What is tomcat?
Apache Tomcat is a free, open-source web server and servlet container that’s used to host Java-based web applications. Apache Tomcat (called “Tomcat” for short) is a free and open-source implementation of the Jakarta Servlet, Jakarta Expression Language, and WebSocket technologies. It provides a “pure Java” HTTP web server environment in which Java code can also run.

How Does Tomcat Work?
Tomcat follows a modular architecture comprising connectors, containers, and the Catalina Servlet container. This architecture enables Tomcat to efficiently handle client requests and generate responses. Tomcat implements the Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages (JSP) specifications. It manages the lifecycle of servlets, loading and unloading them as needed.
Now, will create tomcat on ubuntu instance.
STEP 1:Create a EC2 instance (ubuntu machine).
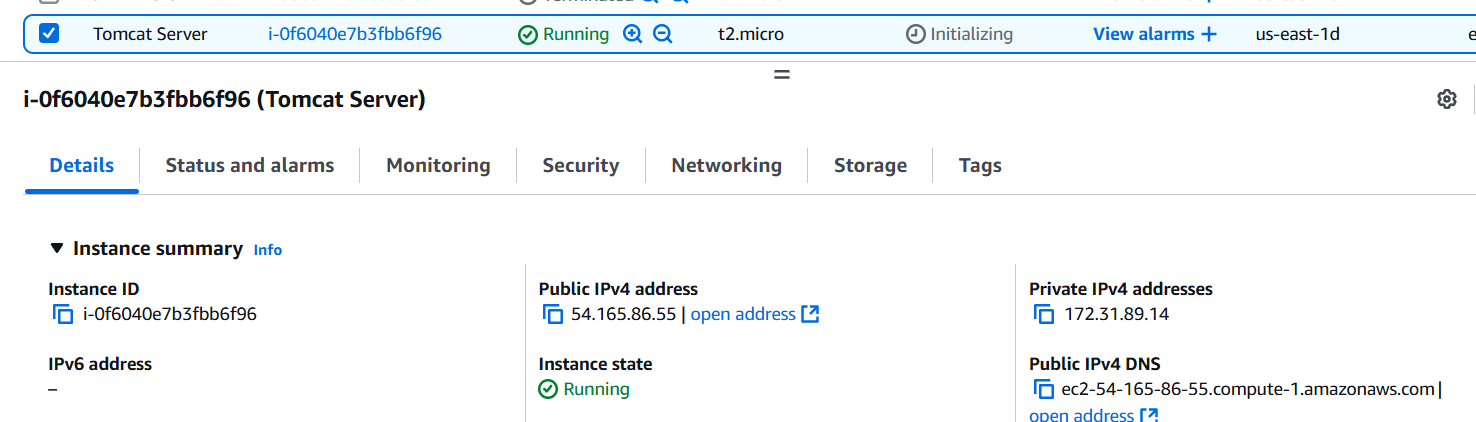
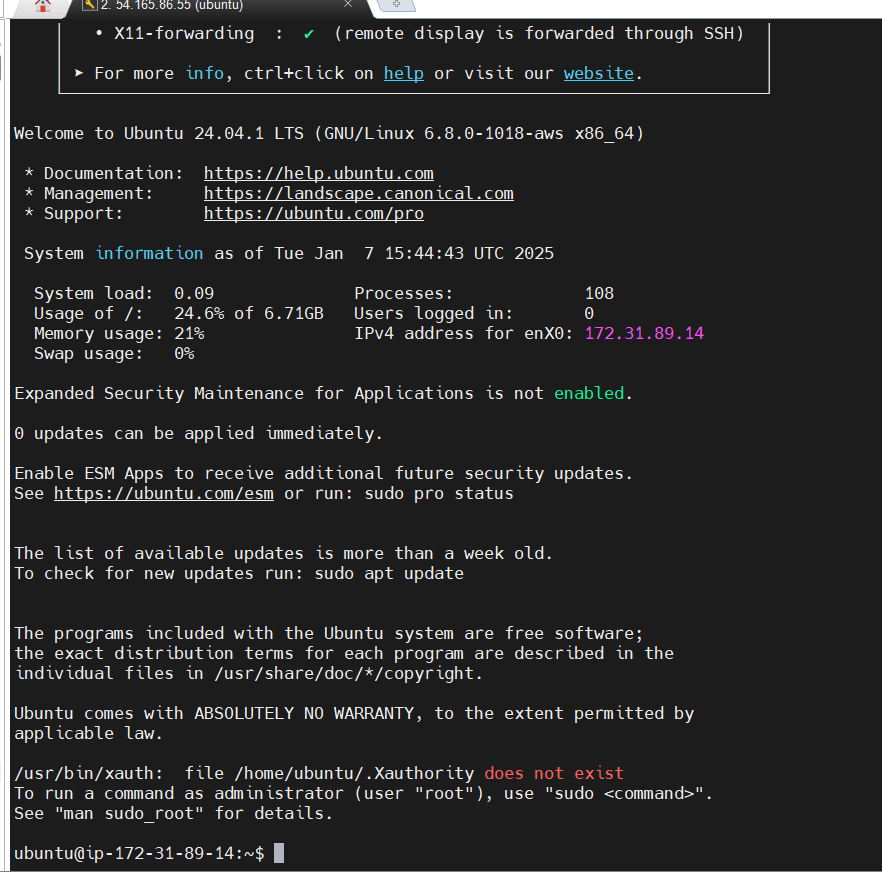
STEP 2: Accessing instance with SSH.
