In this article, you will learn about the 3 major types of cloud computing services: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
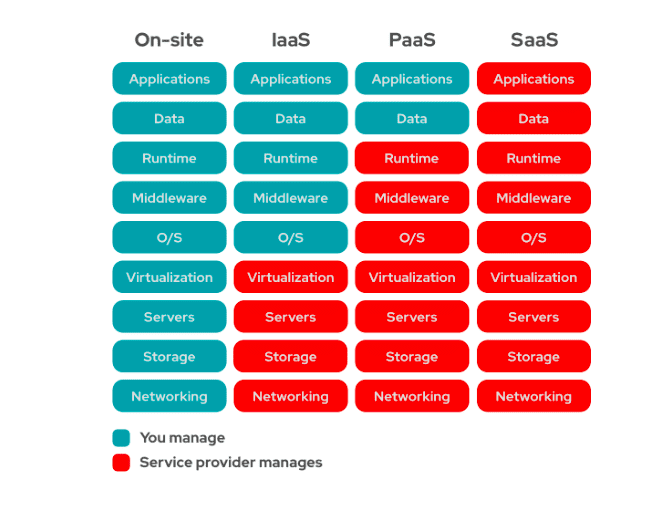
Before mapping or moving your business to the cloud, you need to first decide how much of the services you wish to manage and how much you want the service provider to manage.
To do this, let us compare and analyze who manages what in Infrastructure as a Service (Iaas), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS).

Table of Contents
- SaaS: Software as a Service – Cloud Computing
- The SaaS Delivery Guide – Cloud Computing
- Benefits of SaaS – Cloud Computing
- How to Choose SaaS for Your Business
- PaaS: Platform as a Service – Cloud Computing
- PaaS Delivery Guide – Cloud Computing
- Benefits of PaaS – Cloud Computing
- When to Use PaaS – Cloud Computing
- IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service – Cloud Computing
- IaaS Delivery – Cloud Computing
- Benefits of IaaS – Cloud Computing
- When to Use IaaS – Cloud Computing
- Conclusion
SaaS: Software as a Service – Cloud Computing
Software as a Service (SaaS), also known as cloud application services is the most commonly utilized option chosen by businesses in the cloud market. SaaS is a software distribution model in which a cloud service provider hosts applications at their end and makes the resources available to customers over the internet. Most of the SaaS applications run directly through a web browser; the end-users do not require any downloads or installations on the client-side.
The SaaS Delivery Guide – Cloud Computing
The web delivery model of SaaS eliminates the need to have IT staff download and install applications on each individual computer. With SaaS, vendors or customers can manage all potential technical issues, such as data, servers, storage, and middleware themselves. This model helps companies to streamline maintenance and support for their business.
Some examples of SaaS include:
- Salesforce
- Dropbox
- Google Docs and Sheets
- Concur
Benefits of SaaS – Cloud Computing
SaaS helps companies by greatly reducing the amount of time and money spent on tedious tasks such as installing, managing, and upgrading software. Thanks to SaaS, technical staff can now spend their time resolving more critical issues within their organization.
How to Choose SaaS for Your Business
SaaS is recommended in the following situations:
- The organization is a startup or a small-sized company that needs to launch e-commerce quickly and does not have time for handling server issues or software.
- Organizations that have short-term projects which require quick, easy, and affordable collaboration.
- Applications that are required only on a need basis.
- Applications that need to be accessed over both mobile and web.
PaaS: Platform as a Service – Cloud Computing
Cloud platform services, also known as Platform as a Service (PaaS), is a cloud computing model where a third-party vendor delivers hardware and software tools to end-users over the internet.
PaaS provides a framework for developers that they can build upon and utilize to create customized applications. A third-party provider or an enterprise manages all servers, storage, and networking while the developers maintain management of the applications.
PaaS Delivery Guide – Cloud Computing
In terms of delivery model, PaaS is similar to SaaS. However, instead of delivering software services over the internet, PaaS provides a platform for software creation. This platform is delivered through the internet. Provides developers with the freedom to focus on building the software without having to worry about the operating system, software updates, storage, or infrastructure.
PaaS enables businesses to design and develop applications that are built into the model with special software components. These applications, sometimes referred to as middleware, are scalable and highly available as they exhibit certain cloud characteristics.
Examples of PaaS include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Force.com, Google App Engine, and OpenShift.
Benefits of PaaS – Cloud Computing
Paas offers multiple benefits to organizations of all sizes.
A few benefits are listed below:
- Simple, cost-effective development and deployment of apps
- Scalability
- Highly available services
- The ability to customize apps without the headache of maintaining the software
- Significant reduction of effort in coding
- Automation of business policies
- Seamless migration to the hybrid model
When to Use PaaS – Cloud Computing
Organizations can benefit by utilizing PaaS in several situations. For example, companies can use PaaS to:
- Streamline workflows when multiple developers are working on the same development project.
- Provide great speed and flexibility to the entire process.
- Create customized applications.
PaaS implementation can also greatly reduce costs and simplify a few challenges that come up if a company is rapidly developing or deploying an app.
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service – Cloud Computing
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that offers essential compute, storage, and networking resources on-demand, on a pay-as-you-go basis.
IaaS allows organizations to purchase resources on demand and gives them the flexibility to scale them up or down based on their need.
By migrating their infrastructure to an IaaS solution, a business can reduce maintenance of on-premises data centers, reduce spending on hardware costs and gain real-time business insights.
IaaS Delivery – Cloud Computing
IaaS delivers cloud computing infrastructure, such as servers, networks, operating systems, and storage, through virtualization technology. Through the IaaS model, an organization is provided with cloud servers typically through a dashboard or an API. This model provides clients complete control over their entire infrastructure. IaaS provides the same technologies and capabilities as a traditional data center without having to physically manage all of it.
When compared to SaaS or PaaS, IaaS clients are responsible for managing aspects such as applications, runtime, OSes, middleware, and data. However, the IaaS provider manages the servers, hard drives, networking, virtualization, and storage. A few providers even offer more services beyond the virtualization layer, such as databases or message queues.
A few examples of IaaS include:
Benefits of IaaS – Cloud Computing
IaaS offers benefits, including:
- A very flexible cloud computing model
- Easy to automate the deployment of storage, servers, networking, and processing power
- The ability to purchase hardware based on consumption
- Complete control of infrastructure
- The ability to purchase resources as needed.
- Highly scalable resources
When to Use IaaS – Cloud Computing
IaaS is beneficial in the following scenarios:
- A startup or a small-sized company may prefer IaaS to avoid spending time and money on purchasing and creating hardware and software.
- An MNC or an enterprise may prefer to retain complete control over their applications and infrastructure, but they wish to purchase only resources that they actually consume or need.
- A company that is experienced rapid growth will prefer the scalability of IaaS as it allows them to change out specific hardware and software easily according to their needs.

Conclusion
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
While each cloud model offers a specific set of features and functionalities, your organization needs to understand the differences and choose the cloud model that fits your needs best.
Your needs may vary from purchasing cloud-based software for storage options, opting for a smooth platform that allows you to create customized applications, or having complete control over your entire infrastructure without having to physically maintain it.
Hence, ensure you compare the cloud service models and select the one that fulfills most/all of your needs.

Add a Comment