Step-by-Step Guide to Launching a WordPress Instance on Amazon Lightsail.
Introduction.
In today’s digital age, creating and managing a website has never been easier, thanks to cloud services like Amazon Lightsail. Amazon Lightsail is a simplified cloud computing platform that allows developers and businesses to quickly deploy websites and applications with minimal configuration. Among the many applications you can run on Lightsail, WordPress stands out as one of the most popular content management systems (CMS). With its ease of use, customizable themes, and robust plugin ecosystem, WordPress powers millions of websites worldwide.
One of the biggest challenges for those looking to launch a WordPress website is the complexity of setting up a server, configuring the environment, and ensuring scalability. This is where Amazon Lightsail comes in. With Lightsail, you can deploy a WordPress instance in just a few clicks, without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure. It simplifies the entire process, giving you more time to focus on building and managing your content.
Lightsail provides a low-cost, user-friendly environment for WordPress hosting, with a predictable pricing structure. This makes it an ideal solution for small to medium-sized businesses, personal blogs, portfolios, or anyone who wants to get a WordPress website up and running quickly. Lightsail comes with pre-configured stacks for popular applications like WordPress, meaning you don’t have to worry about manually installing or configuring PHP, MySQL, or Apache.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of launching a WordPress instance using Amazon Lightsail. You’ll learn how to create an account, choose the right configuration for your needs, and easily deploy WordPress on Lightsail. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced web developer, this tutorial will help you get your WordPress site online with minimal hassle.

By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to set up a WordPress instance on Lightsail, manage your website, and start creating content with ease. Let’s dive into the world of WordPress on Amazon Lightsail and get your site up and running in no time!
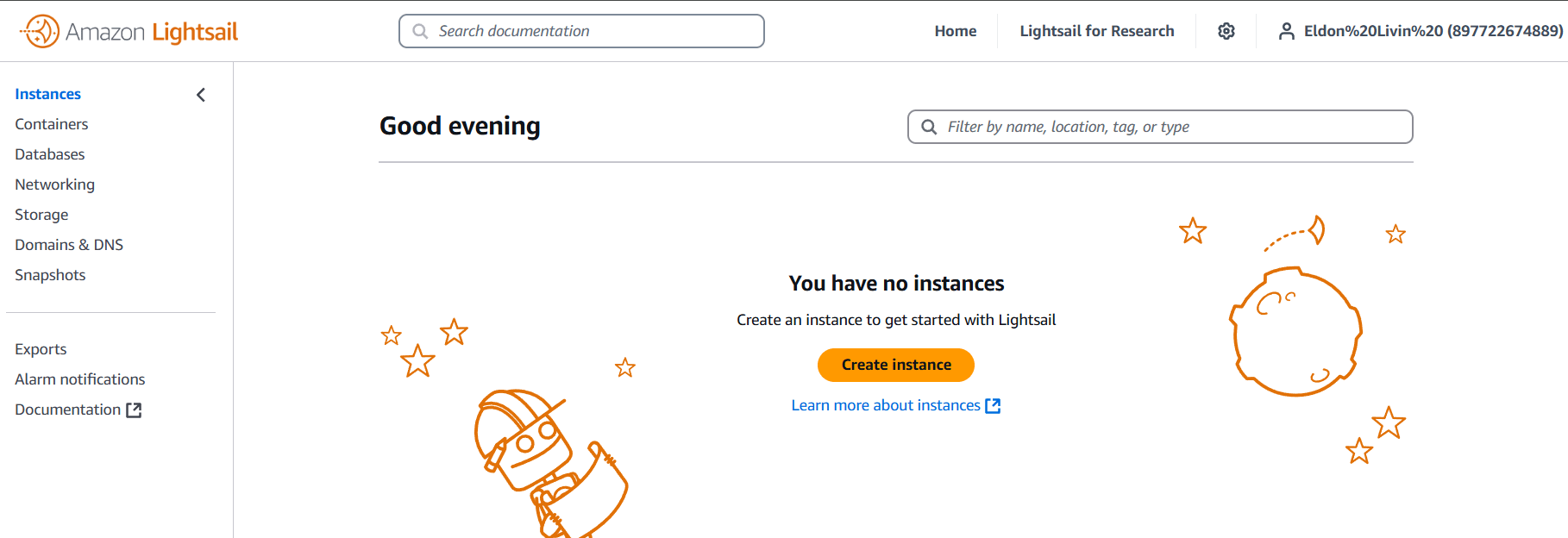
STEP 1: Navigate the lightsail and click on create instance.
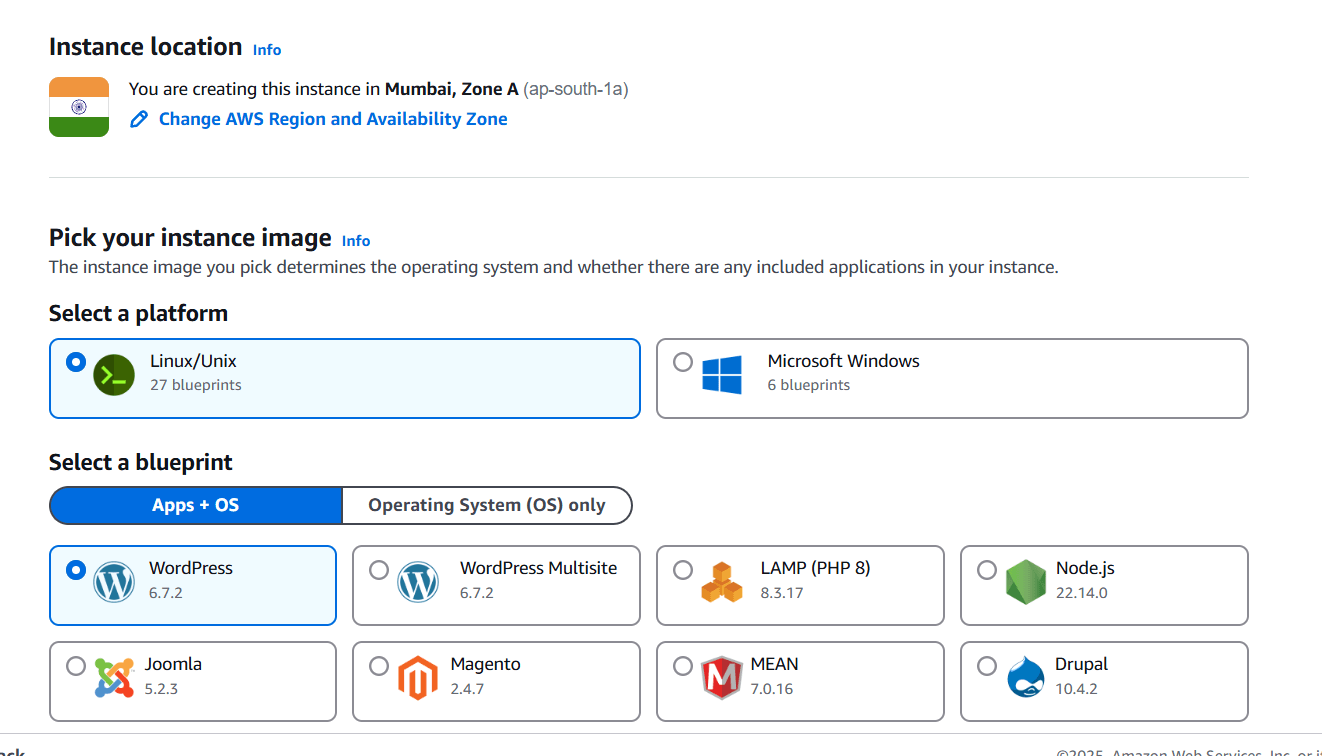
STEP 2: Select the wordpress.
STEP 3: Select the size.
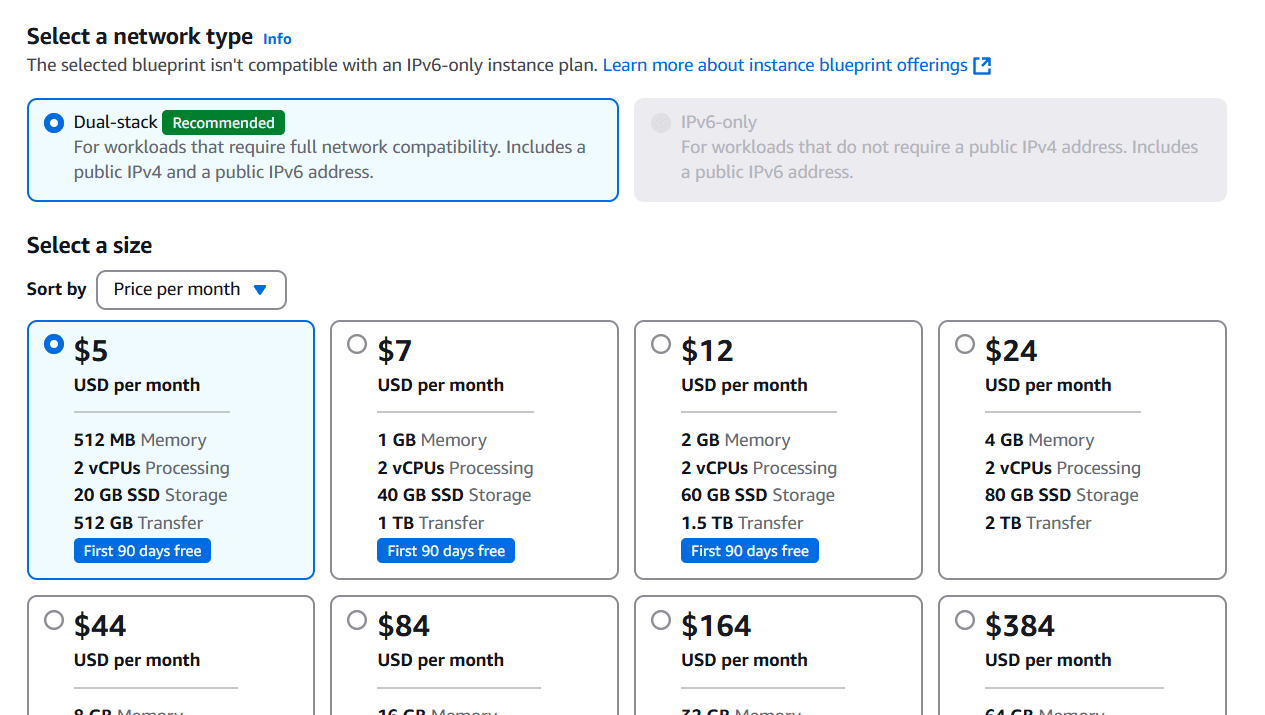
STEP 4: Click on create instance.
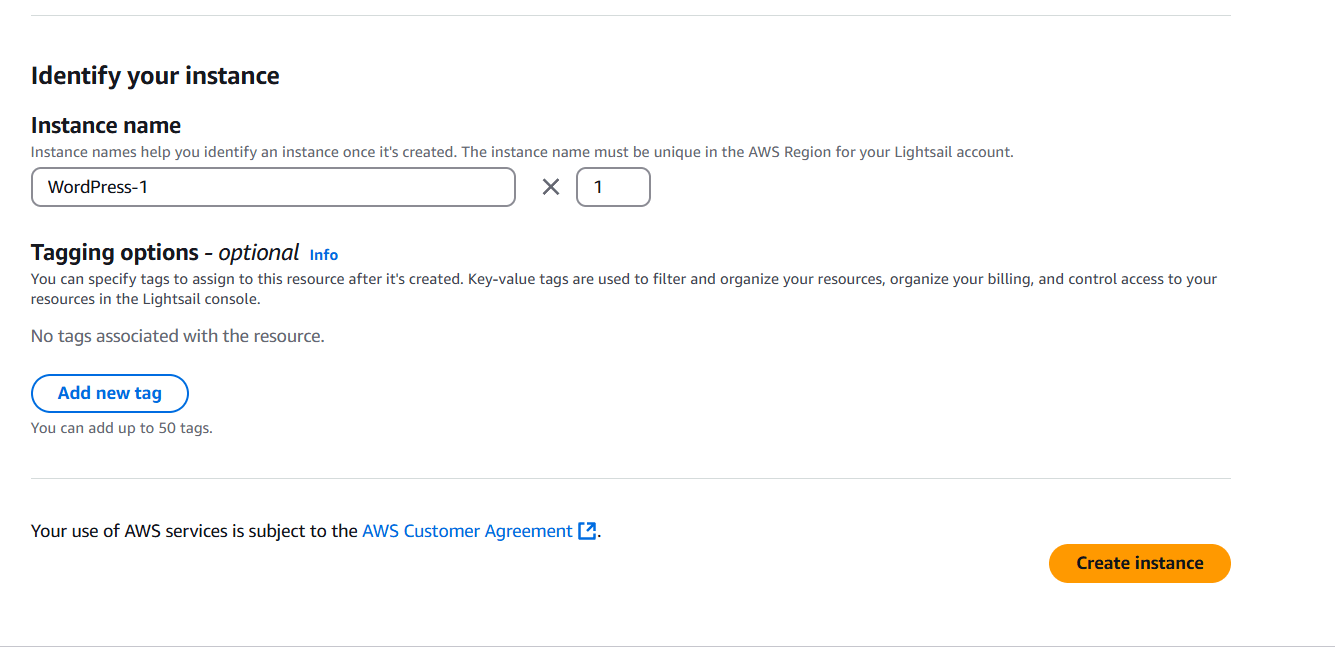
STEP 5: Click on command line.
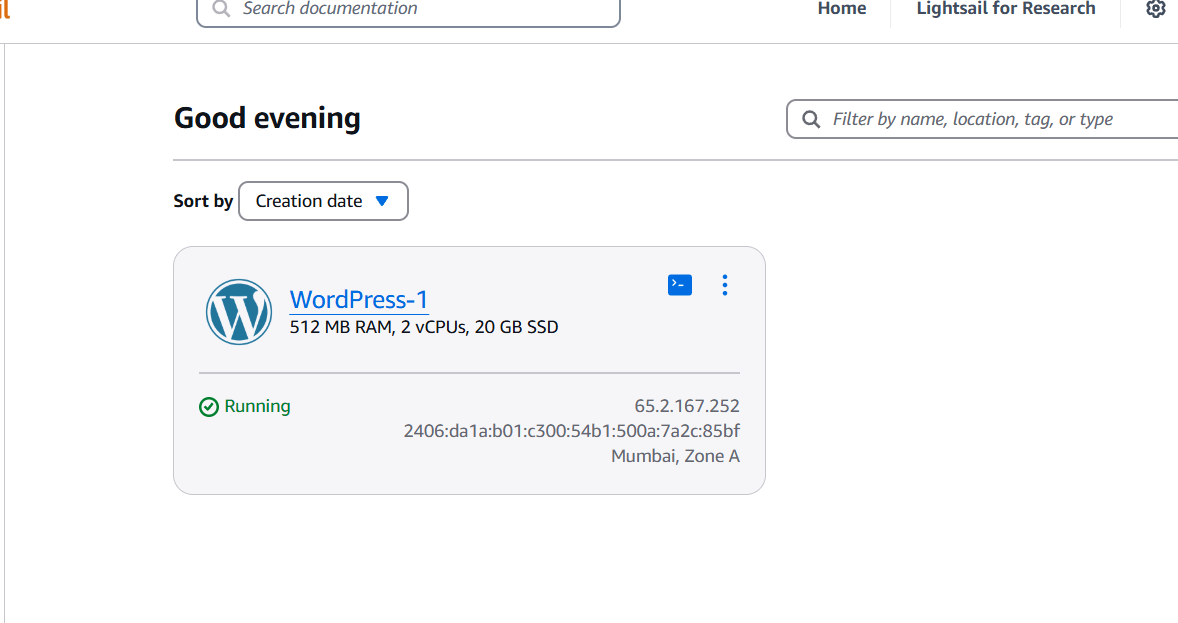
STEP 6: Enter the following command.
cat $HOME/bitnami_application_password 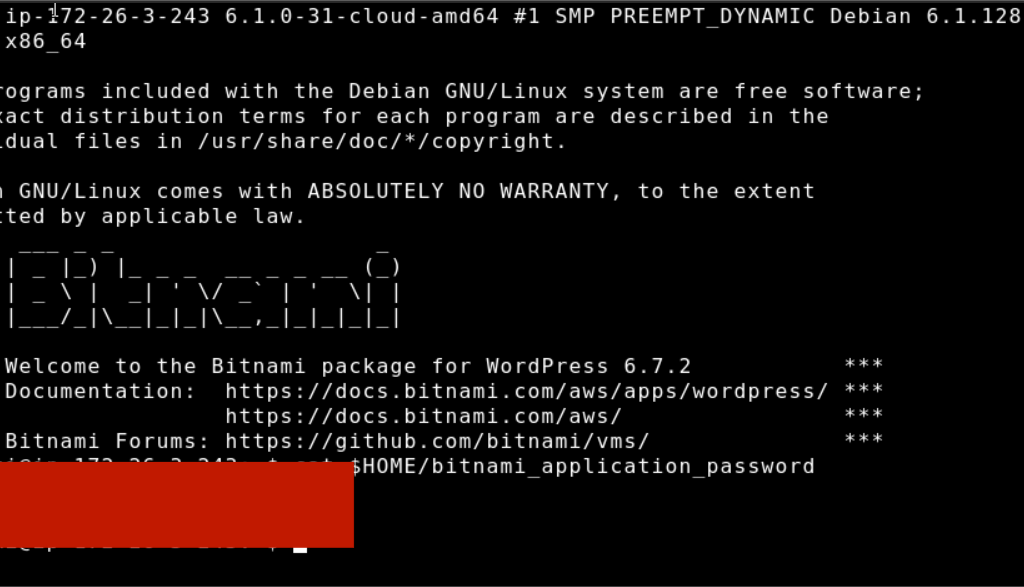
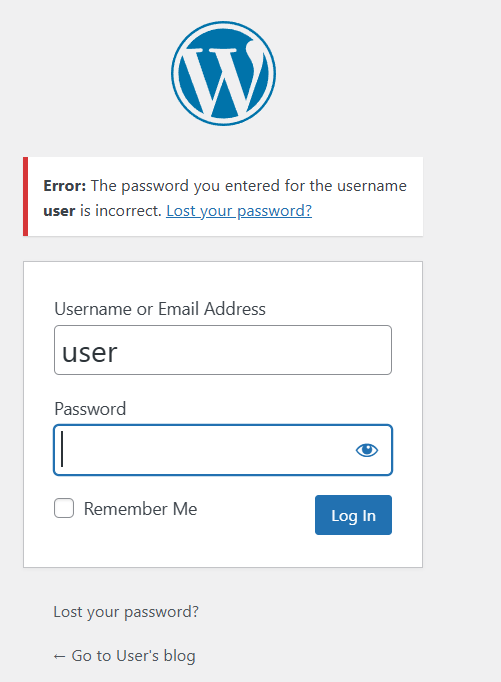
STEP 7: Now enter the browser http://PublicIpAddress/wp-login.php
- Enter the user name and password.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, Amazon Lightsail offers an incredibly simple and efficient way to launch a WordPress website without the need for complex server management or configurations. With its user-friendly interface, affordable pricing, and pre-configured WordPress stacks, Lightsail is an excellent choice for anyone looking to get a website up and running quickly. Whether you’re a blogger, small business owner, or developer, Lightsail provides the tools and flexibility to build and grow your online presence with ease.
By following the steps in this guide, you’ve successfully deployed your WordPress instance on Lightsail and can now focus on customizing your site, adding content, and scaling as your needs evolve. Lightsail takes care of the heavy lifting, so you can concentrate on the creative and strategic aspects of your WordPress site.
As your site grows, Amazon Lightsail makes it easy to manage, upgrade, and even scale your resources without a significant increase in complexity. You can always expand your infrastructure by adding more storage, increasing bandwidth, or configuring additional services through the AWS ecosystem.
With Amazon Lightsail, launching and managing a WordPress site has never been more straightforward. Now that your WordPress instance is live, you’re ready to start engaging with your audience and growing your online presence. Best of luck with your website, and enjoy the seamless experience that Lightsail offers!
Creating Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) in AWS: Tips and Best Practices.
Introduction.
In today’s fast-paced cloud computing world, Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a vast array of tools and services that help businesses and developers streamline their infrastructure and deploy applications at scale. One of the essential tools in AWS’s cloud arsenal is the Amazon Machine Image (AMI). An AMI is a snapshot of an EC2 instance, including the operating system, application server, applications, and other configurations. Essentially, it’s a blueprint that can be used to create and launch EC2 instances quickly and consistently.
Creating and managing AMIs is an essential skill for anyone working with AWS. By leveraging AMIs, you can automate the process of provisioning new instances, maintain consistent environments across various stages of your development pipeline, and even create backups of your instances for disaster recovery.
But what makes AMIs even more powerful is their flexibility. You can customize an AMI to suit your exact needs—whether it’s a simple application server or a complex multi-tier architecture. Once created, an AMI can be shared with other AWS accounts, enabling collaboration and efficient resource management.
In this guide, we will take you step-by-step through the process of creating your own AMI within AWS. From launching an EC2 instance to customizing it with software packages and configurations, and finally creating the AMI, you will learn how to optimize your workflow and ensure that your environments are easily replicable. Whether you’re new to cloud infrastructure or already familiar with AWS, understanding how to create AMIs will open up new possibilities for managing your instances more efficiently.