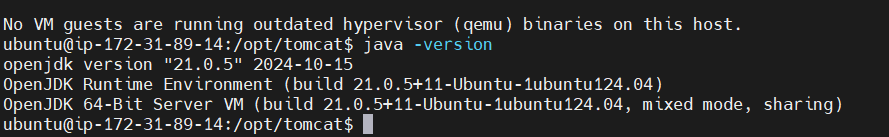
STEP 3: Install Java.
Tomcat requires Java to run. You’ll need at least JDK 11 for Tomcat 11. You can install OpenJDK using the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk -y
java -version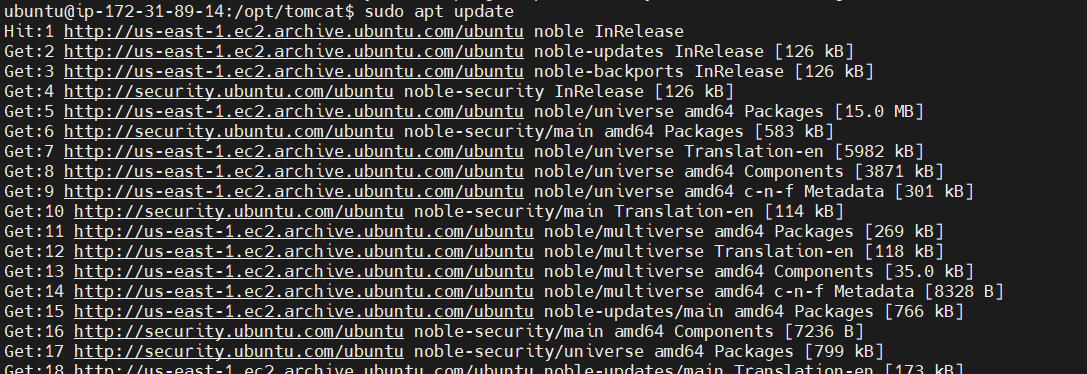
STEP 4: Create a directory named tomcat in the /opt folder.
sudo mkdir /opt/tomcat
cd /opt/tomcatSTEP 5: Download Apache Tomcat
Navigate to the /opt directory and download Tomcat 11.0.2 using wget.
Use the following link for tar.gz file. https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-11/v11.0.2/
https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-11/v11.0.2/bin/apache-tomcat-11.0.2.tar.gz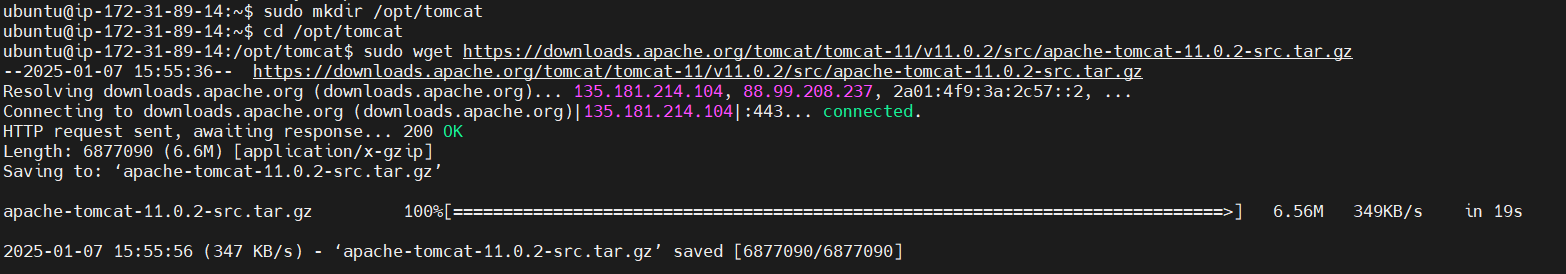
STEP 6: Extract the Tarball
Extract the downloaded tar.gz file.
