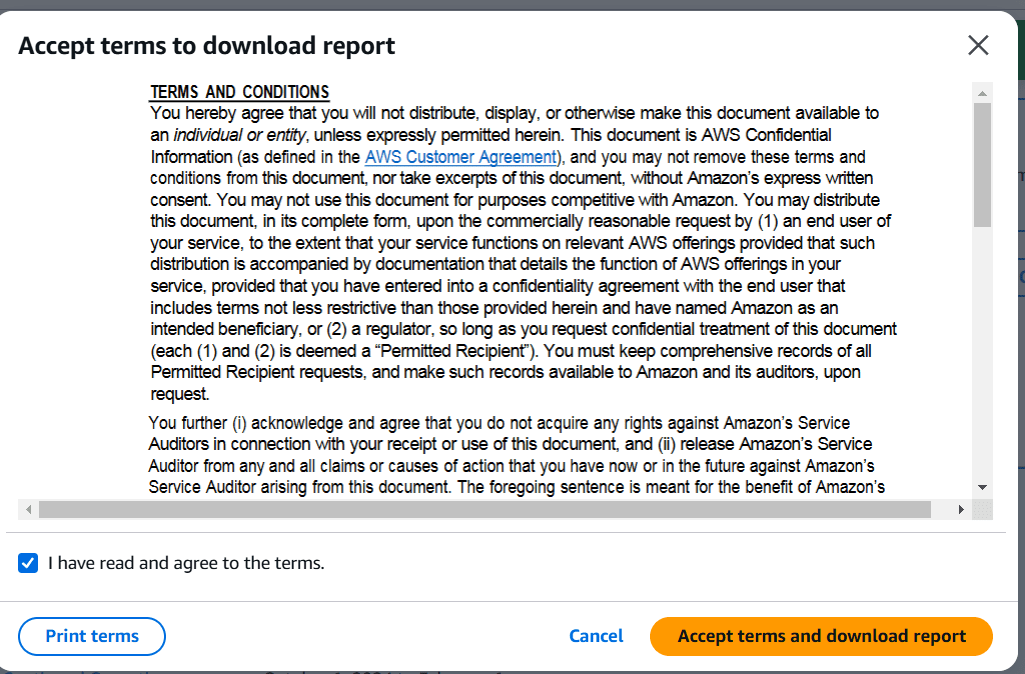
Open the downloaded letter document (usually in PDF format) and carefully review its contents, focusing on the following key sections:
- Introduction and purpose of the letter
- Time period covered by the letter
- Auditor’s assessment of AWS’s continued operations and control environment
- Any changes or updates to AWS’s control environment or services covered
Note: The SOC Continued Operations Letter provides vital assurance that AWS has maintained an effective control environment since the last SOC 1 Type 2 audit. Pay