By the end of this guide, you will have the knowledge to create and maintain AMIs tailored to your specific use cases, improving consistency and reducing setup time across your AWS instances. Let’s begin exploring the world of Amazon Machine Images and how they can help elevate your AWS experience.
STEP 1: Create instance Enter the name and select OS.
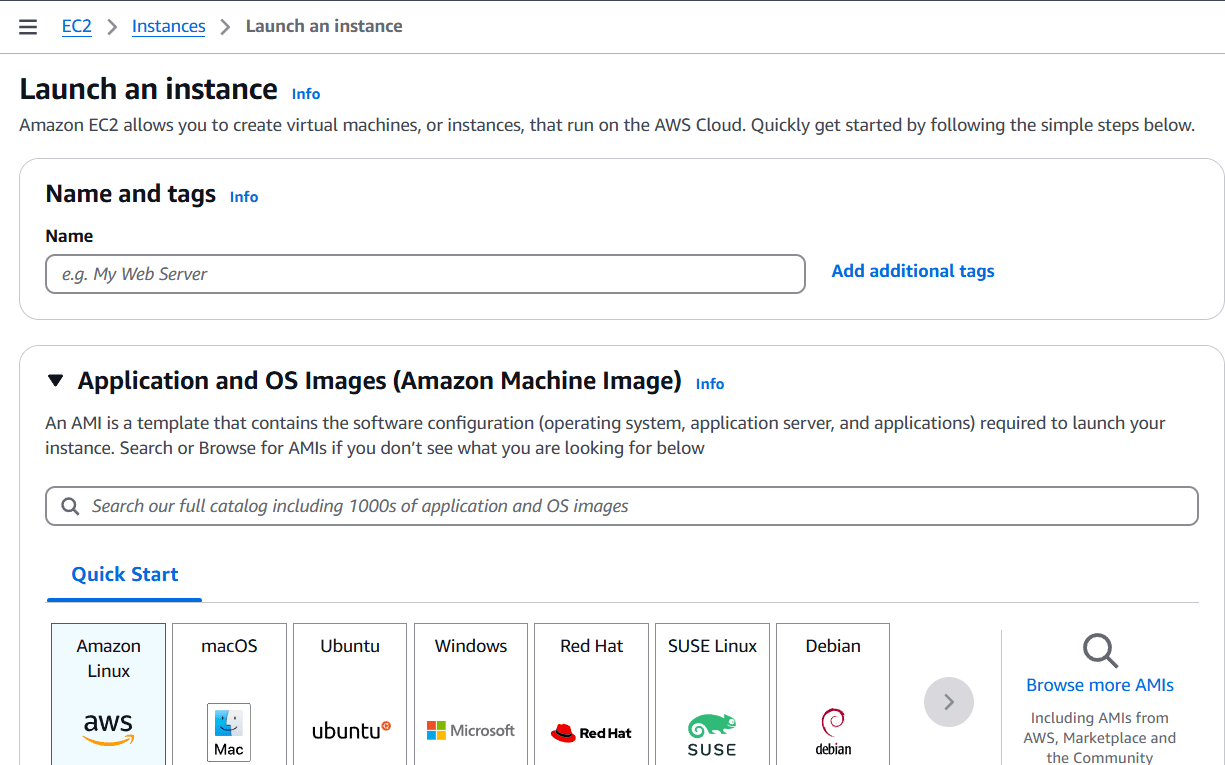
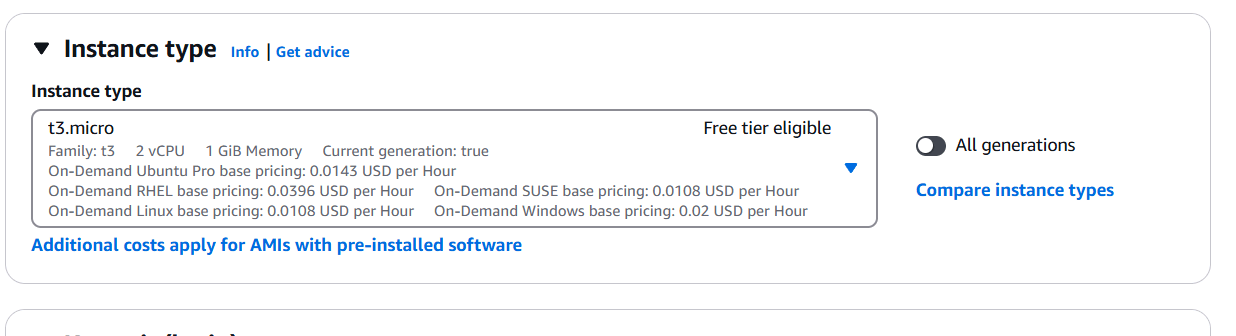
STEP 2: Select the Instance Type.
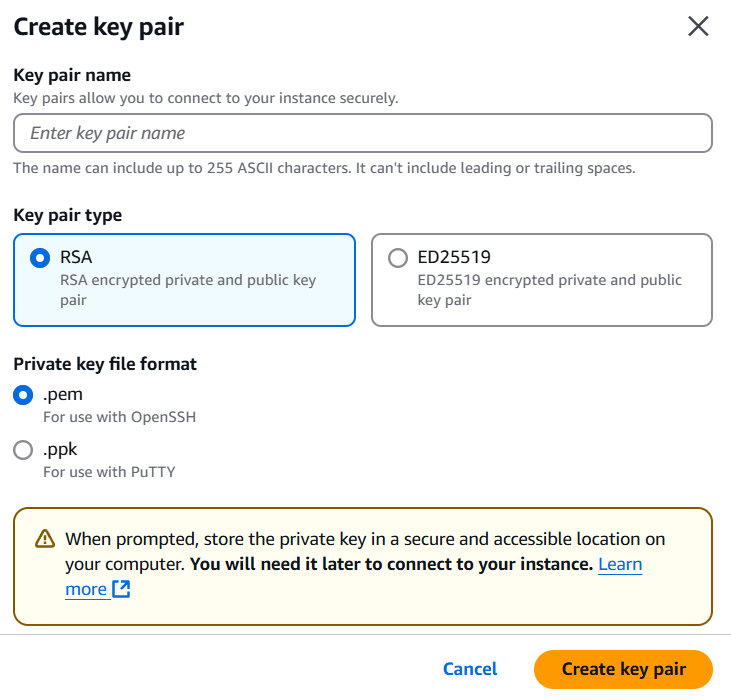
STEP 3: Create a keypair.
STEP 4: Click on launcj instance.
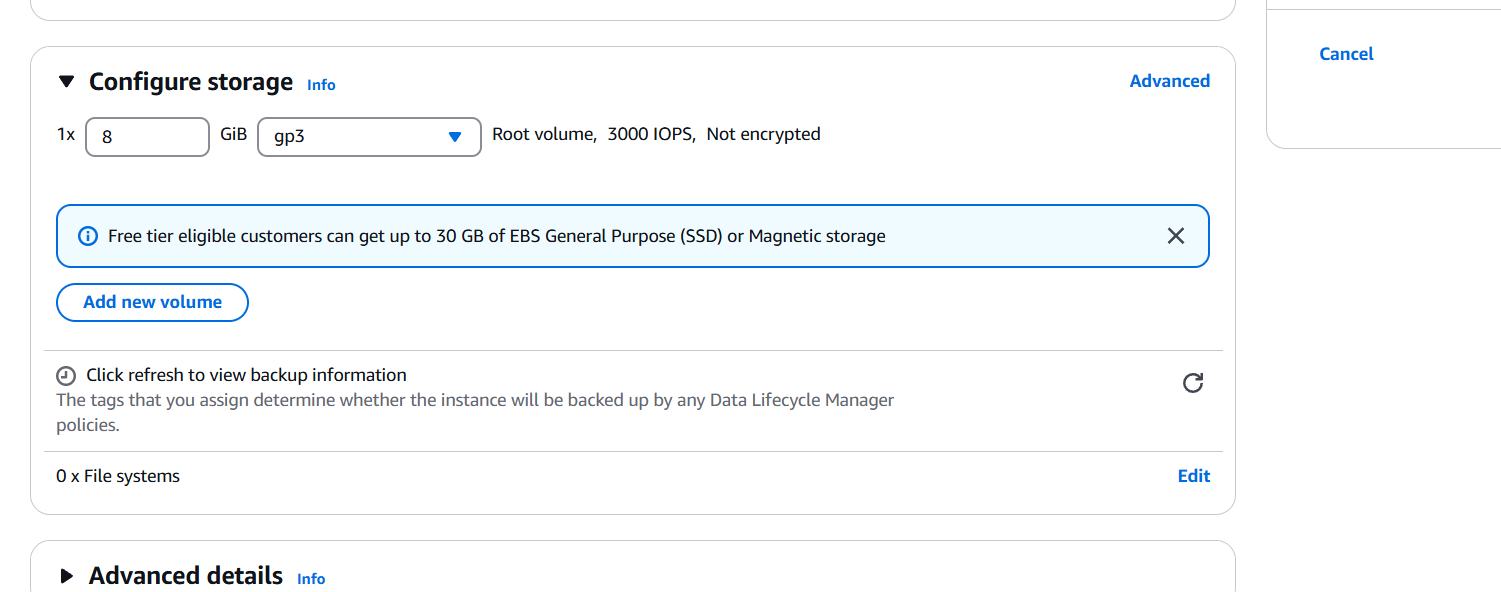
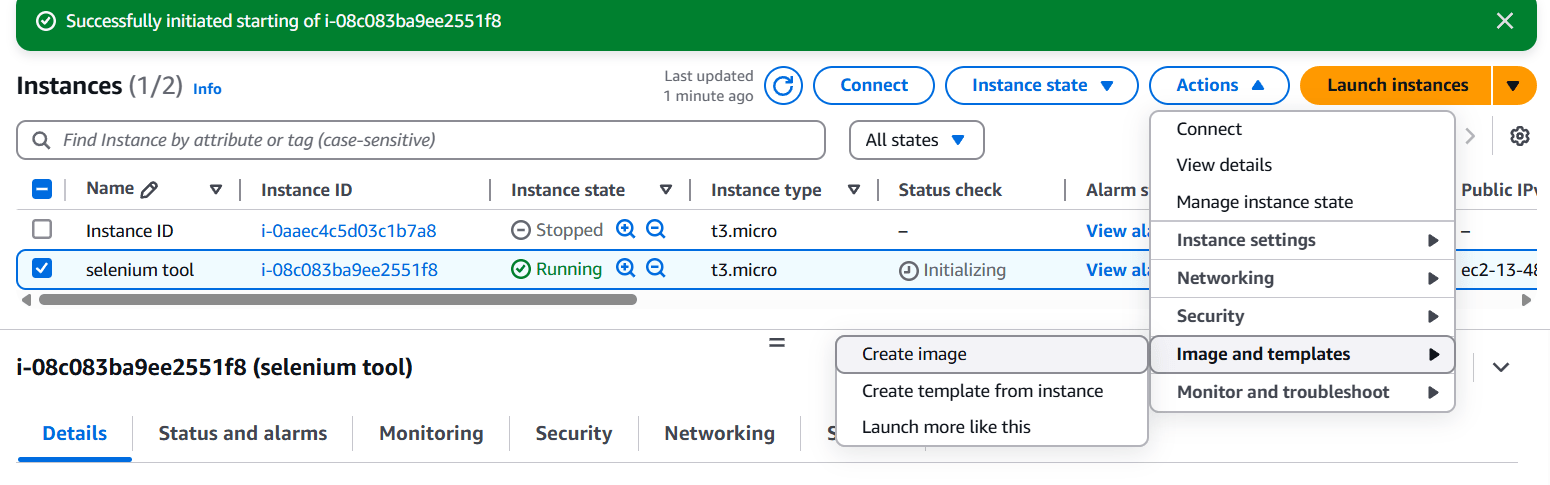
STEP 5: Select the instance click on action.
- Select image and templates.
- Click on create image.
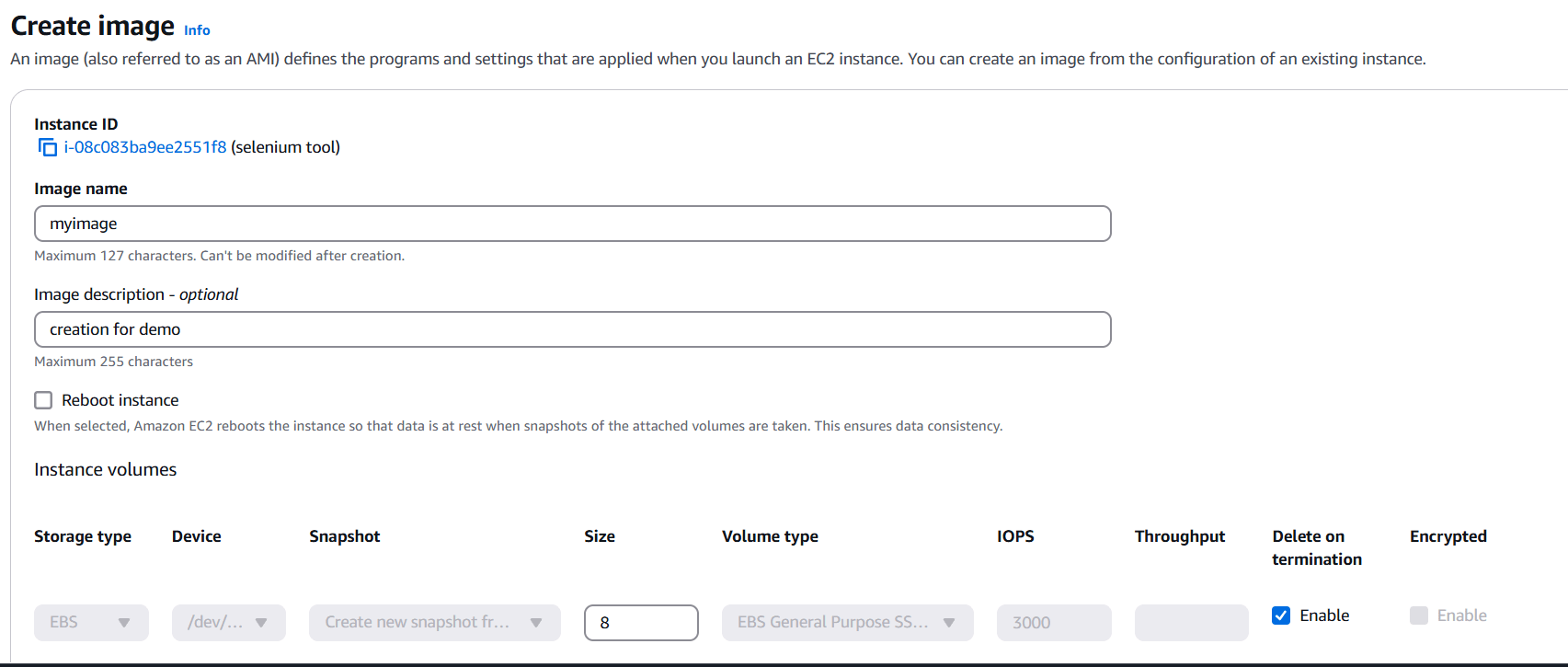
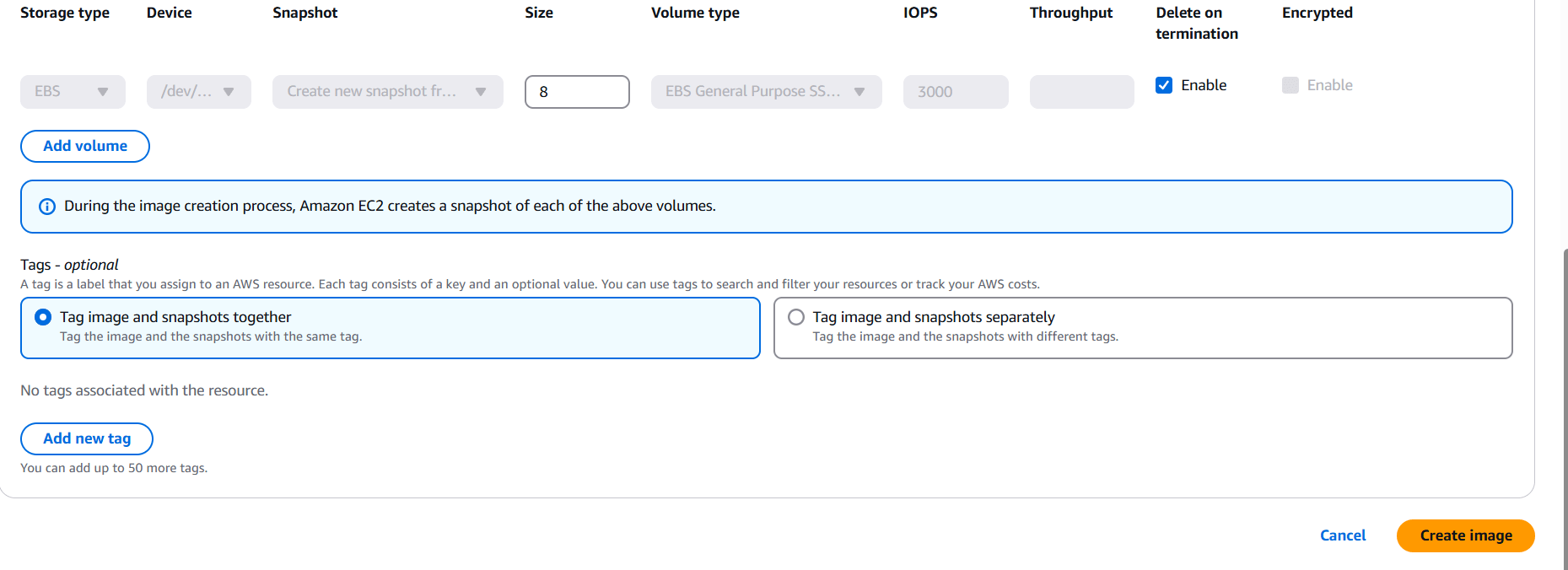
STEP 6: Enter the name and description and Click on create.
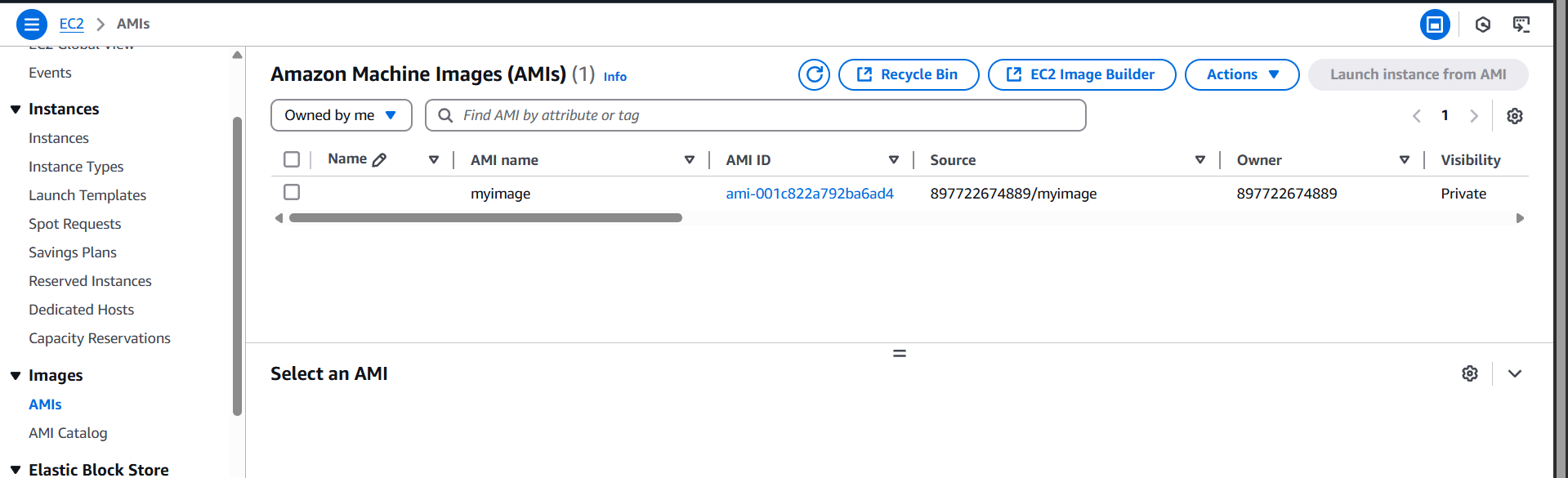

Conclusion.
Creating Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) is a powerful and efficient way to manage and scale your infrastructure on AWS. Whether you’re aiming to automate instance creation, ensure consistency across environments, or back up your configurations for disaster recovery, AMIs provide the flexibility and ease needed to streamline your cloud operations.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently create and customize AMIs to suit your specific needs. With the ability to replicate your instances quickly and share your configurations across different AWS accounts, you can significantly reduce the time and effort required for setting up new environments or recovering from failures.
As you continue working with AWS, mastering AMIs will become a valuable skill in optimizing your workflow, improving scalability, and maintaining the integrity of your cloud infrastructure. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AWS user, understanding AMIs opens up a wide range of possibilities for efficient, consistent, and cost-effective cloud management.
With the knowledge gained from this guide, you are now ready to leverage the full potential of Amazon Machine Images and take your AWS experience to the next level. Happy cloud computing!
How to Launch Your Node.js Application on AWS Lightsail: A Beginner’s Guide.
Introduction.
Deploying applications to the cloud has become an essential part of modern software development. Among the various cloud platforms, AWS Lightsail has gained popularity due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. It’s an ideal choice for developers looking for an easy-to-manage virtual private server (VPS) without the complexity of Amazon Web Services’ (AWS) traditional EC2 instances.
Node.js, a powerful JavaScript runtime, is widely used for building scalable and high-performance applications. When you combine Node.js with AWS Lightsail, you get a robust and easy-to-deploy platform that is well-suited for both small projects and production environments. Whether you’re building a web app, API, or a real-time service, AWS Lightsail offers the resources and tools necessary for seamless deployment.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of deploying a Node.js application to AWS Lightsail step by step. We’ll cover everything from setting up your Lightsail instance, configuring the server, and installing necessary dependencies, to finally running and accessing your Node.js application on the cloud.
No matter if you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, this guide is designed to simplify the deployment process and help you get your Node.js app up and running quickly. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have the skills to deploy and manage your own Node.js applications on AWS Lightsail with ease.