<br>sudo tar -xvzf apache-tomcat-11.0.2.tar.gz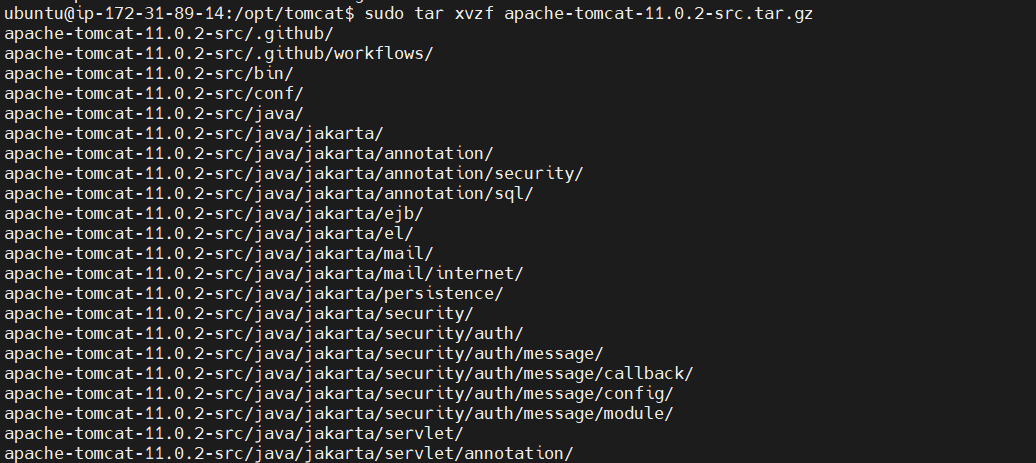
STEP 7: Rename the Tomcat Directory (Optional)
You may want to rename the Tomcat folder for easier access:
sudo mv apache-tomcat-11.0.2 tomcatSTEP 8: If you want Tomcat to start automatically on boot, you can create a systemd service file. Create a file named tomcat.service.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service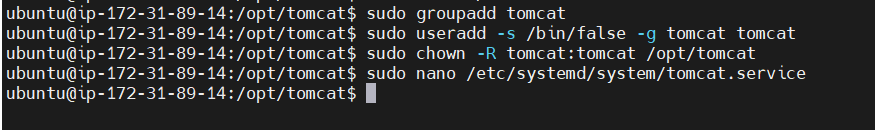
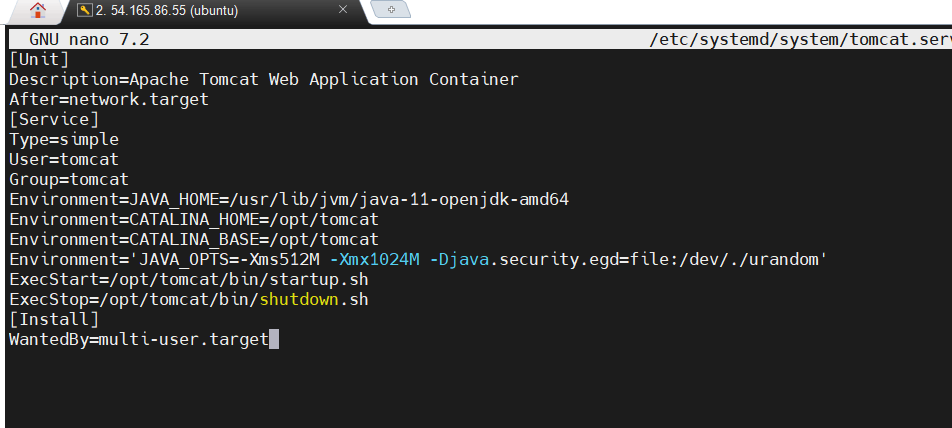
STEP 9: Add the following configuration (adjust paths and user accordingly).
