Introduction.
Docker is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of applications by packaging them into lightweight, portable containers. Containers package up everything an application needs to run: the code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings.
Core Components:
- Images : Docker images are read-only templates, meaning they cannot be altered after creation. Changes result in a new image being created.
- Containers : Containers are created from Docker images and provide an isolated environment for running applications.
- Registries : A Docker registry is a centralized repository where Docker images are stored, managed, and distributed. It allows developers and teams to share and access Docker images, enabling efficient deployment of applications across different environments.
- Docker Engine : Docker Engine provides the foundation for Docker’s functionality, including building images, managing containers, and networking.

Docker installation.
STEP 1: Terminate any running Docker containers and remove their associated files from the system.
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io
sudo apt-get update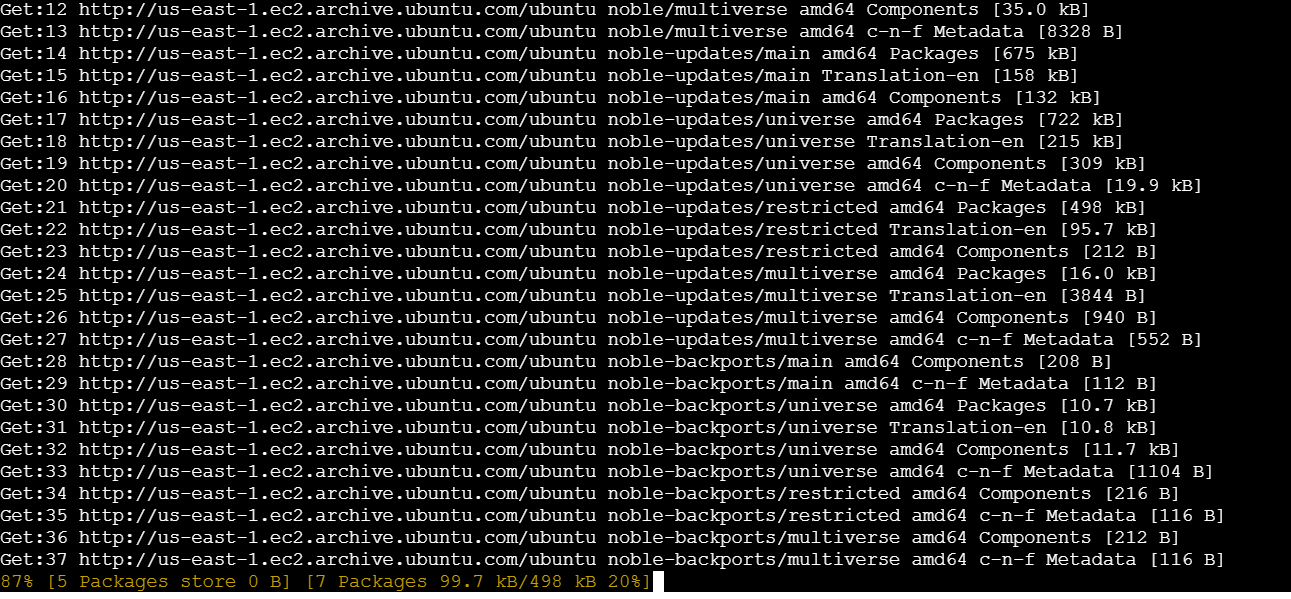
STEP 2: Install the docker use the following command,
sudo apt install docker.io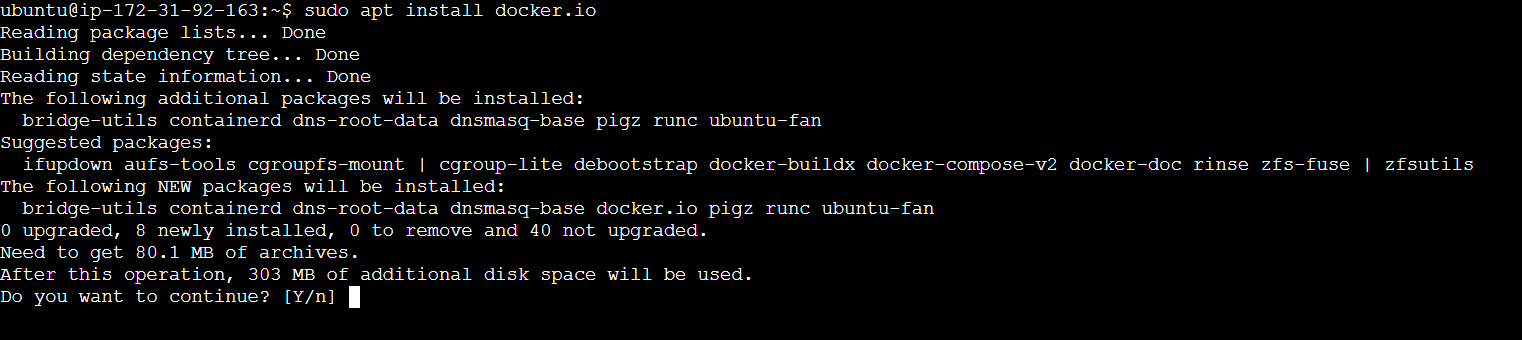
STEP 3: Enable and start the server.