So, let’s dive in and start setting up your Node.js application on AWS Lightsail. With a few simple steps, you’ll be able to bring your app to the cloud and scale it as your project grows.
Features of AWS Lightsail.
1. Simple and User-Friendly Interface
- AWS Lightsail provides an intuitive, easy-to-use interface that simplifies cloud computing tasks. Developers can launch, manage, and scale their applications without needing deep AWS expertise.
2. Pre-configured Application Stacks
- Lightsail offers pre-configured application stacks for quick deployment, including popular frameworks like Node.js, WordPress, LAMP, and more. This feature saves time and reduces manual setup.
3. Affordable Pricing
- Lightsail offers a predictable pricing model with fixed monthly rates, making it ideal for startups and small businesses. This helps developers avoid unexpected costs and better manage their budgets.
4. Automatic Scaling
- With AWS Lightsail, you can easily scale your application up or down based on demand. While Lightsail instances are typically designed for smaller applications, they also integrate with other AWS services to handle more complex or growing needs.
5. Integrated DNS Management
- Lightsail simplifies domain management by providing built-in DNS services. You can easily configure custom domains for your applications and manage them directly through the Lightsail console.
6. Managed Databases
- AWS Lightsail includes managed database options like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and others, making it easy to set up and maintain databases for your applications without managing complex configurations.
7. Snapshots and Backups
- You can create snapshots of your Lightsail instances to take point-in-time backups of your entire server. This helps ensure data safety and makes it easy to recover your app in case of any issues.
8. 24/7 Customer Support
- Lightsail offers customer support available around the clock to help with technical issues, from server configuration to application deployment. AWS also has a large community and extensive documentation for self-help.
9. SSD-based Storage
- Lightsail instances use solid-state drives (SSDs) for fast and reliable storage, ensuring high performance for applications and databases.
10. Free SSL/TLS Certificates
- Lightsail makes it easy to enable HTTPS on your Node.js application by offering free SSL/TLS certificates. This enhances the security of your app and provides a better experience for your users.
STEP 1: Navigate the AWS lightsail.
- Click on create instance.
STEP 2: Select your region and platform and click on node.js.
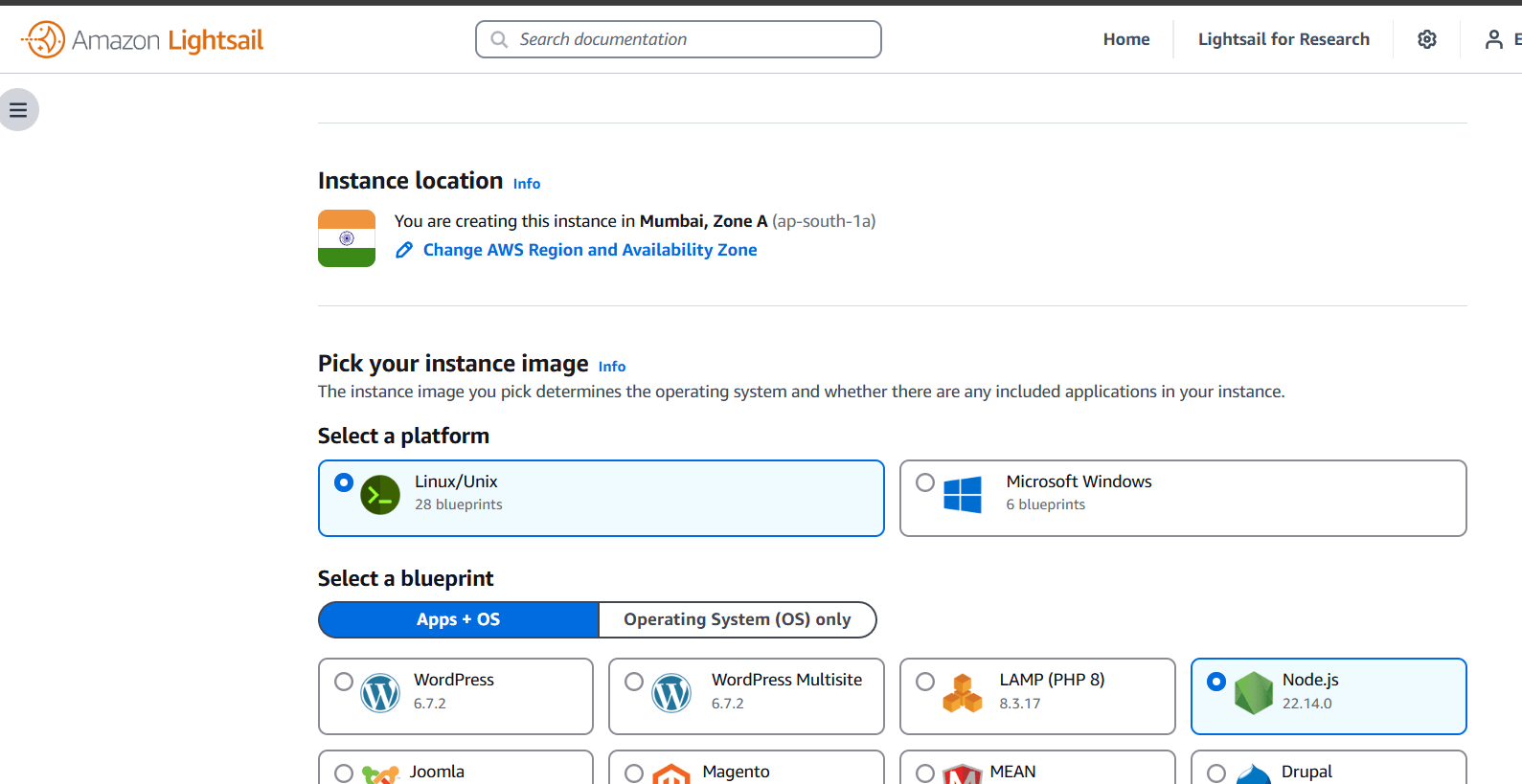
STEP 3: Select a network type.
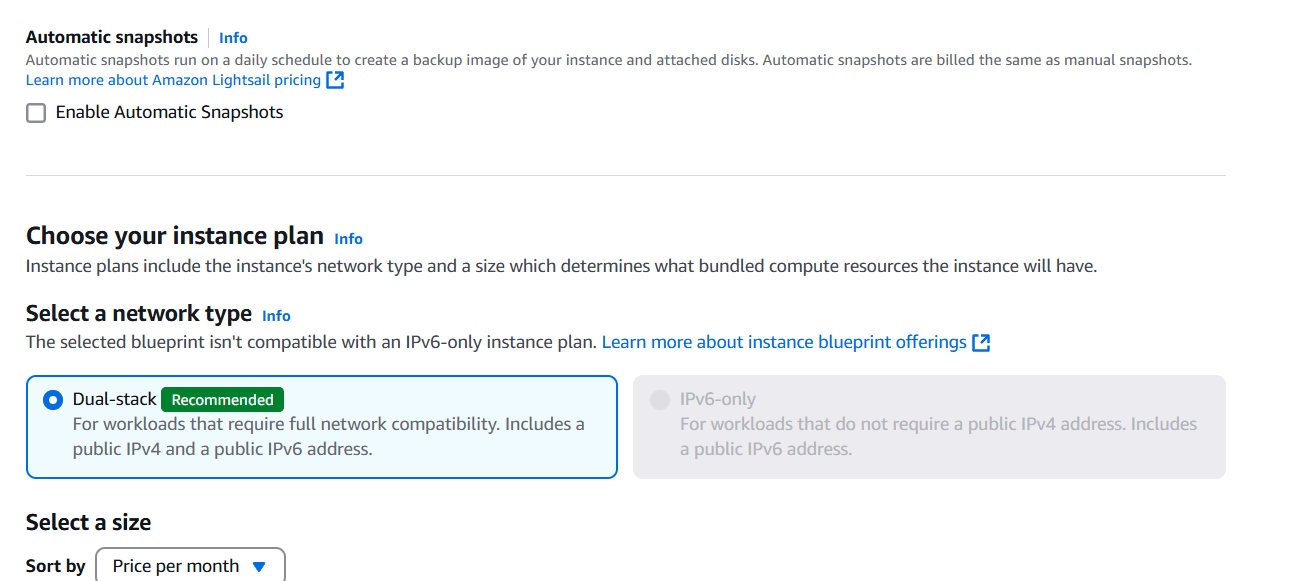
STEP 4: Next, Select a size.
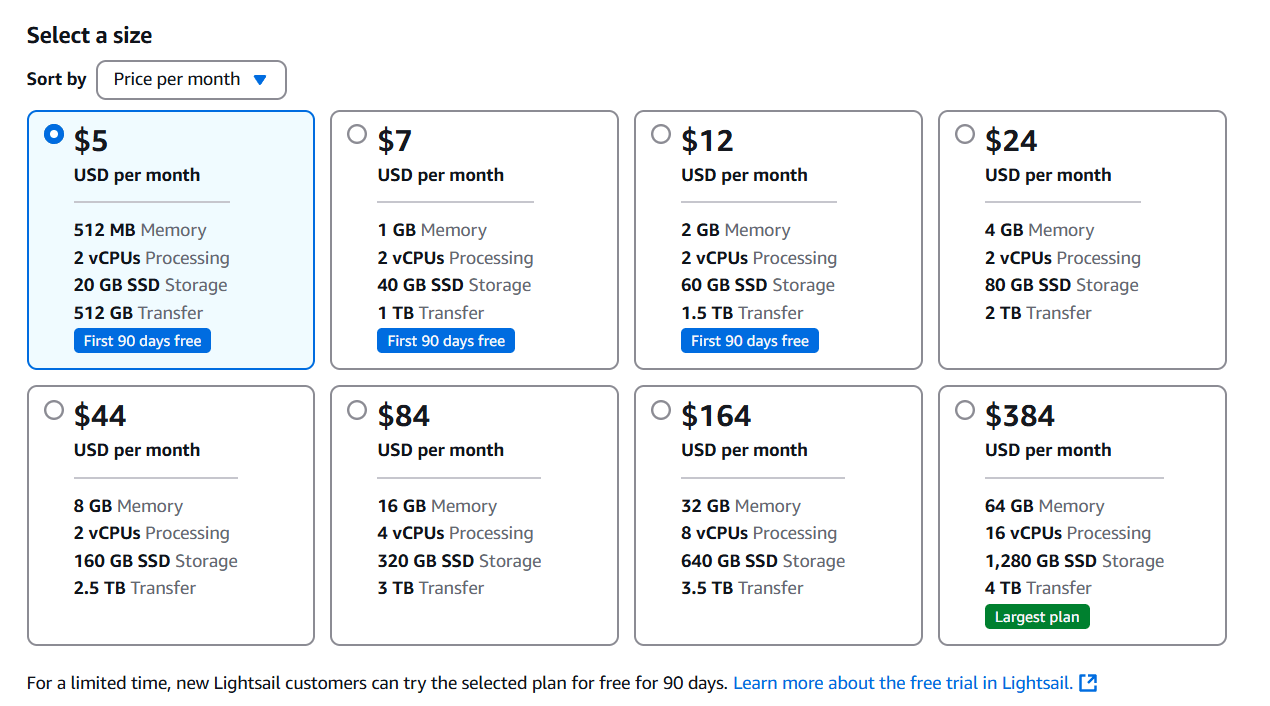
STEP 5: Click on create instance.
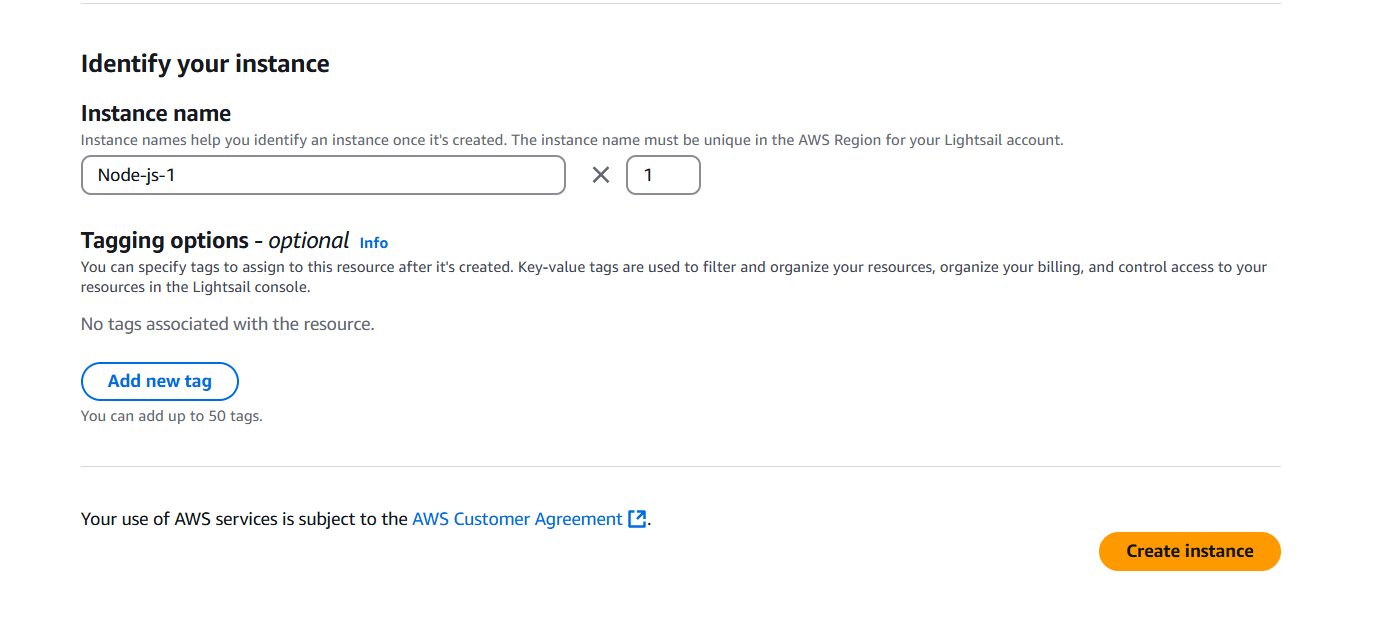
STEP 6: Wait for some time to become application in running state, when its in running state copy the ip address of instance and enter your browser.
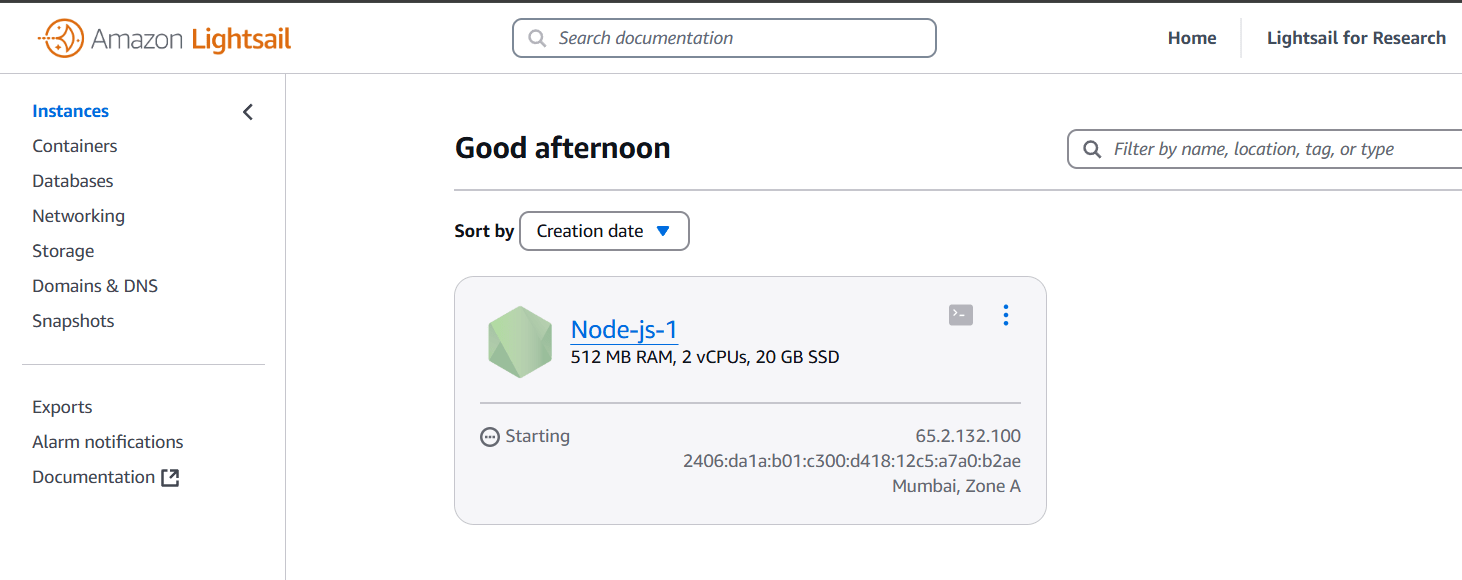
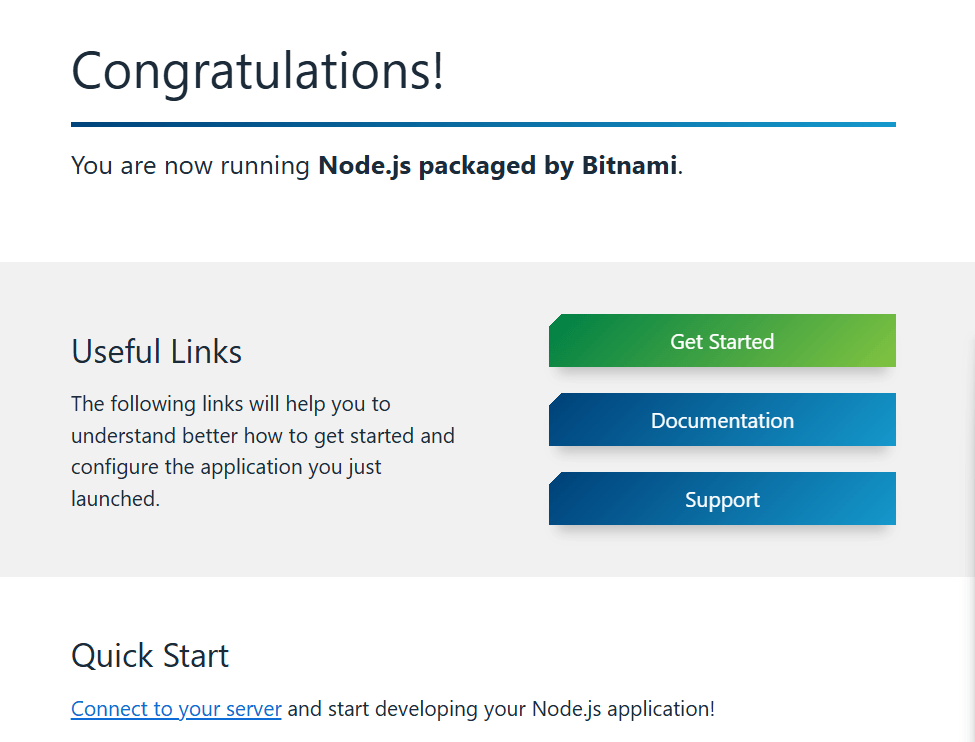

Conclusion.
In conclusion, deploying a Node.js application on AWS Lightsail offers a streamlined and cost-effective solution for developers looking to bring their projects to the cloud. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ve learned how to create a Lightsail instance, configure it, install the necessary dependencies, and successfully deploy your Node.js app.
With Lightsail’s user-friendly interface and Node.js’s powerful capabilities, you can now host your applications in a scalable environment that is easy to manage and maintain. Whether you’re working on a personal project or preparing for production, Lightsail provides a robust platform for deploying and scaling your Node.js apps without the complexity of traditional AWS services.
Remember, AWS Lightsail offers a range of additional features like automated backups, monitoring tools, and seamless integration with other AWS services, all of which can help you grow your application as needed.
Now that you’ve mastered the deployment process, you can focus more on enhancing your application and delivering great user experiences. Keep experimenting, keep building, and make the most of the powerful combination of Node.js and AWS Lightsail!
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install AWS CLI on Windows.
Introduction.
The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a powerful tool that allows users to manage and interact with AWS services directly from the terminal. Whether you’re automating cloud resources, configuring settings, or managing your AWS infrastructure, the AWS CLI provides a streamlined way to perform tasks without needing to navigate through the AWS Management Console.
For Windows users, setting up the AWS CLI can be an essential skill, especially when working with cloud environments or integrating AWS services into your development workflows. Installing AWS CLI on Windows might seem like a daunting task, but it is relatively simple with the right guidance.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of installing and configuring AWS CLI on a Windows machine. Whether you’re a developer, system administrator, or a beginner looking to get started with AWS, this tutorial will ensure that you can use the AWS CLI to efficiently manage AWS resources.
We’ll begin by explaining the prerequisites needed for the installation, including setting up Python (if necessary) and ensuring your Windows environment is ready. Next, we’ll guide you through downloading the AWS CLI installer for Windows, running the installation, and configuring it with your AWS credentials. After the installation, we’ll show you how to verify the setup and ensure it’s working correctly.

By the end of this guide, you’ll have AWS CLI up and running on your Windows machine, empowering you to take control of your AWS services via command-line commands. So, let’s get started!
1st Method: Using the Installer.
STEP 1: Go to the AWS Command line interface.
STEP 2: Click on first link.
STEP 3: Download the file on your desktop.
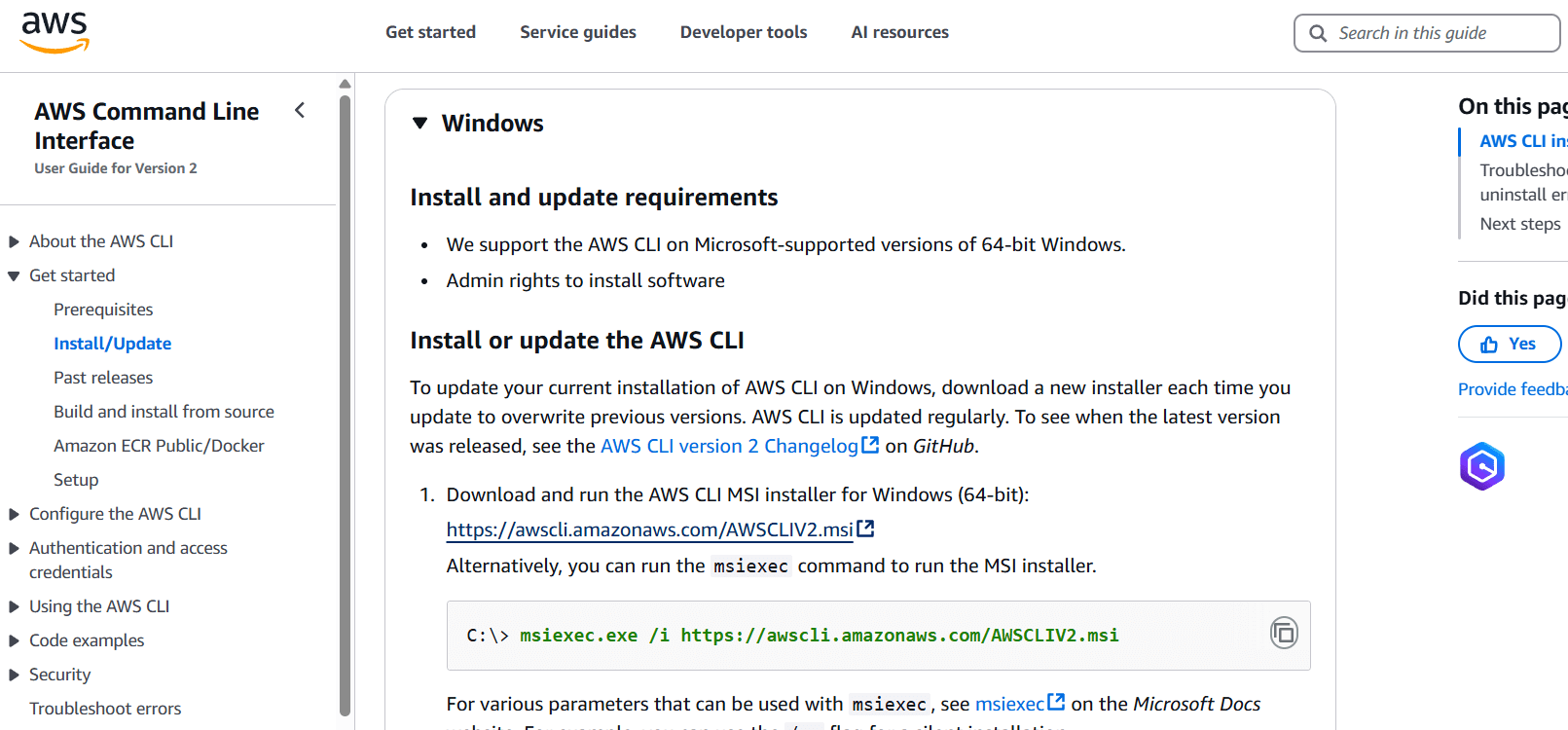

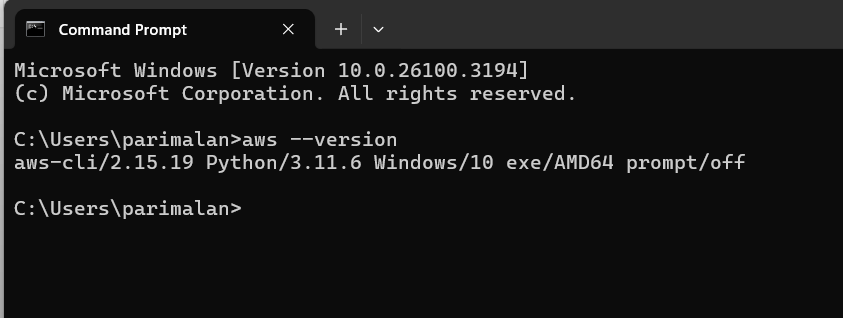
STEP 4: Go to command line interface and enter the aws –version.
2nd Method: Installing AWS CLI Using Pip (Python Package Manager) on Windows
If you prefer to use Python’s package manager, pip, to install the AWS CLI, it’s a simple and efficient method, especially if you already have Python and pip installed on your system. Below, we’ll guide you through the process of installing the AWS CLI using pip on Windows.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, make sure you meet the following prerequisites:
- Python (version 3.6 or later) should be installed on your machine.
- pip (Python’s package installer) should be installed alongside Python.
To verify if Python and pip are already installed on your Windows system, open Command Prompt and run the following commands:
python --version
pip --versionIf these commands return a version number, you’re all set to proceed. If not, you’ll need to install Python and ensure that pip is included in the installation.
Steps to Install AWS CLI Using pip
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell: First, open a Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell window with administrator privileges.
- Install AWS CLI using pip: Once you have the terminal open, run the following command to install the AWS CLI:
pip install awscli --upgrade --userVerify the Installation: After the installation completes, you can verify that AWS CLI has been installed successfully by running:
aws --version
Conclusion.
In this blog, we’ve walked through the process of installing the AWS CLI on Windows, providing you with a straightforward guide to get started with managing your AWS resources from the command line. With the AWS CLI installed, you can interact with your AWS services, automate tasks, and manage infrastructure more efficiently.
By following the steps outlined, you can now:
- Install AWS CLI on your Windows machine.
- Configure it with your AWS credentials to start using the AWS services.
- Troubleshoot common installation issues if they arise.
With AWS CLI set up, you’re now equipped to streamline your workflow, improve productivity, and gain more control over your AWS environment directly from the terminal. Happy cloud computing!
Getting Started with AWS Cognito for Web Application Authentication.
Introduction.
When building modern web applications, user authentication is a crucial component for managing user identities and ensuring secure access. AWS Cognito provides a powerful solution for adding authentication, authorization, and user management to your web app without the need to handle the complexities of server-side infrastructure. With AWS Cognito, you can easily set up user pools, federate identities, and integrate multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of setting up authentication for a sample web application using AWS Cognito. We’ll start by creating a user pool, which acts as a directory for storing user information, and configure an app client to allow your application to communicate securely with Cognito. We’ll then integrate sign-up, sign-in, and password reset functionality into your web app. Along with user registration, you’ll also learn how to manage user sessions and store authentication tokens.
Additionally, AWS Cognito allows you to integrate with other AWS services like API Gateway and Lambda, enabling you to build scalable and secure serverless applications. You’ll also have the flexibility to implement features like social logins (Google, Facebook, etc.) through federated identity pools.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a fully functional authentication system that can handle user sign-ups, sign-ins, and secure access for your web application. AWS Cognito provides an easy-to-use solution that saves time and reduces the complexity of implementing secure authentication, helping developers focus more on building great features rather than managing user data and security. Whether you’re building a small project or scaling up to a large enterprise application, Cognito can support your authentication needs with minimal setup.