ini
[Unit]
Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=username
Group=username
Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat
Environment=JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-amd64
ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
STEP 10: Start the tomcat server.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable tomcat
suto systemctl start tomcat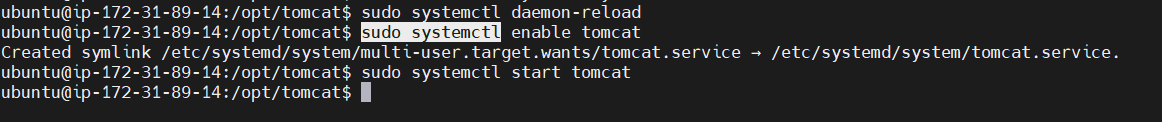
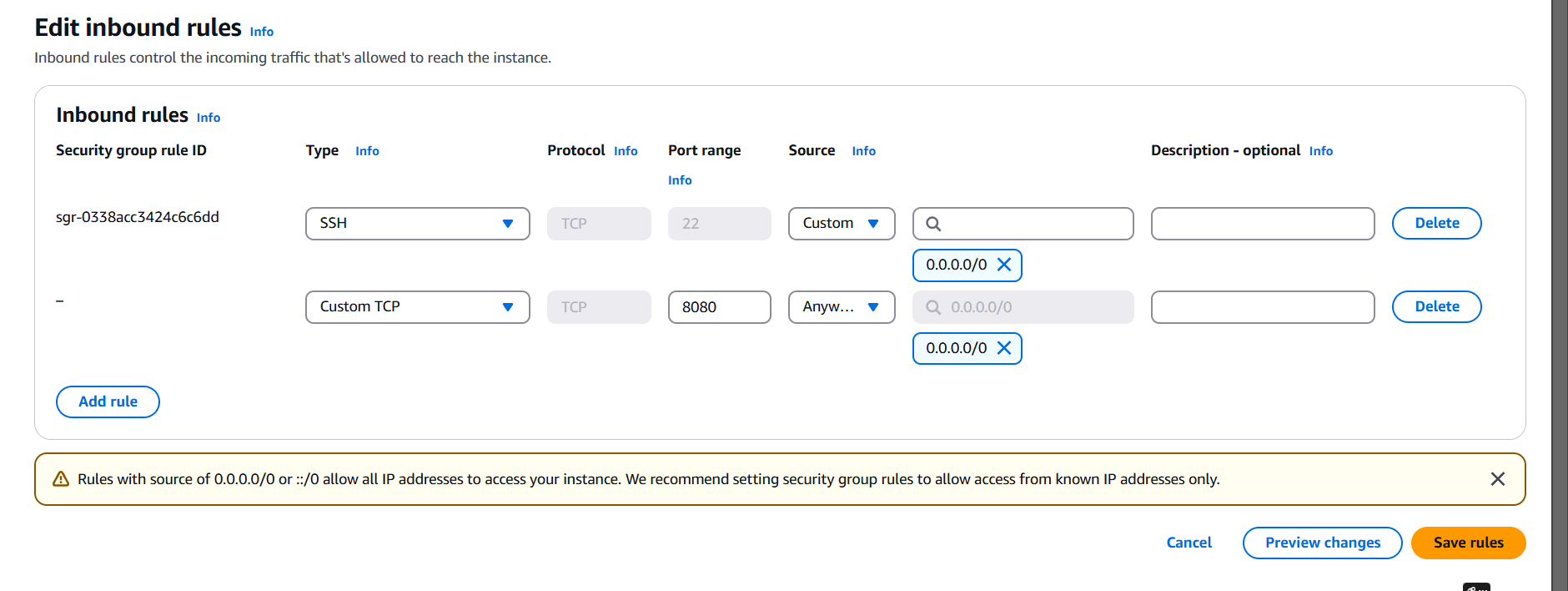
STEP 11: Go to instance and edit inbound rules.
Add the port number 8080 for tomcat.