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl status docker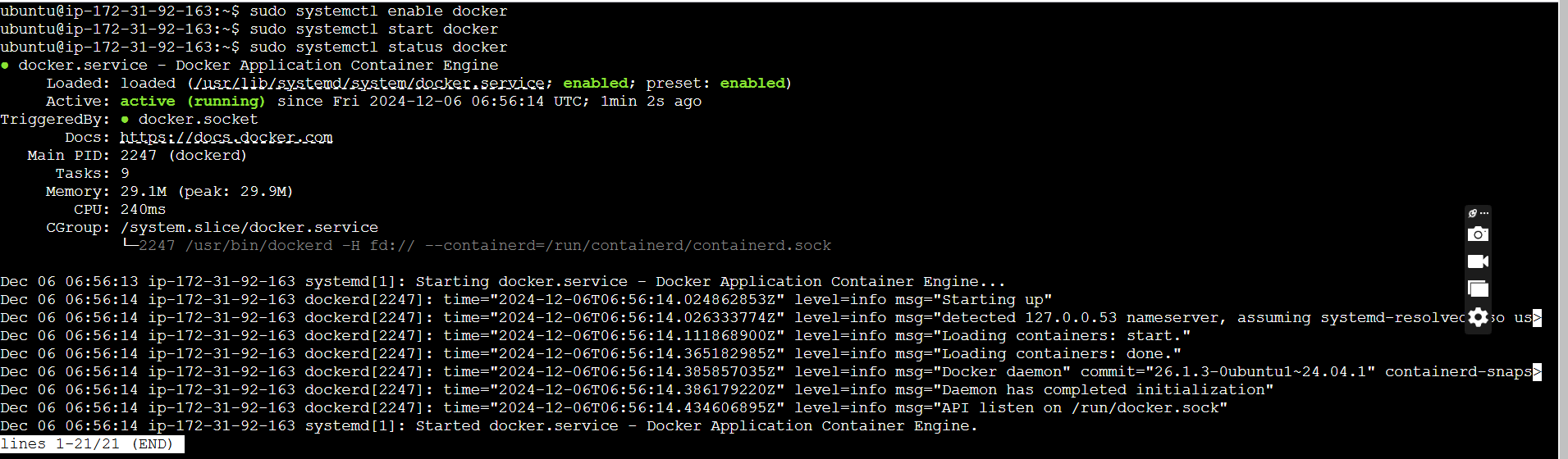
STEP 4: Check the version installed using the following command.
docker --version
STEP 5: Check the docker images.
sudo docker images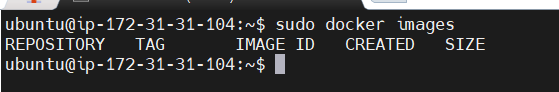
There are no Docker images on my system.
STEP 6: Pull an image from the Docker hub.
sudo docker run hello-world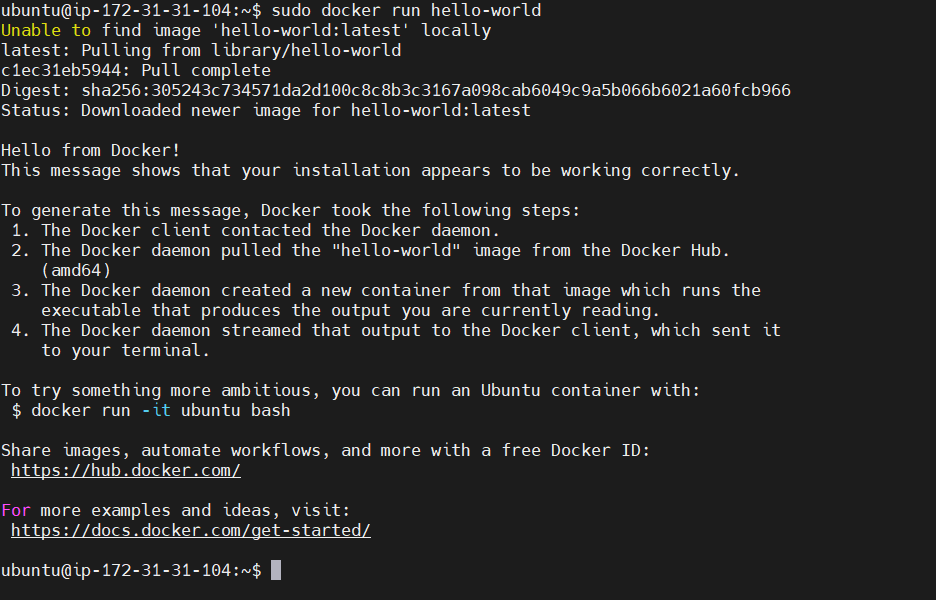
STEP 7: Now I check my images.