Prerequisites:
- An AWS account.
- Basic knowledge of web development (HTML, JavaScript, etc.).
- AWS CLI installed and configured (optional, for easier resource management).
- A sample web application (could be a simple HTML/JavaScript frontend).
Steps to Set Up Authentication Using AWS Cognito:
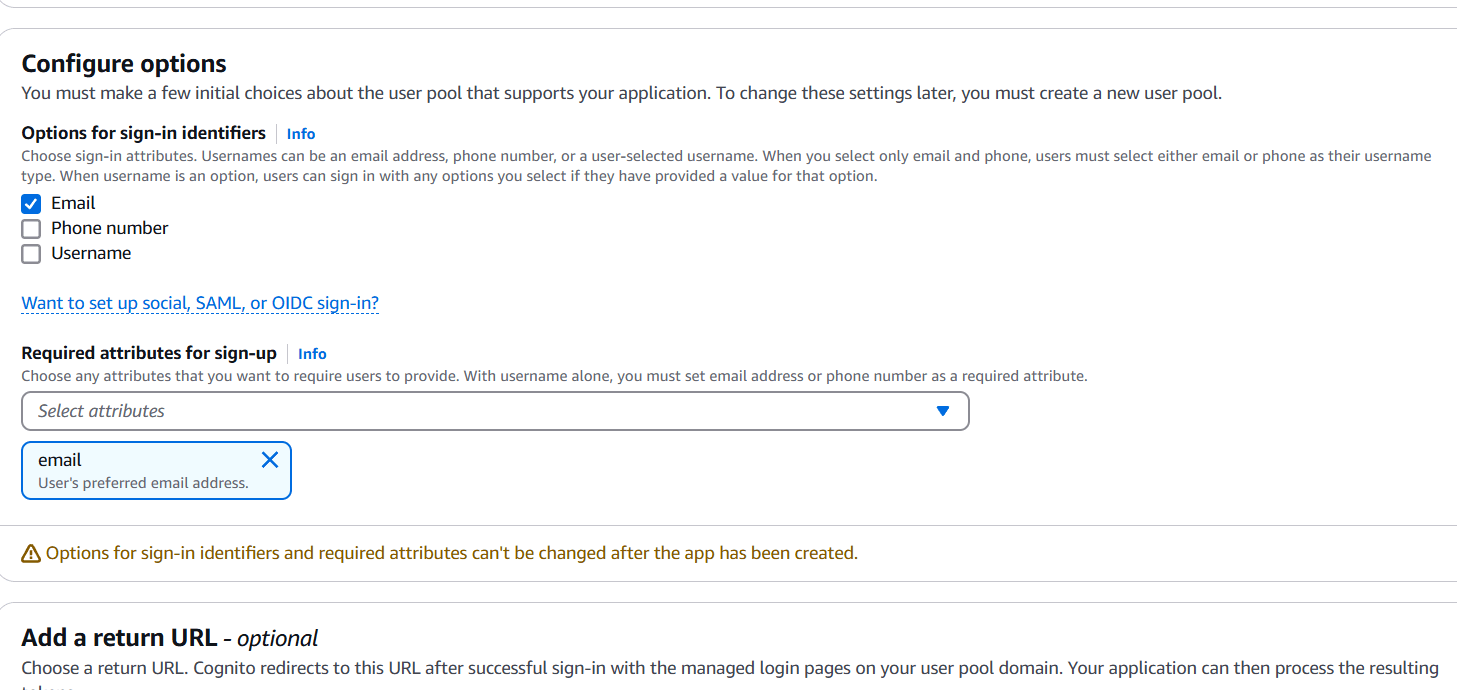
1. Create a Cognito User Pool
A User Pool is a user directory that allows you to manage sign-up and sign-in services.
- Log in to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Amazon Cognito.
- Click Manage User Pools and then Create a pool.
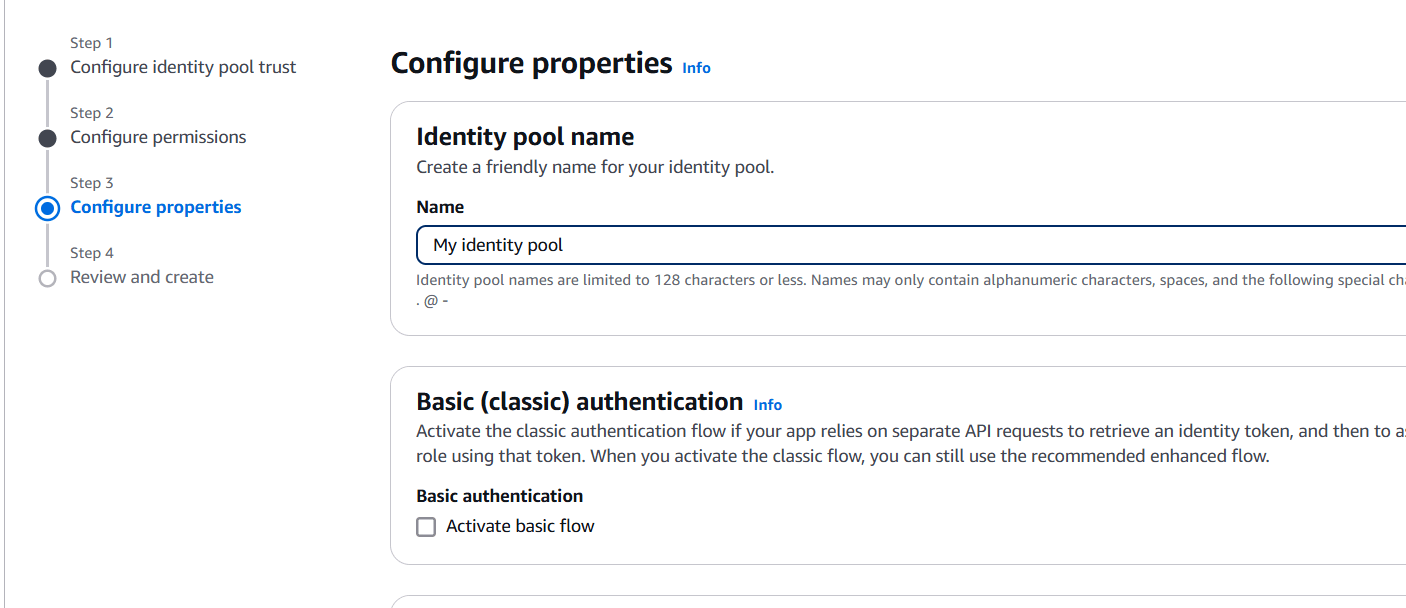
- Enter a name for the pool (e.g.,
SampleUserPool). - Configure pool settings:
- Sign-in options: Choose how users will sign in (email, username, or phone number).
- Password policy: Define the password requirements (optional).
- MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication): You can choose to enable MFA for added security.
- Click Next step and configure App Clients (for frontend communication with Cognito).
- Create an App Client without generating a client secret (as it’s a web app).
- Enable Cognito User Pool as the authentication provider for your app.
- Save the pool configuration.
2. Set Up a Cognito Identity Pool (Optional for Federated Authentication)
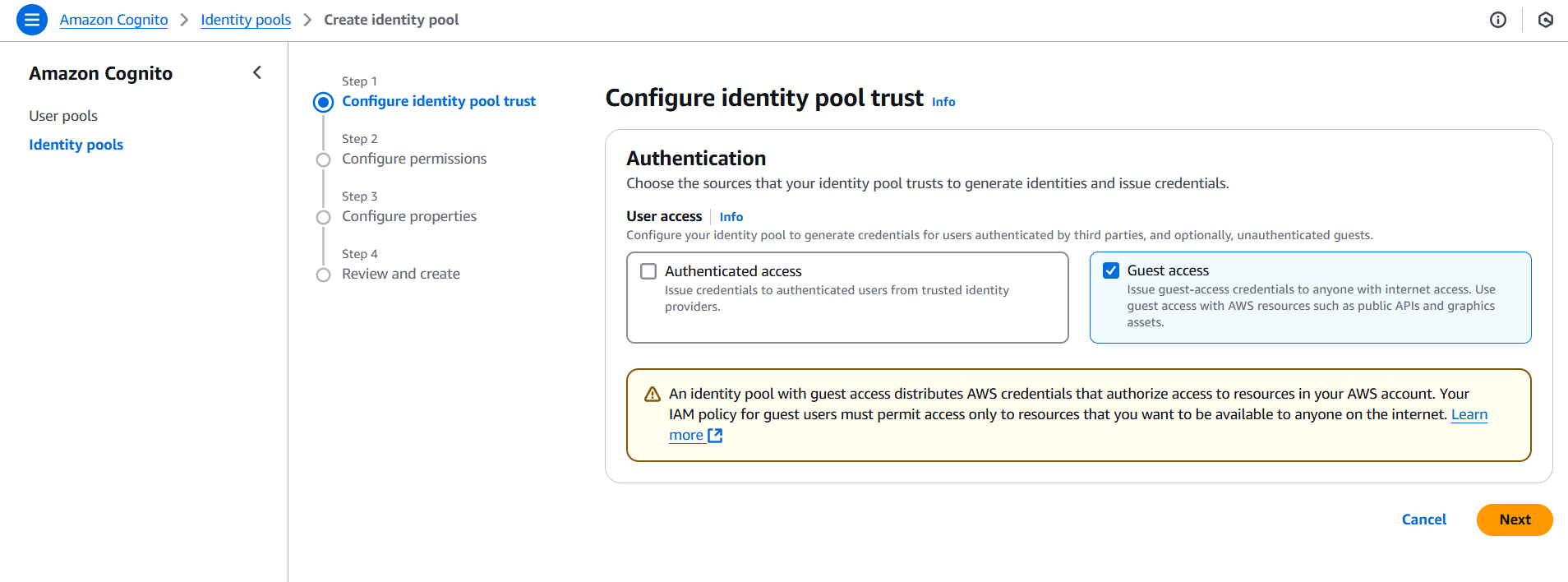
If you want to access AWS services (like S3 or DynamoDB) directly from your web app, you’ll need an Identity Pool to federate the identities from the user pool into AWS services.
- From the Cognito Dashboard, click Manage Identity Pools.
- Click Create new identity pool.
- Name your identity pool (e.g.,
SampleIdentityPool). - Enable Cognito User Pool as a provider and select the user pool you created earlier.
- Allow access to unauthenticated identities (optional, depending on your use case).
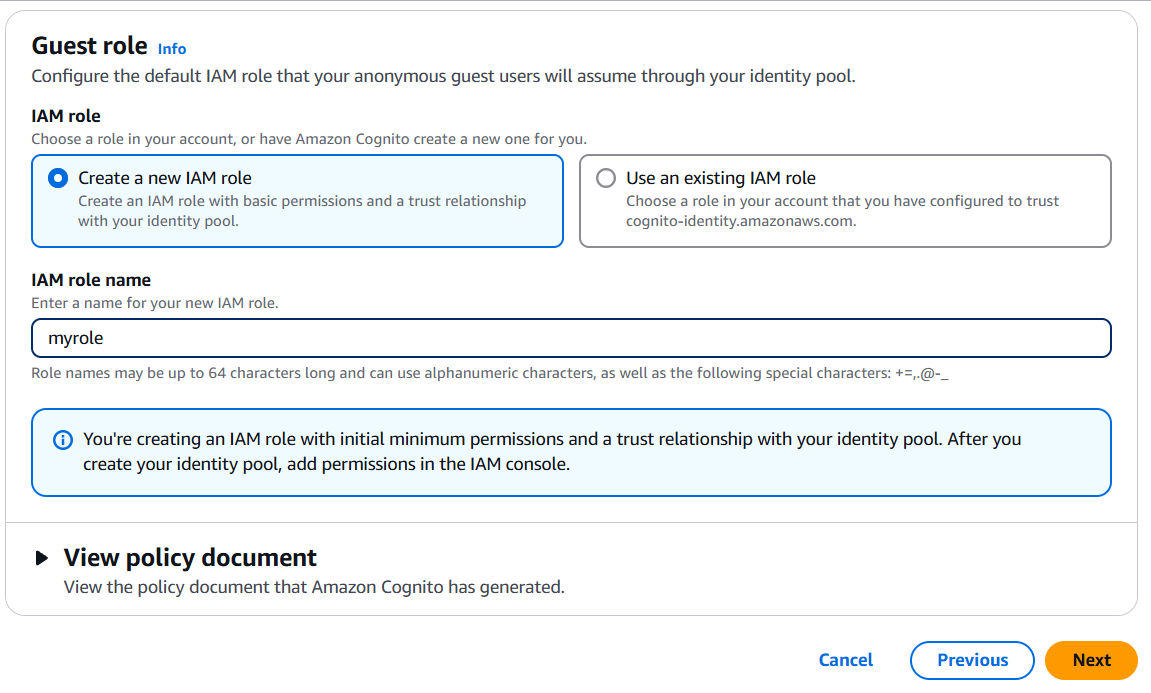
- Click Create Pool, and Cognito will create roles (IAM roles) that allow authenticated and unauthenticated users to interact with AWS services.
3. Configure Your Web Application
- Install the AWS SDK and Amazon Cognito Identity SDK in your web app. This can be done via a CDN or through npm.
Example: Using CDN:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/amazon-cognito-identity-js@3.0.6/dist/amazon-cognito-identity.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/aws-sdk@2.989.0/dist/aws-sdk.min.js"></script>4. Integrate AWS Cognito into Your Frontend (Web App)
Here’s an example of how you can integrate AWS Cognito authentication in your JavaScript frontend:
- Configure the AWS SDK and Cognito Identity Pool:
AWS.config.region = 'us-east-1'; // Your region
AWS.config.credentials = new AWS.CognitoIdentityCredentials({
IdentityPoolId: 'your-identity-pool-id', // Identity Pool ID from Cognito
});Sign Up a New User:
const poolData = {
UserPoolId: 'your-user-pool-id', // Your User Pool ID
ClientId: 'your-app-client-id' // Your App Client ID
};
const userPool = new AmazonCognitoIdentity.CognitoUserPool(poolData);
function signUp() {
const username = document.getElementById('username').value;
const password = document.getElementById('password').value;
const email = document.getElementById('email').value;
const attributeList = [
new AmazonCognitoIdentity.CognitoUserAttribute({
Name: 'email',
Value: email
})
];
userPool.signUp(username, password, attributeList, null, function(err, result) {
if (err) {
alert(err.message || JSON.stringify(err));
return;
}
alert('Registration successful! Please verify your email.');
});
}Sign In Existing Users:
function signIn() {
const username = document.getElementById('username').value;
const password = document.getElementById('password').value;
const authenticationData = {
Username: username,
Password: password,
};
const authenticationDetails = new AmazonCognitoIdentity.AuthenticationDetails(authenticationData);
const userData = {
Username: username,
Pool: userPool,
};
const cognitoUser = new AmazonCognitoIdentity.CognitoUser(userData);
cognitoUser.authenticateUser(authenticationDetails, {
onSuccess: function(result) {
alert('Authentication successful');
console.log(result);
},
onFailure: function(err) {
alert(err.message || JSON.stringify(err));
}
});
}5. Handle User Authentication States
After login or signup, store the authentication tokens (JWT) locally (like in localStorage or sessionStorage) to manage the user session across different pages of your web app.
- On successful login, store the session:
cognitoUser.getSession(function(err, session) {
if (err) {
alert(err.message || JSON.stringify(err));
return;
}
console.log('Session Valid: ' + session.isValid());
localStorage.setItem('idToken', session.getIdToken().getJwtToken());
});- On page load, you can check if the user is authenticated by verifying the presence of the ID token:
const idToken = localStorage.getItem('idToken');
if (idToken) {
console.log('User is authenticated');
} else {
console.log('User is not authenticated');
}6. Test Your Application
- Open your application in a browser.
- Try signing up, confirming the user via email, signing in, and signing out.
- Check the console logs for responses or errors.

Conclusion.
Using AWS Cognito for authentication in a web app allows you to easily manage users, secure their data, and integrate with AWS services for seamless user experiences. With Cognito’s ability to handle user registration, login, and identity federation, you can focus on building your application while ensuring secure and scalable authentication for your users.
Setting Up a Git Repository: A Step-by-Step Guide.
Introduction:
Git is a distributed version control system that enables developers to track changes in their codebase, collaborate with others, and maintain a history of revisions. Setting up a Git repository is the first step in using Git for your project.
A Git repository allows you to track changes to files, manage multiple versions, and work efficiently with others on the same codebase. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of setting up a Git repository both locally and remotely, from installation to making your first commit. Whether you’re working on a personal project or collaborating with a team, setting up a Git repository is an essential step toward version control and collaboration.

By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to:
- Install Git on your system.
- Initialize a local Git repository for your project.
- Create your first commit.
- Set up a remote repository (e.g., GitHub) and push your local changes to it.
This guide is perfect for those who are new to Git or need a refresher on how to get started. Let’s dive in and get your repository up and running!