attention to the auditor’s evaluation of AWS’s operations during the specified period, any changes to the covered services and regions, and its significance for ongoing compliance with regulations such as SOX. Additionally, configure notifications in AWS Artifact to stay updated with the latest versions of this letter, as it helps bridge the gap between SOC 1 audits.
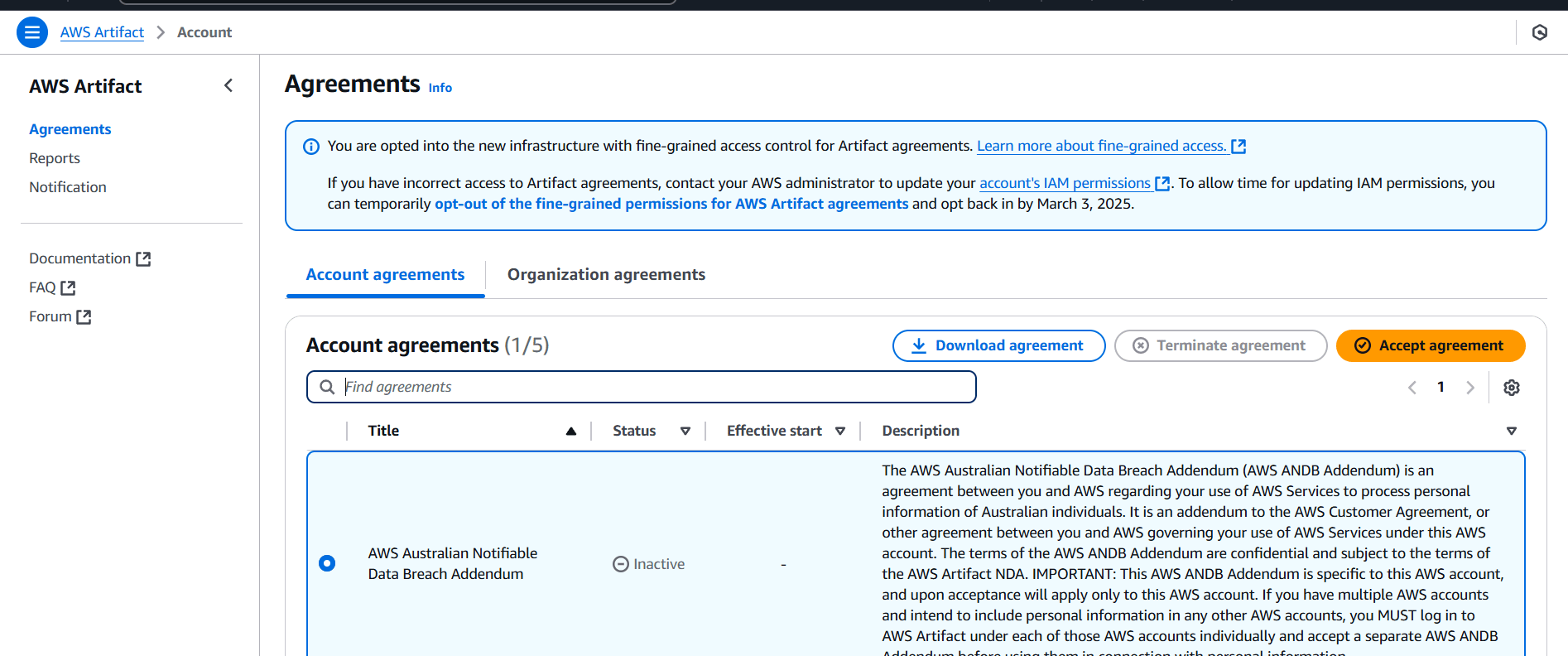
STEP 5: Go to agreements and select One agreement.
- Accept NDA and download.
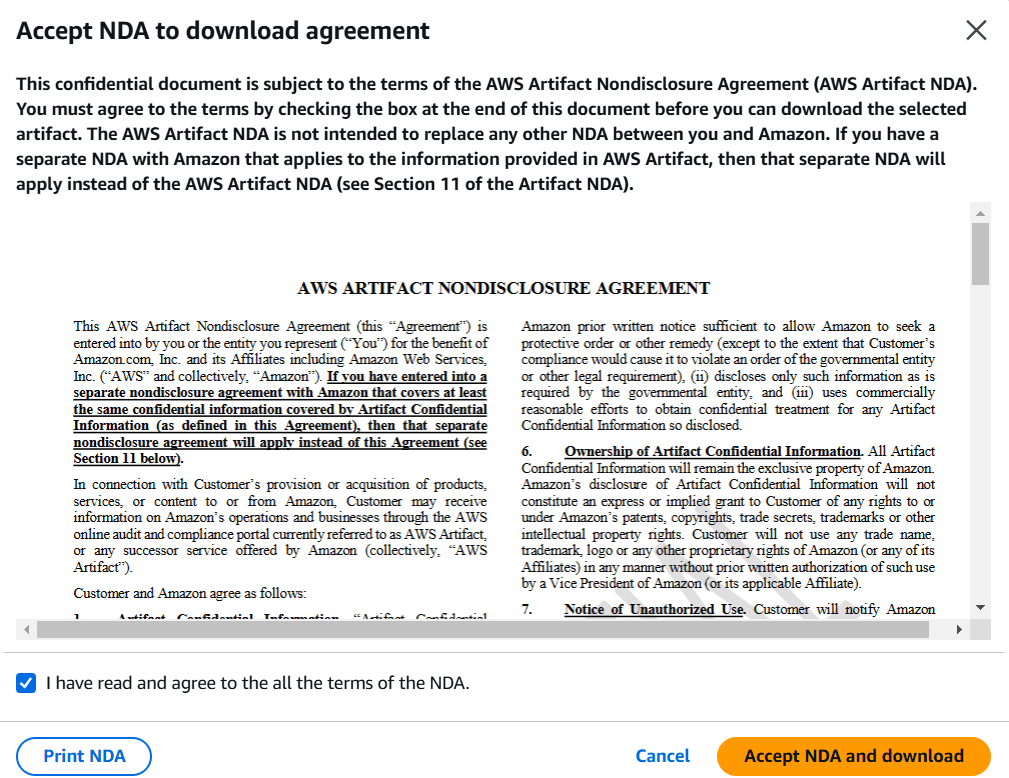
STEP 6: Click on Accept agreement.