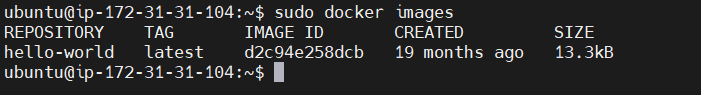
STEP 8: Display all the containers pulled.
sudo docker ps -a
STEP 9: Create the docker group.
sudo groupadd docker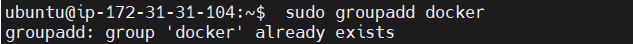
STEP 10: As the next step, add the user to the Docker group by executing the following command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER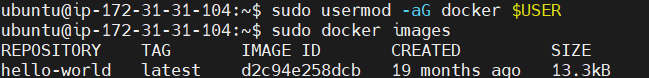
STEP 11: Docker to list all images stored on the system.
sudo docker images -a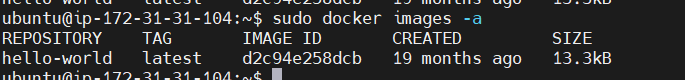
STEP 12: Search for Docker images in the Docker Hub repository.
sudo docker search <image-name>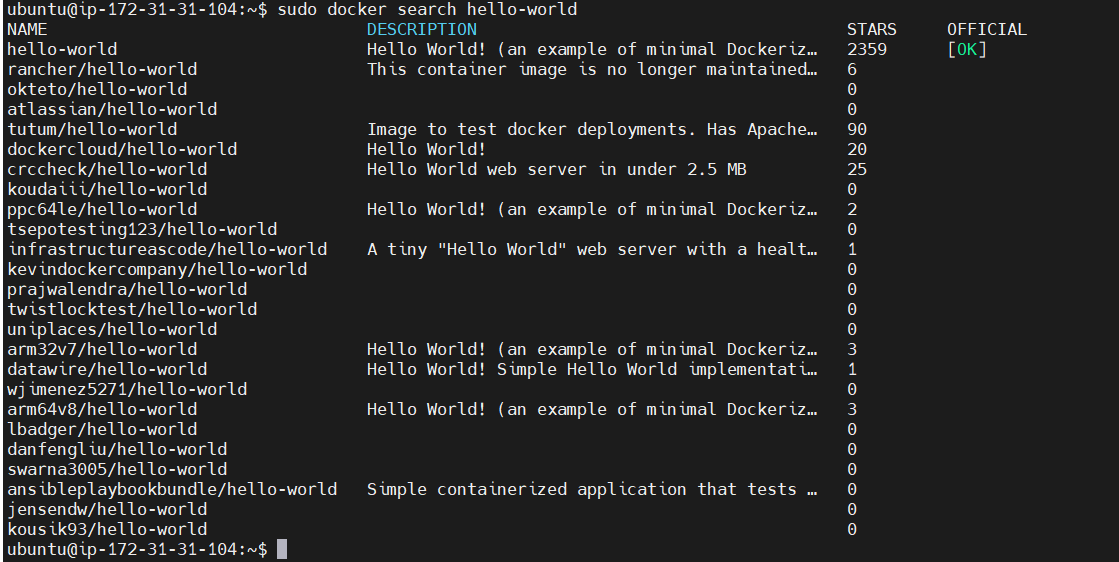
STEP 13: Pull the ubuntu docker image.
sudo docker pull ubuntu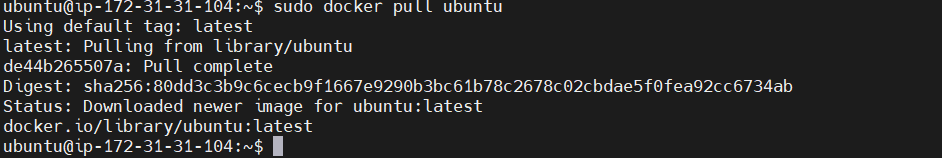
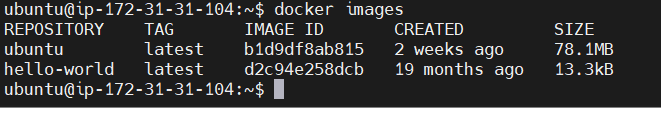
STEP 14: Activate the Container.
“b1d9df8ab815” Replace your Image ID.
sudo docker run -it b1d9df8ab815 bin/bash

Conclusion.
Docker has become an integral tool in modern application development and operations. Its seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines and orchestration tools like Kubernetes ensures that modern teams can adopt faster, more agile, and error-free development practices.

Add a Comment