Step 1: Install Git (if you don’t have it)
- Install Git on Ubuntu: If you don’t have Git installed on your system, you can install it by running the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install git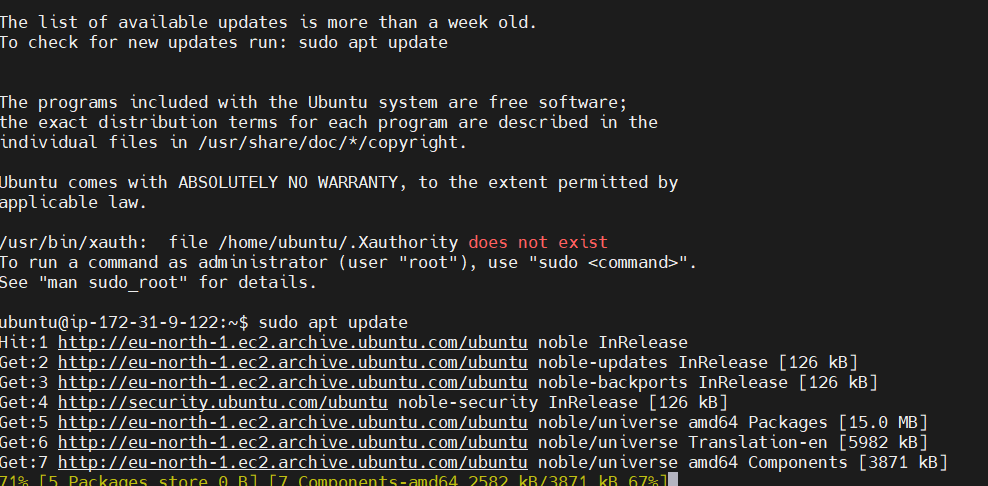
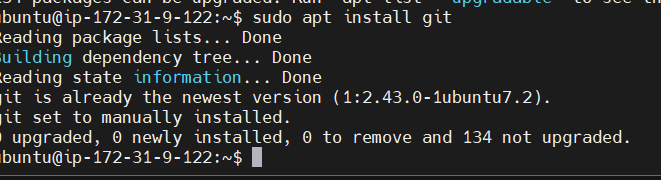
Verify Git Installation: After installation, verify Git by checking its version:
git --version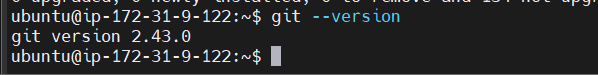
Step 2: Set Up Git Configuration
Before starting to use Git, configure your identity (name and email) to associate commits with your account.
- Set your name:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
Set your email:
git config --global user.email "your-email@example.com"

Verify your Git configuration: You can check your settings by running:
git config --list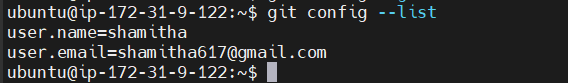
Step 3: Create a New Git Repository
Now that Git is installed and configured, let’s create a new Git repository.
- Create a project directory (if it doesn’t already exist): Navigate to the directory where you want to store your project or create a new one:
mkdir my_project
cd my_project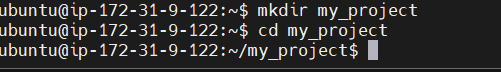
Initialize the repository: To create a new Git repository in the current directory, run:
git init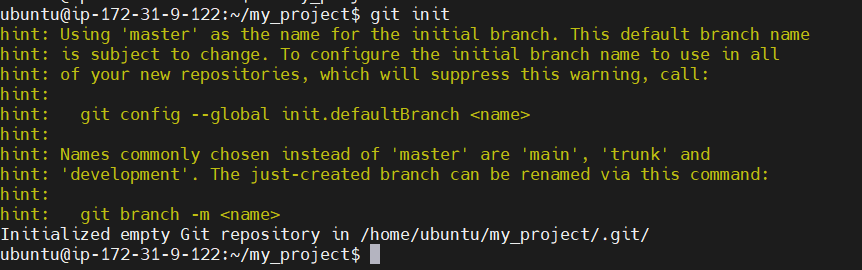
This will create a .git directory in your project folder, which contains all the configuration and history of your repository.
Check the repository status: You can verify that your repository has been initialized by running:
git status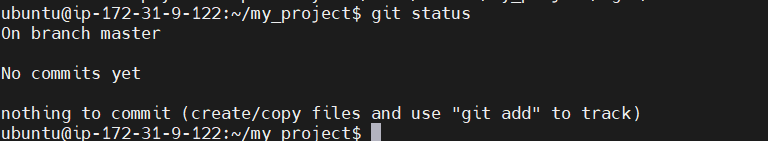
- This will show that there are no commits yet.
Step 4: Add Files to the Repository
- Create some files (if you don’t have any files in the project yet): You can create a simple
README.mdor any other file you want to track.
echo "# My Project" > README.mdStage the files for commit: To start tracking the files, use the git add command:
git add README.md
To add all files in the directory, use:
git add .
Check the status again: To verify that the files are staged for commit:
git status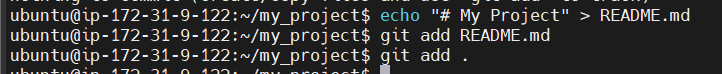
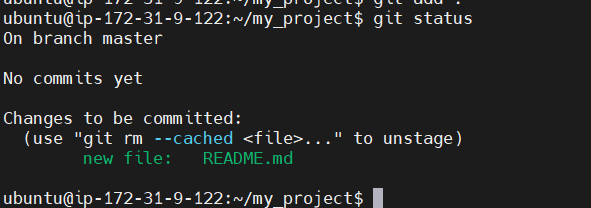
Step 5: Commit the Changes
Now, commit the changes you’ve staged to the repository:
- Commit the changes:
git commit -m "Initial commit with README"-m: This option allows you to specify a commit message. Always write a meaningful message that describes the changes.
Check the commit history: You can verify the commit by running:
git log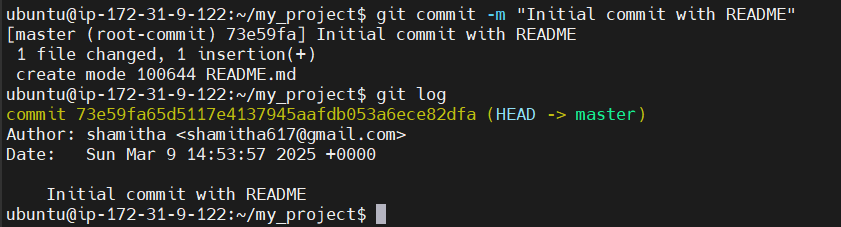
Step 6: Making Further Changes and Committing
- Make changes to files: Open any file and make changes. For example, edit
README.md. - Stage the changes: After editing, add the modified files:
git add README.md
Commit the changes: Commit the changes with a descriptive message:
git commit -m "Updated README with more details"
Push the changes: Push the latest commit to the remote repository:
git push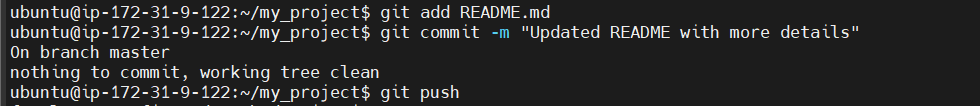

Conclusion.
You have now successfully set up a Git repository on Ubuntu, committed changes to it, and optionally pushed it to a remote repository on GitHub or another Git service. You can continue to make changes, stage them, commit them, and push them to your remote repository as needed.
For more advanced Git usage, you can explore branching, merging, rebasing, and collaborating with others on shared repositories.
Understanding AWS CloudTrail: The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Logging.
Introduction.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, security, and compliance are top priorities for organizations leveraging cloud services. One of the most powerful tools that AWS offers to achieve these goals is AWS CloudTrail. CloudTrail enables you to log, continuously monitor, and retain account activity related to actions taken within your AWS environment. Understanding how to utilize CloudTrail effectively can help you track changes, troubleshoot issues, and ensure compliance across your AWS resources.
At its core, AWS CloudTrail provides a detailed history of API calls made on your account, such as who made the request, the source IP address, and the actions taken. It’s like an activity log for everything happening in your AWS environment. Whether you’re working on a small project or managing a large enterprise environment, CloudTrail’s comprehensive logging capabilities are essential for maintaining visibility and control over your cloud resources.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about AWS CloudTrail, from the basics of setting it up to advanced features like log file integrity validation, integration with other AWS services, and best practices for efficient logging and monitoring. We’ll also cover how CloudTrail helps with security auditing, compliance, and troubleshooting, making it an invaluable tool for both development and operations teams.

Whether you’re a new AWS user or an experienced cloud architect, learning how to effectively use AWS CloudTrail can significantly enhance your ability to monitor and manage cloud activity. Ready to unlock the full potential of CloudTrail? Let’s dive in and explore the key features and practical use cases of this powerful AWS service!
STEP 1: Navigate the AWS Cloud Trail and click on create.
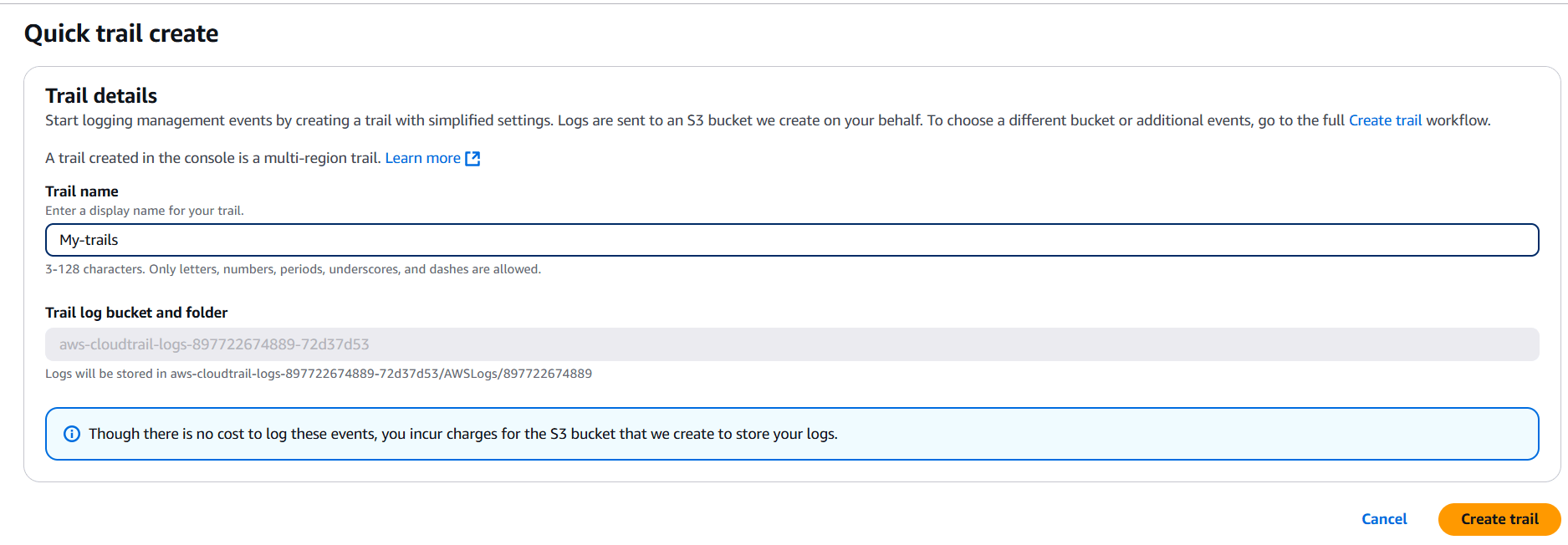
STEP 2: Enter the name and click on create trail.
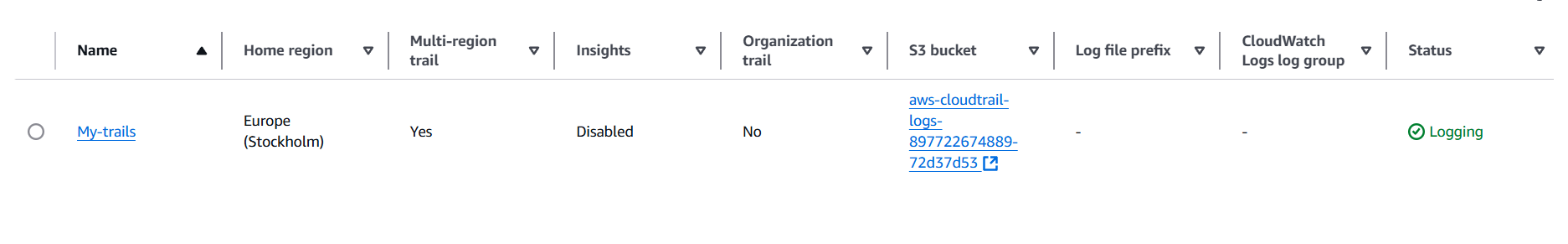
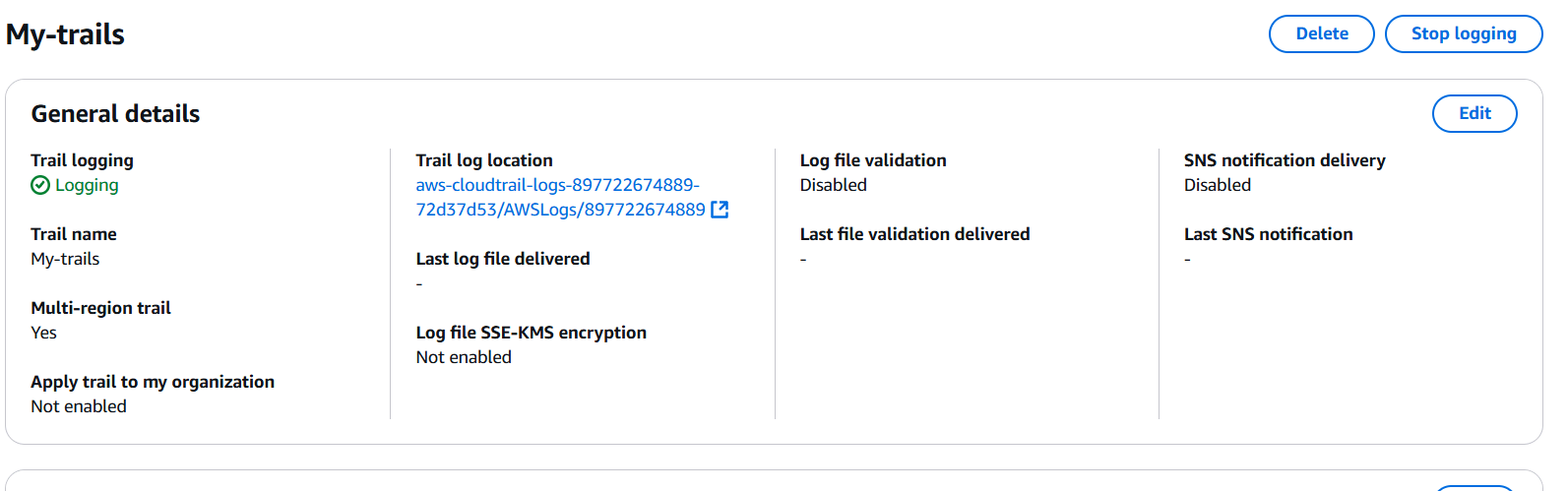
STEP 3: Click on your created trail and Edit the storage Location.
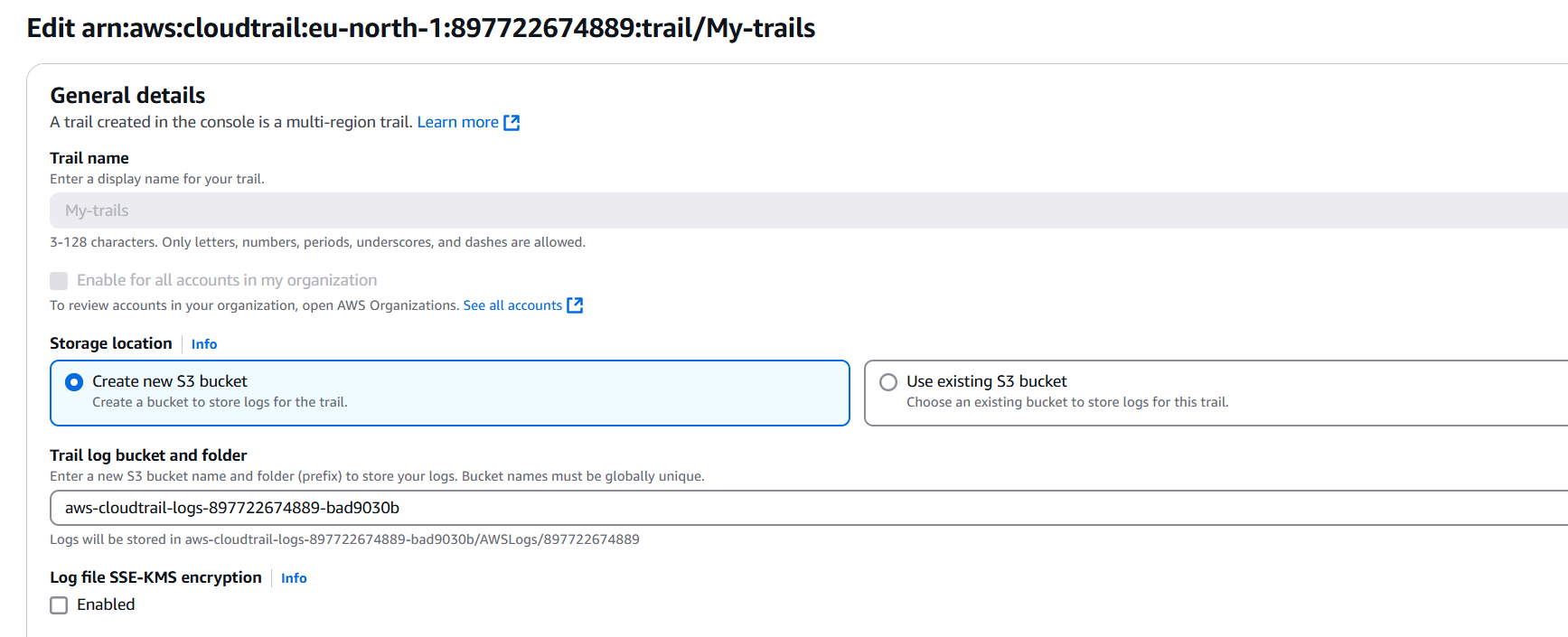
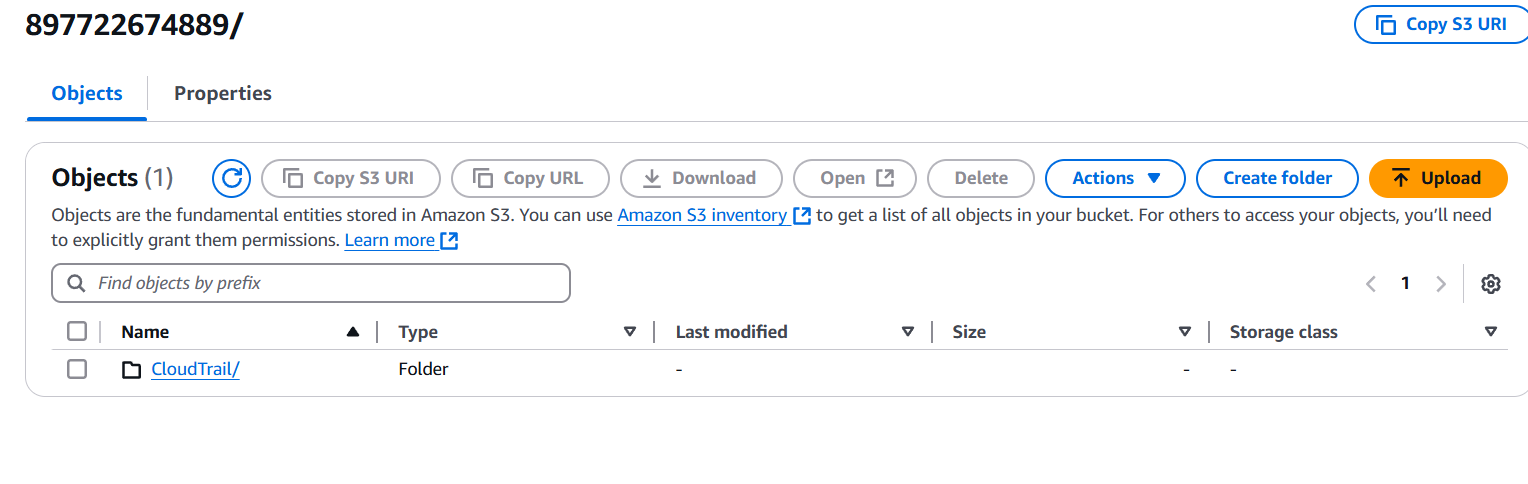
STEP 5: Click on S3 bucket.

Conclusion.
AWS CloudTrail is an indispensable tool for anyone working in the cloud, providing deep visibility into the activity happening within your AWS environment. By logging API calls and tracking user actions, it empowers you to monitor, troubleshoot, and secure your resources more effectively. Whether you’re ensuring compliance, improving security, or optimizing operations, CloudTrail offers the data you need to make informed decisions.
Throughout this guide, we’ve covered the essential features of AWS CloudTrail, including setup, configuration, and best practices for leveraging its full potential. From tracking user activity to integrating with other AWS services for enhanced security, CloudTrail is a versatile tool that helps you maintain governance and improve the overall health of your cloud infrastructure.
By understanding and implementing CloudTrail’s capabilities, you can ensure your AWS environment remains secure, compliant, and well-monitored. It not only allows you to keep a close eye on everything happening within your account but also enables proactive management of resources to prevent and resolve issues quickly.
Now that you have a better understanding of AWS CloudTrail, you’re ready to apply it to your own environment and harness its full power. Cloud logging has never been more critical—so start using CloudTrail to track, analyze, and optimize your AWS operations with confidence!
Launch Your First EC2 Spot Instance: Save Big on Cloud Costs.
Introduction.
In the world of cloud computing, managing costs efficiently is one of the most crucial tasks for developers, businesses, and IT professionals. Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) provides a variety of instance types to meet different computing needs, and one of the most cost-effective ways to leverage EC2 is by using Spot Instances. These instances allow you to tap into unused EC2 capacity at a significantly lower price than On-Demand or Reserved Instances, making them a powerful tool for anyone looking to optimize cloud infrastructure costs.
EC2 Spot Instances are perfect for flexible, stateless applications or workloads that can tolerate interruptions, such as big data processing, web scraping, batch processing, and CI/CD pipelines. These instances offer savings of up to 90% compared to On-Demand prices, but the trade-off is that AWS can terminate them with very little notice if the spot price exceeds your bid or if there’s a higher demand for capacity in the region. However, with proper management, they can be a game-changer in reducing cloud costs.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to launch your first EC2 Spot Instance. From setting up your instance to understanding pricing mechanisms, we’ll cover all the steps to ensure you’re getting the most out of your EC2 Spot Instances. You’ll learn how to bid on capacity, manage interruptions, and scale workloads in an efficient and cost-effective manner.
Whether you’re a startup looking to keep costs low or an enterprise trying to optimize cloud operations, understanding how to launch EC2 Spot Instances is an essential skill. By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to harness the full potential of Spot Instances, save big on your cloud infrastructure, and scale your applications with confidence.