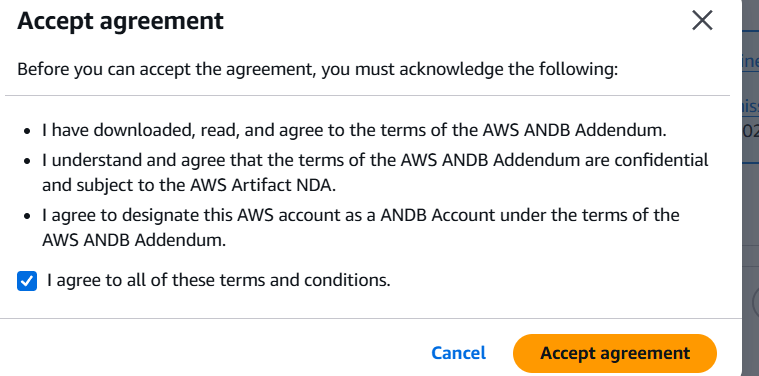
STEP 7: And verify the agreement is active.
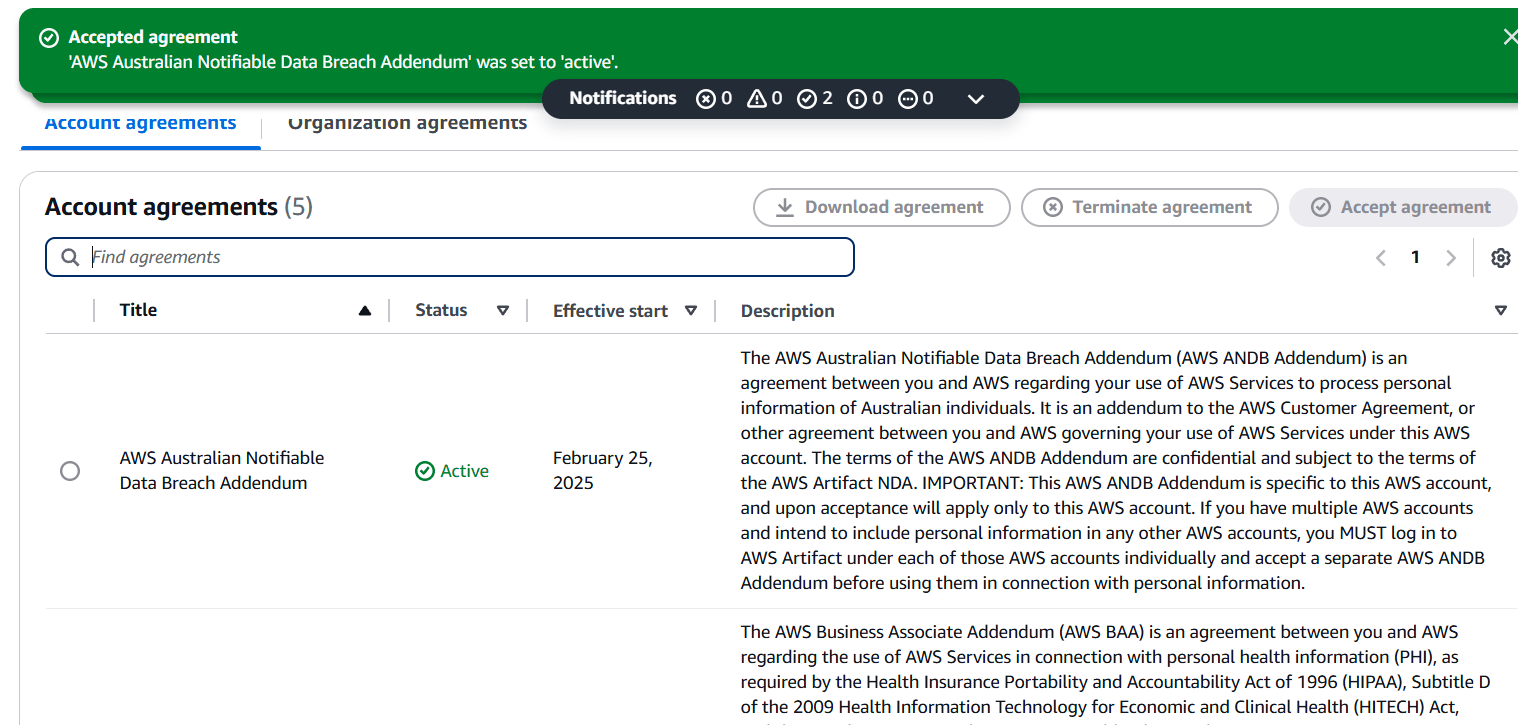

Conclusion.
In conclusion, Amazon Artifact is a powerful tool that streamlines the process of obtaining and managing compliance and security documentation for organizations using AWS services. By providing easy access to audit reports, certifications, and agreements, it helps businesses meet regulatory and industry requirements efficiently. With its self-service model and support for transparency, Artifact simplifies compliance efforts, builds trust, and enables organizations to focus more on their core operations while ensuring they remain secure and compliant in the cloud.