STEP 12: Go to your browser type http://<Public IP address>:8080
- You will see the tomcat dashboard.
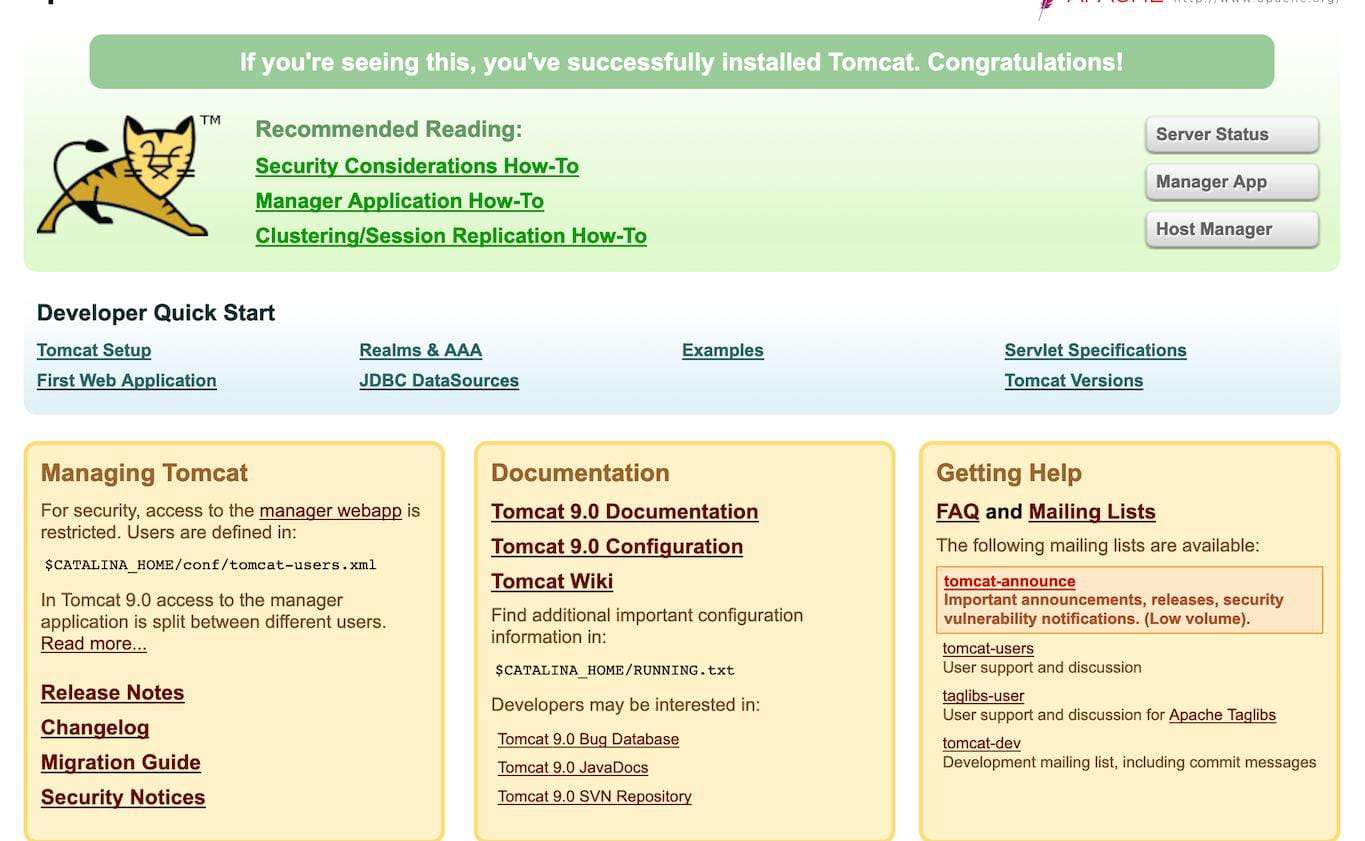

Conclusion.
You have successfully installed Apache Tomcat 11.0.2 on Ubuntu! You can deploy your web applications to the webapps directory in the Tomcat installation directory. Nowadays, Apache Tomcat is widely used by many companies as it implements many of the Jakarta EE specifications, such as: Java Servlet. JavaServer Pages. Java Expression Language.

Add a Comment