Ready to dive in and start saving on your cloud costs? Let’s begin the journey of launching your first EC2 Spot Instance!
STEP 1: Navigate the EC2 instance.
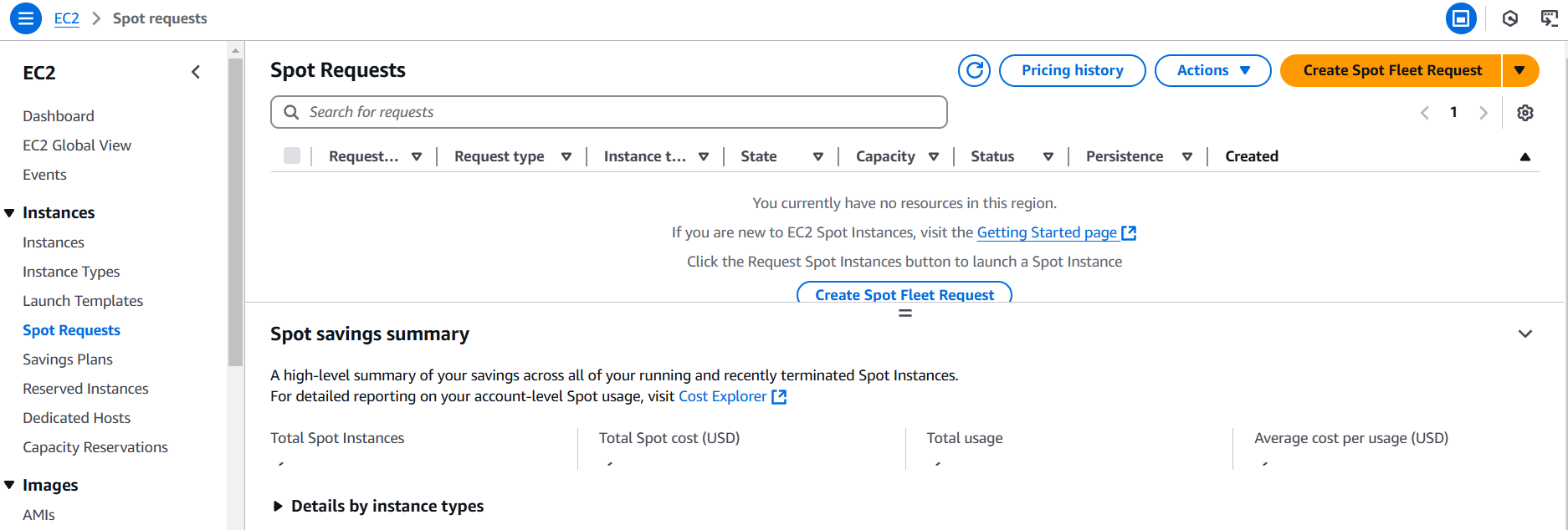
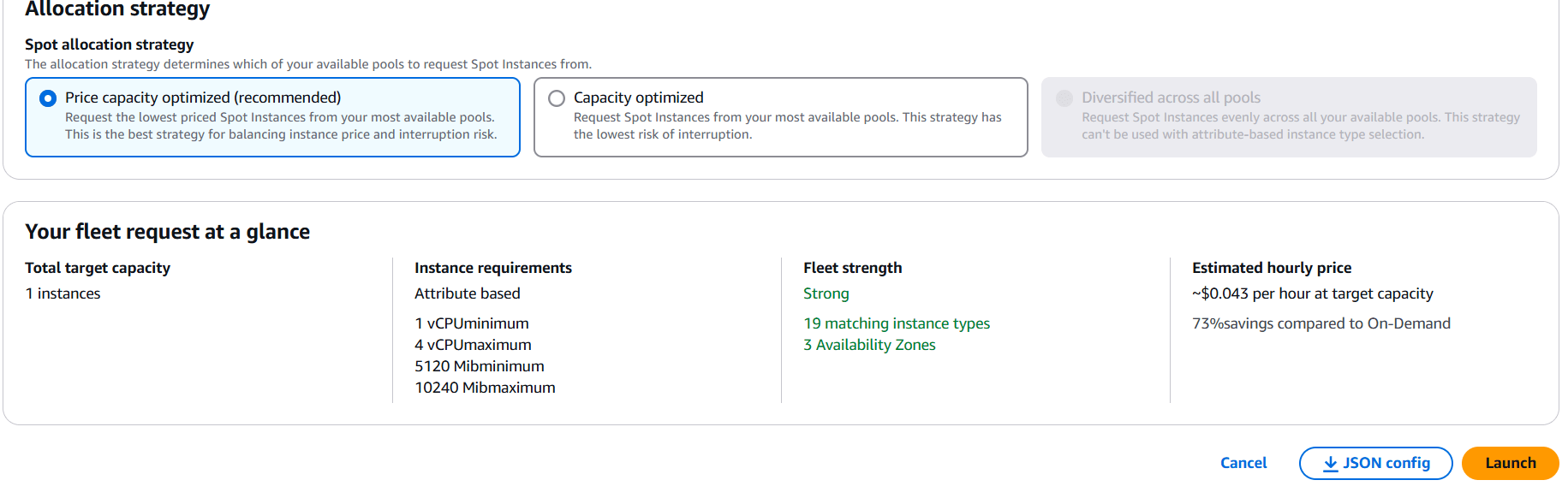
STEP 2: Select Spot Requested and click on create spot fleet requested.
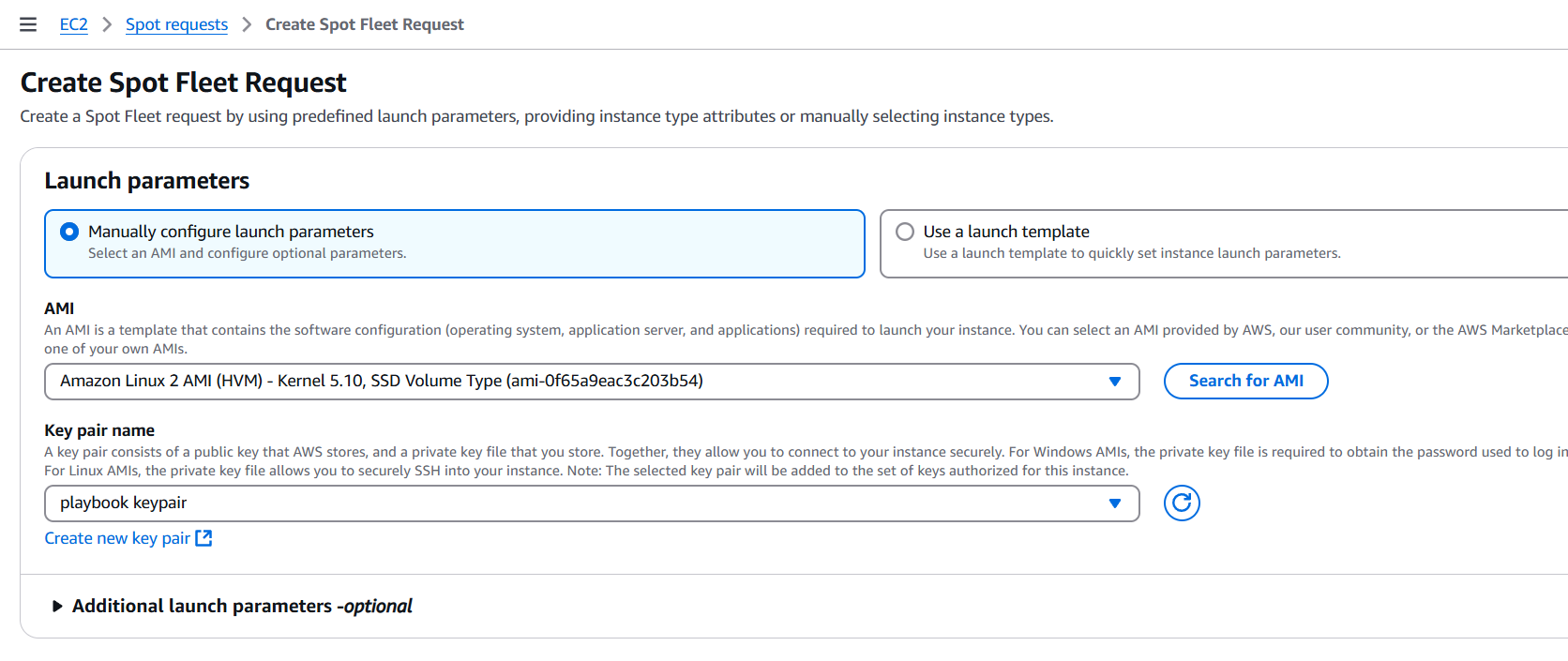
STEP 3: Select launch parameters and AMI, Keypair.
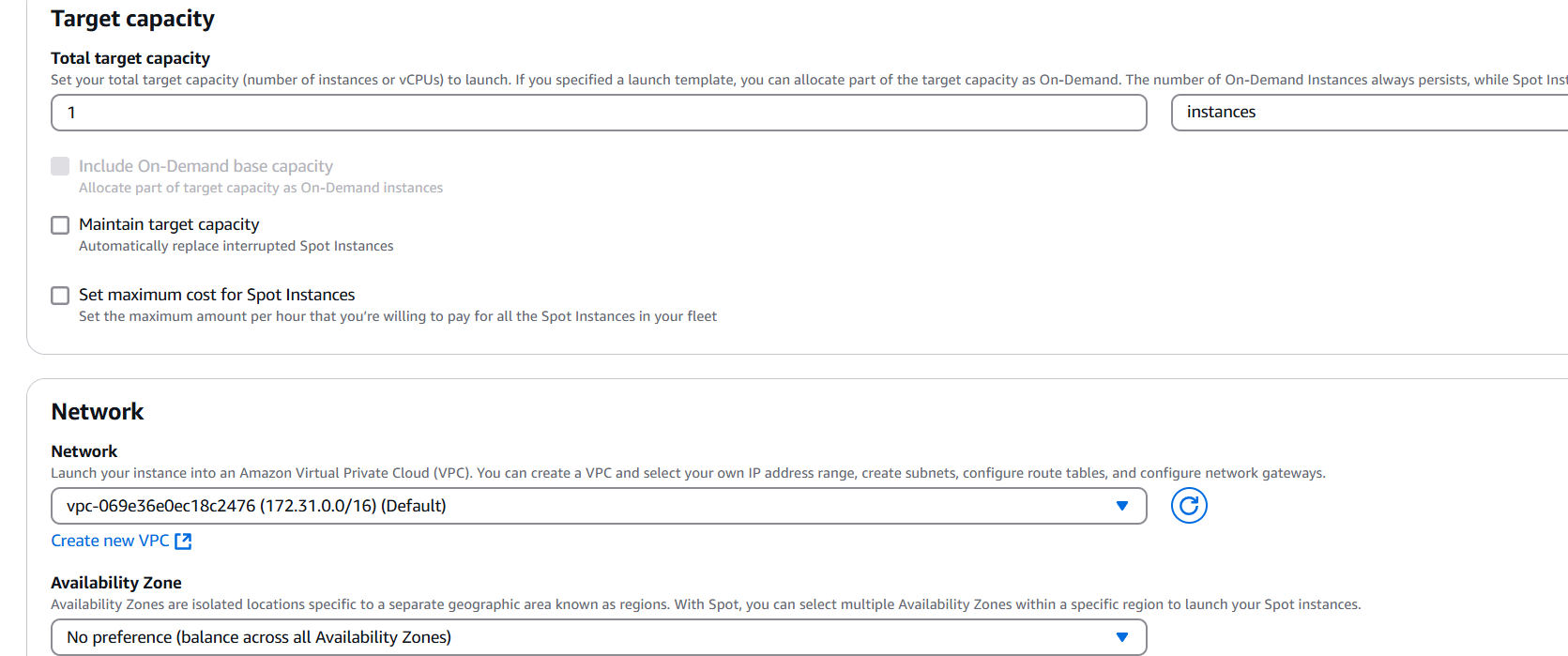
STEP 4: Target capacity 1 and Select the network.
STEP 5: Select the vCPU and memory.

STEP 6: Click on launch.

Conclusion.
Launching an EC2 Spot Instance is one of the smartest ways to optimize your cloud infrastructure costs without sacrificing performance. By taking advantage of unused EC2 capacity at a fraction of the cost of On-Demand instances, you can significantly reduce your cloud expenditure, especially for flexible, stateless applications and non-time-sensitive workloads. While Spot Instances come with the risk of interruptions, with the right strategy and tools in place, you can manage those interruptions effectively and still enjoy massive savings.
Throughout this guide, you’ve learned the essential steps to launch your first EC2 Spot Instance, from setting up the instance and bidding on capacity to managing scaling and interruptions. By understanding how Spot Instances work and using best practices for managing them, you can fully leverage their cost-saving potential and optimize your cloud infrastructure.
Whether you’re scaling up your application or experimenting with new workloads, EC2 Spot Instances offer the flexibility and affordability to keep your cloud costs in check. With careful planning and monitoring, Spot Instances can become a powerful part of your cloud strategy, enabling you to scale your applications efficiently while minimizing overhead.
Now that you’re equipped with the knowledge of how to launch and manage EC2 Spot Instances, it’s time to take the next step—implementing these instances in your environment and enjoying the savings. Start optimizing your cloud infrastructure today and see the difference Spot Instances can make to your bottom line. Happy cloud computing!
ECS Containers Made Easy: A Complete Guide to Launching Your Challenge.
Introduction.
Launching containers in AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service) can feel overwhelming for beginners, but it doesn’t have to be. In this guide, we’ll break down the process of deploying your first ECS container into manageable steps, giving you the confidence to tackle your containerization projects. Whether you’re new to ECS or just looking to refine your skills, this article will walk you through everything you need to know to successfully launch and manage ECS containers.
Containerization is a powerful way to scale and manage applications, and ECS simplifies the process for developers. AWS ECS allows you to deploy, manage, and scale containers without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. With ECS, you can focus on building your app, while AWS takes care of the heavy lifting.
In this guide, we will cover key topics such as creating ECS clusters, configuring task definitions, and launching containers in just a few simple steps. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how ECS works and how to set up and manage containers effectively.

Join us as we embark on the ECS container challenge—let’s make containerization easier than ever! Whether you’re optimizing for performance, cost, or scalability, this guide will ensure you’re on the right path. Ready to get started? Let’s dive in!
STEP 1: Navigate the Amazon ECS and Click on get started.

STEP 2: Select Cluster and click on create cluster.
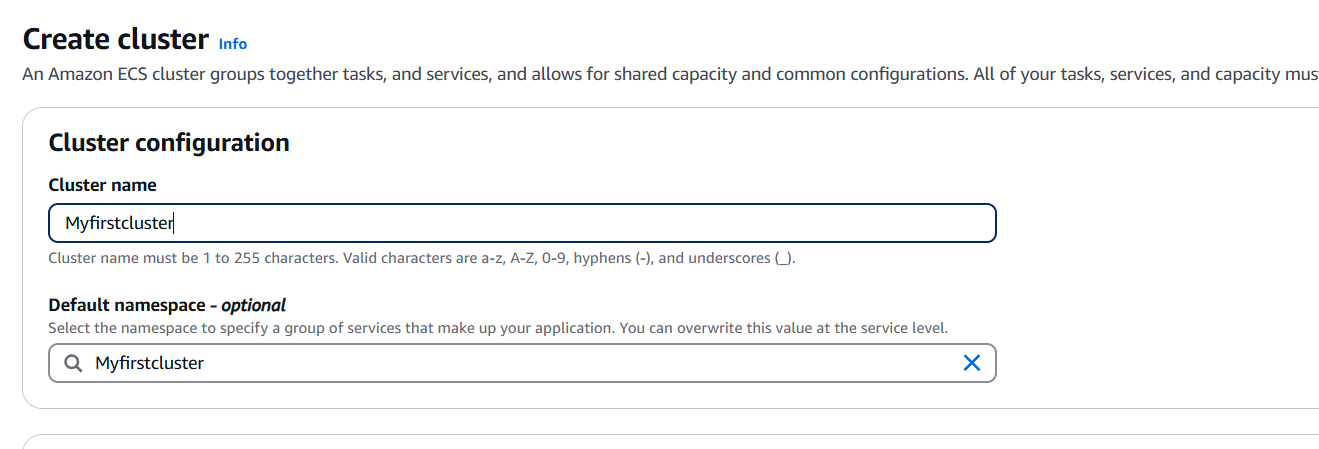
STEP 3: Enter the name and click on create.
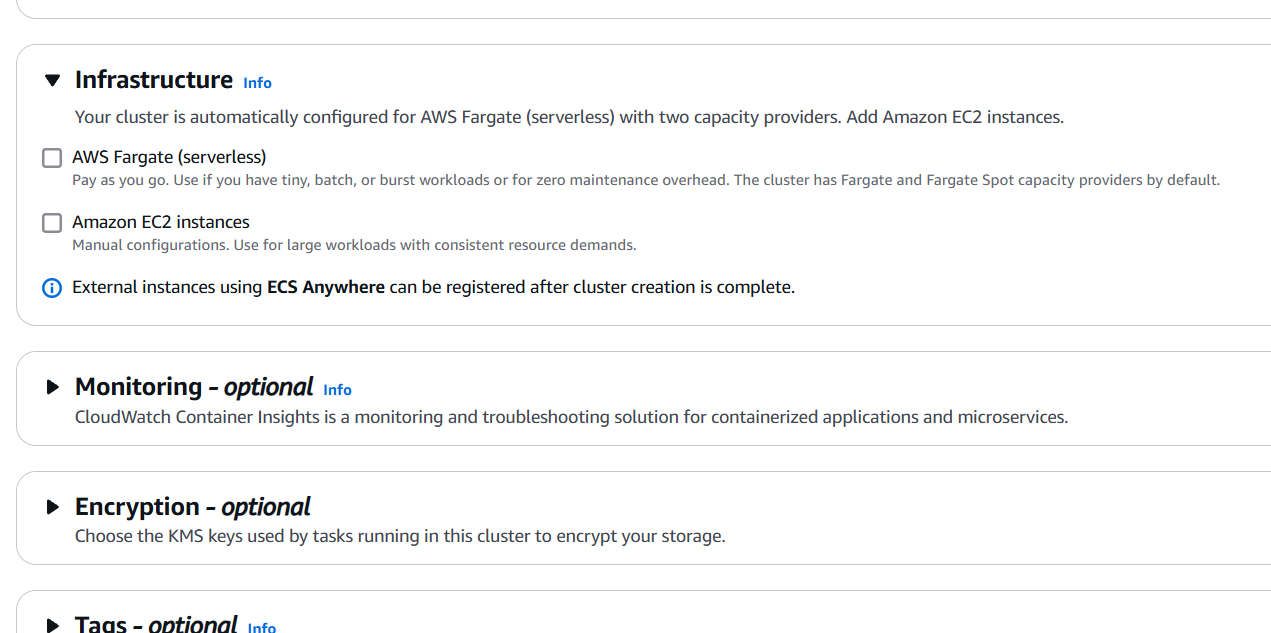
STEP 4: Next, select task definition and click on create.
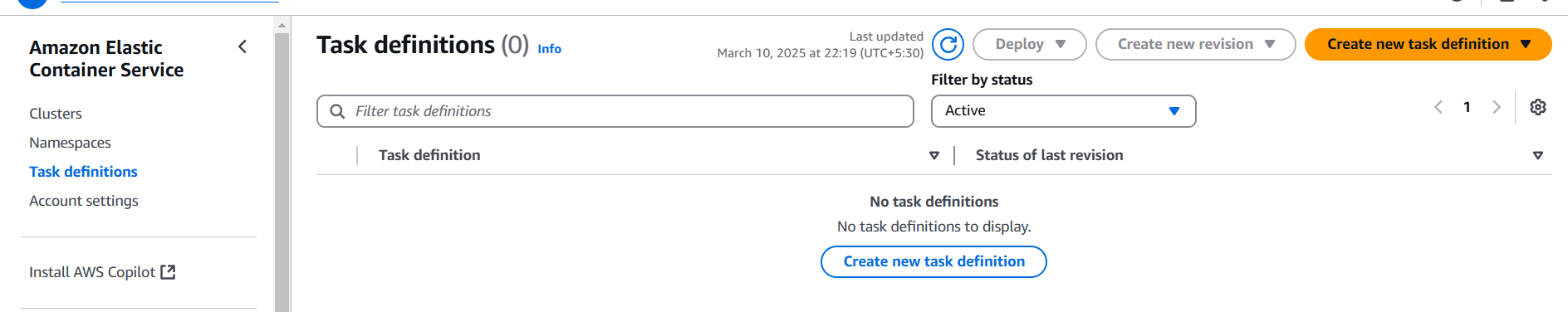
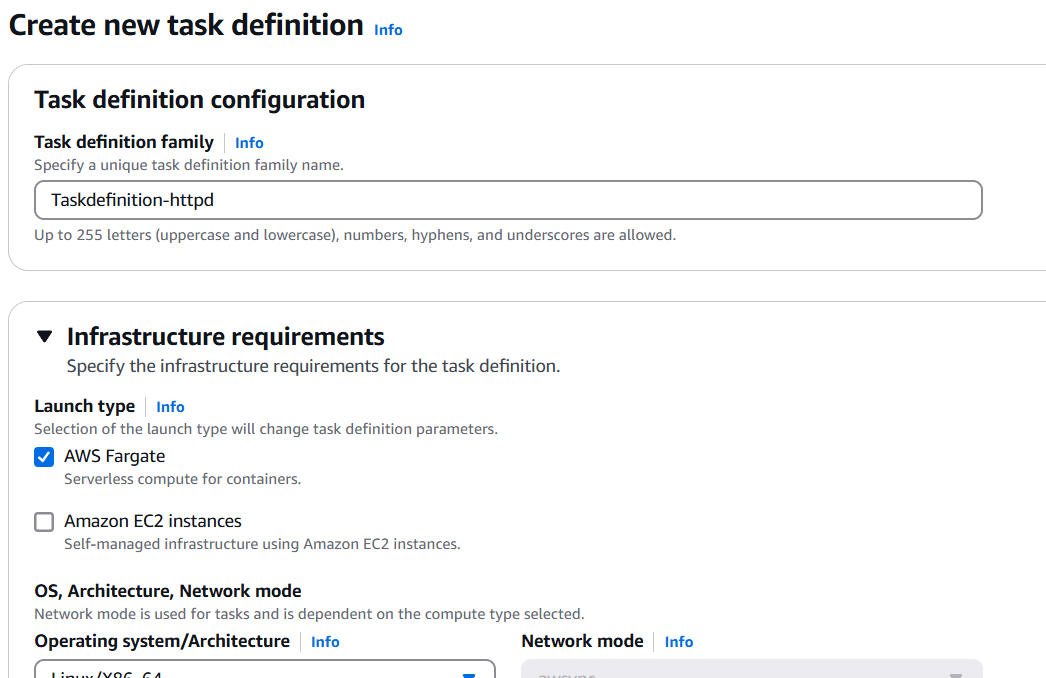
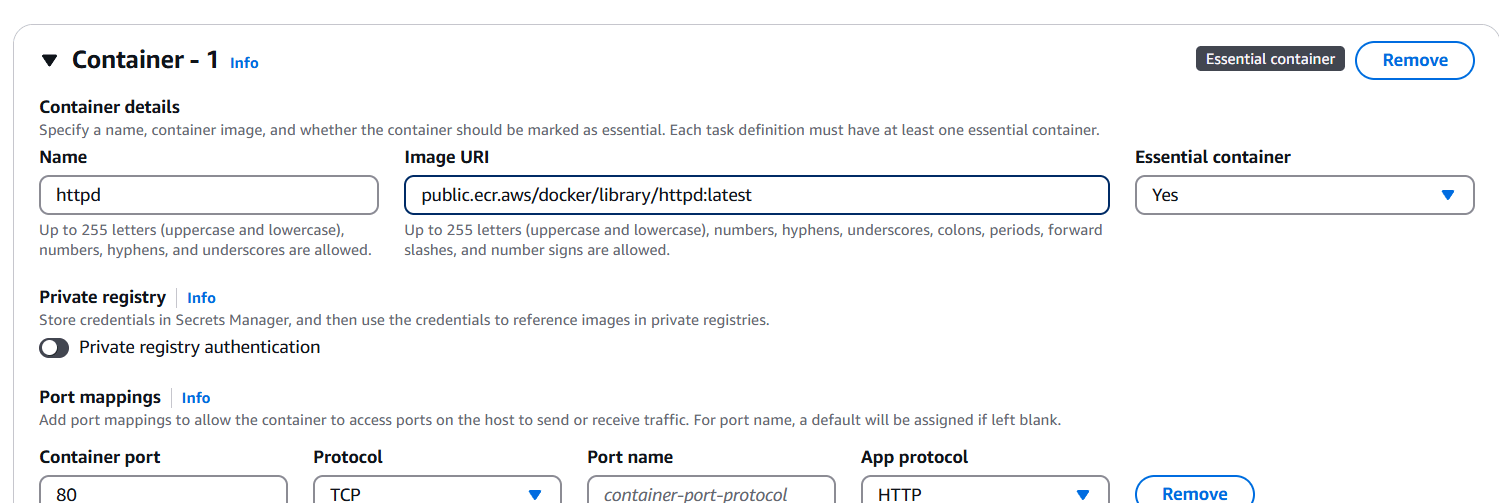
STEP 5: Enter task definition family and Launch type.
- Enter the image.
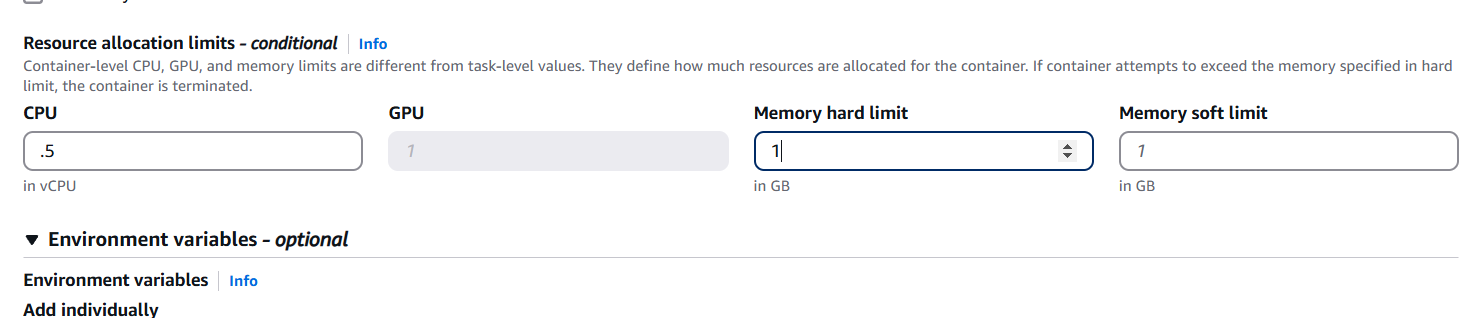
- CPU : 0.5.
- Memory : 1
STEP 6: Click on your created task and create the service.
- Select compute Option and select the following Options.
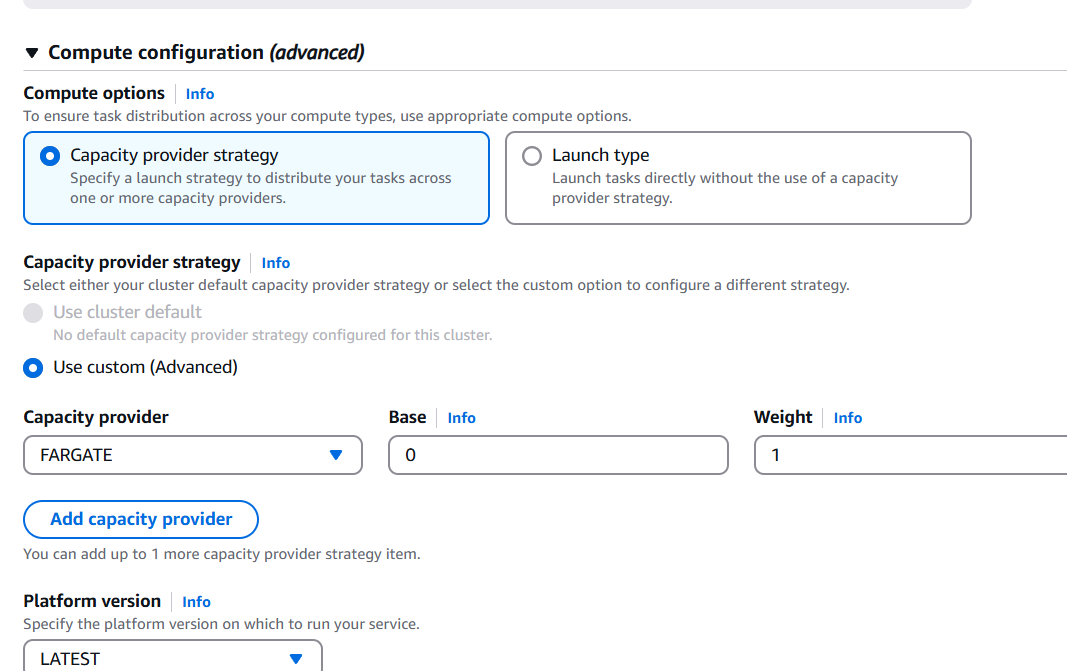
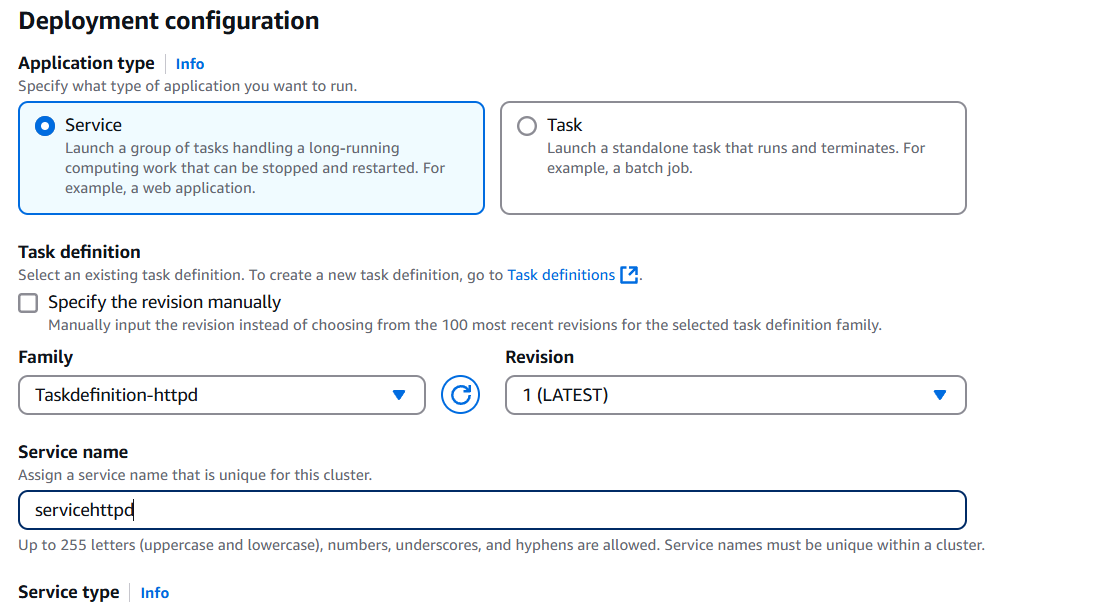
STEP 7: Service will created take a 2-3 mins.
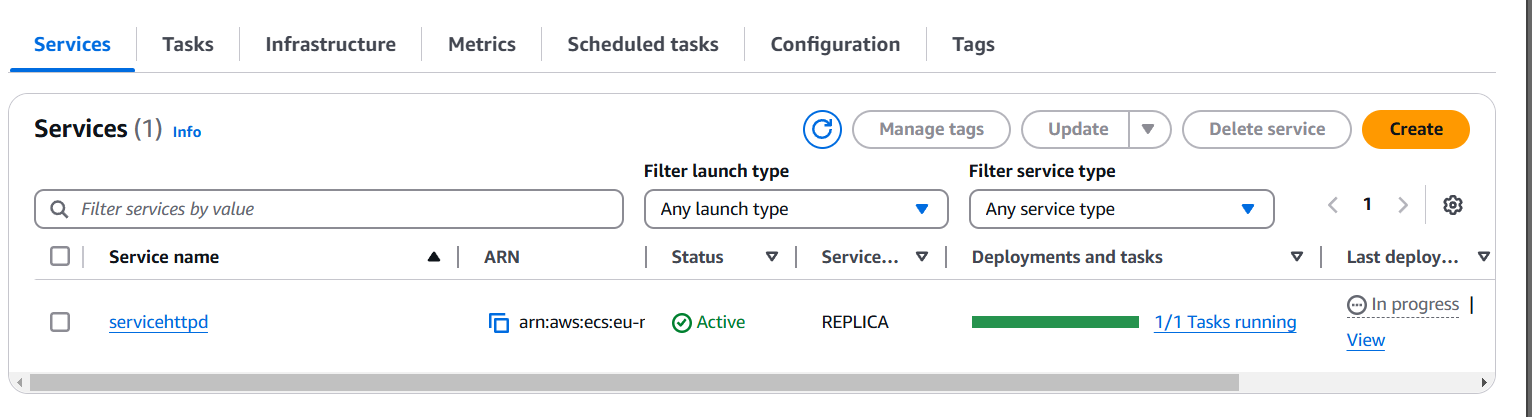
STEP 8: And task will be running.
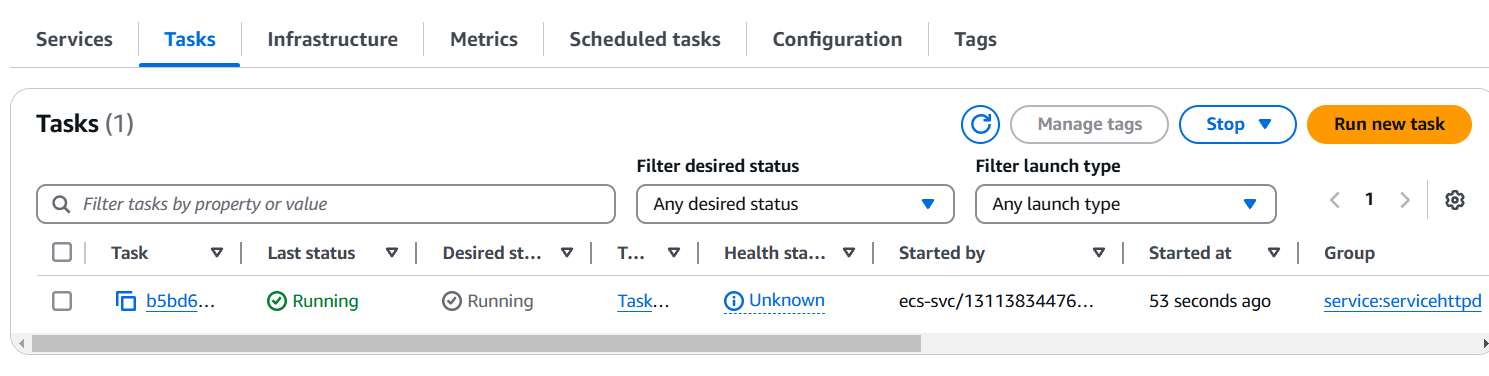
STEP 9: Next, Select your cluster name and Copy your public IP with port 80 on your browser.
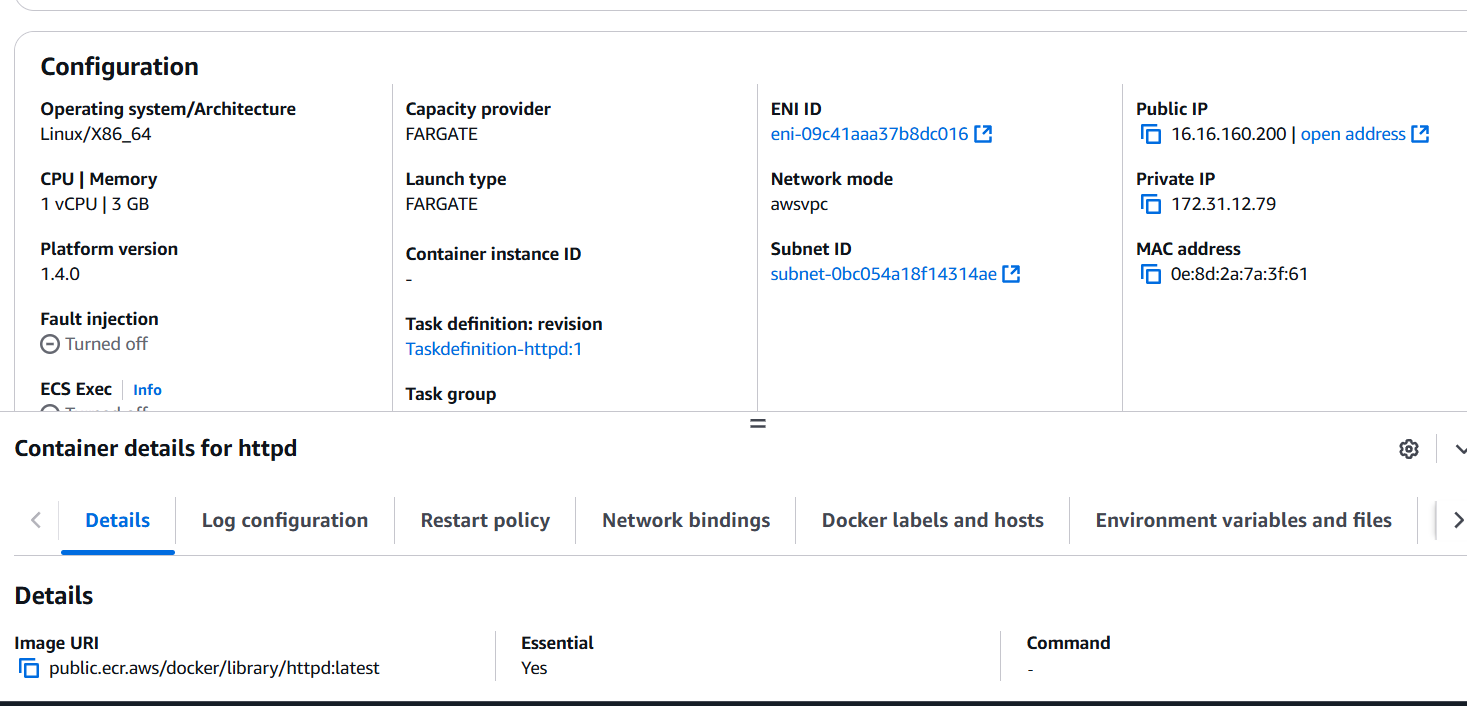

Conclusion.
Launching and managing ECS containers doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With the right guidance and a step-by-step approach, you can harness the power of AWS ECS to streamline your containerization process and take your applications to the next level. From setting up ECS clusters to deploying containers, we’ve covered the key steps to help you launch with confidence.
As you continue to explore ECS, remember that practice is key. The more you work with containers and ECS, the more comfortable you’ll become with its features and capabilities. By mastering these skills, you’re not only optimizing your application deployments but also future-proofing your development workflow for scalability and efficiency.
So, take the first step in your ECS container journey today and embrace the challenge! With the knowledge gained here, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any containerization task that comes your way. Happy coding, and good luck on your ECS adventure!
How to Build a Serverless Web Application Using AWS Lambda.
Introduction.
Building a serverless web application using AWS Lambda allows you to create highly scalable and cost-efficient applications without managing servers. AWS Lambda lets you run code in response to HTTP requests, events, or other triggers, automatically scaling with demand. The application typically consists of Lambda functions that handle backend logic, integrated with API Gateway for HTTP access. With services like Amazon S3 for static file hosting, you can easily deploy both frontend and backend components. Lambda’s pay-per-use model ensures you’re only billed for the resources consumed. It simplifies infrastructure management, making it ideal for small projects or scalable production apps. You can also enhance security with tools like AWS Cognito for user authentication. Monitoring and debugging are simplified with integrated CloudWatch logs. AWS Lambda supports various languages, making it flexible for different use cases. This serverless architecture improves development speed, reduces costs, and allows developers to focus on code rather than infrastructure.

Prerequisites:
- AWS Account
- AWS CLI installed and configured
- Basic knowledge of JavaScript (Node.js), Python, or other supported languages
- AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) permissions to create resources like Lambda functions, API Gateway, and others.
Steps to Build a Serverless Web Application Using AWS Lambda:
1. Set Up AWS Lambda
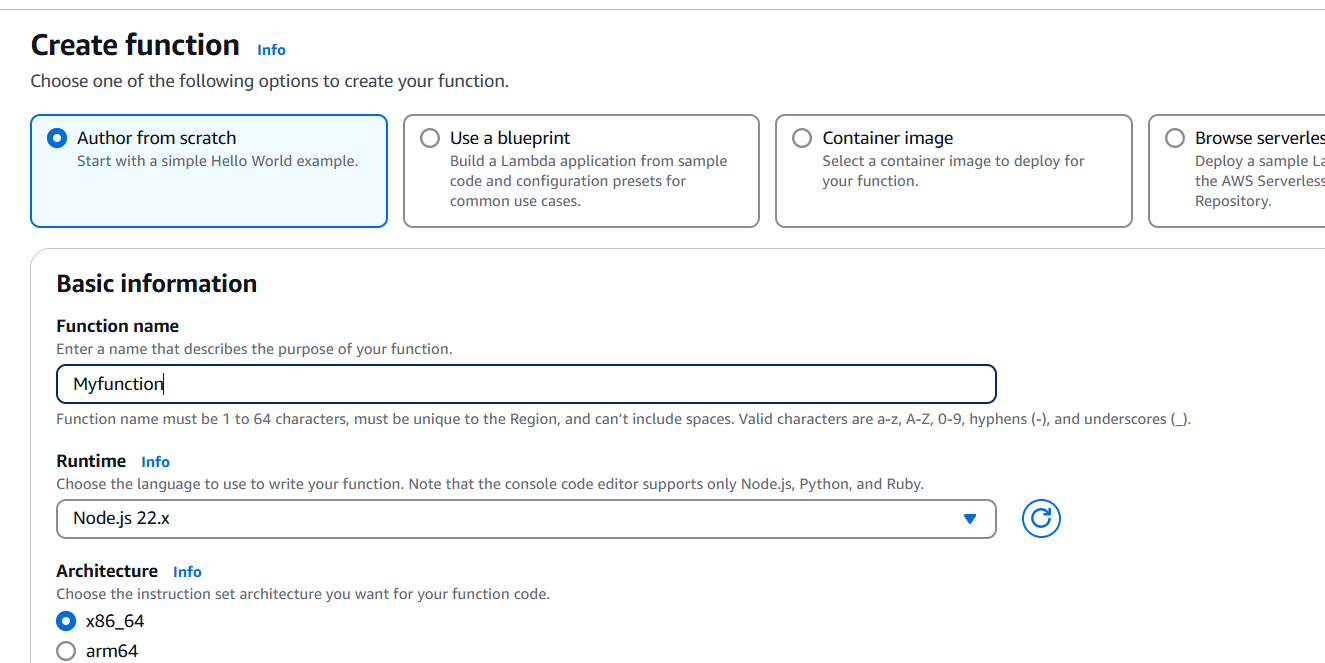
- Create a Lambda function:
- Go to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Lambda and click Create function.
- Choose a runtime (e.g., Node.js, Python).
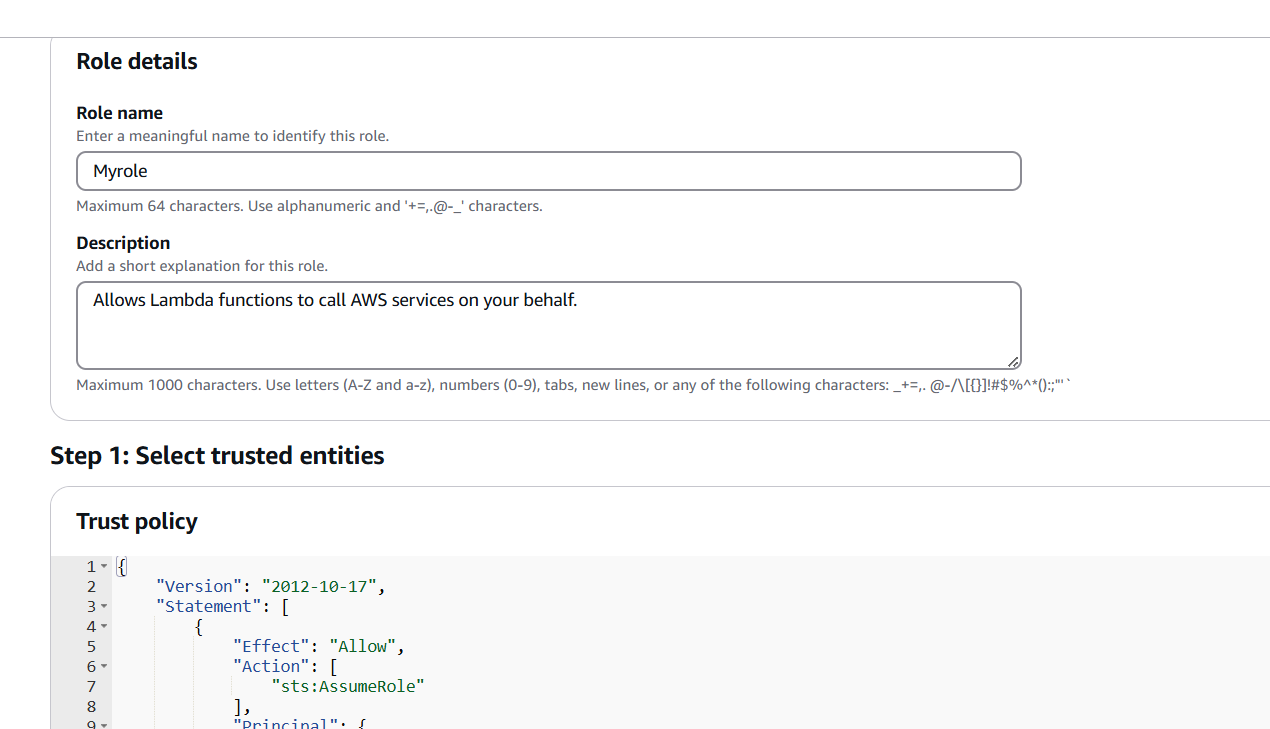
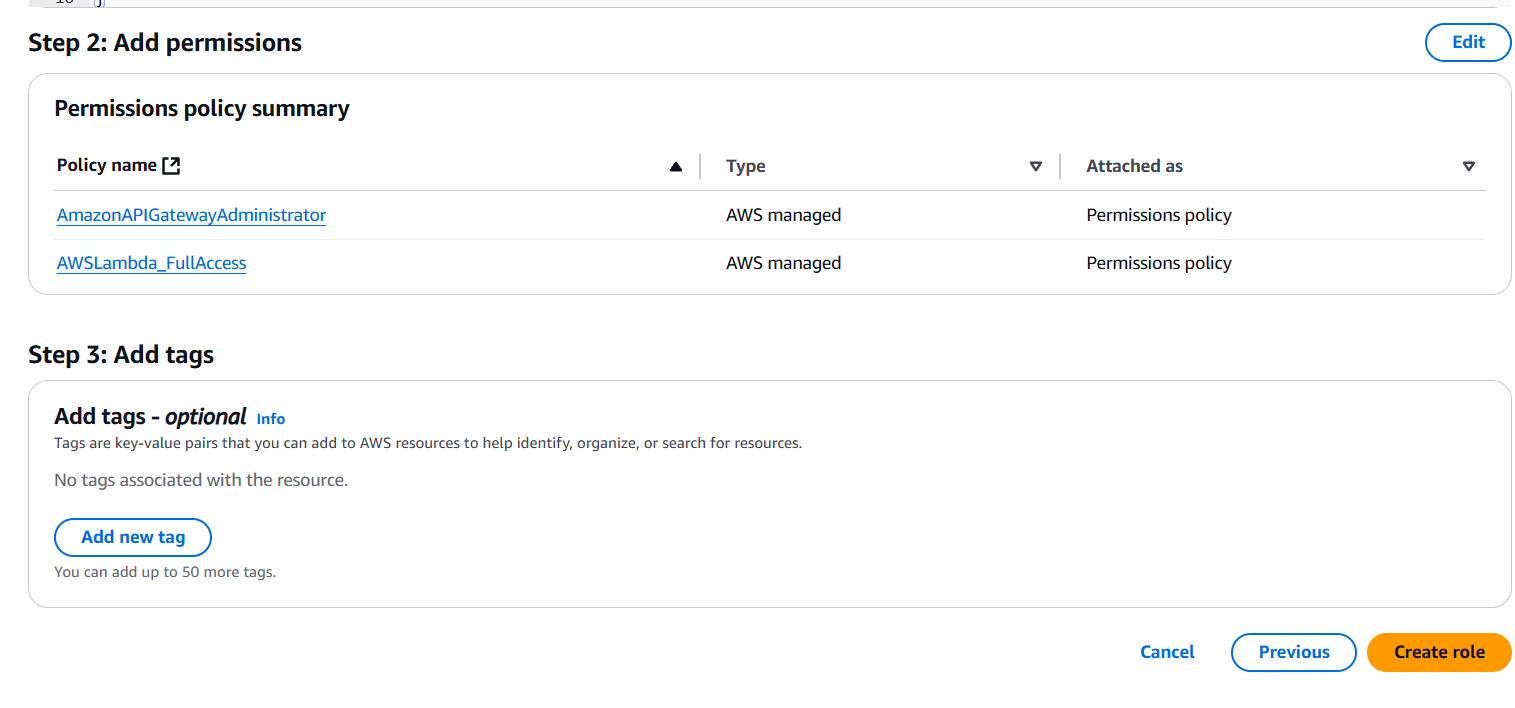
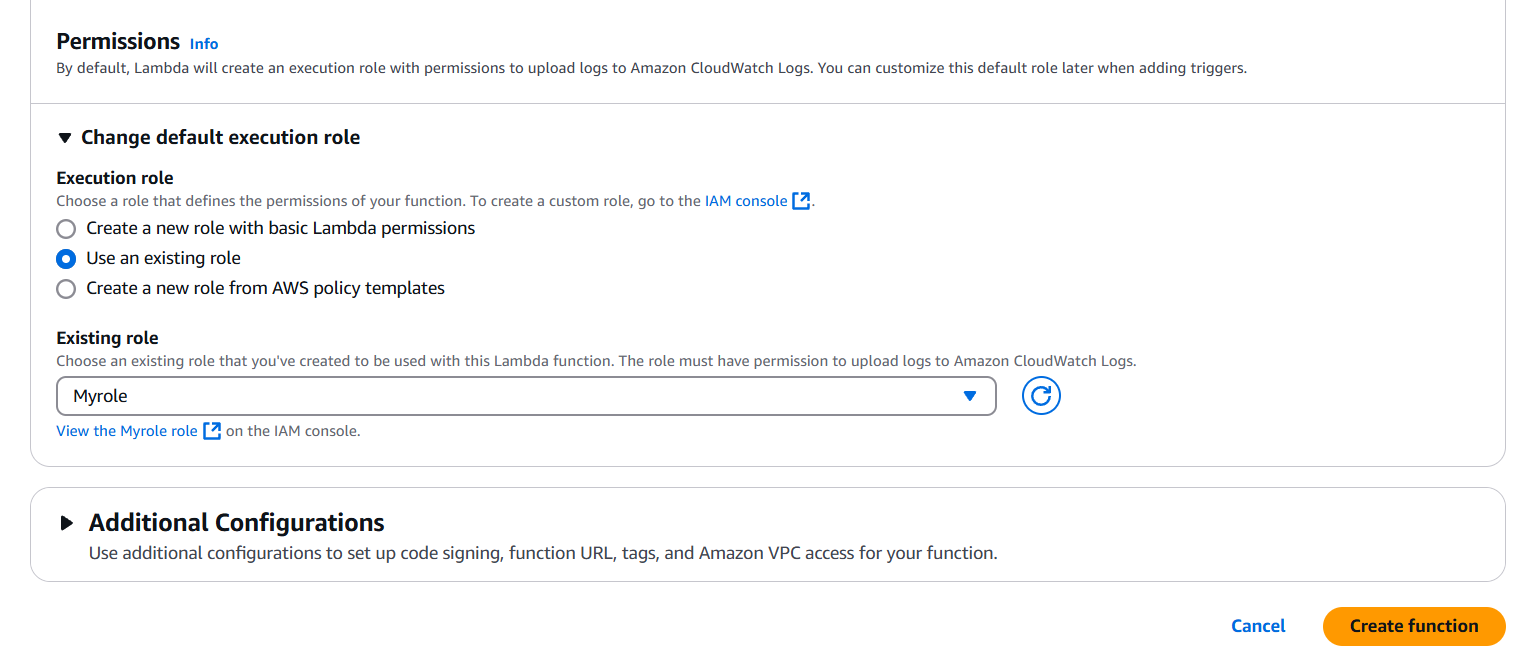
- Configure the function name and role permissions.
- Write the function code in the inline editor or upload a ZIP file if you have complex code.
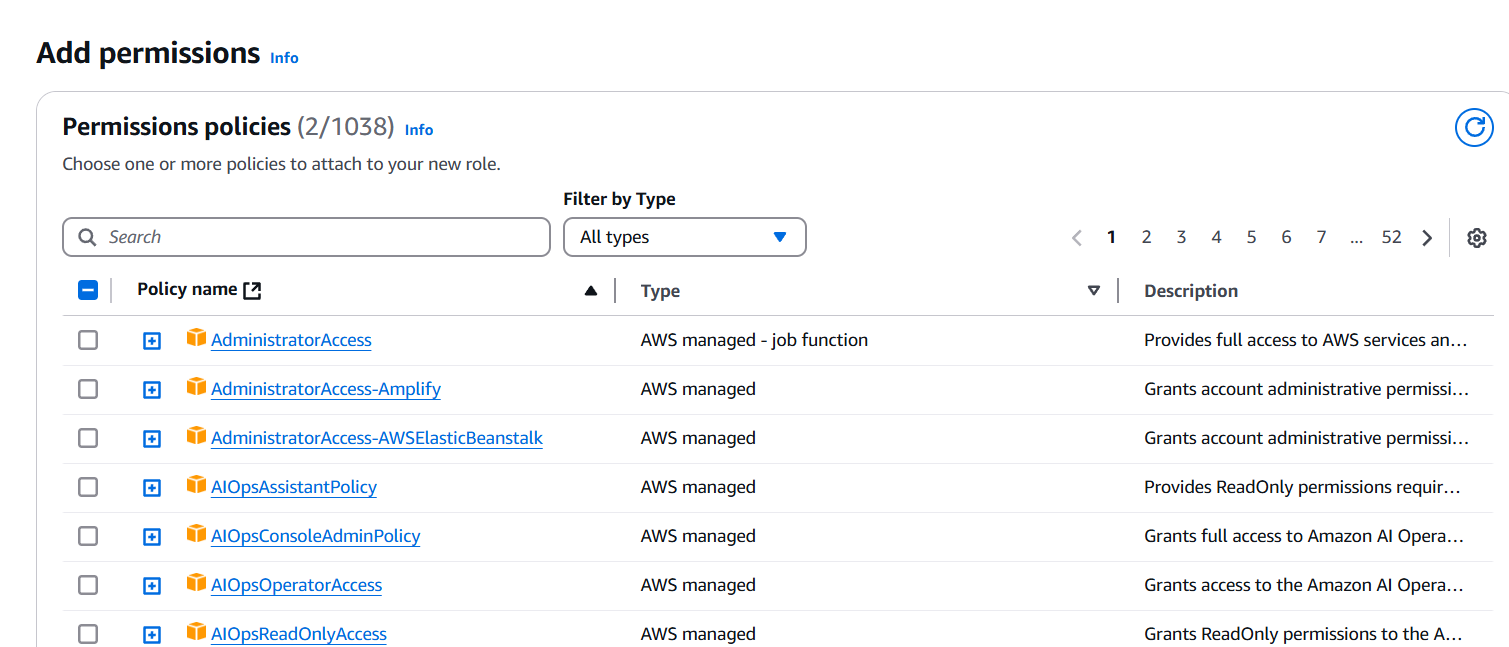
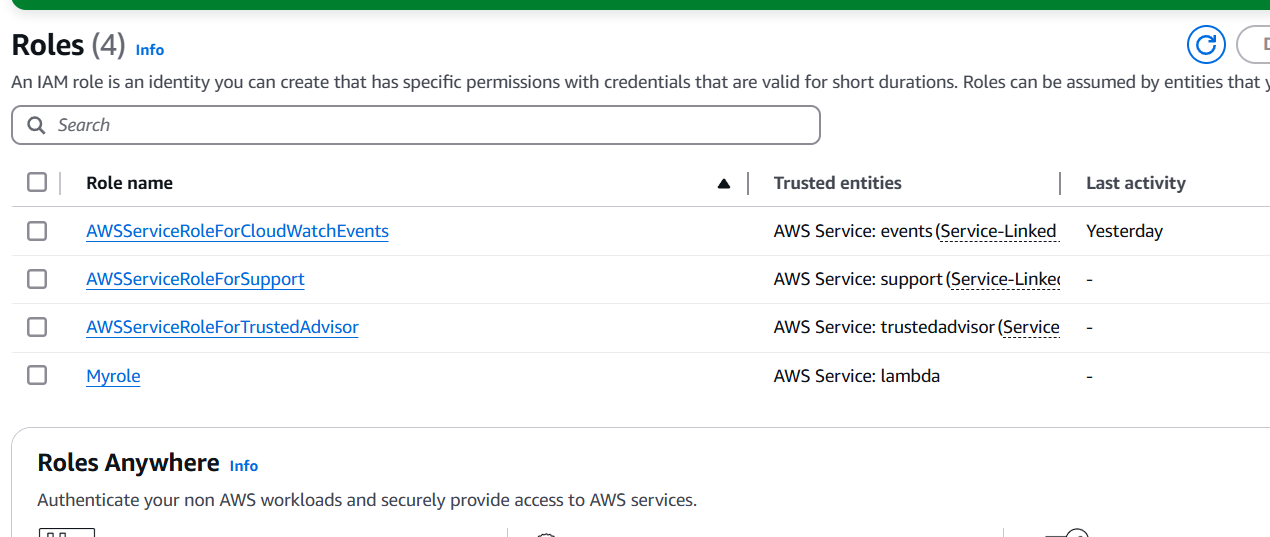
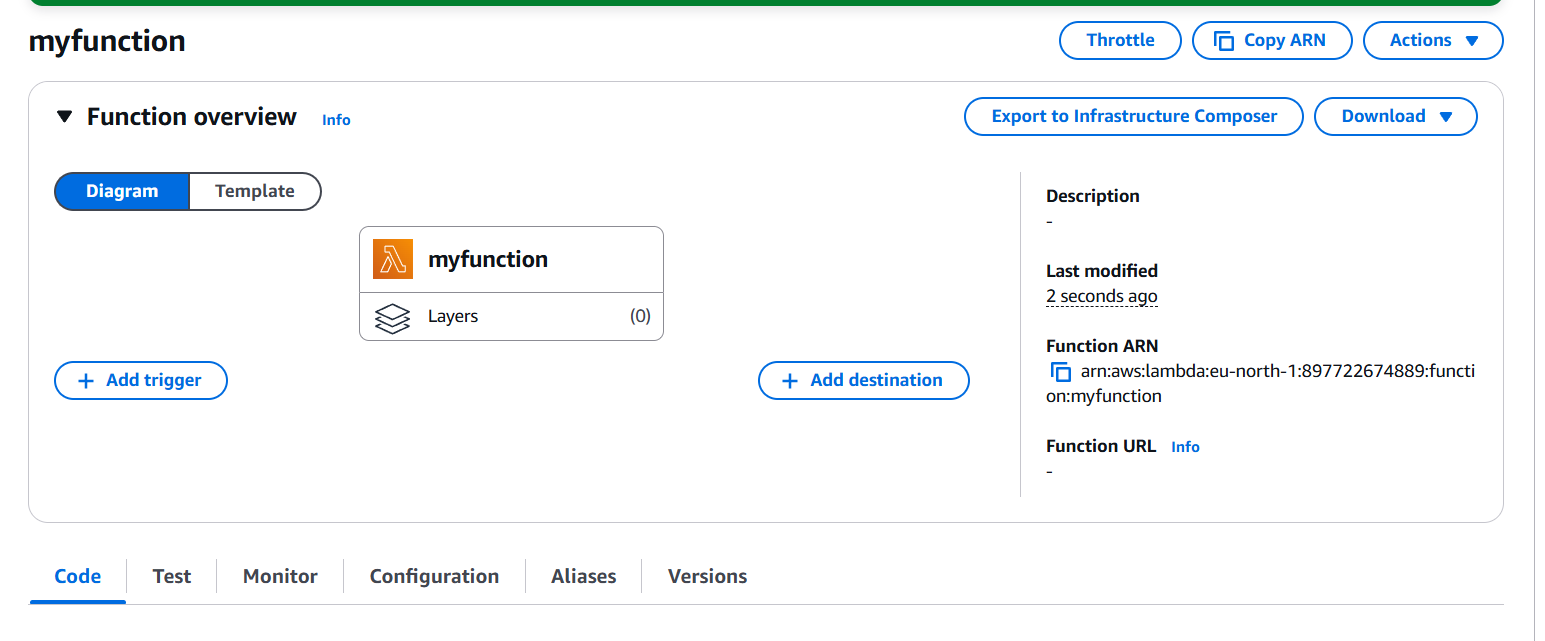
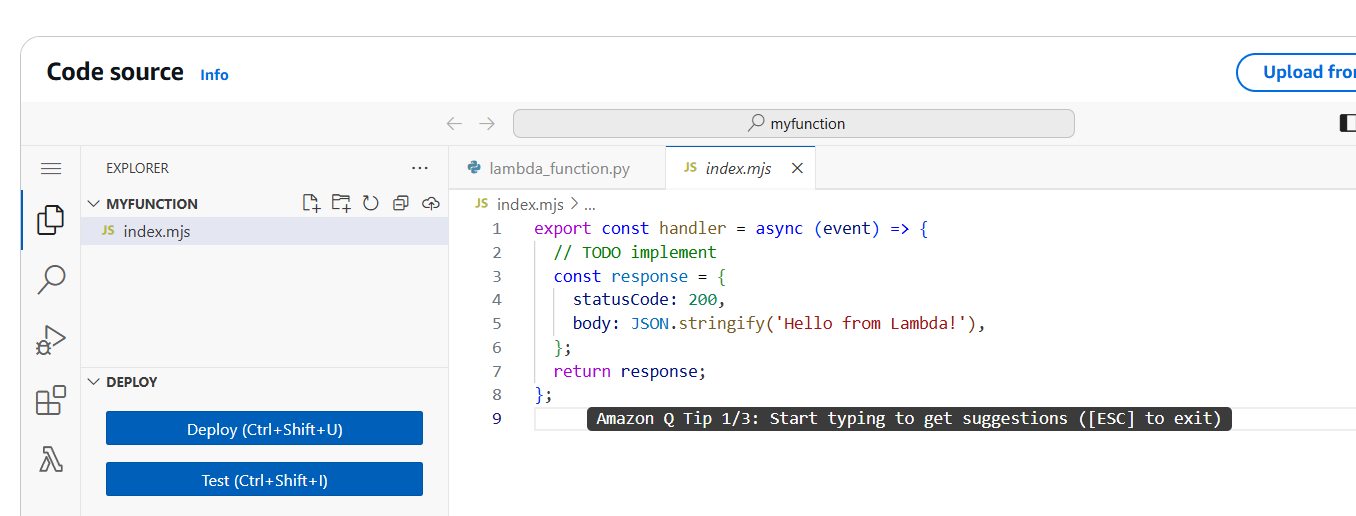
2. Set Up API Gateway
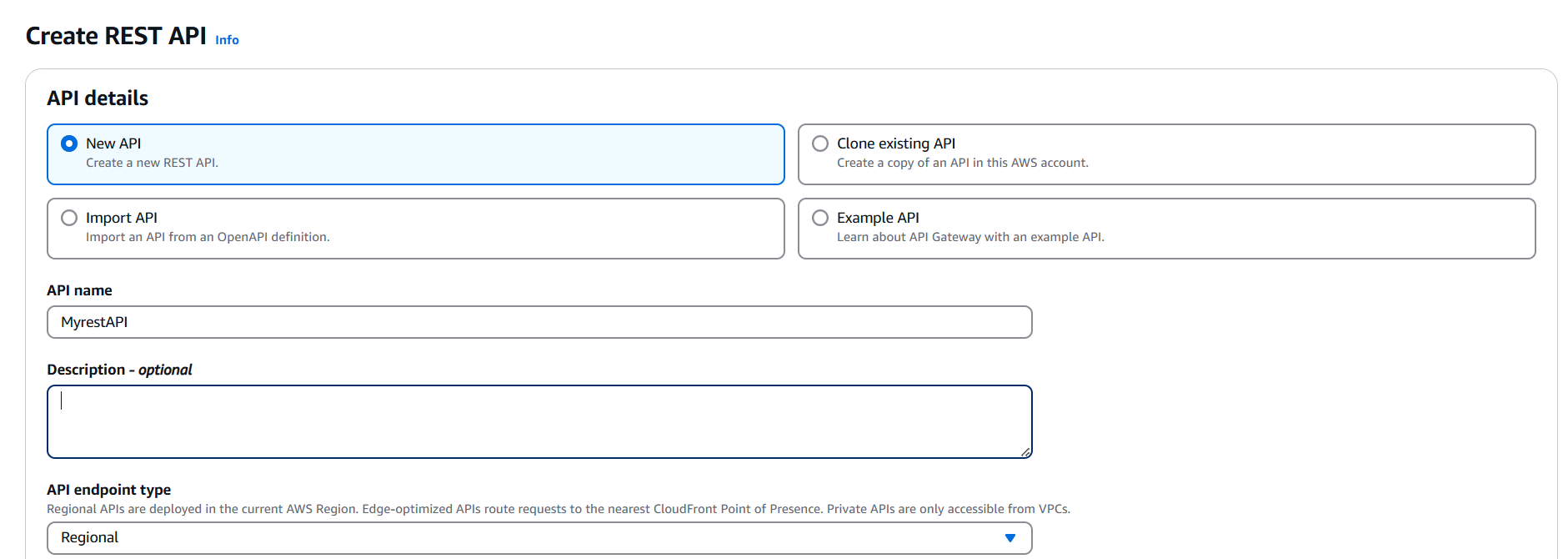
- Create an API:
- Go to API Gateway in the AWS Console and choose Create API.
- Select REST API (for most web apps).
- Define your API resource (e.g.,
/hello). - Create a method (e.g., GET) and link it to your Lambda function.
- Deploy the API to a new or existing stage.
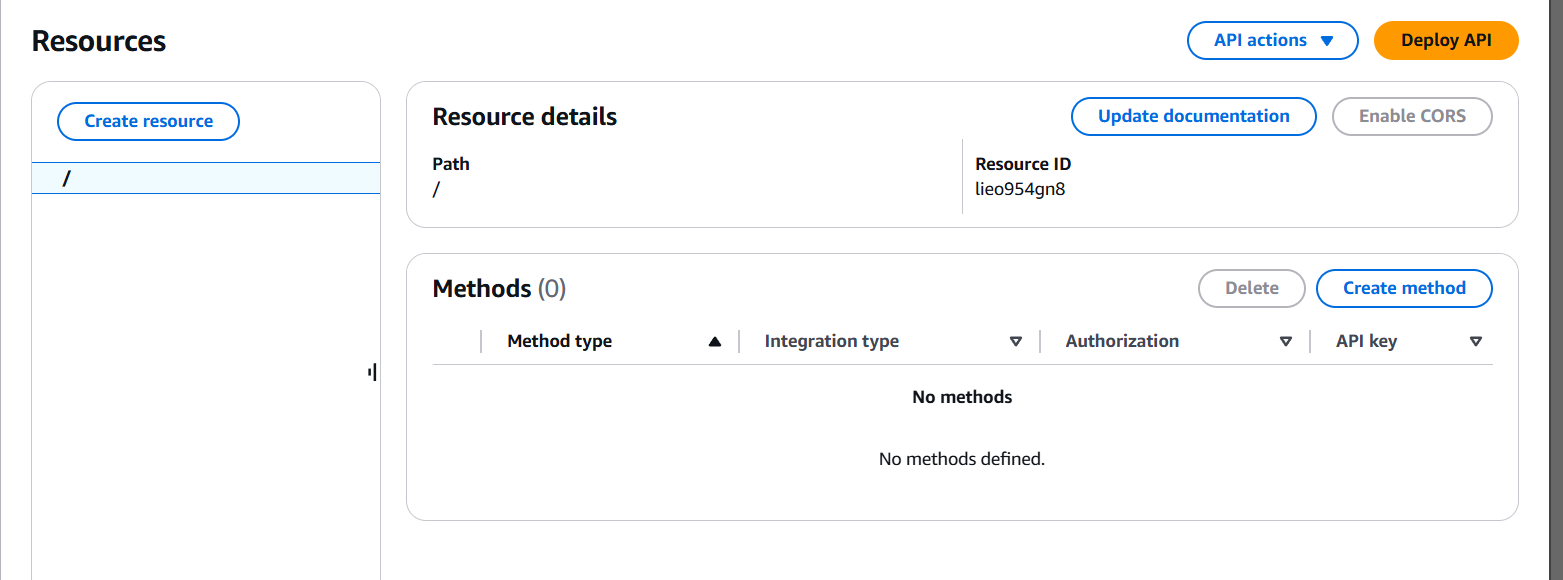
3. Testing Your Web Application
- Once everything is set up, you can test the API Gateway endpoint to ensure that it triggers the Lambda function and returns the expected result.
- You can test it by using a browser, Postman, or curl.
curl https://your-api-id.execute-api.region.amazonaws.com/stage/hello4. Monitor and Optimize
- CloudWatch Logs: AWS Lambda automatically logs output to CloudWatch. You can view logs for debugging or monitoring performance.
- Optimize Lambda Functions: Use memory and timeout settings wisely to minimize costs and ensure efficient execution of Lambda functions.
5. Deploying the Application
- Once you’ve tested everything, you can deploy the API and make your Lambda functions public for use.
- CI/CD: You can set up AWS CodePipeline or other CI/CD tools for automated deployment.
Benefits of a Serverless Web App Using AWS Lambda:
- With AWS Lambda, you only pay for the compute time your code consumes. There are no charges for idle server time, making it highly cost-effective, especially for applications with variable or low traffic.
- AWS Lambda automatically scales the application in response to the number of incoming requests. It adjusts resources as needed, handling traffic spikes without any manual intervention.
- There’s no need to manage or provision servers. AWS takes care of the infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code.
- Lambda supports multiple programming languages, including Node.js, Python, Java, and C#, allowing developers to use their preferred languages for backend logic.
- Serverless architecture accelerates development by reducing the need to manage infrastructure. You can quickly prototype and deploy applications, speeding up the overall development lifecycle.
- With AWS CloudWatch, you get real-time monitoring and logging of Lambda functions, making it easier to troubleshoot, optimize, and keep track of application performance.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, building a serverless web application with AWS Lambda offers a powerful solution for developers looking to create scalable, cost-efficient, and low-maintenance applications. By leveraging AWS Lambda’s event-driven model, you can seamlessly integrate backend logic with API Gateway, while utilizing services like Amazon S3 for static content hosting. This architecture allows you to focus more on application development rather than infrastructure management. With pay-as-you-go pricing, automatic scaling, and easy monitoring through CloudWatch, serverless applications are ideal for a wide range of use cases, from small projects to large-scale production systems. AWS Lambda’s flexibility, combined with other AWS services, enables developers to build robust and efficient web applications with minimal overhead.